Additional Tests You Might Need
Once youve been diagnosed with Hepatitis C, your doctor will likely order a number of tests to find out about the health of your liver and decide on a treatment plan thats most appropriate for you.
Hepatitis C genotype
The Hepatitis C genotype refers to a specific strain or type of the Hepatitis C virus. There are six major types of Hepatitis C around the world: genotypes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6. In the United States, genotypes 1, 2, and 3 are common:
- Genotype 1: Most Americans with Hepatitis C have this type
- Genotype 2: About 10% of Americans with Hepatitis C have this type
- Genotype 3: About 6% of Americans with Hepatitis C have this type
The genotype of Hepatitis C does not change over time, so you only need to get tested once.
Genotype tests are done before a person starts treatment. Hepatitis C treatment works differently for different genotypes, so knowing your genotype helps your doctor choose the best treatment for you.
Testing for Hepatitis A and Hepatitis B
Your doctor may test to see if your body is immune to Hepatitis A and Hepatitis B. If these tests show no prior exposure or protection, he or she will recommend that you be vaccinated against these two viruses to eliminate the chance of becoming infected.
Liver function tests or liver enzymes
- ALT
- AST
Liver function tests also include ALP and total bilirubin, among other things.
Tests to measure liver scarring or fibrosis
- Liver Biopsy
- Elastography
- Serum markers
Imaging tests
What Are The Treatments For Hepatitis C
Treatment for hepatitis C is with antiviral medicines. They can cure the disease in most cases.
If you have acute hepatitis C, your health care provider may wait to see if your infection becomes chronic before starting treatment.
If your hepatitis C causes cirrhosis, you should see a doctor who specializes in liver diseases. Treatments for health problems related to cirrhosis include medicines, surgery, and other medical procedures. If your hepatitis C leads to liver failure or liver cancer, you may need a liver transplant.
How Will I Know If My Treatment Works
The goal of treatment is to reduce the amount of the hepatitis C virus in your blood to levels that cant be detected after 24 weeks of therapy. The amount of the virus in your blood is called your viral load. At the end of your treatment, your doctor will need to measure your viral load and find out how healthy your liver is. He or she may repeat many of the same tests that were done when you were first diagnosed with hepatitis C.
If your blood has so few copies of the virus that tests cant measure them, the virus is said to be undetectable. If it stays undetectable for at least 6 months after your treatment is finished, you have what is called a sustained virologic response . People who have an SVR have a good chance of avoiding serious liver problems in the future.
Treatment may not reduce your viral load. You may not have an SVR after treatment. If thats true, your doctor will discuss other treatment options with you. For example, if 1 round of treatment did not decrease your viral load enough, your doctor may recommend a second round. Even if treatment doesnt keep you from having active liver disease, lowering your viral load and controlling chronic liver inflammation may help you feel better for a longer time.
Recommended Reading: Can You Get Rid Of Hepatitis B
What Laboratory Tests Diagnose Hepatitis C
Laboratory blood tests will be done to evaluate the patient’s liver function and to look for hepatitis C antibodies . If these tests indicate that the person has hepatitis C, a hepatitis C “viral load” test will be done. This looks for genetic material from the hepatitis C virus and measures the quantity of hepatitis C virus that is circulating in the patient’s blood. This is helpful in determining if treatment is appropriate and to monitor the success of the treatment .
Individuals who had hepatitis C in the past and cleared the virus on their own will have a positive HCV antibody test, but there will be no hepatitis C virus genetic material in the blood. If a person is immunosuppressed due to an immunological condition, cancer chemotherapy, immunotherapy or HIV/AIDS, the test results may be different and need to be evaluated accordingly.
What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis C
The treatment for hepatitis C has advanced in recent years which has greatly improved the outlook for people with hepatitis C. The main aim of treatment is to clear HCV from the body and so prevent severe liver damage leading to cirrhosis.
If you have acute hepatitis C, you may not need treatment, but will be monitored carefully to see if your body clears the virus on its own, and to keep an eye out for liver damage. Treatment with medicines is advised for most people with chronic hepatitis C. The type of treatment will depend on various factors, including the type of HCV, the severity of the infection and your own health. The treatments recommended are changing all the time as the treatment of hepatitis C is a developing area of medicine. New treatments continue to be developed. The specialist who knows your case can give more accurate information about the outlook for your particular situation. They can also advise on the side-effects you can expect with each individual treatment. Treatment length varies, depending on your situation, and can last from two months to nearly a year.
