Who Is Most At Risk Of Contracting Hepatitis C
You have a high risk of contracting hepatitis C if you:
- use or have used injection drugs even if it was just once or many years ago
- have received blood or blood products or an organ transplant before July 1990 in Canada
- have been in jail or
- have been injected or scratched during vaccination, surgery, blood transfusion or a religious/ceremonial ritual in regions where hepatitis C is common.
You have a high moderate risk of contracting hepatitis C if you:
- have tattoos or body piercing
- have multiple sexual partners
- have a sexually transmitted infection , including HIV or lymphogranuloma venereum
- have experienced traumatic sex or rough sex or have used sex toys or fisting that can tear body tissue
- have vaginal sex during menstruation
- have received a kidney treatment
- have received an accidental injury from a needle or syringe
- have another infectious disease
- were born to a hepatitis C infected mother or
- have a sexual partner infected with hepatitis C.
Hepatitis C is NOT passed from person to person by:
- coughing, sneezing
- breastfeeding unless your nipples are cracked and bleeding or
- oral sex, unless blood is present.
How Can You Prevent The Spread Of Hepatitis C
Now that you know how you get hepatitis C, you can take steps to protect yourself from the virus. For instance:
- Avoid sharing needles or other paraphernalia related to intravenous drugs.
- Wear gloves if youre a health care worker or otherwise exposed to needles or potentially infected blood.
- Use barrier methodsaka condomsoutside of sexually monogamous relationships.
- Dont share toothbrushes or other dental equipment, nail clippers, or shaving tools.
- If youre getting a tattoo or piercing, make sure the artist or piercer uses sterile ink and needles.
If you have the hepatitis C virus, you can prevent passing it along to others by following those same steps, in addition to:
- Covering any open sores or wounds.
- Telling all your health and dental care providers you have the virus.
- Avoiding donating blood.
What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis
Each type of hepatitis is treated differently.
