What Is The Difference Between Hepatitis B Surface Antibody And Antigen
An antigen is a substance that induces antibody production. Hepatitis B surface antigen is a protein on the surface of hepatitis B virus.
Hepatitis B surface antibodies are produced by the bodys immune system in response to HBsAg. The presence of adequate hepatitis B surface antibodies in the blood indicates protection against hepatitis B virus infection.
How Is Hepatitis B Treated
There is no specific treatment for acute hepatitis B infections. Symptoms are usually treated with supportive care. This usually involves making sure that you are getting plenty of rest and enough fluids and nutrition by eating and drinking small amounts several times a day.
Chronic forms of hepatitis B may be treated with antiviral medications such as interferon, entecavir, tenofovir, lamivudine, and adefovir. However, some antiviral drugs can have serious side effects and not all people need to be treated. Often, people with chronic hepatitis will be closely monitored to see if they develop cirrhosis or liver cancer. It is important to talk to your healthcare provider about your treatment options and the risks and benefits of those currently available.
What Is The Purpose Of A Hepatitis B Test
Hepatitis B test is performed to detect, classify, and treat hepatitis B virus infection.
Hepatitis B blood tests involve the measurement of several HBV-specific antigens and antibodies. In addition, HBV blood tests also include liver enzymes and liver function tests to assess and monitor the condition of the liver and provide appropriate treatment.
The HBV specific tests include the following:
- HBsAg: HBsAg is an antigen found on the surface of hepatitis B virus. HBsAg may be detected in the blood any time after 1 week post-exposure to HB virus, but usually appears after 4 weeks.
- Anti-HBs: Anti-HBs are antibodies produced by the bodys immune system to fight HBsAg. Anti-HBs from a prior infection or vaccination provides immunity against further infection.
- Hepatitis B core antigen : HBcAg is an antigen found in the core layer which covers the hepatitis B viral DNA.
- Hepatitis B core antibody : Anti-HBc is the antibody that fights HBcAg. Anti-HBc is the first detectable antibody after HBV infection. There are two kinds of Anti-HBc:
- Immunoglobulin M hepatitis B core antibody : IgM anti-HBc indicates acute or reactivated recent infection within the previous 6 months.
- Immunoglobulin G hepatitis B core antibody : IgG anti-HBc may indicate previous or chronic infection. Once present, IgG anti-HBc persists for a lifetime.
You May Like: Is Hepatitis C Considered An Std
Hep B Titer Test Required By Most Schools And Employers
This assay is used to determine immune status for Hepatitis B.
Hepatitis B Surface Antibody : The surface antibody is formed in response to the hepatitis B virus. Your body can make this antibody if you have been vaccinated, or if you have recovered from a hepatitis B infection. If this test is positive, then your immune system has successfully developed a protective antibody against the hepatitis B virus. This will provide long-term protection against future hepatitis B infection. Someone who is surface antibody positive is not infected, and cannot pass the virus on to others.
This is a Quantitative test required by many schools and medical programs. Levels of anti-HBs will be provided.
Taking A Hepatitis B Test
Testing for hepatitis B is performed on a sample of blood. A doctor, nurse, or other health care provider can obtain a blood sample using a small needle to draw blood from a vein.
At-home hepatitis B testing requires that users carefully follow instructions provided in the test kit to collect a small sample of blood, package the sample, and mail it to a lab for testing.
Don’t Miss: How Would You Know If You Have Hepatitis C
How Much Does The Test Cost
The cost of hepatitis B testing depends on the tests that are performed, where the test is conducted, and a patientâs health insurance coverage. When testing is ordered by a doctor, patients with health insurance may find it helpful to discuss the cost of testing with their health insurance company as they may be responsible for testing costs as well as other out-of-pocket costs such as copays and deductibles.
For patients without health insurance or for whom insurance doesnât cover the cost of testing, it may be helpful to discuss the cost of hepatitis B testing with a doctor or hospital administrator.
The cost of at-home hepatitis B testing starts around $45. At-home test kits may also test for additional types of viral hepatitis in the same sample. The cost of test panels that look for more than one type of viral hepatitis start around $80.
Evaluation Of Individuals Suspected Of Having An Hbv Infection
Given the perinatal and childhood vaccination programs already in place in North America, most HBV-infected individuals will likely present with chronic infection. Such individuals are likely to have risk factors that include immigration from high endemicity regions, injection drug use or sexual contact with an infected person 1) . Therefore, the present guideline will provide diagnostic recommendations first for individuals suspected of having chronic HBV infection and, subsequently, for those with acute infection. The diagnosis of HBV infection in any individual has important management implications, including appropriate counselling, monitoring and/or treating and vaccinating family or at-risk contacts.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Medication Side Effects
Spontaneous Decrease In Anti
To confirm the spontaneous decreases in anti-HB titers, we re-measured anti-HB titers in 247 and 91 subjects who did not receive a booster HBV vaccination at 1 and 2 years after completing the initial vaccination schedule, respectively . Overall, the mean anti-HB titers at 1 and 2 years after vaccination were lower than the mean primary response titers . During the observation period, 18 of the 247 and 17 of the 91 subjects showed anti-HB titers of < 10 mIU/mL at 1 and 2 years after vaccination, respectively.