However, newer treatment combinations have been found to be more effective in many cases. Sometimes these are used along with ribavirin. There are quite a few different medicines used and recommendations change frequently in this rapidly developing field.
Also Check: Hepatomegaly With Diffuse Hepatic Steatosis
Symptoms Of Hepatitis C In Women
Many women dont have symptoms until the disease is in a later stage. Women who have signs of the disease in the earliest stage may brush off symptoms or attribute them to other factors, such as anemia, depression, or menopause.
Early symptoms of hepatitis C in women can include:
- fatigue
- muscle and joint pain
- poor appetite
Some hepatitis C infections are acute and the infection clears or improves on its own without treatment within a few months. Acute infections are more common in women .
Hepatitis C can also be chronic, meaning the infection doesnt clear on its own, but rather progresses and damages the liver. Symptoms of chronic hepatitis and liver damage include:
- bruising or bleeding
- spider veins
- confusion
The symptoms of chronic hepatitis C occur in both men and women, but the disease can progress slower in women. However, some women experience rapid progression of the disease and liver damage after menopause.
Having these symptoms doesnt mean you have hepatitis C.
Hepatitis C spreads from person-to-person through contact with infected blood. If you work in an industry where you might come in contact with blood, theres a slight risk of exposure. This includes personal care such as:
- manicurists
- housekeeping
- nursing
Hepatitis C can also be spread to a sexual partner during a menstrual cycle.
Can Hepatitis C Be Prevented
There is no vaccine for hepatitis C. But you can help protect yourself from hepatitis C infection by
- Not sharing drug needles or other drug materials
- Wearing gloves if you have to touch another person’s blood or open sores
- Making sure your tattoo artist or body piercer uses sterile tools and unopened ink
- Not sharing personal items such toothbrushes, razors, or nail clippers
- Using a latex condom during sex. If your or your partner is allergic to latex, you can use polyurethane condoms.
NIH: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
Read Also: What Is Hepatitis B Vaccine For
Some People Can Fight Infection
Before we get into the available treatments for hepatitis C, its important to note that not everyone needs treatment. According to Healthline, some people have immune systems that are strong enough to fight the infection and clear it from their body. In this case, the doctor will monitor the state of your liver with regular blood tests.
Hepatitis C Testing And Diagnosis
Doctors will start by checking your blood for:
Anti-HCV antibodies: These are proteins your body makes when it finds the hep C virus in your blood. They usually show up about 12 weeks after infection.
It usually takes a few days to a week to get results, though a rapid test is available in some places.
The results can be:
- Nonreactive, or negative:
- That may mean you donât have hep C.
- If youâve been exposed in the last 6 months, youâll need to be retested.
If your antibody test is positive, youâll get this test:
HCV RNA: It measures the number of viral RNA particles in your blood. They usually show up 1-2 weeks after youâre infected.
- The results can be:
- Negative: You donât have hep C.
- Positive: You currently have hep C.
You might also get:
Liver function tests: They measure proteins and enzyme levels, which usually rise 7 to 8 weeks after youâre infected. As your liver gets damaged, enzymes leak into your bloodstream. But you can have normal enzyme levels and still have hepatitis C. Learn the reasons why you should get tested for hepatitis C.
Also Check: How Is Hepatitis B Transmitted
Life Expectancy And Prognosis
Can you die from hepatitis? Technically, the complications of chronic hepatitis C are fatal. About 30,000 people in the U.S. die each year from cirrhosis.
How long can you live with untreated hep C? The disease affects everyone differently, so thereâs no rule. But about 70% to 80% of people with will get chronic help C. Within 20 years, about 20% to 30% of those people will get cirrhosis. From there, it depends on what type of cirrhosis you have, your treatment, and if you can get a liver transplant.
Can hepatitis C go away on its own? Yes. From 15% to 20% of people with hep C clear it from their bodies without treatment. Itâs more likely to happen in women and people who have symptoms. But it usually happens between 4 and 18 months after symptoms start.
