What Are The Side Effects
Vaccines are very safe. It is much safer to get the vaccine than to get hepatitis B.
Many people have no side effects from the vaccine. However, for those that do, common side effects may include soreness, redness and swelling where the vaccine was given. Some may experience a mild fever.
It is important to stay in the clinic for 15 minutes after getting any vaccine because there is a very rare possibility, between one in 100,000 and one in a million, of a life-threatening allergic reaction called anaphylaxis. This may include hives, difficulty breathing, or swelling of the throat, tongue or lips. Should this reaction occur, your health care provider is prepared to treat it. Emergency treatment includes administration of epinephrine and transfer by ambulance to the nearest emergency department. If symptoms develop after you leave the clinic, call 9-1-1 or the local emergency number.
It is important to always report serious or unexpected reactions to your health care provider.
Persons With Inadequate Immunization Records
Evidence of long term protection against HB has only been demonstrated in individuals who have been vaccinated according to a recommended immunization schedule. Independent of their anti-HBs titres, children and adults lacking adequate documentation of immunization should be considered susceptible and started on an immunization schedule appropriate for their age and risk factors. Refer to Immunization of Persons with Inadequate Immunization Records in Part 3 for additional information.
Babies That Need To Stay In Hospital
If your baby needs to stay in hospital they should receive the second dose of vaccine when they reach 4 weeks old and then continue to follow the schedule below.
Keep a record of your babys appointments and vaccination dates. These will also be recorded by your midwife, health visitor, practice nurse and GP in your babys Red Book . Bring your childsRed Book to every appointment.
If you have questions you can speak to your midwife, health visitor, practice nurse or GP.
You May Like: What Vitamins Are Good For Hepatitis B
What Hepatitis B Immunisation Involves
Full protection involves having 3 injections of the hepatitis B vaccine at the recommended intervals.
Babies born to mothers with hepatitis B infection will be given 6 doses of hepatitis B-containing vaccine to ensure long-lasting protection.
If you’re a healthcare worker or you have kidney failure, you’ll have a follow-up appointment to see if you’ve responded to the vaccine.
If you’ve been vaccinated by your employer’s occupational health service you can request a blood test to see if you’ve responded to the vaccine.
A Look At Each Vaccine: Hepatitis B Vaccine
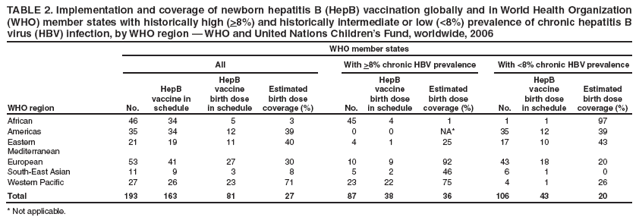
The hepatitis B vaccine is given to prevent the severe liver disease that can develop when children or adults are infected with hepatitis B virus. The hepatitis B vaccine is given as a series of three shots. The first dose is given within 24 hours of birth. The second dose is given one to two months after the first dose, and the third dose is given between 6 months and 18 months of age.
You May Like: Antiviral Drugs For Hepatitis A
People With Chronic Hepatitis B
The vaccine does not affect people with chronic hepatitis B virus infection there are no therapeutic benefits or associated adverse events. The vaccine is also safe in people who are already immune to hepatitis B through past natural infection, but it offers no additional benefit.
Hepatitis B is an infection caused by hepatitis B virus. It affects the liver.
Many People With Hbv Dont Know They Have It
HBV infections are becoming less common in the United States. But HBV is still widespread in other parts of the world. Around 257 million people living around the world currently have HBV, and many of them dont know it. Chronic HBV is often asymptomatic, and even when it isnt, it can take months for symptoms to show up.
HBV can be transmitted through sexual contact and the use of IV drugs , and other risk factors. Although rare, there
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
Does The Hepatitis B Vaccine Have Side Effects
Some children will develop pain or soreness in the local area of the shot, and low-grade fever.
There is one extremely rare, but serious, side effect. About 1 out of every 600,000 doses of the hepatitis B vaccine will cause a severe allergic reaction, called anaphylaxis, with symptoms including swelling of the mouth, difficulty breathing, low blood pressure or shock. Anaphylaxis usually occurs within 15 minutes of receiving the vaccine. Although anaphylaxis can be treated, it is quite frightening. People should remain at the doctors office for about 15 minutes after getting the vaccine.
