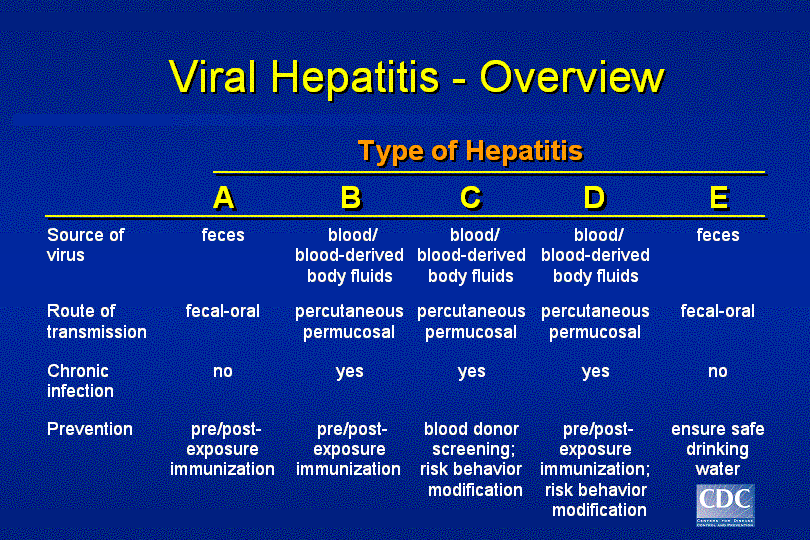
What Are Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C
Although hep A is a short-term illness that goes away completely, hepatitis B and hepatitis C can turn into serious long-term illnesses for some people. Teens and young adults are most at risk for getting these two viruses.
Hep B and C get passed from person to person the same ways that HIV does through direct contact with infected body fluids. Hepatitis B and C are even more easily passed in fluids and needles than HIV. This can happen through sexual contact and by sharing needles that have been contaminated with infected blood. Even when infected people don’t have any symptoms, they can still pass the disease on to others.
Sometimes mothers with hep B or C pass the virus along to their babies when they’re born. Hep B and C also can get passed in ways you might not expect such as getting a manicure or pedicure with unsterilized nail clippers or other dirty instruments. Getting a tattoo, if dirty needles are used, is another way someone can get hep B or C.
What Is Hepatitis A
For kids, hep A is the most common type of hepatitis to get. The virus lives in poop from people who have the infection. That’s why it’s so important to wash your hands before eating and after going to the bathroom. If you don’t, and then go make yourself a sandwich, hep A virus might end up on your food, and then in you!
Vegetables, fruits, and shellfish also can carry hepatitis if they were harvested in contaminated water or in unsanitary conditions. Hepatitis A affects people for a short time, and when they recover, it does not come back.
There Is No ‘worst’ Type Of Hepatitis
While some types of hepatitis are more likely to be fatal or cause chronic long-term problems, there is really is not one type of hepatitis that is worse than another when it comes to individual people.
For example, though there are many more deaths from hepatitis B than hepatitis A, an individual person may fare better with hepatitis B than hepatitis A. The severity of these diseases depends on many factors, including access to good medical care, whether or not a carrier state develops, and much more.