Correlation between the primary response and the anti-HB titer at 1 and 2 years after vaccination. The vertical axis shows the anti-HB titers at 1 year and 2 years after vaccination. The horizontal axis shows the primary response to vaccination. Spearmans correlation coefficient was used to assess the correlation between the anti-HB titer and the primary response at both time periods both values were statistically significant: r=0.893, p< 0.0001 r=0.902, p< 0.001.
Preparation Prior To Transport
Label the specimen container with the patients full name, date of collection and one other unique identifier such as the patients date of birth or Health Card Number. Failure to provide this information may result in rejection or testing delay.
Centrifuge if using SST. Place specimen in biohazard bag and seal. Specimens should be stored at 2-8°C following collection.
Specimens more than the following number of days post collection will not be tested:
- > 6 days for Hepatitis B surface antigen
- > 7 days for Hepatitis B e Antigen and Hepatitis B e Antibody
- > 10 days for Hepatitis B core Antigen and Hepatitis B surface Antibody
Recommended Reading: What Are The Symptoms Of Having Hepatitis C
How To Get Tested
Hepatitis B testing is typically prescribed by a doctor and performed in a hospital, lab, or other medical setting. Taking a hepatitis B test requires a blood sample, which can be collected by a health care professional.
For laboratory-based testing, blood is drawn from a patientâs vein. After blood is collected, the sample is sent to a laboratory for analysis.
Sequence Following An Initial Negative Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Titer
As you obtain documentation, please submit documentation of each step to CastleBranch
- Initial Hepatitis B titer negative for immunity
- Receive Hepatitis B challenge dose/booster
- Repeat Hepatitis B titer 4-6 weeks after challenge/booster vaccine
Read Also: Does Medicare Cover Hepatitis C Screening
When To Get Tested
When you have risk factors for HBV infection or when you have signs and symptoms of hepatitis, such as jaundice or unexplained elevated blood levels of alanine aminotransferase , a liver-associated enzyme when you have a condition that requires chemotherapy or drugs that suppress your immune system when you are being treated for HBV or hepatitis C when it is unclear whether you have immunity and your healthcare practitioner is considering giving you the hepatitis B vaccine
What Does The Test Result Mean
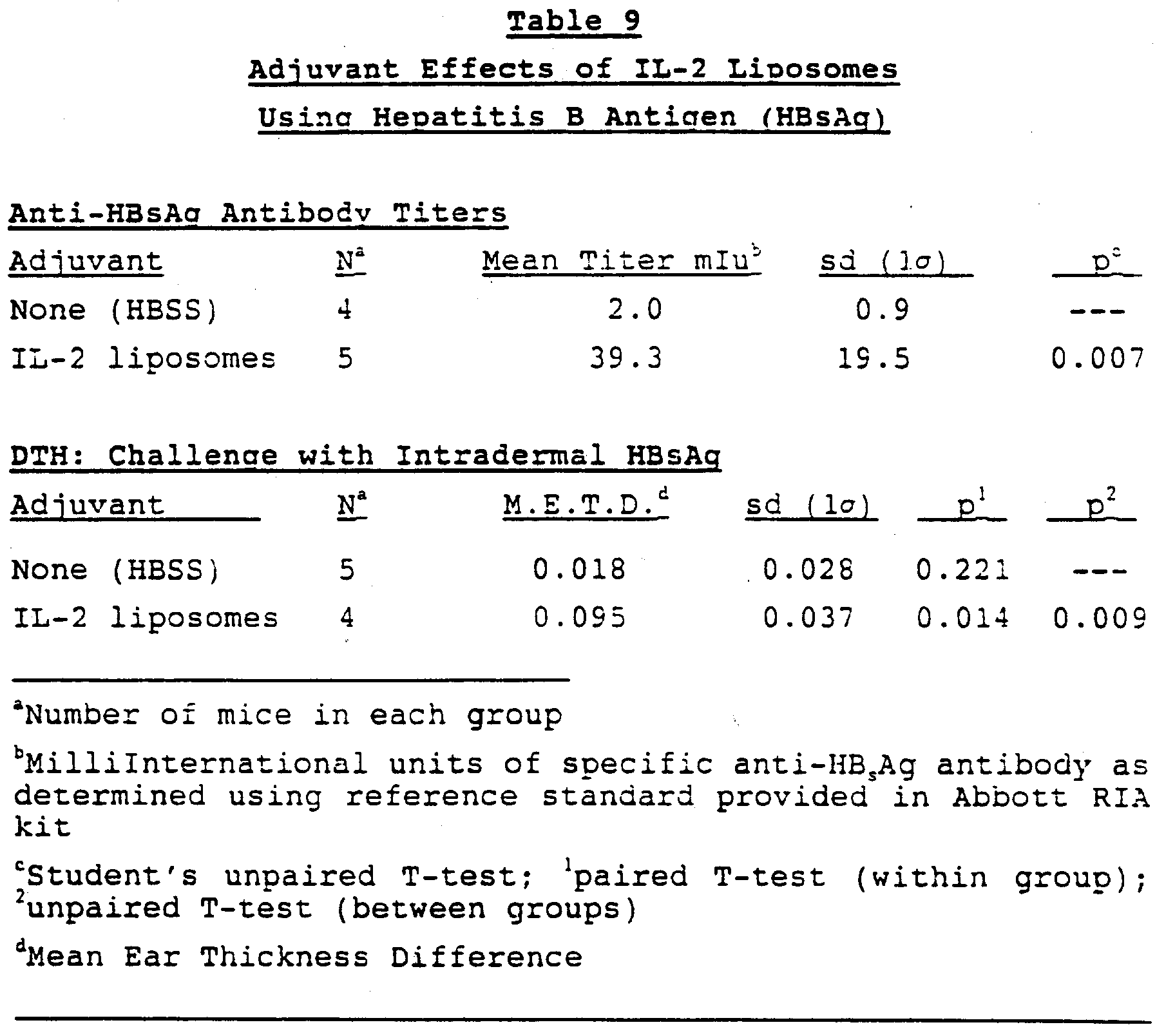
The tests for hepatitis B may be ordered individually but are often ordered in some combination, depending on the reason for testing. Results of the tests are typically evaluated together. Sometimes the meaning of one result depends on the result of another test. However, not all tests are performed for all people.
The table below summarizes possible interpretations of some common patterns of results.
