Resolution Time And Clinical Course Of Infection
The majority of immunocompetent adults will recover within 6 months and develop lifelong immunity the remainder will be chronically infected. Immunocompromised adults are at a particular risk of developing chronic infection. The risk of developing chronic infection is also much higher for those who acquired the infection in infancy or before 7 years of age .Endnote 3, Endnote 13, Endnote 14
Acute HBV does not require antiviral treatment. Management should focus on relief of symptoms, monitoring and prevention of hepatic complications, as well as counselling aimed at preventing transmission. Persistence of HBsAg for 6 months indicates chronic infection.
Baseline laboratory testing to assess liver function and screen for other infections:
- Bilirubin , albumin, INR , creatinine
- ALT, AST, ALP
- anti-HBc IgM
- Testing for STIs, including HIV, and for HCV, where appropriate
- Repeat HBsAg at least 6 months after baseline, to confirm / rule out chronic infection. . See Module 6 for additional testing recommendations for those with confirmed chronic HBV
Treatment Options For Hepatitis B
Acute hepatitis B usually doesnt require treatment. Most people will overcome an acute infection on their own. However, rest and hydration will help you recover.
Antiviral medications are used to treat chronic hepatitis B. These help you fight the virus. They may also reduce the risk of future liver complications.
You may need a liver transplant if hepatitis B has severely damaged your liver. A liver transplant means a surgeon will remove your liver and replace it with a donor liver. Most donor livers come from deceased donors.
Workforce Screening Digitally Delivered
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Options
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen
Frequently Asked Questions
Quick Links:
bolt
What Is the Difference Between a Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test and a Hepatitis B Antibody Test?
The hepatitis B surface antigen test can detect current hepatitis B infection, while the hepatitis B antibody test checks for the antibodies that are presumed to provide immunity to hepatitis B.
expand_less
When Should Someone Get a Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test?
If someone is suspected to have hepatitis B, this test is intended to identify a chronic or current infection.
expand_less
What Does a Positive Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test Mean?
A positive test means the person is currently infected or has a chronic infection of hepatitis B. This means that the person has the hepatitis B virus in their blood and can be contagious.
expand_less
About Our Other Services
For industries that require specific occupational health testing, such as healthcare, construction, and manufacturing, Health Street offers quick and easy scheduling. Simply enter your ZIP code and choose the location nearest to you or the person being tested. When the registration process has been completed, we will email you the registration barcode to and a map to the facility.
Why Choose Health Street
Related Services
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Ab W Refl To Hcv Rna Qn Pcr
Persons With Inadequate Immunization Records
Evidence of long term protection against HB has only been demonstrated in individuals who have been vaccinated according to a recommended immunization schedule. Independent of their anti-HBs titres, children and adults lacking adequate documentation of immunization should be considered susceptible and started on an immunization schedule appropriate for their age and risk factors. Refer to Immunization of Persons with Inadequate Immunization Records in Part 3 for additional information.
What Is A Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Test
Hepatitis B surface antibody test is part of a panel of blood tests to diagnose HBV infection. Hepatitis B surface antibody test determines the presence and quantity of anti-HBs in the blood serum, which can indicate protection from HBV infection.
Hepatitis B disease affects the liver and commonly spreads through body fluids such as blood, semen, and vaginal secretions.
