Autoimmune Disorders And Liver
Along with hepatitis, theres significant evidence suggesting that certain autoimmune disorders also can subside to liver-related diseases, several which include the following:
Autoimmune hepatitis
This autoimmune disease is understood to trigger inflammation within the hepatic organ and may cause organ failure if left untreated. On a side note, autoimmune hepatitis is more common in women than in men.
First biliary cholangitis
Also more common in women than men, primary biliary cholangitis is an autoimmune disease that blocks the ducts within the hepatic organ that secretes bile to assist digest food. If these ducts are blocked, the bile will inevitably damage the hepatic organ and cause one among many liver-related diseases.
First sclerosing cholangitis
This autoimmune disease not only blocks bile ducts within the hepatic organ but also causes it to become overworked. To further complicate matters, when bile becomes trapped within the organ, it can cause it to pack up, which results in a better chance of developing liver-related cancer.
Unlike autoimmune hepatitis and first biliary cholangitis, men are more likely to develop primary sclerosing cholangitis than women.
Is There A Cure
Not yet. Since we do not know exactly what causes autoimmune hepatitis, we do not yet have a medical cure for the condition. Steroids and other anti-inflammatory drugs can certainly control the inflammation in the majority of cases. However, in certain patients in whom the inflammation continues or who have not been detected and diagnosed until very late in the course, cirrhosis can occur. Cirrhosis is a condition characterized by increased scar tissue that destroys the normal architecture of the liver.
Even if cirrhosis occurs, patients who have a mild disease without active inflammation generally do well and can live many years or decades without problems. If inflammation continues, the cirrhosis usually worsens, eventually reaching a stage called end-stage liver failure. If this stage has been reached, liver transplantation can be used in some patients to successfully treat the condition.
What Do Researchers Know About What Causes Autoimmune Hepatitis
Autoimmune hepatitis is believed to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. The condition can be triggered by an environmental factor when you are already genetically predisposed to it. The genes HLA DRB1*03 and HLA DRB1*04 have both been linked to an increased risk of autoimmune hepatitis. Autoimmune hepatitis can also be triggered by certain medications or other diseases.
Read Also: Can I Get Rid Of Hepatitis C
Is There Anything I Can Do To Help My Liver Heal Itself
No, not directly. However, you can help by giving your liver favourable working conditions, by eating a healthy well-balanced diet, not smoking, and drinking alcohol only in modest amounts or abstaining altogether. Obesity may result in fat deposits in the liver and increases the surgical risk with transplantation. Therefore, if you are overweight, strive for a gradual and sustained weight loss. Introduce exercise into your routine: you can enjoy walking, swimming, gardening, stretching. Please remember that a healthy diet and exercise are important components of any weight-loss regimen.
Hepatitis Cassociated Autoimmune Disorders
- Author Footnotes* From the Division of Rheumatology and Molecular Immunology, