About The Hepatitis B Virus
The hepatitis B virus is a small DNA virus that belongs to the Hepadnaviridae family. Related viruses in this family are also found in woodchucks, ground squirrels, tree squirrels, Peking ducks, and herons.
Structure of the Hepatitis B Virus The hepatitis B virus contains an outer envelope and an inner core.
- The outer envelope of the virus is composed of a surface protein called the hepatitis B surface antigen or HBsAg. The HBsAg can be detected by a simple blood test and a positive test result indicates a person is infected with the hepatitis B virus.
- The inner core of the virus is a protein shell referred to as the hepatitis B core antigen or HBcAg, which contains the hepatitis B virus DNA and enzymes used in viral replication.
Life Cycle of the Hepatitis B Virus
The hepatitis B virus has a complex life cycle. The virus enters the host liver cell and is transported into the nucleus of the liver cell. Once inside the nucleus, the viral DNA is transformed into a covalently closed circular DNA , which serves as a template for viral replication . New HBV virus is packaged and leaves the liver cell, with the stable viral cccDNA remaining in the nucleus where it can integrate into the DNA of the host liver cell, as well as continue to create new hepatitis B virus. Although the life cycle is not completely understood, parts of this replicative process are error prone, which accounts for different genotypes or genetic codes of the hepatitis B virus.
Hesitations Toward Blood Donation
Although 37% of the U.S. population is eligible to donate blood, less than 5% do so annually, according to a 2012 study published in the journal Transfusion. Among the commonly cited reasons why people avoid donating is the presumption that they are medically disqualified to donate.
Many of these attitudes stem back to the 1970s and 1980s when reports of infection among hemophiliacs given tainted blood fueled fears among donors and recipients alike. During those years, no less than 6,000 hemophiliacs in the United States became infected with HIV, hepatitis, or both.
Although doubts about the safety of the U.S. blood supply have largely subsided due to advances in blood screening, there are some who avoid donating because it may reveal that they havean infection like HIV or hepatitis.
If you have hepatitis and have a type that does not restrict you from donating, it is worth considering given the public need. If you think you might have hepatitiseither due to the presence of symptoms or because of a known exposurebut are fearful of donating because it may confirm your concern, know that the sooner hepatitis is identified, the more sooner you can access treatment that can keep you well and healthy for many years.
Hbv Dna Hbv Genotype And Hbv Drug Resistance Assays
Specimen: Serum or plasma
Container: Red-top tube, yellow-top tube , gel-barrier tube, plasma preparation tube, or lavender tube
Collection method: Routine venipuncture
The specimen should be transfused to separate plasma/serum from cells within 6 hours and kept frozen when testing cannot be done promptly.
The tests use PCR amplification, DNA probe hybridization, and sequencing method.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Hepatitis C
Treatment For Hepatitis B
may include antiviral medicine to help fight HBV and keep it from spreading in your body. You may need a transfusion of plasma or platelets if your blood is not clotting as it should. Plasma and platelets are parts of your blood that help your blood clot. You will get the transfusion through an IV. Surgery for a liver transplant may be done if you have severe liver disease or liver failure.
Hep B Titer Test Required By Most Schools And Employers
This assay is used to determine immune status for Hepatitis B.
Hepatitis B Surface Antibody : The surface antibody is formed in response to the hepatitis B virus. Your body can make this antibody if you have been vaccinated, or if you have recovered from a hepatitis B infection. If this test is positive, then your immune system has successfully developed a protective antibody against the hepatitis B virus. This will provide long-term protection against future hepatitis B infection. Someone who is surface antibody positive is not infected, and cannot pass the virus on to others.
This is a Quantitative test required by many schools and medical programs. Levels of anti-HBs will be provided.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Virus Can Cause
Hepatitis B And Your Liver
The liver is such an important organ that we can survive only one or two days if it completely shuts down â if the liver fails, your body will fail, too. Fortunately, the liver can function even when up to 80% of it is diseased or removed. This is because it has the amazing ability to regenerate â or create â itself from healthy liver cells that still exist.
If your body were an automobile, your liver would be considered the engine. It does hundreds of vital things to make sure everything runs smoothly:
- Stores vitamins, sugar and iron to help give your body energy
- Controls the production and removal of cholesterol
- Clears your blood of waste products, drugs and other poisonous substances
- Makes clotting factors to stop excessive bleeding after cuts or injuries
- Produces immune factors and removes bacteria from the bloodstream to combat infection
- Releases a substance called âbileâ to help digest food and absorb important nutrients
The word hepatitis actually means inflammation of the liver. Thus, hepatitis B refers to inflammation of the liver caused by the hepatitis B virus. With early detection and appropriate follow-up medical care, people living with a chronic hepatitis B infection can expect to enjoy a long and healthy life.
