How Is Hepatitis C Transmitted
Because HCV is primarily spread through contact with infected blood, people who inject drugs are at increased risk for HCV infection. HCV can also be transmitted from an infected mother to child at the time of birth, from unregulated tattoos or body piercings, and from sharing personal items that may be contaminated with infected blood, even in amounts too small to see. Much less often, HCV transmission occurs through sexual contact with an HCV-infected partner, especially among people with multiple sex partners and men who have sex with men. Currently in the United States, health care related transmission of HCV is rare, but people can become infected from accidental needle sticks and from breaches in infection control practices in health care facilities.
What Is Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a contagious liver infection caused by the hepatitis C virus .
The hepatitis C virus was discovered in 1989. Prior to that, it was associated with blood transfusions, but was called non-A, non-B hepatitis because the virus could not be identified. It is now known that there are several genetic types of the hepatitis C virus.
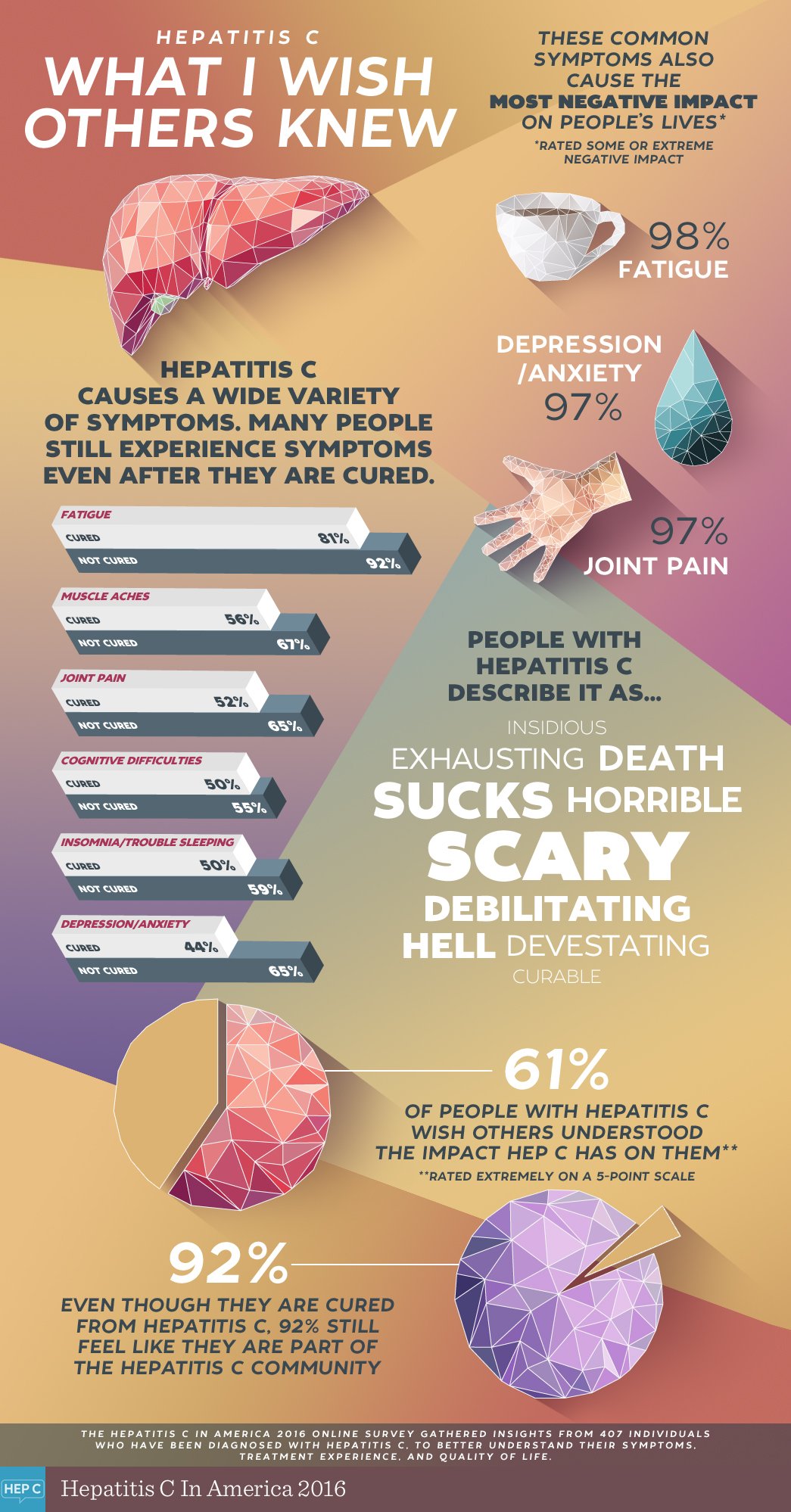
The natural course of hepatitis C disease varies from one person to another.
