What Is Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a contagious liver infection caused by the hepatitis C virus .
The hepatitis C virus was discovered in 1989. Prior to that, it was associated with blood transfusions, but was called non-A, non-B hepatitis because the virus could not be identified. It is now known that there are several genetic types of the hepatitis C virus.
The natural course of hepatitis C disease varies from one person to another.
Hepatitis C can be treated and cured. Almost everyone living with HCV can now be cured with a one-pill-a-day regimen in eight-to-twelve weeks. These new medications are generally well-tolerated. In order to access HCV treatment, it is necessary to see your doctor to discuss treatment options. Access to treatment continues to improve as new medication regimens are made available by private health insurers and public health programs like the VA Medical Centers, the AIDS Drug Assistance Program, Medicaid, and MediCal.
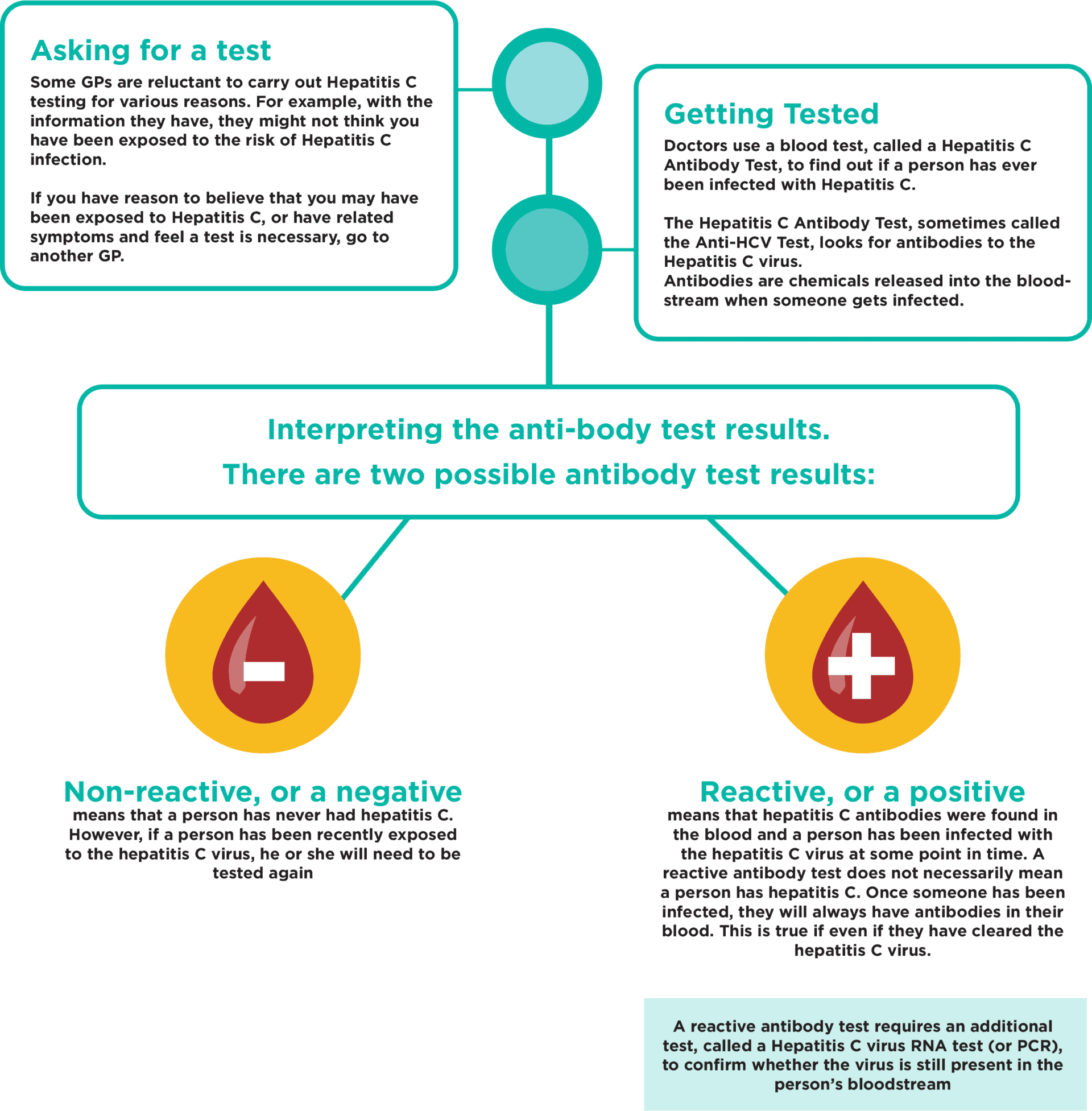
What Does It Mean When Different Types Of Blood Tests For Hepatitis C Give Different Results
The first test your provider probably will perform is called an “antibody” test. A positive result means that you were exposed to the hepatitis C virus at some point in your life.