Taking A Hepatitis B Test
Testing for hepatitis B is performed on a sample of blood. A doctor, nurse, or other health care provider can obtain a blood sample using a small needle to draw blood from a vein.
At-home hepatitis B testing requires that users carefully follow instructions provided in the test kit to collect a small sample of blood, package the sample, and mail it to a lab for testing.
Don’t Miss: How Bad Is Hepatitis C
What Tests Will You Have To Do
Hepatitis B
You can be tested for hepatitis B at your VA medical center. This test is done by taking a sample of your blood.
Your provider may recommend the following tests:
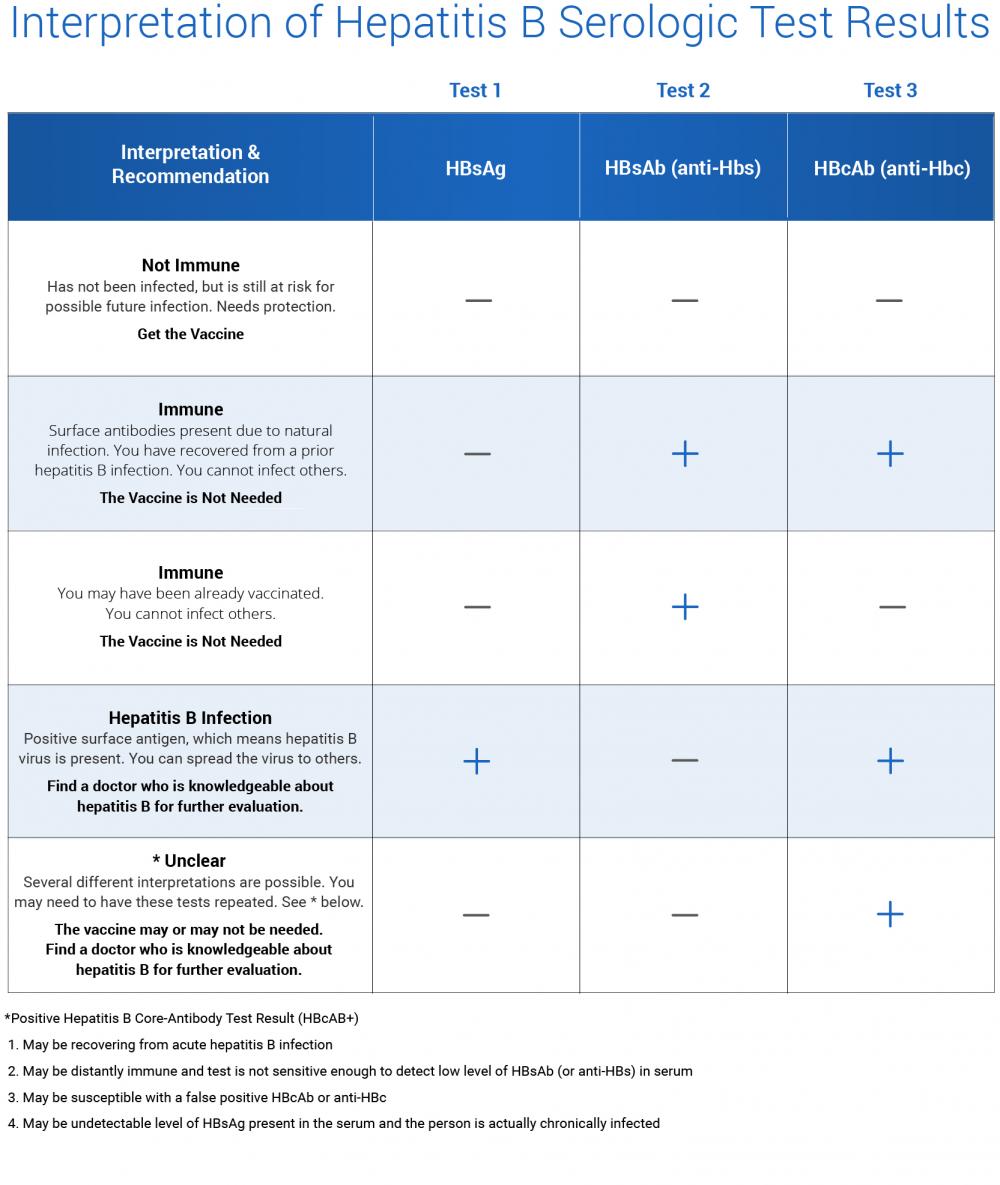
Hepatitis B surface antibody If this test is positive, it means that:
- you have antibodies against hepatitis B and are safe from getting the disease
- you were either vaccinated against hepatitis B or exposed to it at some point in your lifetime
Hepatitis B core antibody If the test is positive, it means that:
- you have been exposed to hepatitis B and have developed an antibody to only part of the virus
- they will do more tests to find out if you currently have the disease
Hepatitis B surface antigen If the test is positive, it means that:
- you currently have hepatitis B infection
- you can spread the virus to others
Hepatitis B e antigen If the test is positive, it means that:
- you may have active hepatitis B and should be followed closely by your provider and possibly take hepatitis B medications
- you may be very contagious to others
What Is The Normal Range For Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
Hepatitis B surface antibodies are measured in blood samples in milli-International Units/milliliter mIU/mL). The ranges for hepatitis B surface antibodies are:
- Anti-HBs greater than 10-12 mIU/mL: Protected against hepatitis B virus infection, either from vaccination or successful recovery from a previous HBV infection.