Although the hepatitis B vaccine is made in yeast cells, no one has ever been shown to be allergic to the yeast proteins contained in the hepatitis B vaccine .
Hepatitis B Vaccine Can Protect Your Baby
A complete course of 6 doses of vaccines is needed to fully protect your baby against long lasting hepatitis B infection. The vaccine is given as a small injection into the thigh.
Your midwife will know that your baby should have the first dose of hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth.
Your baby may also need hepatitis B immunoglobulin at the same time as their birth dose of vaccine, if there is a higher risk of infection. Your midwife will tell you if it is needed. HBIG is also given as a single injection in the thigh.
The second dose of single hepatitis B vaccine needs to be given at 4 weeks of age.
The next 3 doses of hepatitis B containing vaccine are routinely given to all babies at 8, 12 and 16 weeks old. These also protect against other serious infections including diphtheria, tetanus, polio, whooping cough and haemophilus influenzae type B.
Your babys final dose of single hepatitis B vaccine should be given when they reach 1 year of age. This dose can be given at the same time as their other routine vaccines.
If you are not able to attend any of the appointments, please let your GP know as soon as possible so that anotherappointment can be arranged.
You May Like: What Is Hepatitis B Virus
Facts About Hepatitis B
- Two billion people, or one in three, have been infected with hepatitis B worldwide. Of these, about 260 million live with chronic hepatitis B.
- Each year about 900,000 people die from hepatitis B worldwide, and about 2,000 of these deaths occur in the United States.
- Hepatitis B is transmitted through blood and is 100 times more infectious than HIV. An estimated one billion infectious viruses are in one-fifth of a teaspoon of blood of an infected person, so exposure to even a minute amount, such as on a shared toothbrush can cause infection.
- Hepatitis B is sometimes referred to as the silent epidemic because most people who are infected do not experience any symptoms.
- Liver cancer is the fourth leading cause of cancer deaths throughout the world, behind lung, colorectal and stomach cancers.
- Almost half of liver cancers are caused by chronic infection with hepatitis B.
- The World Health Organization recommends the inclusion of hepatitis B vaccine in immunization programs of all countries in 2017, about 8 of 10 infants born throughout the world received three doses of hepatitis B vaccine.
When To Delay Vaccinating
Although the Hepatitis B Foundation stresses that parents should not voluntarily delay vaccinating their babies against hepatitis B, there are situations in which doctors may choose to delay the vaccination.
For instance, sometimes the hepatitis B vaccination is delayed if a baby is premature, has a low birth weight, or is medically challenged.
The CDC’s report, Prevention of Hepatitis B Virus Infection in the United States: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, says that all healthy newborns who weigh more than 4.4 pounds should receive the hepatitis B vaccination.
Still, parents always have the option to refuse a vaccination if they want to. But the risks associated with a hepatitis B infection far outweigh the risks of the vaccine.
Don’t Miss: How To Catch Hepatitis C
What To Do If You Miss A Scheduled Dose
The recommended schedule for the HBV vaccine follows a three-dose pattern, with all doses complete within 6 months. The good news is that if you miss a dose, you dont need to start the series of shots all over.
If you missed getting the second dose 1 month after the first, make an appointment as soon as possible. If you miss the third dose, you should also try to get it as quickly as possible. Keep in mind that the second and third doses
Immunogenicity Safety And Efficacy Of Pentavalent Vaccine
Numerous immunogenicity studies have been performed in India, and have shown that immunogenicity against each of the vaccine component and reactogenicity is same as that of simultaneous but separate site administration of DPT, Hep B and Hib vaccines.- In a study from India, on post-primary immunization with Serum Institute of Indias and GSKs pentavalent vaccine, 100% seroprotection was detected for diphtheria, tetanus, hepatitis B and Hib components in both SII and GSK groups and for pertussis, efficacy was 96.1% in SII group and 95.4% in GSK group.