American Liver Foundation Hep C 123: âFrequently Asked Questions.â
Gastroenterology: âExtrahepatic morbidity and mortality of chronic hepatitis C.â
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: âHepatitis C.â
Therapeutic Advances in Infectious Disease: âExtrahepatic Manifestations of Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection.â
The Hepatitis C Support Project: âAn Overview of Extrahepatic Manifestations of Hepatitis C.â
BioDrugs: âManagement of hepatitis C virus-related arthritis.â
Frontiers in Endocrinology: âDiabetes and Hepatitis C: A Two-Way Association.â
U.S. National Library of Medicine: âAtherosclerosis,â âPreventing Hepatitis B or C.â
Blood And Vessel Problems
People with hepatitis C often get a condition called cryoglobulinemia. This happens when certain proteins in your blood stick together in cold weather. They can build up in vessels and block blood flow, which causes swelling and damage. The condition can affect your skin, organs, nerves, and joints.
Hepatitis C also can cause problems with blood itself. You may not make enough white blood cells, which fight infections, or platelets, which help your blood clot.
The infection can also make you bruise easily or get red or purple spots under your skin. Those are signs of a bleeding disorder called immune thrombocytopenic purpura.
Don’t Miss: Is Hepatitis C Contagious After Being Cured
What Are The Side Effects Of Drug Treatment
Common side effects for some treatments for hepatitis C may include the following:
- nausea
- fatigue
- depression
Side effects are usually worst during the first few weeks of treatment. They become less severe over time. If you are having trouble dealing with the side effects of your medicine, talk to your doctor. He or she can suggest ways to relieve some of the side effects. For example, if your medicine makes you feel nauseated, it may help to take it right before you go to sleep.
Complications Of Hepatitis C

Hepatitis C can be a long-term, progressive disease. It can eventually lead to cirrhosis, or scarring of the liver tissue. If this happens, the liver doesnt function as well. Some people with hepatitis C also develop liver cancer.
A liver transplant may be necessary if the virus has significantly damaged your liver. Even with a new liver, youll have to take antiviral medication to avoid infecting the new organ.
You May Like: Can You Get Hepatitis C From Food
Contaminated Needles And Infected Blood
You can get hepatitis C from sharing contaminated needles, syringes and other injecting equipment during recreational drug use. Banknotes and straws used for snorting may also pass the virus on.
Being exposed to unsterilised tattoo and body piercing equipment can also pass hepatitis C on. Occasionally, you can get it from sharing a towel, razor blades or a toothbrush if there is infected blood on them.
Hepatitis C infection is also passed on in healthcare settings, from needle stick injuries or from medical and dental equipment that has not been properly sterilised. In countries where blood products are not routinely screened, you can also get hepatitis C by receiving a transfusion of unscreened blood and blood products.
You can prevent hepatitis C by:
- never sharing needles and syringes or other items that may be contaminated with infected blood
- only having tattoos, body piercings or acupuncture in a professional setting, where new, sterile needles are used
- following the standard infection control precautions, if youre working in a healthcare setting.
Stages Of Hepatitis C
The hepatitis C virus affects people in different ways and has several stages:
- Incubation period. This is the time between first exposure to the start of the disease. It can last anywhere from 14 to 80 days, but the average is 45
- Acute hepatitis C. This is a short-term illness that lasts for the first 6 months after the virus enters your body. After that, some people who have it will get rid of, or clear, the virus on their own.
- Chronic hepatitis C. For most people who get hepatitis C — up to 85% — the illness moves into a long-lasting stage . This is called a chronic hepatitis C infection and can lead to serious health problems like liver cancer or cirrhosis.
- Cirrhosis. This disease leads to inflammation that, over time, replaces your healthy liver cells with scar tissue. It usually takes about 20 to 30 years for this to happen, though it can be faster if you drink alcohol or have HIV.
- Liver cancer. Cirrhosis makes liver cancer more likely. Your doctor will make sure you get regular tests because there are usually no symptoms in the early stages.
Learn more about the stages and progression of hepatitis C.