Hepatitis A often goes away on its own and home treatment is all that is needed to help the liver recover, such as:
- Rest
- Avoiding alcohol
- Avoiding certain medicines that can be harmful to the liver
Hepatitis B often goes away on its own in about 6 months, and can also be treated at home with the above remedies. Other treatments for hepatitis B include:
- Antiviral medications
- Liver transplant in severe cases
Treatment for hepatitis C is effective on certain forms of the hepatitis C virus. The choice of medications depends on the type of hepatitis C you have, whether you have been treated for the illness before, how much liver damage has occurred, any other underlying medical issues, and other medicines you take. Treatment for hepatitis C usually involves 8 to 12 weeks of oral antiviral medications, such as:
- Elbasvir-grazoprevir
Also Check: What Kind Of Doctor Treats Hepatitis C
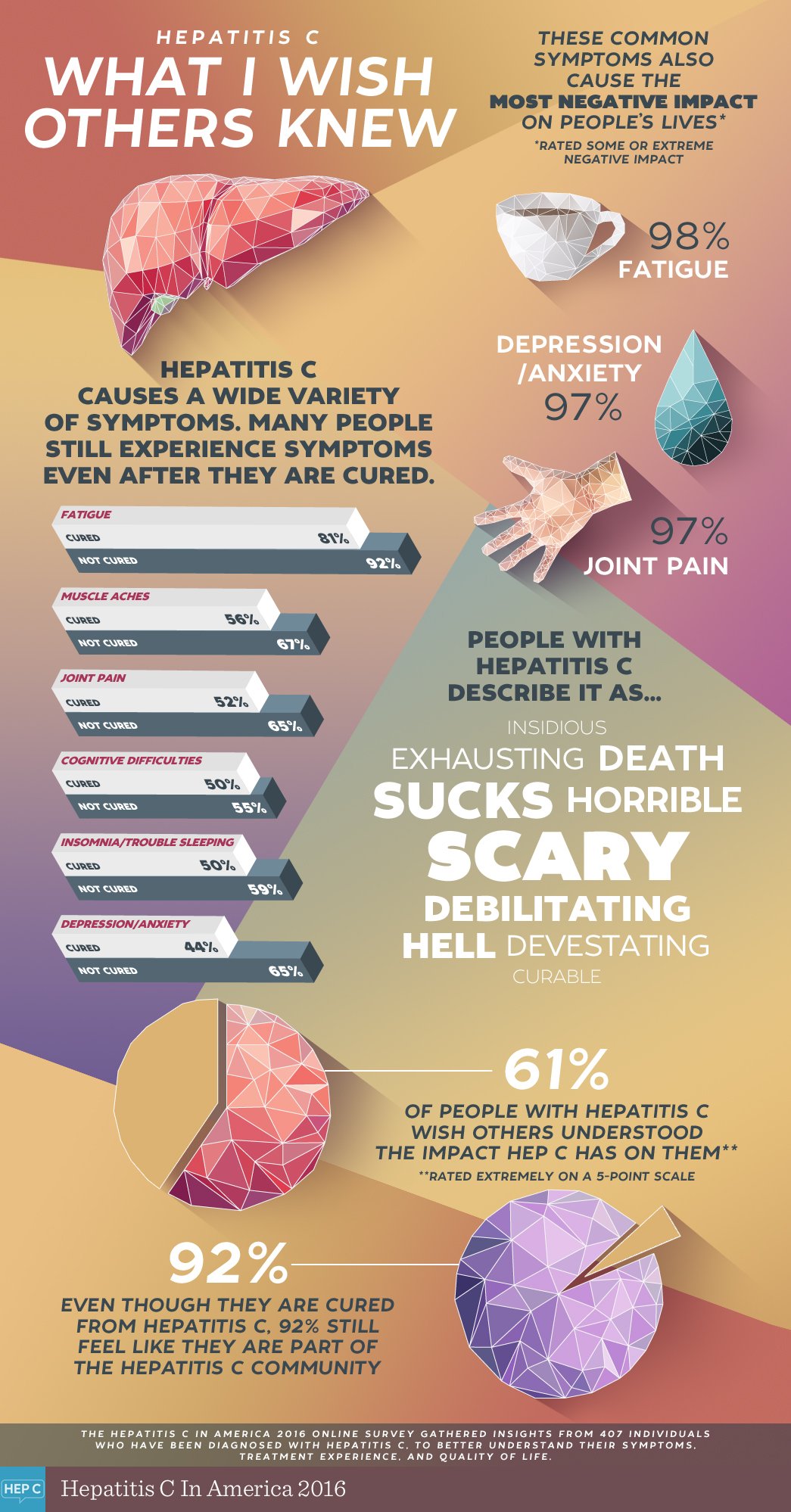
Hepatitis C Symptoms & Treatment
FAST FACTS:
-
Hepatitis C is found in infected blood. It is also rarely found in semen and vaginal fluids.
-
Hepatitis C is mainly passed on through using contaminated needles and syringes or sharing other items with infected blood on them. It can also be passed on through unprotected sex, especially when blood is present.
-
You can prevent hepatitis C by never sharing needles and syringes, practising safer sex, and avoiding unlicensed tattoo parlours and acupuncturists.
-
Hepatitis C will often not have any noticeable symptoms, but a simple blood test carried out by a healthcare professional will show whether you have hepatitis C.
-
In the early stages, some peoples bodies can clear a hepatitis C infection on their own, others may develop chronic hepatitis C and will need to take antiviral treatment to cure the infection.
-
Without treatment, chronic hepatitis C can lead to permanent liver damage.
Hepatitis C is part of a group of hepatitis viruses that attack the liver.
Its mainly passed on through contaminated needles, either from injecting drugs or from needle stick injuries in healthcare settings. It can also be transmitted sexually, especially during anal sex or other types of sex that may involve blood.