Hepatitis C can be treated and cured. Almost everyone living with HCV can now be cured with a one-pill-a-day regimen in eight-to-twelve weeks. These new medications are generally well-tolerated. In order to access HCV treatment, it is necessary to see your doctor to discuss treatment options. Access to treatment continues to improve as new medication regimens are made available by private health insurers and public health programs like the VA Medical Centers, the AIDS Drug Assistance Program, Medicaid, and MediCal.
How Common Is Hepatitis C In The United States
In the United States, hepatitis C is the most common chronic viral infection found in blood and spread through contact with blood.14
Researchers estimate that about 2.7 million to 3.9 million people in the United States have chronic hepatitis C.13 Many people who have hepatitis C dont have symptoms and dont know they have this infection.
Since 2006, the number of new hepatitis C infections has been rising, especially among people younger than age 30 who inject heroin or misuse prescription opioids and inject them.15,16
New screening efforts and more effective hepatitis C treatments are helping doctors identify and cure more people with the disease. With more screening and treatment, hepatitis C may become less common in the future. Researchers estimate that hepatitis C could be a rare disease in the United States by 2036.17
Also Check: Types Of Hepatitis B Virus
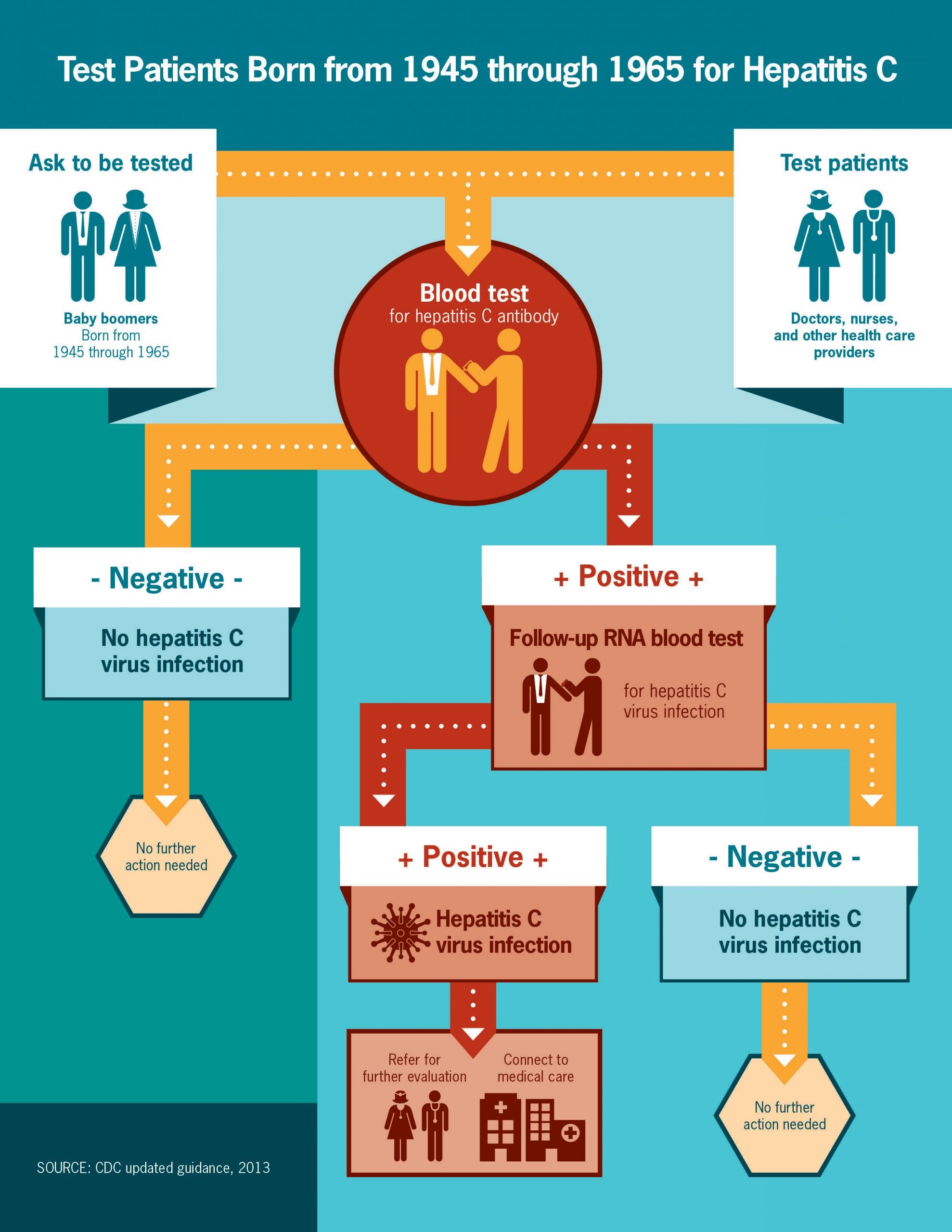
Getting Tested Is The Only Way To Know If You Have Hepatitis C
A blood test called a hepatitis C antibody test can tell if you have been infected with the hepatitis C viruseither recently or in the past. If you have a positive antibody test, another blood test is needed to tell if you are still infected or if you were infected in the past and cleared the virus on your own.