If the result is positive, your provider will perform a second test called hepatitis C virus RNA to see if the virus is still in your body. If the RNA test result is positive, then you have chronic hepatitis C infection.
So what does it mean if you have a positive result for the first test but a negative result for the second?
How Is Hepatitis C Treated
Significant progress has been made in treating and even curing hepatitis C. Older hepatitis C treatments usually required weekly injections, had serious side effects, and often were not effective.
New and better oral medicines now can cure HCV for many people within 3 months. The new medicines were very expensive at first, but their prices have come down, a trend that health experts hope will continue as the incidence of HCV rises and increased screening brings more cases to light.
These medicines successfully cure about 90% of HCV patients. A new oral medicine under development looks promising for the 10% who don’t respond to the standard treatment. This new antiviral combination pill is currently under review by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration .
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Is More Infectious Than Hiv
Sharing Toothbrushes Scissors And Razors
There’s a potential risk that hepatitis C may be passed on through sharing items such as toothbrushes, razors and scissors, as they can become contaminated with infected blood.
Equipment used by hairdressers, such as scissors and clippers, can pose a risk if it has been contaminated with infected blood and not sterilised or cleaned between customers. However, most salons operate to high standards, so this risk is low.
How Should I Take Care Of Myself If I Have Hepatitis C

Good health habits are essential for those who have hepatitis C, especially avoidance of alcohol and other medicines and drugs that can put stress on the liver. You should eat a healthy diet and start exercising regularly. Your family healthcare provider can help you plan a diet that is healthy and practical.
Contact your healthcare provider about any medicines that you are taking, including overthe-counter medicine. Many medicines, including acetaminophen are broken down by the liver and may increase the speed of liver damage. You should also limit alcohol use, as it also speeds the progression of liver diseases like hepatitis C. An occasional alcoholic drink may be okay, but check with your healthcare provider first.
Recommended Reading: Can Hepatitis A Be Cured
If You Have Hepatitis C Should You Get A Flu Shot
Yes. Having chronic hepatitis C is actually a good reason to get the flu shot. Chronic hepatitis C is a condition that can increase your risk of complications if you do get influenza. That’s why it is recommended for people with hepatitis C, and most chronic liver diseases, to be vaccinated against the flu.
To stay up to date with your influenza vaccinations, you need to be vaccinated every year–ideally, early in the flu season or as soon as the vaccine becomes available. Typically, flu season is considered to be October to March. It’s best to get vaccinated annually because the vaccine is designed differently each year to target the strains of influenza that are expected to circulate during that particular flu season.
How Is The Virus Spread
Like hepatitis B virus, hepatitis C virus is spread when blood of an infected person enters the body of a person who is not infected, such as through sharing needles or “works” when shooting drugs or occupational needle stick injury. The risk of sexual transmission has not been thoroughly studied but appears to be low in long-term, monogamous relationships. There is no evidence that the hepatitis C virus can be transmitted by casual contact such as hugging or shaking hands, through foods, by sharing eating utensils or drinking glasses, or by coughing or sneezing. Hepatitis C is not spread by breastmilk.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Surface Ab Immunity
Activities That Can Pass Hepatitis C
- Sharing personal care items: Shared razors, toothbrushes, nail clippers and other household items that might have infected blood on them can pass hepatitis C.
- Condomless sex: In general, sexual transmission of hepatitis C is not common. The risk increases when certain factors are present, such as condomless anal sex, HIV, sexually transmitted infections, sex where blood is present, group sex and chemsex . Thus, the risk of transmission may be higher among some groups of men who have sex with men .
- Transmission from a parent to child during pregnancy or childbirth : The risk of perinatal transmission is about 5%.
- Needlestick injuries: An injury caused by a needle that punctures the skin can pass hepatitis C because of the possibility of exposure to hepatitis C from contact with blood in the needle or syringe.
How Does Hcv Spread From Person To Person
HCV is spread mainly through contact with the blood of a person who has HCV. In the United States, HCV is spread mainly by sharing needles or other injection drug equipment with someone who has HCV. HCV can also be spread through sexual contact. While the risk of transmission through sexual contact is low, the risk is increased in people with HIV.