Read Also: Where Can I Go To Get A Hepatitis B Vaccination
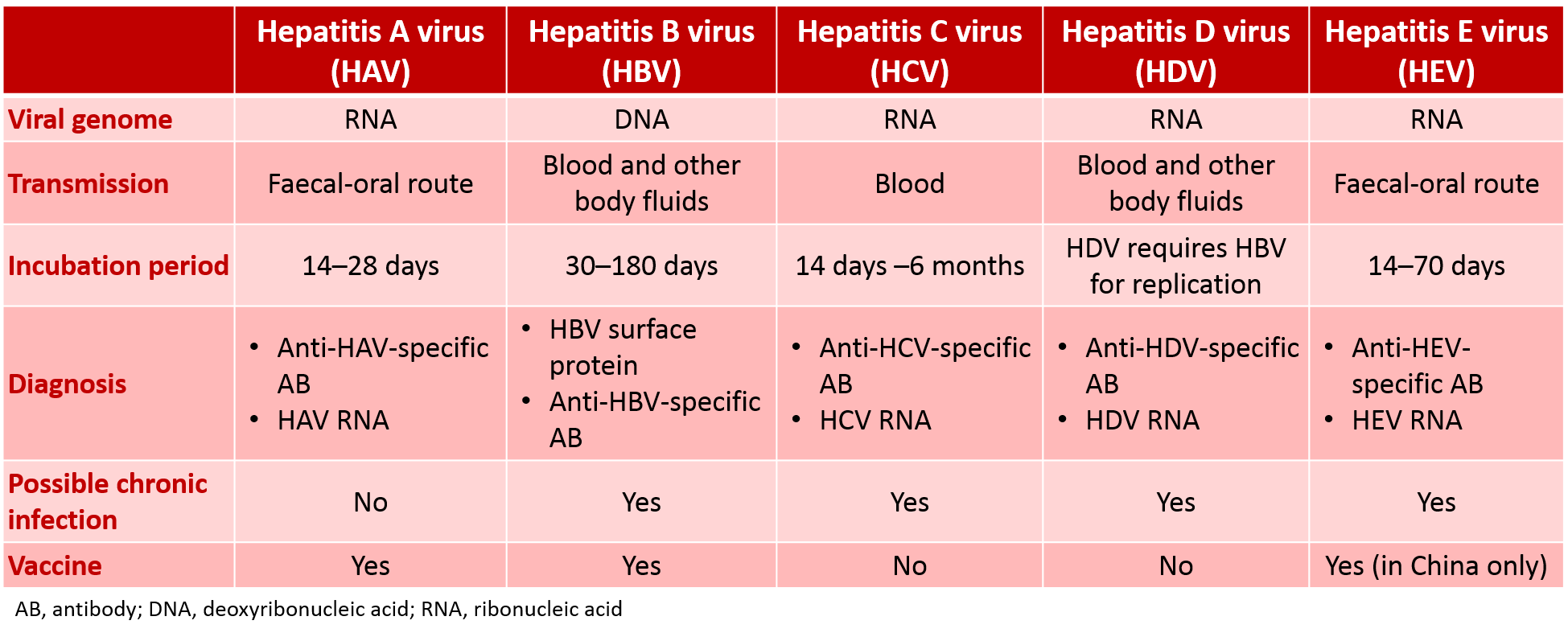
How Is Viral Hepatitis Diagnosed
Diagnosis of viral hepatitis is based on symptoms and physical findings as well as blood tests for liver enzymes, viral antibodies, and viral genetic materials.
Symptoms and physical findings
Diagnosis of acute viral hepatitis often is easy, but the diagnosis of chronic hepatitis can be difficult. When a patient reports symptoms of fatigue, nausea, abdominal pain, darkening of urine, and then develops jaundice, the diagnosis of acute viral hepatitis is likely and can be confirmed by blood tests. On the other hand, patients with chronic hepatitis due to HBV and HCV often have no symptoms or only mild nonspecific symptoms such as chronic fatigue. Typically, these patients do not have jaundice until the liver damage is far advanced. Therefore, these patients can remain undiagnosed for years to decades.
Blood tests
There are three types of blood tests for evaluating patients with hepatitis: liver enzymes, antibodies to the hepatitis viruses, and viral proteins or genetic material .
Liver enzymes: Among the most sensitive and widely used blood tests for evaluating patients with hepatitis are liver enzymes, called aminotransferases. They include aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase . These enzymes normally are contained within liver cells. If the liver is injured , the liver cells spill the enzymes into the blood, raising the enzyme levels in the blood and signaling that the liver is damaged.
Examples of tests for viral antibodies are:
What Is The Long Term Prognosis For Hepatitis C
The future looks promising for those with Hepatitis C. Fortunately, scientific advances and intense research and development have led to the development of many oral antiviral drugs. In addition, research shows that combining specific supplements such as milk thistle shows promise in assisting the liver of patients with Hepatitis C.