- Are 18 years of age and older
- Are pregnant
- Currently inject drugs
- Have ever injected drugs, even if it was just once or many years ago
- Have HIV
- Have abnormal liver tests or liver disease
- Are on hemodialysis
Blood Transfusion/receipt Of Blood Products
Early case-control studies of patients with newly acquired, symptomatic non-A, non-B hepatitis found a significant association between disease acquisition and a history six months prior to illness of blood transfusions, injection drug use, health care employment with frequent exposure to blood, personal contact with others who had hepatitis, multiple sexual partners or low socioeconomic status. Today, HCV is rarely transmitted by blood transfusion or transplantation of organs due to thorough screening of the blood supply for the presence of the virus and inactivation procedures that destroy bloodborne viruses. In the last several years, blood banks have instituted techniques that utilize nucleic acid amplification of the hepatitis C virus, which will detect the presence of virus even in newly-infected patients who are still hepatitis C antibody-negative. These techniques are estimated to have prevented 56 transfusion-associated HCV infections per year in the U.S. since 1999, and have lowered the current risk of acquiring HCV via transfused blood products to 1 in 2 million.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Early Signs Of Hepatitis C
How Is Hepatitis C Infection Prevented
Unfortunately, there is no vaccine to prevent hepatitis C. To reduce your risk of getting hepatitis C:
- Injection drug use is the most common way people get hepatitis C. Avoid injecting drugs to reduce your risk. If you do inject drugs, use sterile injection equipment. Avoid reusing or sharing.