Also Check: Royal Canin Veterinary Diet Hepatic Formula Dry Dog Food
Who Gets Hepatitis C
Persons at highest risk for HCV infection include:
- persons who ever injected illegal drugs, including those who injected once or a few times many years ago,
- people who had blood transfusions, blood products or organ donations before June 1992, when sensitive tests for HCV were introduced for blood screening, and
- persons who received clotting factors made before 1987.
Other persons at risk for hepatitis C include:
- long-term kidney dialysis patients,
- health care workers after exposures to the blood of an infected person while on the job,
- infants born to HCV-infected mothers,
- people with high-risk sexual behavior, multiple partners and sexually transmitted diseases,
- people who snort cocaine using shared equipment, and
- people who have shared toothbrushes, razors and other personal items with a family member who is HCV-infected.
What Do Hepatitis C Symptoms Look Like
Hepatitis C infection can go through two stages: acute and chronic. In the early, or acute stage, most people don’t have symptoms. If they do develop symptoms, these can include:
- flu-like symptoms, tiredness, high temperature and aches and pains
- loss of appetite
- tummy pain
- jaundice, meaning your skin and the whites of your eyes turn yellow
While for some people, the infection will clear without treatment, in most cases, acute infection will develop into long-term chronic infection. Chronic infection may not become apparent for a number of years until the liver displays signs of damage. These symptoms can include:
- mental confusion and depression these are specific to hepatitis C
- constantly feeling tired
- nausea, vomiting or tummy pain
- dark urine
- feeling bloated
- joint and muscle pain
Without treatment, chronic hepatitis C can cause scarring of the liver , which can cause the liver to stop working properly. A small number of people with cirrhosis develop liver cancer and these complications can lead to death. Other than a liver transplant, theres no cure for cirrhosis. However, treatments can help relieve some of the symptoms.
Recommended Reading: Can You Get Hepatitis C Sexually
Can You Have Hep C And Not Know It
We said this illness is sneaky, and in fact, most people with hepatitis C dont have any symptoms at the time they are diagnosed, says Dr. Goff. That makes it difficult to trace exactly where and when someone contracted the virus. Unfortunately, it also gives the virus time to wreak havoc on the liver before you feel sick enough to seek treatment.
Until we started actively screening the population, patients could be infected with hepatitis C and have absolutely no idea they had it, Dr. Fox says. Weve had to change our screening recommendations over time so that were not only testing people who self-report a history of a risk factor.
Currently, the CDC recommends all adults get screened for hepatitis C at least once in their lifetime, and pregnant women should be screened during each pregnancy. For people with ongoing risk factorsfor example, for people who regularly inject drugs or share needlesmore frequent testing is recommended.
Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
It is very important to know that not everyone with hepatitis C has symptoms. The only way to know if you have hepatitis is by talking to your doctor and getting a blood test.
Many people living with hepatitis C feel well and only have symptoms once the disease has progressed and there is serious liver damage.
If you do not have symptoms this does not mean that the virus isnt causing damage.
When first infected, some people may find:
- their urine becomes dark
- their eyes and skin turn yellow
- they experience a minor flu-like illness.
These symptoms may disappear within a few weeks, but this does not necessarily mean that the infection has been cleared.
Over time, symptoms that may develop include:
- tiredness and fatigue
- flu-like symptoms
- pain in the abdomen where the liver is located
- not feeling hungry and indigestion.
Around 30% of people who have been infected may clear the virus from their blood naturally, with no treatment, within 6 months. These people no longer have the hepatitis C virus and are not infectious, but will always have hepatitis C antibodies in their blood. The presence of hepatitis C antibodies shows that someone has been exposed to the virus, but does not offer any immunity against hepatitis C. People can become reinfected after clearing the virus naturally, or after treatment.
You May Like: Is Hepatitis A Virus Or Bacteria
Can Hcv Infection Be Prevented
The best protection against HCV is to never inject drugs. If you do inject drugs, always use new, sterile needles, and do not reuse or share needles, syringes, or other injection drug equipment.
People, including people with HIV, can also take the following steps to reduce their risk of HCV infection:
- Do not share toothbrushes, razors, or other personal items that may come in contact with another personâs blood.
- If you get a tattoo or body piercing, make sure the instruments used are sterile.
- Use condoms during sex. The risk of HCV infection through sexual contact is low, but the risk increases in people with HIV. Condoms also reduce the risk of HIV transmission and infection with other sexually transmitted diseases, such as gonorrhea and syphilis.