The odds of living well with Hepatitis C rather than dying from Hepatitis C are very good. By maintaining a positive attitude, working closely with ones physician after diagnosis, getting support from as many areas as possible , and making positive lifestyle changes, Hepatitis C doesnt have to be the death sentence it was once believed to be.
Don’t Miss: Antibody Titer Test For Hepatitis B
Effective Treatments Are Available For Hepatitis C
New medication to treat for HCV have been approved in recent years. These treatments are much better than the previously available treatment because they have few side effects and do not need to be injected. There are several direct-acting antiviral HCV treatments that cure more than 95% of people who take them in 8 to 12 weeks. HCV treatment dramatically reduces deaths among people with HCV infection, and people who are cured of HCV are much less likely to develop cirrhosis or liver cancer.
Take Action! CDCs National Prevention Information Network Service Locator helps consumers locate hepatitis B and hepatitis C prevention, care, and treatment services.
You May Like: Genotype 2a Hepatitis C Virus
Hepatitis Infections In The Us And Worldwide
If you’ve been diagnosed with one of the forms of hepatitis, you aren’t alone. It’s thought that roughly two percent of people in the United States are living with a chronic hepatitis B or hepatitis C infection, not to mention the other three forms. Hepatitis can cause illness or death due to both the symptoms of the infection and to complications that may develop.
Worldwide, hepatitis was responsible for 1.34 million deaths in 2015. The World Health Organization also reports that deaths from hepatitis have increased 22 percent since 2000.
Hepatitis B and hepatitis C are responsible for 96 percent of deaths from viral hepatitis of any kind worldwide and cause an estimated 78 percent of all liver cancer and 57 percent of all liver cirrhosis.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Dna Or Rna
Are There Complications From Hepatitis A
In extremely rare cases, hepatitis A can lead to acute liver failure. This complication is most common in older adults and people who already have chronic liver disease. If this occurs, you will be hospitalized. Even in cases of liver failure, a full recovery is likely. Very rarely is a liver transplant required.
What Are The Types Of Hepatitis
There are many types of hepatitis which cause symptoms that range from mild to very serious.
Five types of viral hepatitis are:
- hepatitis A an illness that can last from a few weeks to 6 months
- hepatitis B a serious infection that can lead to liver damage
- hepatitis C a disease that is now easily treatable
- hepatitis D a disease that only affects people infected with hepatitis B, and is a rarer type of hepatitis in Australia
- hepatitis E a short-term illness that can be severe in pregnant women, but is rare in Australia
There are other types of hepatitis that are not infectious, including:
- autoimmune hepatitis
Having one type of hepatitis doesnt stop you from getting other types.
Recommended Reading: How Do They Test For Hepatitis
What Are The Symptoms And Signs Of Viral Hepatitis
The period of time between exposure to hepatitis and the onset of the illness is called the incubation period. The incubation period varies depending on the specific hepatitis virus. Hepatitis A virus has an incubation period of about 15 to 45 days Hepatitis B virus from 45 to 160 days, and Hepatitis C virus from about 2 weeks to 6 months.
Many patients infected with HAV, HBV, and HCV have few or no symptoms of illness. For those who do develop symptoms of viral hepatitis, the most common are flu-like symptoms including:
How Is Viral Hepatitis Prevented
Prevention of hepatitis involves measures to avoid exposure to the viruses, using immunoglobulin in the event of exposure, and vaccines. Administration of immunoglobulin is called passive protection because antibodies from patients who have had viral hepatitis are given to the patient. Vaccination is called active protection because killed viruses or non-infectious components of viruses are given to stimulate the body to produce its own antibodies.
Avoidance of exposure to viruses
Prevention of viral hepatitis, like any other illness, is preferable to reliance upon treatment. Taking precautions to prevent exposure to another individual’s blood , semen , and other bodily secretions and waste will help prevent the spread of all of these viruses.