Some groups are more at risk of getting hepatitis C than others, including people who use drugs, people in prisons, men who have sex with men, health workers and people living with HIV.
Hiv And Hepatitis C Coinfection
HCV infection is common among people with HIV who also inject drugs. Nearly 75% of people living with HIV who report a history of injection drug use are co-infected with HCV. All people who are diagnosed with HIV are recommended to be tested for HCV at least once. People living with HIV are at greater risk for complications and death from HCV infection. Fortunately, direct acting antivirals that are used to treat HCV work equally well in people with and without HIV infection. For more information about HIV and HCV coinfection, visit the HIV.govs pages about hepatitis C and HIV coinfection.
You May Like: Hepatitis C Symptoms Mayo Clinic
Questions To Ask Your Doctor
- Do I need treatment?
- What treatment is best for me?
- What medicines should I take?
- Are there any medicines I should avoid?
- How can I cope with the side effects of treatment?
- Is there a therapist I can talk to?
- How long will my treatment last?
- Can hepatitis C be cured?
- Are organ transplants and blood transfusions safe?
- Is it safe for me to get pregnant?
What Are The Treatments For Hepatitis C
Treatment for hepatitis C is with antiviral medicines. They can cure the disease in most cases.
If you have acute hepatitis C, your health care provider may wait to see if your infection becomes chronic before starting treatment.
If your hepatitis C causes cirrhosis, you should see a doctor who specializes in liver diseases. Treatments for health problems related to cirrhosis include medicines, surgery, and other medical procedures. If your hepatitis C leads to liver failure or liver cancer, you may need a liver transplant.
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatitis C Screening Test
How Does Hepatitis C Spread
Hepatitis C is spread only through exposure to an infected person’s blood.
High-risk activities include:
- Sharing drug use equipment. Anything involved with injecting street drugs, from syringes, to needles, to tourniquets, can have small amounts of blood on it that can transmit hepatitis C. Pipes and straws to smoke or snort drugs can have blood on them from cracked lips or nosebleeds. Get into a treatment program if you can. At the very least, don’t share needles or equipment with anyone else.
- Sharing tattoo or piercing tools. Nonsterile items and ink can spread contaminated blood.
- Blood transfusions in countries that donât screen blood for hepatitis C.
- Nonsterile medical equipment. Tools that arenât cleaned properly between use can spread the virus.
- Blood or cutting rituals. Sharing the tools or exchanging blood can transmit hepatitis C.
Medium-risk activities include:
Can You Be A Blood Or Organ Donor
People with hepatitis C cant currently donate blood. The American Red Cross eligibility guidelines prohibit people who have ever tested positive for hepatitis C from donating blood, even if the infection never caused symptoms.
According to the Department of Health and Human Services , information on organ donation, those with underlying medical conditions shouldnt rule themselves out as organ donors. This reflects new guidelines for organ donation announced by the HHS.
People with HCV are now able to be organ donors. This is because advances in testing and medical technology can help the transplant team determine which organs or tissues can be safely used for transplantation.
Also Check: Can You Cure Hepatitis B
Should I Be Screened For Hepatitis C
Doctors usually recommend one-time screening of all adults ages 18 to 79 for hepatitis C. Screening is testing for a disease in people who have no symptoms. Doctors use blood tests to screen for hepatitis C. Many people who have hepatitis C dont have symptoms and dont know they have hepatitis C. Screening tests can help doctors diagnose and treat hepatitis C before it causes serious health problems.
Hiv And Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C Coinfection
Hepatitis B and hepatitis C are liver infections caused by a virus. Because these infections can be spread in the same ways as HIV, people with HIV in the United States are often also affected by chronic viral hepatitis.
Viral hepatitis progresses faster and causes more liver-related health problems among people with HIV than among those who do not have HIV. Liver disease, much of which is related to HBV or HCV, is a major cause of non-AIDS-related deaths among people with HIV.