You May Like: Cirrhosis Caused By Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B Immunization And Postimmunizationserology
Michael John, MB, Ch.B., FRCP
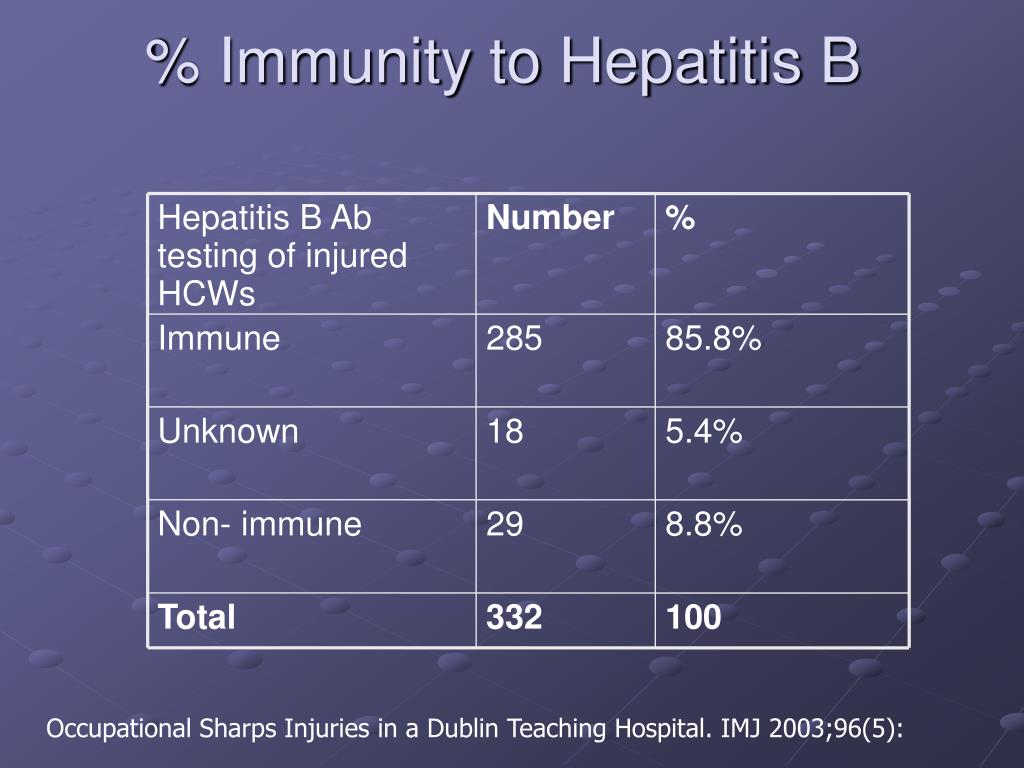
Before the introduction of avaccine, hepatitis B virus was a major occupational risk to health care workers.Some of the highest infection rates were found in dentists and surgeons.1Infected health care workers have a 5-10% risk of developing chronic hepatitis B. A numberof clusters of dentist-to-patient HBV transmissions have been reported over the years,although these have decreased since the introduction of universal precautions.2Recent guidelines from Health Canada recommend restriction of practice of health careworkers who test positive for hepatitis B e antigen.3
The development of hepatitis vaccines in the 1980s has substantially decreased dentalworkers risk of acquiring HBV. A recent survey4 of dentists in Canadashowed that more than 90% had completed an immunization series and an additional 3% hadnatural immunity. However, rates of immunization among dental assistants and hygienistswas found to be much lower.
Hepatitis B Vaccines
The vaccine is administered intramuscularly into the deltoid muscle, as glutealinjection may result in decreased response rates. Response to vaccine following a 3-doseseries is typically greater than 95% in young, healthy people, although it decreases withage . Other factors such assmoking, obesity and chronic disease decrease vaccine efficacy and may be used to predictrisk of nonresponse.6 Adverse events are minimal, although mild injection-sitereactions may occur in 20% of recipients.
References
Persons With Chronic Diseases
Refer to Immunization of Persons with Chronic Diseases in Part 3 for additional general information about vaccination of people with chronic diseases.
Chronic renal disease and patients on dialysis
People with chronic renal disease may respond sub-optimally to HB vaccine and experience more rapid decline of anti-HBs titres, and are therefore recommended immunization with a higher vaccine dose. Individuals undergoing chronic dialysis are also at increased risk for HB infection. In people with chronic renal disease anti-HBs titre should be evaluated annually and booster doses using a higher vaccine dose should be given as necessary.
Neurologic disorders
People with conditions such as autism spectrum disorders or demyelinating disorders should receive all routinely recommended immunizations, including HB-containing vaccine.
Chronic liver disease
HB immunization is recommended for non-immune persons with chronic liver disease, including those infected with hepatitis C, because they are at risk of more severe disease if infection occurs. Vaccination should be completed early in the course of the disease, as the immune response to vaccine is suboptimal in advanced liver disease. Post-immunization serologic testing may be used to confirm vaccine response.
Non-malignant hematologic disorders
Persons with bleeding disorders and other people receiving repeated infusions of blood or blood products are considered to be at higher risk of contracting HB and should be offered HB vaccine.
Also Check: What Does Hepatitis B Do
What Does The Test Result Mean
The tests for hepatitis B may be ordered individually but are often ordered in some combination, depending on the reason for testing. Results of the tests are typically evaluated together. Sometimes the meaning of one result depends on the result of another test. However, not all tests are performed for all people.