Use of immunoglobulins
Immune serum globulin is human serum that contains antibodies to hepatitis A. ISG can be administered to prevent infection in individuals who have been exposed to hepatitis A. ISG works immediately upon administration, and the duration of protection is several months. ISG usually is given to travelers to regions of the world where there are high rates of hepatitis A infection and to close or household contacts of patients with hepatitis A infection. ISG is safe with few side effects.
Hepatitis A
Individuals at increased risk of acquiring hepatitis A are:
Some local health authorities or private companies may require hepatitis A vaccination for food handlers.
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B vaccine is recommended for:
Read Also: Can You Get Hepatitis C From Oral Sex
Can Hepatitis Be Prevented
There are different ways to prevent or lower your risk for hepatitis, depending on the type of hepatitis. For example, not drinking too much alcohol can prevent alcoholic hepatitis. There are vaccines to prevent hepatitis A and B. Autoimmune hepatitis cannot be prevented.
NIH: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
What Is The Treatment For Viral Hepatitis
Treatment of acute viral hepatitis and chronic viral hepatitis are different. Treatment of acute viral hepatitis involves resting, relieving symptoms, and maintaining an adequate intake of fluids. Treatment of chronic viral hepatitis involves medications to eradicate the virus and taking measures to prevent further liver damage.
Acute hepatitis
In patients with acute viral hepatitis, the initial treatment consists of relieving the symptoms of nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain . Careful attention should be given to medications or compounds, which can have adverse effects in patients with abnormal liver function . Only those medications that are considered necessary should be administered since the impaired liver is not able to eliminate drugs normally, and drugs may accumulate in the blood and reach toxic levels. Moreover, sedatives and “tranquilizers” are avoided because they may accentuate the effects of liver failure on the brain and cause lethargy and coma. The patient must abstain from drinking alcohol since alcohol is toxic to the liver. It occasionally is necessary to provide intravenous fluids to prevent dehydration caused by vomiting. Patients with severe nausea and/or vomiting may need to be hospitalized for treatment and intravenous fluids.
Chronic hepatitis
Medications for chronic hepatitis C infection include:
- oral daclatasvir
Medications for chronic hepatitis B infection include:
- oral entecavir
- oral tenofovir
Fulminant hepatitis
Read Also: What Is Hepatitis A And B And C
What Are The Treatments For Hepatitis
Treatment for hepatitis depends on which type you have and whether it is acute or chronic. Acute viral hepatitis often goes away on its own. To feel better, you may just need to rest and get enough fluids. But in some cases, it may be more serious. You might even need treatment in a hospital.
There are different medicines to treat the different chronic types of hepatitis. Possible other treatments may include surgery and other medical procedures. People who have alcoholic hepatitis need to stop drinking. If your chronic hepatitis leads to liver failure or liver cancer, you may need a liver transplant.
What Are The Common Types Of Viral Hepatitis
Although the most common types of viral hepatitis are HAV, HBV, and HCV, some clinicians had previously considered the acute and chronic phases of hepatic infections as “types” of viral hepatitis. HAV was considered to be acute viral hepatitis because the HAV infections seldom caused permanent liver damage that led to hepatic failure. HBV and HCV produced chronic viral hepatitis. However, these terms are outdated and not currently used as frequently because all of the viruses that cause hepatitis may have acute phase symptoms . Prevention techniques and vaccinations have markedly reduced the current incidence of common viral hepatitis infections however, there remains a population of about 1 to 2 million people in the U.S. with chronic HBV, and about 3.5 million with chronic HCV according to the CDC. Statistics are incomplete for determining how many new infections occur each year the CDC documented infections but then goes on to estimate the actual numbers by further estimating the number of unreported infections .
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis C
Types D, E, and G Hepatitis
Individuals who already have chronic HBV infection can acquire HDV infection at the same time as they acquire the HBV infection, or at a later time. Those with chronic hepatitis due to HBV and HDV develop cirrhosis rapidly. Moreover, the combination of HDV and HBV virus infection is very difficult to treat.