- Avoid sharing personal care items that might have blood on them
- If you are a health care or public safety worker, follow universal blood/body fluid precautions and safely handle needles and other sharps
- Consider the risks if you are thinking about tattooing, body piercing, or acupuncture are the instruments properly sterilized?
- If youre having sex with more than one partner, use latex condoms correctly and every time to prevent the spread of sexually transmitted diseases, including hepatitis C.
Complications Of Hepatitis C
If the infection is left untreated for many years, some people with hepatitis C will develop scarring of the liver .
Over time, this can cause the liver to stop working properly.
In severe cases, life-threatening problems, such as liver failure, where the liver loses most or all of its functions, or liver cancer, can eventually develop.
Treating hepatitis C as early as possible can help reduce the risk of these problems happening.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B And C Test Price
Hepatitis C An Introduction
Caused by the HCV or Hepatitis C virus, this condition manifests through liver inflammation which could further lead to severe liver damage. This inflammation and infection of the liver quickly spread through contaminated blood, rendering either chronic or acute symptom.
In case of acute hepatitis C, the symptoms onset is swift which may last for a few weeks. On the other hand, chronic hepatitis C is characterized by a gradual development of symptoms, which may stretch over a period of few months. Owing to the slow yet debilitating dawn of the chronic symptoms in a patient, this condition has also been called as sleeping dragon.
This is a relatively common disease, affecting almost 71 million people worldwide.
Being viral in nature, Hepatitis C is extremely contagious with no vaccines devised to prevent its occurrence yet .
The hepatitis C virus is difficult to eliminate from the body by the immune system.
This is why infections caused by this virus spread easily and aggressively.
Under severe conditions, it can lead to liver failure or even cause liver cancer.
Stages Of Hepatitis C
Incubation Period: This is the period between initial exposure to onset of the disease, and can last between two to ten weeks.
Acute Hepatitis: This stage is titled as a separate condition if it progresses no further than six months, after which the virus is removed from the body naturally.
Chronic Hepatitis: If the condition persists after six months, it is known as chronic hepatitis, which makes up about 85% of all cases. At this point, the risk of severe liver damage and cirrhosis grows larger with every passing day.
Cirrhosis: This refers to the stage at which liver damage is so extensive that scar tissue replaces healthy cells as a result of inflammation. It may take decades for Hepatitis C to do such severe damage.
Liver Cancer: This is not a guaranteed result of cirrhosis, however, the likelihood of you developing it is a lot higher if you do have cirrhosis.
Don’t Miss: How To Treat Hepatitis A And B
Diagnosis And Treatment Of Hcv Infection
Hepatitis C is rarely diagnosed at the time of infection, since few individuals are symptomatic. Asymptomatic cases may be detected, however, through recommended screening in high-risk populations, such as intravenous drug users and recipients of blood transfusions or organ transplants in which the tissues were not initially tested for HCV. Diagnostic testing and screening for hepatitis C centres on the detection of circulating antibodies and RNA specific to HCV. HCV RNA is detectable within 1 to 3 weeks of infection, and the antibodies are usually detectable within 8 to 12 weeks.
Treatment of hepatitis C is focused on the elimination of viral infection, improvement of liver function, and the prevention of cirrhosis and liver cancer. Liver function may be improved with the use of interferon, which reduces HCV replication and stimulates the immune system to fight HCV infection. Interferon is often given in combination with ribavirin, an antiviral drug that mimics nucleosides and thereby interferes with viral reproduction. Ribavirin may also be used in combination with agents known as sofosbuvir and velpatasvir, which inhibit key molecules involved in HCV RNA replication. Treatment of end-stage or advanced liver disease and cirrhosis caused by HCV infection is also possible with liver transplantation, though recurrence of detectable HCV infection is almost universal after transplantation.