The table below summarizes possible interpretations of some common patterns of results.
| Initial Tests | |
| None detected or detected at very low level | Chronic infection but low risk of liver damage carrier state |
*Note: There are some types of HBV that do not make e-antigen. In areas where these strains of HBV are common , testing for HBeAg is not very useful. In these cases, a negative HbeAg result does not necessarily mean that the person is not infectious it may be that the person is infected with a strain that does not make the e-antigen.
Monitoring treatment of chronic infection: If the results from initial and follow-up testing indicate that a person has chronic hepatitis B, then the individual may be treated with medication and the effectiveness of that treatment may be monitored using the tests for HBe and HBs antigen and antibody and HBV DNA:
Igm Class Antibody To Hav
-
If the IgM class antibody to HAV is negative, HAV infection is ruled out in immunocompetent patients .
-
If positive, acute HAV infection is likely. As the anti-HAV-IgM may remain detectable for up to two years after infection in a small subset of patients, the history and clinical presentation must be considered in making an accurate diagnosis .
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Can It Be Cured
Question 1 What Is The Clinical Indication For Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Quantitation
Hepatitis B surface antibody quantitation is used to determine hepatitis B immune status, ie, to determine if the patient has developed immunity against the hepatitis B virus. Such immunity may develop following exposure to the hepatitis B virus or its vaccine.
Patients at higher risk of exposure to the virus include:
- Infants born to infected mothers
- Sex partners of infected persons
- People with more than 1 sex partner in the last 6 months
- People with a history of sexually transmitted infection
- Men who have sex with men
- Injection drug users
- Household contacts of an infected person
- Healthcare and safety workers who have contact with blood and body fluids
- People who have lived or traveled in an area in which hepatitis B is common
- People who live or work in a prison
Testing is not recommended routinely following vaccination. It is advised only for people whose subsequent clinical management depends on knowledge of their immune status. These people include:
- Chronic hemodialysis patients
- Immunocompromised people, including those with HIV infection, hematopoietic stem-cell transplant recipients, and people receiving chemotherapy
- Infants born to women who test positive for the hepatitis B surface antigen
- Sex partners of people who test positive for the hepatitis B surface antigen
- Healthcare and public safety workers who have contact with blood or body fluids
What Do Hepatitis B Test Results Mean
Hepatitis B test results help determine if HBV infection is negative or positive, and if positive, whether the infection is acute or chronic, or if recovery is complete. A combination of results are considered to identify and classify HBV infection status.
The following are some interpretations of hepatitis B test results:
Table: Hepatitis B test results and interpretations
| Test |
|---|
Also Check: What Is Hepatic Function Panel
Management Of Pregnant Hbv Carriers
Pregnant HBV carrier mothers present a unique opportunity to prevent transmission of HBV to their neonates. All infants born to HBsAg-positive mothers should receive hepatitis B immune globulin and a full course of HBV vaccination . Vaccine failure in the neonate is rare but does occur , and may be accounted for by transplacental transmission before birth. Follow-up testing of the neonate should be performed to confirm vaccination effectiveness. Testing should be performed for HBsAg to detect vaccine failures, anti-HBs to confirm a successful vaccine response and anti-HBc-Total to determine if the anti-HBs response was due to vaccination or resolution of natural infection. While testing for these markers is recommended one to two months after completion of the vaccine series, testing at approximately 18 months would ensure that the anti-HBc-Total test does not represent maternal antibody. This may be important because vaccination failures have occasionally been associated with HBV vaccine escape mutants that may only demonstrate a positive anti-HBc-Total as the sole marker of infection. These mutations occur in the open reading frame of the HBsAg, may not be recognized by antibodies induced by current HBV vaccine, and may not be detected by currently available HBsAg enzyme immunoassays . Clearly, surveillance systems need to be in place to ensure that HBV vaccines remain effective and vaccine escape mutants do not replace current HBV strains.