- HIV patients
- People with hemophilia who receive blood clotting factors
Read Also: Is Hepatitis A Sexually Transmitted
How Long Before I Have Symptoms
Many people have mild symptoms or no symptoms, which is why hepatitis is sometimes called a âsilentâ disease.
Hepatitis A. The symptoms usually show up 2 to 6 weeks after the virus enters your body. They usually last for less than 2 months, though sometimes you can be sick for as long as 6 months.
Some warning signs that you may have hepatitis A are:
Hepatitis B. The symptoms are the same as hepatitis A, and you usually get them 3 months after you’re infected. They could show up, though, anywhere from 6 weeks to 6 months later.
Sometimes the symptoms are mild and last just a few weeks. For some people, the hep B virus stays in the body and leads to long-term liver problems.
Hepatitis C. The early symptoms are the same as hepatitis A and B, and they usually happen 6 to 7 weeks after the virus gets in your body. But you could notice them anywhere from 2 weeks to 6 months later.
For about 25% of people who get hep C, the virus goes away on its own without treatment. In other cases, it sticks around for years. When that happens, your liver might get damaged.
Remember, it’s possible to spread all the types of hepatitis even if you don’t show any signs of being sick.
How Long Do The Viruses That Cause Hepatitis Survive Outside The Body
The hepatitis A virus can live outside the body for months.
ishonestNo.233 – Pigmentation & Blemishes
Hepatitis B survives for at least 7 days while still being able to cause an infection.
Hepatitis C can live on household and clinic surfaces for up to 6 weeks at room temperature. In open air, it can survive for at least 4 days.
Read Also: What Are The Side Effects Of Hepatitis
How Is It Spread
Hepatitis A is spread when a person ingests fecal mattereven in microscopic amountsfrom contact with objects, food, or drinks contaminated by feces or stool from an infected person.
Hepatitis B is primarily spread when blood, semen, or certain other body fluids- even in microscopic amounts from a person infected with the hepatitis B virus enters the body of someone who is not infected. The hepatitis B virus can also be transmitted from:
- Birth to an infected mother
- Sex with an infected person
- Sharing equipment that has been contaminated with blood from an infected person, such as needles, syringes, and even medical equipment, such as glucose monitors
- Sharing personal items such as toothbrushes or razors
- Poor infection control has resulted in outbreaks in health care facilities
Hepatitis C is spread when blood from a person infected with the Hepatitis C virus even in microscopic amounts enters the body of someone who is not infected. The hepatitis C virus can also be transmitted from:
- Sharing equipment that has been contaminated with blood from an infected person, such as needles and syringes
- Receiving a blood transfusion or organ transplant before 1992
- Poor infection control has resulted in outbreaks in health care facilities
- Birth to an infected mother
Can Hepatitis B And C Be Prevented
Today, all babies get vaccinated against the hepatitis B virus in a series of three shots over a 6-month period. Doctors also recommend “catch-up” vaccination for all kids and teens younger than 19 years old who didn’t get the vaccine as babies or didn’t get all three doses.
Unfortunately, there’s no vaccine for hep C yet.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Treat Hepatitis B
What Causes Hepatitis A And How Is It Contracted
People develop hepatitis A infection after contracting HAV. This virus is typically transmitted by ingesting food or liquid contaminated with fecal matter that contains the virus. Once transmitted, the virus spreads through the bloodstream to the liver, where it causes inflammation and swelling.
In addition to transmission from eating food or drinking water containing HAV, the virus can also be spread by close personal contact with an infected person. HAV is contagious, and a person who has hepatitis A can easily pass the disease to others living in the same household.
You can contract hepatitis A by:
- eating food prepared by someone with the hepatitis A virus
- eating food handled by preparers who dont follow strict hand-washing routines before touching food that you eat
- eating sewage-contaminated raw shellfish
- not using condoms when having sex with someone who has the hepatitis A virus
- drinking polluted water
- coming in contact with hepatitis A-infected fecal matter
If you contract the virus, you will be contagious two weeks before symptoms even appear. The contagious period will end about one week after symptoms appear.