How Will I Know If My Treatment Works
The goal of treatment is to reduce the amount of the hepatitis C virus in your blood to levels that cant be detected after 24 weeks of therapy. The amount of the virus in your blood is called your viral load. At the end of your treatment, your healthcare provider will need to measure your viral load and find out how healthy your liver is. They may repeat many of the same tests that were done when you were first diagnosed with hepatitis C.
If your blood has so few copies of the virus that tests cant measure them, the virus is said to be undetectable. If it stays undetectable for at least 6 months after your treatment is finished, you have what is called a sustained virologic response . People who have an SVR have a good chance of avoiding serious liver problems in the future.
If treatment doesnt reduce your viral load, or if you dont have an SVR after treatment, your healthcare provider will discuss other treatment options with you. For example, if 1 round of treatment did not decrease your viral load enough, your healthcare provider may recommend a second round of treatment. Even if treatment doesnt keep you from having active liver disease, lowering your viral load and controlling chronic liver inflammation may help you feel better for a longer time.
You May Like: Hepatitis C Antibody Negative Means
What Can I Do To Stay As Healthy As Possible
To promote good health while living with HCV infection, learn about the disease and consider the following:
- Get more information about hepatitis C from your health care provider, local health unit, or support groups. See Hepatitis Education Canada at , Canadian Liver Foundation at www.liver.ca/ and Help4Hep at www.help4hep.org/
- Avoid alcohol as it can cause damage to the liver and increases the liver damage caused by HCV. If you do use alcohol, try to reduce the amount that you use. To learn more about support options, visit CATIE www.catie.ca/en/practical-guides/hepc-in-depth/treatment/hepatitis-c-treatment-and-drug-use
- Avoid illegal drug use and smoking. To find a needle exchange site, take home naloxone kits and training, or an overdose prevention site, see the toward the heart site and HealthLinkBC File #102a Understanding Harm Reduction: Substance Use
What Causes Hepatitis C And How Is It Spread
Hepatitis C is caused by infection with the hepatitis C virus. The virus is spread from person to person through contact with blood or bodily fluids. People who use intravenous drugs can get hepatitis C when they share needles with someone who has the virus. Health care workers can get these infections if they are accidentally stuck with a needle that was used on an infected patient. You are also at a higher risk if you got a blood transfusion or an organ transplant before 1992 .
Hepatitis C cant be spread unless a person has direct contact with infected blood or bodily fluids. This means a person who has hepatitis C cant pass the virus to others through casual contact such as sneezing, coughing, shaking hands, hugging, kissing, sharing eating utensils or drinking glasses, swimming in a pool, using public toilets, or touching doorknobs.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Is It Contagious Sexually
How Do I Prevent Hepatitis C
The only way to prevent hepatitis C is to avoid coming in contact with an infected persons blood or bodily fluids. Always have protected sex . Dont do intravenous drugs. Dont share personal care items with a person who has hepatitis C. If youre a health care worker, follow your workplaces standard safety practices.
What Are The Symptoms And Consequences Of Infection
Approximately 20 percent of persons exposed to the virus develop symptoms which may include jaundice , fatigue, dark-colored urine, stomach pain, loss of appetite and nausea. After the initial infection, 15-25 percent will recover and 75-85 percent will become chronically infected . Approximately 70 percent of persons chronically infected may develop liver disease, sometimes decades after initial infection.
Also Check: How Can Someone Contract Hepatitis C
What Is The Difference Between Relapse And Nonresponse
The goal of treating chronic hepatitis C is to completely clear the virus. This means that your “viral load” is zero or so low that the virus can’t be detected with standard blood tests.
Without treatment, the hepatitis C virus in liver cells constantly makes copies of itself, and the virus ends up not just in liver cells but also in the bloodstream. Treatment is intended to completely stop reproduction of the virus so that it doesn’t continue to enter the bloodstream or cause any more injury to liver cells.
Successful treatment results in a “sustained virological response.” This means the virus becomes completely undetectable before the treatment is finished, and it remains undetectable for 6 months after treatment is stopped.
A “relapse” means the viral load drops to an undetectable level before treatment is completed, but becomes detectable again within 6 months after treatment is stopped. Even if the virus returns at a level that is lower than it was before treatment, a relapse is still considered to have occurred. A relapse can be determined if the viral load starts to rise during treatment, or at any time after the virus becomes undetectable.
A “nonresponse” means the viral load never drops significantly and the virus remains detectable throughout the course of treatment.