- Anti-HBs less than 5 mIU/mL: Negative for HBV infection, but susceptible and hence requires vaccination.
- Anti-HBs from 5-12 mIU/mL: Inconclusive results and the test should be repeated.
However, there is no standardization of these values so it is advisable to check the manufacturers values it is the reason values are mainly reported as positive or negative.
Read Also: Does Hepatitis C Affect The Liver
Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Quantitative
The Hepatitis B Panel of Blood Tests
Only one sample of blood is needed for a hepatitis B blood test, but the Hepatitis B Panel includes three parts. All three test results are needed to fully understand whether a person is infected or not. Below is an explanation of the 3-part Hepatitis B Panel of blood test results.
Can I Take The Test At Home
Samples for hepatitis B testing can be collected at home. At-home hepatitis B testing requires a patient to collect a blood sample, typically from a fingerstick using a very small needle provided in the test kit. Once a blood sample is collected, it is prepared according to the instructions contained in the test kit and mailed to a laboratory for testing.
Because there are numerous types of tests for HBV, it is important to look closely at the specific components of any at-home test kit. Many at-home test kits only look for hepatitis B surface antigen .
Don’t Miss: Does Hepatitis C Have A Vaccine
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test
A hepatitis B surface antigen test shows if youre contagious. A positive result means you have hepatitis B and can spread the virus. A negative result means you dont currently have hepatitis B. This test doesnt distinguish between chronic and acute infection. This test is used together with other hepatitis B tests to determine the .
The Immunological Effect Of Booster Vaccination In Non
To confirm the efficacy of booster HBV vaccination in non-responders and low-responders, we evaluated 33 subjects at 1 year after booster vaccination and 10 subjects at 2 years after booster vaccination. Although the anti-HBs titer increased significantly after booster vaccination, this response was not sustained .
Serial changes in the anti-HB titers of subjects who received a booster vaccination. The vertical axis shows the change in anti-HB titer over time. The horizontal axis shows the indicated time points at which the anti-HB titer was measured at 1 year and 2 years after vaccination. Statistical significance was evaluated using the Friedman test. P values of < 0.05 were considered to indicate statistical significance. n.s.: not significant
Read Also: Hepatitis C Genotype 2 Treatment
Reasons For Other Deferrals Explained
I was diagnosed with hepatitis at a young age. Am I still deferred?
Under Title 21 CFR 610.41, persons with a history of a positive test for hepatitis B virus surface antigen , regardless of age at the time of the positive test, may not serve as a donor of human blood, plasma, or serum.
Donor suitability in regard to a history of viral hepatitis at the age of 11 years or later should be assessed by asking the donor for recollections of experiencing physical signs or symptoms of clinical hepatitis , or having received a diagnosis of viral hepatitis from a physician. Records of laboratory data , if available, may assist the medical director in making the donor suitability determination in the face of an inconclusive history. However, certain isolated laboratory test results should not be considered equivalent to a history of viral hepatitis. In particular, a history of an elevated alanine aminotransferase or a reactive test for antibodies to Hepatitis A Virus or Antibodies to Hepatitis B surface antigen need not be a cause to defer a donor.