The vaccines have excellent tolerability profile with only minor adverse events. All the infants who reported common systemic reactions i.e., fever, irritability and unusual crying, recovered with symptomatic treatment. No vaccine-related neurological, hypersensitivity reactions or other serious adverse events were reported in infants.-
Read Also: What Is Hepatitis A And B And C
Why Is The Hepb Vaccine Recommended
People who dont know they’re infected can spread the hepatitis B virus. So it cant be avoided just by being careful. That’s why health experts recommend that all babies get the vaccine right from birth.
The HepB injection usually creates long-term immunity. Most infants who get the HepB series are protected from hepatitis B infection beyond childhood, into their adult years.
Eliminating the risk of infection also decreases risk for cirrhosis of the liver, chronic liver disease, and liver cancer.
Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedule: Standard Accelerated And Combination
Getting poked with a needle is never fun, but its an extremely important part of protecting yourself and others from infectious diseases! The hepatitis B vaccine is known to be one of the most effective vaccines in the world and very safe too! As a blood-borne disease that typically has no symptoms, hepatitis B can easily be spread by accident simply because people are unaware that they have it! Modes of transmission include mother-to-child during birth, unprotected sex, injection drug use, unsafe medical procedures, and the sharing of personal items that may contain blood remnants, such as body jewelry, razors, and toothbrushes. Although certain precautions can be taken to prevent transmission, the only way to completely protect yourself is to get vaccinated. Once you have been vaccinated, you are protected for life!
There are a few options for receiving the hepatitis B vaccination. In most countries, the vaccine is available through a doctors office or a health clinic. The most common option is the standard three-dose vaccine. This consists of three separate doses of the vaccine given through intramuscular injections. In order for the vaccine to be effective, there must be a minimum amount of time between doses. If the minimum amount of time is not followed, the vaccine will not provide full, long term protection from the infection.
3 Dose Schedule:
2-Dose Schedule :
- 1st shot At any given time
- 2nd shot At least 28 days after the first shot.
You May Like: Does Hepatitis C Weaken Your Immune System
How Does Hepatitis A Spread
Hepatitis A virus is found in the stool of a person who has the virus. It spreads when a person puts something in his or her mouth that has the hepatitis A virus on it. Even if the item looks clean, it can still have virus on it that can spread to others. The amount of stool can be so tiny that it cannot be seen with the naked eye. You can get it by touching objects such as doorknobs or diapers or eating food that has the virus on it.
Immunisation Against Hepatitis B For People At Risk
In Victoria free hepatitis B vaccine is provided for people who are at increased risk, including:
- Men who have sex with men.
- People living with HIV.
- People living with hepatitis C.
- Prisoners.
- People no longer in a custodial setting who commenced, but did not complete, a free vaccine course while in custody.
- Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people.
- People born in priority hepatitis B endemic countries who arrived in Australia in the last 10 years priority countries include China, Philippines, Malaysia, Vietnam, Afghanistan, Thailand, South Korea, Myanmar , Indonesia, Singapore, Hong Kong, Taiwan and Cambodia.
- Vulnerable citizens people who have experienced hardship that prevented them from accessing the vaccine earlier. Vulnerable citizens are vaccinated based on an individual assessment by an immunisation provider.
Immunisation is also recommended, but not free, for people who are at increased risk including:
If you think you have been exposed to hepatitis B, see a doctor immediately. Your doctor can give you treatment that, in some instances, can greatly reduce your risk of infection with hepatitis B.
Remember that being immunised against hepatitis B does not protect you against HIV, hepatitis C or other diseases spread by blood or bodily fluids. It is important that you take precautions to make sure you are not exposed to these diseases.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Blood Test Results
Testing Your Baby For Infection
Each year, a very small number of babies may develop infection so your baby will be offered a blood test when they are 1 years old. This is to check that the course of vaccines have prevented them from developing hepatitis B.
There are 2 ways that this may be done and your GP, health visitor or practice nurse will advise you which test your baby will have:
If they do have the infection, they will be referred to a specialist for treatment to reduce their risk of developingserious liver disease.
If a young infant is infected, they are more likely to develop long lasting infection without any signs or symptoms of infection. Even if your baby has no signs or symptoms of infection they should still have the blood test.
Infection can be prevented in 90% of cases if the first dose of vaccine is given at birth and the full course of vaccines is completed on time.