Enteric Routes: Transmission Of Hepatitis A And Hepatitis E
The Hepatitis A and hepatitis E viruses are both transmitted by enteric, that is digestive or by fecal, routes. This is also known as the fecal-oral route. To be exposed to these viruses, you must ingest fecal matter that is infected with the virus. While there are several ways in which this fecal-oral route can be established, poor hygiene and poor sanitary conditions in some countries lead to higher rates of infection of these viruses.
As a result, some areas of the world, like India, Bangladesh, and Central and South America, are particularly prone to the hepatitis E virus. About one-third of people in the United States have been exposed to the hepatitis A virus.
It is believed that the hepatitis F virus may also be spread by enteric routes.
Read Also: How Do You Contract Hepatitis B Virus
What Other Tests Diagnose Hepatitis C
Once the diagnosis of hepatitis C is established, other tests may be done to determine whether the patient has developed liver fibrosis or scarring . This can be done with a needle biopsy of the liver, and examining the biopsied liver tissue under the microscope. Liver biopsy is less commonly done today because noninvasive tests are more readily available, more easily accomplished and less costly.
Liver imaging can evaluate fibrosis using ultrasound and MRI scans. Additionally, calculations using a variety of blood tests also can predict the degree of inflammation and fibrosis present. Genotype testing will typically be done to determine what subtype of hepatitis C the patient has, as this will impact what drugs are used for treatment.
Testing for other infections including HIV, hepatitis A, and hepatitis B is typically done to determine if the patient might have other conditions that could impact patient’s treatment and prognosis.
With the newest forms of antiviral treatment, the most common types of chronic hepatitis C can be cured in most individuals.
Use Licensed Tattoo Piercing And Acupuncture Studios
Tattoos and piercings can be the source of HCV infection if a contaminated needle is used. If the needles or equipment used on your body are not properly sterilized, you could be exposed to blood-borne diseases, such as hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and HIV.
Acupuncture, fillers, cosmetic injections and other therapeutic procedures can also be sources of HCV transmission. Make sure that any facility you use is licensed and that sterile needles are used for all bodywork.
You May Like: Can You Live A Normal Life With Hepatitis C
How Common Is Hepatitis C
There are approximately 30,000 new cases of acute hepatitis C every year in the United States as estimated by the CDC. In 2015, it was estimated that approximately 3.5 million Americans were infected with hepatitis C.
On a global scale, the prevalence of hepatitis C is greatest in Central and East Asia, North Africa, and the Middle East. In 2016, it was estimated that 177 million people worldwide had antibodies to hepatitis C virus.
- exposure to other people who do or might have hepatitis C.
Interpreting Hcv Rna Test Results
It is essential that the provider understands how to interpret HCV RNA test results, especially during the course of HCV treatment.
| Result of HCV RNA Test | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| A quantified viral load — any exact number | Ongoing HCV infection |
| “Detected” | The HCV RNA is detectable but the number of international units is so low that it cannot be quantified accurately. This indicates extremely low level of virus is present. |
| “< 12 IU/mL” or “< 15 IU/mL” or “< 25 IU/mL” All of these are “less than the LLOQ” | HCV RNA is undetectable. No virus is detected at all in the patient’s serum specimen. |
Read Also: How Do You Pass Hepatitis C
What Are The Treatments For Hepatitis C
Treatment for hepatitis C is with antiviral medicines. They can cure the disease in most cases.
If you have acute hepatitis C, your health care provider may wait to see if your infection becomes chronic before starting treatment.
If your hepatitis C causes cirrhosis, you should see a doctor who specializes in liver diseases. Treatments for health problems related to cirrhosis include medicines, surgery, and other medical procedures. If your hepatitis C leads to liver failure or liver cancer, you may need a liver transplant.
How Does Hepatitis C Spread
Hepatitis C is spread only through exposure to an infected person’s blood.
High-risk activities include:
- Sharing drug use equipment. Anything involved with injecting street drugs, from syringes, to needles, to tourniquets, can have small amounts of blood on it that can transmit hepatitis C. Pipes and straws to smoke or snort drugs can have blood on them from cracked lips or nosebleeds. Get into a treatment program if you can. At the very least, don’t share needles or equipment with anyone else.