| Initial Tests | |
| None detected or detected at very low level | Chronic infection but low risk of liver damage carrier state |
*Note: There are some types of HBV that do not make e-antigen. In areas where these strains of HBV are common , testing for HBeAg is not very useful. In these cases, a negative HbeAg result does not necessarily mean that the person is not infectious it may be that the person is infected with a strain that does not make the e-antigen.
Monitoring treatment of chronic infection: If the results from initial and follow-up testing indicate that a person has chronic hepatitis B, then the individual may be treated with medication and the effectiveness of that treatment may be monitored using the tests for HBe and HBs antigen and antibody and HBV DNA:
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Titer Lab Test
When Should I Get Hepatitis B Testing
Using hepatitis B tests to screen for HBV is recommended for certain groups that are at an increased risk of infection. Groups that may benefit from hepatitis B screening include:
- Pregnant people
- People born in parts of the world where hepatitis B is more common, including Africa, Asia, Eastern Europe, South America, and parts of the Middle East
- People who didnât receive a hepatitis B vaccine
- HIV-positive people
- Pain in the joints or abdomen
- Loss of appetite, nausea, or vomiting
- Yellowish skin and eyes
Using hepatitis B testing to assess immunity to HBV may be used before or after vaccination. Pre-vaccination testing is not always needed but may be performed if there is a chance that a patient has previously been infected with HBV or has already been vaccinated. Post-vaccination testing is used in certain groups of people who are at an especially elevated risk for HBV infection, including infants born to mothers with a hepatitis B infection.
Hepatitis B Immunization And Postimmunizationserology
Michael John, MB, Ch.B., FRCP
Before the introduction of avaccine, hepatitis B virus was a major occupational risk to health care workers.Some of the highest infection rates were found in dentists and surgeons.1Infected health care workers have a 5-10% risk of developing chronic hepatitis B. A numberof clusters of dentist-to-patient HBV transmissions have been reported over the years,although these have decreased since the introduction of universal precautions.2Recent guidelines from Health Canada recommend restriction of practice of health careworkers who test positive for hepatitis B e antigen.3
The development of hepatitis vaccines in the 1980s has substantially decreased dentalworkers risk of acquiring HBV. A recent survey4 of dentists in Canadashowed that more than 90% had completed an immunization series and an additional 3% hadnatural immunity. However, rates of immunization among dental assistants and hygienistswas found to be much lower.