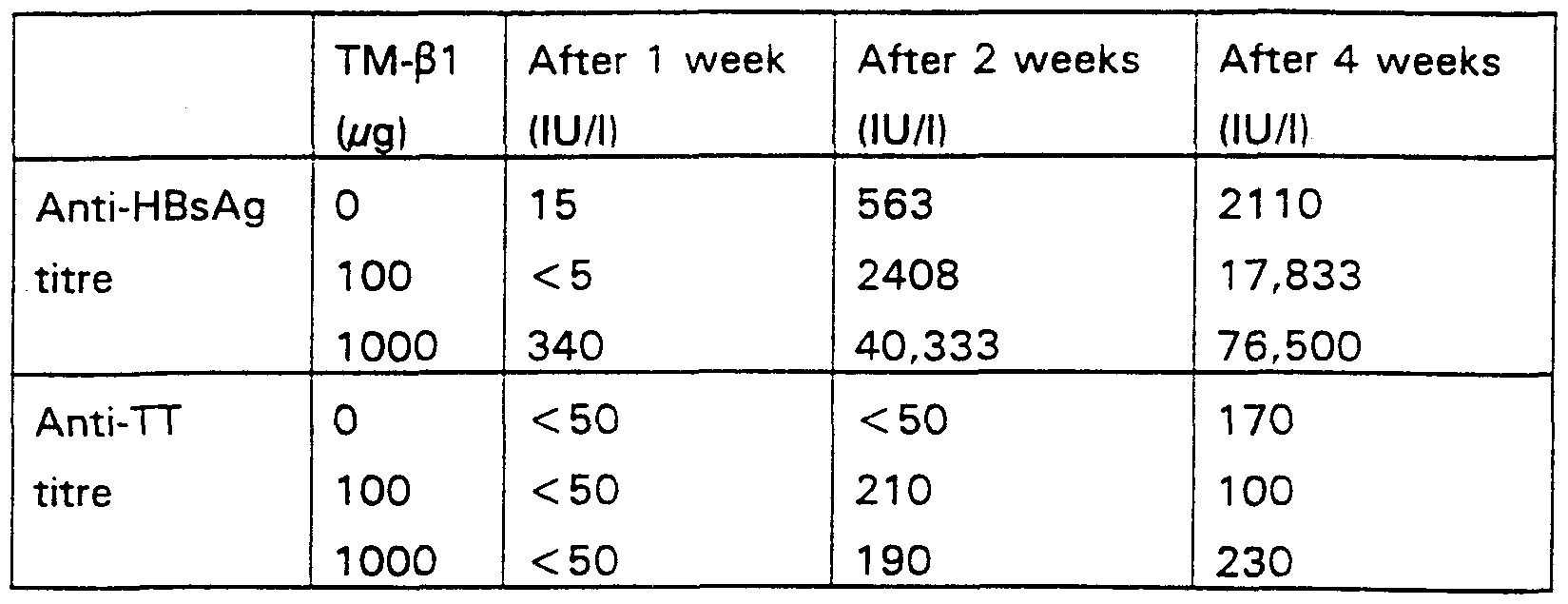
Chronic Hbv Carriers At Greatest Risk Of Hepatic Sequelae
Sustained elevations in ALT, although an imperfect marker for hepatic damage, can help identify chronic HBV carriers at greatest risk of sequelae and those most likely to benefit from current treatments . Chronically infected patients with sustained ALT elevations greater than the upper limit of normal may be candidates for treatment and should undergo additional prognostic hepatitis marker testing as outlined below. Chronic carriers whose ALT is within the normal range should be tested for this marker periodically because ALT levels can fluctuate with this illness. Determination of ALT levels and HBV serological and nucleic acid markers, although valuable in following infection, is not adequate to assess the severity of infection and the resulting liver damage. Before appropriate treatment can be initiated, consultation with a specialist and assessment of the disease through histological examination of a liver biopsy is strongly recommended.
Recommended Reading: Where Can I Get Tested For Hepatitis B
What Is The Purpose Of A Hepatitis B Test
Hepatitis B test is performed to detect, classify, and treat hepatitis B virus infection.
Hepatitis B blood tests involve the measurement of several HBV-specific antigens and antibodies. In addition, HBV blood tests also include liver enzymes and liver function tests to assess and monitor the condition of the liver and provide appropriate treatment.
The HBV specific tests include the following:
- HBsAg: HBsAg is an antigen found on the surface of hepatitis B virus. HBsAg may be detected in the blood any time after 1 week post-exposure to HB virus, but usually appears after 4 weeks.
- Anti-HBs: Anti-HBs are antibodies produced by the bodys immune system to fight HBsAg. Anti-HBs from a prior infection or vaccination provides immunity against further infection.
- Hepatitis B core antigen : HBcAg is an antigen found in the core layer which covers the hepatitis B viral DNA.
- Hepatitis B core antibody : Anti-HBc is the antibody that fights HBcAg. Anti-HBc is the first detectable antibody after HBV infection. There are two kinds of Anti-HBc:
- Immunoglobulin M hepatitis B core antibody : IgM anti-HBc indicates acute or reactivated recent infection within the previous 6 months.
- Immunoglobulin G hepatitis B core antibody : IgG anti-HBc may indicate previous or chronic infection. Once present, IgG anti-HBc persists for a lifetime.