What Is Hepatitis B Virus
Hepatitis B virus attacks the liver. Hepatitis B virus infections are known as the “silent epidemic” because many infected people don’t experience symptoms until decades later when they develop hepatitis , cirrhosis , or cancer of the liver . Every year in the United States about 22,000 new hepatitis B infections occur and about 2,000 people die from their infections.
Also Check: Can You Get Hepatitis C Twice
Interchangeability Of Hepatitis B Vaccines
The Engerix-B and H-B-Vax II vaccines are manufactured by different processes, and the hepatitis B surface antigen content of an equivalent dose of these vaccines is different. Switching vaccine brands is not recommended.
If the brand of vaccine used for previous doses is not known, use another age-appropriate equivalent dose brand. See:
For example, a study in healthy neonates showed comparable high levels of immunogenicity between 2 different mixed regimens that used 2 monovalent hepatitis B vaccines from different manufacturers.33
Provincial And Territorial Routine And Catch
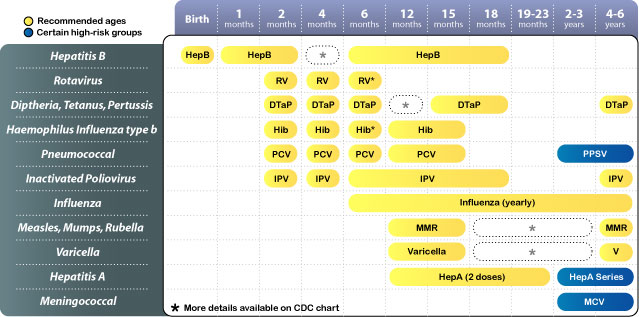
This table summarizes the current routine vaccination schedule for infants and children in all provinces and territories across Canada. Changes to this schedule are updated regularly in collaboration with the Canadian Nursing Coalition for Immunization and the Canadian Immunization Committee Schedules for each province or territory are available. Additional information is available on Canada.ca/vaccines.
Read Also: How Do You Contact Hepatitis A
Tetanus Diphtheria And Pertussis Vaccination
Routine vaccination
- Adolescents age 1112 years: 1 dose Tdap
- Pregnancy: 1 dose Tdap during each pregnancy, preferably during the early part of gestational weeks 2736
- Tdap may be administered regardless of the interval since the last tetanus- and diphtheria-toxoid-containing vaccine.
Catch-up vaccination
- Adolescents age 1318 years who have not received Tdap: 1 dose Tdap, then Td or Tdap booster every 10 years
- Persons age 718 years not fully vaccinated* with DTaP: 1 dose Tdap as part of the catch-up series if additional doses are needed, use Td or Tdap.
- Tdap administered at age 710 years
- Children age 79 years who receive Tdap should receive the routine Tdap dose at age 1112 years.
- Children age 10 years who receive Tdap do not need the routine Tdap dose at age 1112 years.
Special situations
*Fully vaccinated = 5 valid doses of DTaP OR 4 valid doses of DTaP if dose 4 was administered at age 4 years or older.
Aboriginal And Torres Strait Islander People
Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people are recommended to:
- have their risks and vaccination status for hepatitis B reviewed
- receive testing for previous hepatitis B virus infection
- receive vaccination if non-immune
Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people have a higher risk of acquiring new hepatitis B virus infection than non-Indigenous Australians.2,3
Adult-formulation hepatitis B vaccine should be given in a 3-dose schedule.
Children with HIV are recommended to receive 3 doses of hepatitis B vaccine using an adult formulation. This is double the recommended dose for children. In a limited number of studies, children who were immunocompromised responded better when given higher doses in a 3-dose schedule.4,5
Levels of antibody to hepatitis B surface antigen should be checked after the vaccination course. See Serological testing after hepatitis B vaccination.
Adults with HIV are recommended to receive larger-than-usual doses of hepatitis B vaccine. They should receive 2 injections of the standard adult dose on each occasion at 0, 1, 2 and 6 months. Limited studies in adults with HIV have revealed an improved and accelerated serological response to a schedule that consists of 4 double doses.6,7
A 3-dose schedule at 6, 8 and 12 months after transplant is required using:
Don’t Miss: How Does One Get Hepatitis C