Hepatitis B Vaccines
The vaccine is administered intramuscularly into the deltoid muscle, as glutealinjection may result in decreased response rates. Response to vaccine following a 3-doseseries is typically greater than 95% in young, healthy people, although it decreases withage . Other factors such assmoking, obesity and chronic disease decrease vaccine efficacy and may be used to predictrisk of nonresponse.6 Adverse events are minimal, although mild injection-sitereactions may occur in 20% of recipients.
References
Don’t Miss: Can You Catch Hepatitis C From Having Sex
Question 3 How Is The Quantitative Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Test Performed
An immunometric technique is used. The anti-HBs binds to HBsAg ad and ay subtypes, which are coated on the test wells. Binding of a horseradish peroxidase-labeled HBsAg conjugate to the anti-HBs completes the sandwich formation. Unbound materials are then washed away. In the next step, the horseradish peroxidase catalyzes oxidation of a luminogenic substrate, producing light. Light signals are detected and quantified. Intensity of the light is proportional to the amount of anti-HBs present in the patient sample. The result is standardized to an international unit system and reported as milliinternational units per milliliter .
Simple Linear Regression Changes In Hbsab Titers With Age
Linear regression equations were estimated for the correlation between age and HBsAb titer, with a slope of 18.969 and a constant of 255.082 . The initial titer was 224 IU/L, reaching a level of 100 IU/L at 7.9 years old, a level of 10 IU/L at 12.9 years old, and a level of zero at 13.4 years old .
Fig. 3
Also Check: Hepatitis B Liver Cancer Symptoms
Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Blood Test
This test is used to determine the status of a persons immunity to the Hepatitis B virus . Immunity is determined by screening for antibodies which provide protection against infection. The results of this test are quantitative.
Hepatitis B is a viral infection of the liver spread through contact with contaminated bodily fluids including blood. Transmission can occur through various types of exposure including sexual contact. It is possible for a pregnant woman to spread the infection to her infant during childbirth. More than half of Hep B infections display no symptoms. When symptoms do occur, the most common are loss of appetite, fatigue, nausea, abdominal pain, jaundice, and dark colored urine. Chronic Hepatitis B infections may lead to the development of Cirrhosis or Liver Cancer.
A person can have immunity to Hepatitis B for several reasons.
1.) They have been vaccinated for Hep B. Vaccinations do not always provide permanent immunity. It is possible for a person to have been vaccinated and lose their immunity over time.
2.) They have been infected with Hep B, recovered, and now have a natural immunity. Because Hepatitis B does not always display symptoms, it is possible for a person to have been exposed and not be aware of it.
A person who wishes to screen for a current Hepatitis B infection may want to order the Hep B Surface Antigen test.
The Hepatitis B Surface Antibody test typically sees results in 1 business day.
Detection Period:
Hepatitis B Blood Tests
The Hepatitis B Panel of Blood Tests
Only one sample of blood is needed for a hepatitis B blood test, but the Hepatitis B Panel includes three parts. All three test results are needed to fully understand whether a person is infected or not. Below is an explanation of the 3-part Hepatitis B Panel of blood test results.
You May Like: Difference Between Hepatitis A And B
Evaluation Of The Booster Effect
Seventy-two HBsAb-negative children received a single booster vaccination. Titer tests were performed a month after receiving the booster vaccination. At this time, 46 were positive, 23 were weakly positive, and 3 were negative. Only 3 children received a booster vaccination, according to the schedule of 0, 1, and 6 months. All 3 showed positive findings a month after completing the booster schedule.
Specimen Choice Collection And Transport
The specimen of choice for the diagnosis of HBV infection is blood. Serological tests for viral antigens and antibodies are typically used for diagnostic screening and can be performed on either serum or plasma. Both HBV antigens and antibody are stable at room temperature for days, at 4°C for months, and frozen at -20°C to -70°C for many years. Because modern testing involves automated enzyme immunoassays that depend on colourimetic or chemiluminescence signal measurement, care should be taken to avoid hemolysis of the sample because it may interfere with the ability of the assay to accurately detect these markers.
A number of nucleic acid-based tests, which have been the subject of recent reviews , are available to directly detect HBV-DNA in serum or plasma. Care must be taken to avoid the degradation of the viral nucleic acid in the specimen, which can result in falsely low or no measurable viral load. Serum should therefore be removed from clotted blood within 4 h of collection and stored at -20°C to -70°C , and can be subjected to up to eight short-term freeze-thaw cycles without significant loss of detectable HBV-DNA . Alternatively, the presence of EDTA in plasma is known to stabilize viral nucleic acids. EDTA blood can be stored for up to five days at 4°C without affecting the viral load . Polymerase chain reaction-based tests can use either serum or plasma, while hybridization-based assays recommend the use of serum.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C And Liver Failure