Given the risks of hepatitis B or hepatitis C coinfection to the health of people living with HIV, it is important to understand these risks, take steps to prevent infection, know your status, and, if necessary, get medical care from someone who is experienced in treating people who are coinfected with HIV and HBV, or HIV and HCV.
Read Also: Is Hepatitis C An Autoimmune Disease
Reactive Or Positive Hepatitis C Antibody Test
- A reactive or positive antibody test means that Hepatitis C antibodies were found in the blood and a person has been infected with the Hepatitis C virus at some point in time.
- Once people have been infected, they will always have antibodies in their blood. This is true even if they have cleared the Hepatitis C virus.
- A reactive antibody test does not necessarily mean that you have Hepatitis C. A person will need an additional, follow-up test.
Persons for Whom HCV Testing Is Recommended
- Adults born from 1945 through 1965 should be tested once
- Those who:
- Ever injected drugs, including those who injected once or a few times many years ago
- Have certain medical conditions, including persons:
- who received clotting factor concentrates produced before 1987
- who were ever on long-term hemodialysis
- with persistently abnormal alanine aminotransferase levels
- who have HIV infection
Contaminated Needles And Infected Blood
You can get hepatitis C from sharing contaminated needles, syringes and other injecting equipment during recreational drug use. Banknotes and straws used for snorting may also pass the virus on.
Being exposed to unsterilised tattoo and body piercing equipment can also pass hepatitis C on. Occasionally, you can get it from sharing a towel, razor blades or a toothbrush if there is infected blood on them.
Hepatitis C infection is also passed on in healthcare settings, from needle stick injuries or from medical and dental equipment that has not been properly sterilised. In countries where blood products are not routinely screened, you can also get hepatitis C by receiving a transfusion of unscreened blood and blood products.
You can prevent hepatitis C by:
- never sharing needles and syringes or other items that may be contaminated with infected blood
- only having tattoos, body piercings or acupuncture in a professional setting, where new, sterile needles are used
- following the standard infection control precautions, if youre working in a healthcare setting.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Is It Contagious Sexually
What Are The Side Effects Of Drug Treatment
Common side effects for some treatments for hepatitis C may include the following:
- nausea
- fatigue
- depression
Side effects are usually worst during the first few weeks of treatment. They become less severe over time. If you are having trouble dealing with the side effects of your medicine, talk to your doctor. He or she can suggest ways to relieve some of the side effects. For example, if your medicine makes you feel nauseated, it may help to take it right before you go to sleep.
Effective Treatments Are Available For Hepatitis C
New medication to treat for HCV have been approved in recent years. These treatments are much better than the previously available treatment because they have few side effects and do not need to be injected. There are several direct-acting antiviral HCV treatments that cure more than 95% of people who take them in 8 to 12 weeks. HCV treatment dramatically reduces deaths among people with HCV infection, and people who are cured of HCV are much less likely to develop cirrhosis or liver cancer.
Take Action! CDCs National Prevention Information Network Service Locator helps consumers locate hepatitis B and hepatitis C prevention, care, and treatment services.
Don’t Miss: How Long Does Hepatitis C Last
Antiviral Medication For Hepatitis B
Doctors may recommend antiviral medication for people with chronic hepatitis B, which occurs when the virus stays in your body for more than six months.
Antiviral medication prevents the virus from replicating, or creating copies of itself, and may prevent progressive liver damage. Currently available medications can treat hepatitis B with a low risk of serious side effects.
NYU Langone hepatologists and infectious disease specialists prescribe medication when they have determined that without treatment, the hepatitis B virus is very likely to damage the liver over time. People with chronic hepatitis B may need to take antiviral medication for the rest of their lives to prevent liver damage.
There are many different types of antiviral medications available, and your doctor recommends the right type for you based on your symptoms, your overall health, and the results of diagnostic tests. A doctor may take a wait-and-see approach with a person who has a healthy liver and whose blood tests indicate a low viral load, the number of copies of the hepatitis B virus in your bloodstream.