- Sharing tattoo or piercing tools. Nonsterile items and ink can spread contaminated blood.
- Blood transfusions in countries that donât screen blood for hepatitis C.
- Nonsterile medical equipment. Tools that arenât cleaned properly between use can spread the virus.
- Blood or cutting rituals. Sharing the tools or exchanging blood can transmit hepatitis C.
Medium-risk activities include:
You May Like: How Can You Catch Hepatitis B
How To Prevent Hepatitis C Infection
Hepatitis C is a blood-borne infection. To reduce the risk of infection, avoid sharing personal items with others. Do not use injected drugs. If you do use injected drugs, never share needles and equipment with others. Getting tattoos and body piercings can put you at risk. Use condoms during sex. Health care workers should take precautions to avoid needlesticks and properly dispose of needles and other materials that encounter blood. Speak to your doctor about your risk factors and follow recommended screening standards for hepatitis C.
How to Prevent Giving Hepatitis C
If you have hepatitis C, these common precautions should be followed to prevent spreading or giving hepatitis C to others:
- Cover cuts and blisters
- Properly dispose of any used bandages, tissues, tampons, or anything else containing your blood
- Wash your hands or any objects that have encountered your blood
- Clean spilled blood on surfaces with household bleach and water
- Don’t share personal items that have your blood on it
- Do not breastfeed if your nipples becomes cracked and bleed
- Do not donate blood, sperm, or organs
Hepatitis C : Symptoms, Treatments, Antivirals
- WHO: “Hepatitis C.”
- Medscape: “What is the mortality and morbidity of hepatitis C ?”
- US Dept. of Veterans Affairs: “Is there a cure for HIV or hepatitis C?” “Viral Hepatitis and Liver Disease.”
- Medscape: “Liver transplantation.”
Do Not Inject Drugs Or Share Needles
Drug Use
Intravenous drug use, or injecting drugs in any way, is the leading single cause of the spread of HCV. To protect yourself, avoiding the use of used needles is the single best way to stop the spread of HCV.
It is difficult to abruptly stop using addictive drugs. If you are addicted to illegal drugs, a needle exchange program may be available in your area. These programs offer ways to get sterile syringes and many of these programs provide additional services, such as referrals to drug treatment centers, counseling, and primary health care. For more information, check with your local department of public health.
Medical Use
If you use needles for medical care, always use sterile equipment and do not share needles for any reason.
Read Also: What Medication Cures Hepatitis C
How Can We Prevent Hepatitis C In The Workplace
There is currently no vaccine for hepatitis C. The risk of hepatitis C can be significantly reduced by implementing infection control guidelines suitable for the specific workplace.
Infection control precautions are the first line of defense to protect workers from hepatitis C and other blood-borne diseases. For this reason, the Public Health Agency of Canada recommends routine practices when there is a risk of exposure to blood or certain body fluids.
Please see the OSH Answers document Routine Practices for more information.
CLOSE ALL
Add a badge to your website or intranet so your workers can quickly find answers to their health and safety questions.
Poor Infection Control For Tattooing And Piercing
The notes that HCV may be transmitted by receiving tattoos or piercings from unregulated settings with poor infection control standards.
Commercially licensed tattooing and piercing businesses are generally thought to be safe.
More informal settings may not have adequate safeguards to help avoid the spread of infections. Receiving a tattoo or piercing in settings such as in a prison or in a home with friends carries a of HCV transmission
Recommended Reading: How You Get Hepatitis B And C
Who Is At Risk For Hepatitis C
You are more likely to get hepatitis C if you:
- Have injected drugs
If you have chronic hepatitis C, you probably will not have symptoms until it causes complications. This can happen decades after you were infected. For this reason, hepatitis C screening is important, even if you have no symptoms.