Please be aware, however, that a blood center may voluntarily elect to adopt more stringent donor deferral criteria in its Standard Operating Procedures than those required or recommended by the FDA. Under these circumstances, FDA does require that the blood center follow its own SOPs.
There are two relevant documents available that can further clarify FDAs current donor deferral criteria:
Transmission Of Hepatitis B
The hepatitis B virus is transmitted through blood and sexual fluids. This can most commonly occur in the following ways:
Direct contact with infected blood
Unprotected sex
Use of illegal or street drugs
Needles and other medical/dental equipments or procedures that are contaminated or not sterile
From an infected woman to her newborn during pregnancy and childbirth
Body piercing, tattooing, acupuncture and even nail salons are other potential routes of infection unless sterile needles and equipment are used. In addition, sharing sharp instruments such as razors, toothbrushes, nail clippers, earrings and body jewelry can be a source of infection.
Hepatitis B is NOT transmitted casually. It cannot be spread through toilet seats, doorknobs, sneezing, coughing, hugging or eating meals with someone who is infected with hepatitis B.
You May Like:What Does Hepatitis B Do
You May Like: How Many Types Of Hepatitis Are There
Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Blood Test
This test is used to determine the status of a persons immunity to the Hepatitis B virus . Immunity is determined by screening for antibodies which provide protection against infection. The results of this test are quantitative.
Hepatitis B is a viral infection of the liver spread through contact with contaminated bodily fluids including blood. Transmission can occur through various types of exposure including sexual contact. It is possible for a pregnant woman to spread the infection to her infant during childbirth. More than half of Hep B infections display no symptoms. When symptoms do occur, the most common are loss of appetite, fatigue, nausea, abdominal pain, jaundice, and dark colored urine. Chronic Hepatitis B infections may lead to the development of Cirrhosis or Liver Cancer.
A person can have immunity to Hepatitis B for several reasons.
1.) They have been vaccinated for Hep B. Vaccinations do not always provide permanent immunity. It is possible for a person to have been vaccinated and lose their immunity over time.
2.) They have been infected with Hep B, recovered, and now have a natural immunity. Because Hepatitis B does not always display symptoms, it is possible for a person to have been exposed and not be aware of it.
A person who wishes to screen for a current Hepatitis B infection may want to order the Hep B Surface Antigen test.
The Hepatitis B Surface Antibody test typically sees results in 1 business day.
Detection Period:
Understanding Your Test Results
Understanding your hepatitis B blood tests can be confusing. It is important to talk to your health care provider so you understand your test results and your hepatitis B status. Are you infected? Protected? Or at risk? The Hepatitis B Panel of blood tests includes 3 tests and all three results must be known in order to confirm your status.
Below is a chart with the most common explanation of the test results, but unusual test results can occur. Please note that this chart is not intended as medical advice, so be sure to talk to your health care provider for a full explanation and obtain a printed copy of your test results. In some cases, a person could be referred to a liver specialist for further evaluation.
More Detailed Information About Hepatitis B Blood Tests
An acute hepatitis B infection follows a relatively long incubation period – from 60 to 150 days with an average of 90 days. It can take up to six months, however, for a person to get rid of the hepatitis B virus. And it can take up to six months for a hepatitis B blood test to show whether as person has recovered from an acute infection or has become chronically infected .
The following graphic from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention represents the typical course of an acute hepatitis B infection from first exposure to recovery.
According to the CDC, a hepatitis B blood test result varies depending on whether the infection is a new acute infection or a chronic infection.
You May Like: Patient Has Immunity To Hepatitis B Virus
Question 7 Is Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Antibody Always Acquired After A Completed Vaccination Protocol
No. After 3 intramuscular doses of vaccine, > 90% of healthy adults and > 95% of those < 19 years of age develop immunity .1 However, there is an age-specific decline in development of immunity. After age 40 years, about 90% of people become immune, but by age 60 years, only 75% of people become immune.1 Larger vaccine doses or an increased number of doses are required to induce immunity in many hemodialysis patients and in other immunocompromised people.1
References
This FAQ is provided for informational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice. A clinicians test selection and interpretation, diagnosis, and patient management decisions should be based on his/her education, clinical expertise, and assessment of the patient.Document FAQS.105 Revision: 0
Quest, Quest Diagnostics, the associated logo, Nichols Institute, and all associated Quest Diagnostics marks are the registered trademarks of Quest Diagnostics. All third-party marks®’ and ‘are the property of their respective owners. © 2000- 2021 Quest Diagnostics Incorporated. All rights reserved.Image content features models and is intended for illustrative purposes only.