Someone with HIV infection or AIDS may have a weakened immune system and is therefore more likely to develop liver damage. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention strongly recommends that people with HIV infection who are diagnosed with hepatitis B immediately begin treatment with antiviral medication.
Sharing Toothbrushes Scissors And Razors
There’s a potential risk that hepatitis C may be passed on through sharing items such as toothbrushes, razors and scissors, as they can become contaminated with infected blood.
Equipment used by hairdressers, such as scissors and clippers, can pose a risk if it has been contaminated with infected blood and not sterilised or cleaned between customers. However, most salons operate to high standards, so this risk is low.
Don’t Miss: Just Food For Dogs Hepatic
Hepatitis C Testing And Diagnosis
Doctors will start by checking your blood for:
Anti-HCV antibodies: These are proteins your body makes when it finds the hep C virus in your blood. They usually show up about 12 weeks after infection.
It usually takes a few days to a week to get results, though a rapid test is available in some places.
The results can be:
- Nonreactive, or negative:
- That may mean you donât have hep C.
- If youâve been exposed in the last 6 months, youâll need to be retested.
If your antibody test is positive, youâll get this test:
HCV RNA: It measures the number of viral RNA particles in your blood. They usually show up 1-2 weeks after youâre infected.
- The results can be:
- Negative: You donât have hep C.
- Positive: You currently have hep C.
You might also get:
Liver function tests: They measure proteins and enzyme levels, which usually rise 7 to 8 weeks after youâre infected. As your liver gets damaged, enzymes leak into your bloodstream. But you can have normal enzyme levels and still have hepatitis C. Learn the reasons why you should get tested for hepatitis C.
Cost Of Hepatitis C Medicines
The newer direct-acting antiviral medicines for hepatitis C can be costly. Most government and private health insurance prescription drug plans provide some coverage for these medicines. Talk with your doctor about your health insurance coverage for hepatitis C medicines.
Drug companies, nonprofit organizations, and some states offer programs that can help pay for hepatitis C medicines. If you need help paying for medicines, talk with your doctor. Learn more about financial help for hepatitis C medicines.
Also Check: Can You Get Hepatitis C Sexually
How Many People Have Hepatitis C
During 2013-2016 it was estimated that about two and half million people were chronically infected with HCV in the United States. The actual number may be as low as 2.0 million or as high as 2.8 million.Globally, hepatitis C is a common blood-borne infection with an estimated 71 million people chronically infected according to the World Health Organization .
How Is Hepatitis C Treated
Significant progress has been made in treating and even curing hepatitis C. Older hepatitis C treatments usually required weekly injections, had serious side effects, and often were not effective.
New and better oral medicines now can cure HCV for many people within 3 months. The new medicines were very expensive at first, but their prices have come down, a trend that health experts hope will continue as the incidence of HCV rises and increased screening brings more cases to light.
These medicines successfully cure about 90% of HCV patients. A new oral medicine under development looks promising for the 10% who don’t respond to the standard treatment. This new antiviral combination pill is currently under review by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration .
Recommended Reading: How Bad Is Hepatitis C
How Is Hepatitis C Infection Prevented
Unfortunately, there is no vaccine to prevent hepatitis C. To reduce your risk of getting hepatitis C:
- Injection drug use is the most common way people get hepatitis C. Avoid injecting drugs to reduce your risk. If you do inject drugs, use sterile injection equipment. Avoid reusing or sharing.
- Avoid sharing personal care items that might have blood on them
- If you are a health care or public safety worker, follow universal blood/body fluid precautions and safely handle needles and other sharps
- Consider the risks if you are thinking about tattooing, body piercing, or acupuncture are the instruments properly sterilized?
- If youre having sex with more than one partner, use latex condoms correctly and every time to prevent the spread of sexually transmitted diseases, including hepatitis C.