Also Check: Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedule For Child
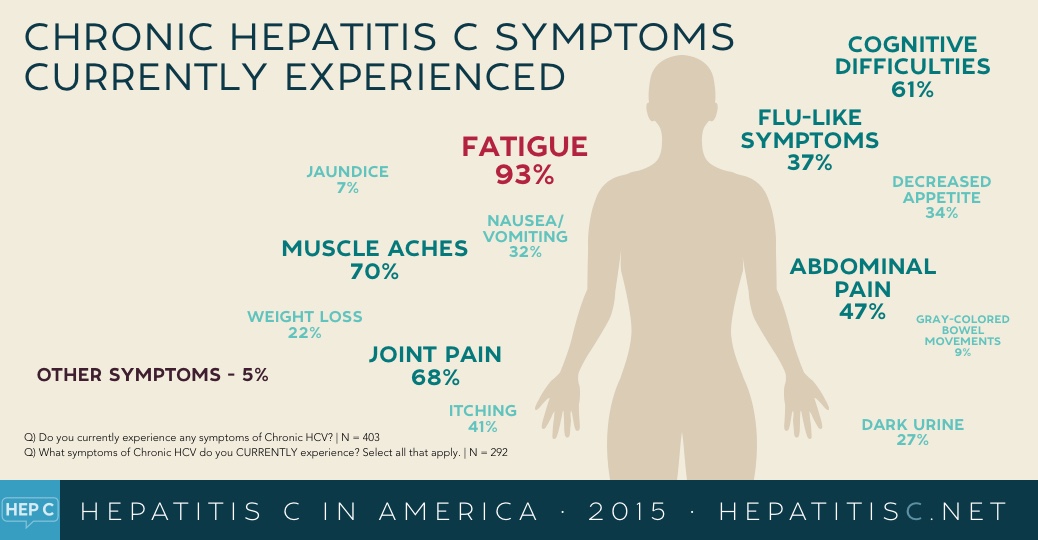
Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
It is very important to know that not everyone with hepatitis C has symptoms. The only way to know if you have hepatitis is by talking to your doctor and getting a blood test.
Many people living with hepatitis C feel well and only have symptoms once the disease has progressed and there is serious liver damage.
If you do not have symptoms this does not mean that the virus isnt causing damage.
When first infected, some people may find:
- their urine becomes dark
- their eyes and skin turn yellow
- they experience a minor flu-like illness.
These symptoms may disappear within a few weeks, but this does not necessarily mean that the infection has been cleared.
Over time, symptoms that may develop include:
- tiredness and fatigue
- flu-like symptoms
- pain in the abdomen where the liver is located
- not feeling hungry and indigestion.
Around 30% of people who have been infected may clear the virus from their blood naturally, with no treatment, within 6 months. These people no longer have the hepatitis C virus and are not infectious, but will always have hepatitis C antibodies in their blood. The presence of hepatitis C antibodies shows that someone has been exposed to the virus, but does not offer any immunity against hepatitis C. People can become reinfected after clearing the virus naturally, or after treatment.
Hepatitis C Symptoms & Treatment
FAST FACTS:
-
Hepatitis C is found in infected blood. It is also rarely found in semen and vaginal fluids.
-
Hepatitis C is mainly passed on through using contaminated needles and syringes or sharing other items with infected blood on them. It can also be passed on through unprotected sex, especially when blood is present.
-
You can prevent hepatitis C by never sharing needles and syringes, practising safer sex, and avoiding unlicensed tattoo parlours and acupuncturists.
-
Hepatitis C will often not have any noticeable symptoms, but a simple blood test carried out by a healthcare professional will show whether you have hepatitis C.
-
In the early stages, some peoples bodies can clear a hepatitis C infection on their own, others may develop chronic hepatitis C and will need to take antiviral treatment to cure the infection.
-
Without treatment, chronic hepatitis C can lead to permanent liver damage.
Hepatitis C is part of a group of hepatitis viruses that attack the liver.
Its mainly passed on through contaminated needles, either from injecting drugs or from needle stick injuries in healthcare settings. It can also be transmitted sexually, especially during anal sex or other types of sex that may involve blood.
Some groups are more at risk of getting hepatitis C than others, including people who use drugs, people in prisons, men who have sex with men, health workers and people living with HIV.
Recommended Reading: Symptoms Of Hepatitis C Flare Up