Provides Information To Assist In Interpretation Of The Test Results
A positive result indicates recovery from acute or chronic hepatitis B virus infection or acquired immunity from HBV vaccination. This assay does not differentiate between a vaccine-induced immune response and an immune response induced by infection with HBV. A positive total antihepatitis B core result would indicate that the hepatitis B surface antibody response is due to past HBV infection.
Per assay manufacturer’s instructions for use, positive results, defined as anti-HBs levels of 12.0 mIU/mL or greater, indicate adequate immunity to hepatitis B from past hepatitis B or HBV vaccination. However, per current CDC guidance, individuals with anti-HBs levels greater than 10 mIU/mL after completing an HBV vaccination series are considered protected from hepatitis B.
Negative results, defined as anti-HBs levels of less than 5.0 mIU/mL, indicate a lack of recovery from acute or chronic hepatitis B or inadequate immune response to HBV vaccination. The US Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices does not recommend more than 2 HBV vaccine series in nonresponders.
Indeterminate results, defined as anti-HBs levels in the range from 5 to 11.9 mIU/mL, indicate inability to determine if anti-HBs is present at levels consistent with recovery or immunity. Repeat testing is recommended in 1 to 3 months.
Also Check: Ways To Contract Hepatitis C
Epidemiology Of Acute And Chronic Hbv In Canada
Acute HBV: Canada is a region of low endemicity however, certain vulnerable populations are disproportionately affected. These include Aboriginal peoples, MSM, street-involved youth, and people who are or have been incarcerated.Endnote 2 Peak incidence is among those aged 3039 years. The most commonly identified risk factors are high-risk sexual activities and injection drug use.
Canada has had universal HBV immunization programs in place since the mid-1990s. All provinces and territories have programs that target children aged 913 years, and some have also implemented a neonatal immunization program.Endnote 3 In addition, some provinces/territories provide coverage for high-risk individuals, but eligibility varies across jurisdictions . Despite the success of these programs, there may be many who remain at risk of acquiring HBV.
Immunization contributes to disease control by interrupting disease transmission and decreasing the pool of susceptible people. It is essential to identify those at risk who would benefit from receiving the HBV vaccine.
There is an urgent need to screen, diagnose, and treat chronic HBV infection so as to reduce associated morbidity and mortality and to prevent further transmission.
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen
Health Streets Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test checks for a current infection of the hepatitis B virus. If the test is positive, then the person can be contagious to others.
Online registration is simple. You choose the lab location based on ZIP code during registration. An authorization barcode is instantly emailed to you and texted directly to the phone of the person being tested. A map of the clinic location will accompany the barcode. The registrant can then walk into the testing facility and show the barcode along with photo ID. Results are fast and stored securely online. Individuals and employers can register online or call to order tests.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Test Non Reactive
Should I Get The Hbv Vaccine
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that adults in high-risk groups get vaccinated. Some of these groups include people:
- In close contact with someone who has hepatitis B
- Who undergo dialysis
- With chronic liver or kidney disease
- With HIV or who seek treatment for other sexually transmitted diseases or drug treatment
- Who travel to countries where hepatitis B is common
- Who are healthcare workers with potential exposure to HBV
Unless there is something in your medical history to the contrary, it is prudent to get the series of vaccinations. Babies, children and adolescents are routinely given the series of shots if you have already been vaccinated, you probably are protected for many years, perhaps for life, and will not usually need to get the vaccine again.
Assessment Of Hbv Immune Status
Immunity to HBV is acquired from a resolved infection or from vaccination .2). The HBV vaccine has been shown to induce protective immunity in 90% to 95% of vaccinees. Most vaccinees will have protective levels of anti-HBs for five to 10 years after vaccination, although the exact duration of immunity remains undefined. When anti-HBs levels have waned below the protective threshold of 10 mIU/mL, a booster dose of HBV vaccine has been shown to induce a strong anamnestic immune response in such individuals. It is therefore probable that protection from chronic HBV infection may last for decades and may well be lifelong .
Investigation of hepatitis B virus immunity. Anti-HBc-Total Total antibody to hepatitis B core protein Anti-HBs/HBsAb Antibody to hepatitis B surface antigen
The HBV immune status can be determined using the tests outlined below, but testing for vaccine immunity in the general population is not indicated unless the individual is at high risk of infection .3). Nonimmune individuals should be offered HBV vaccination where clinically appropriate.
Also Check: Hepatitis B What Is It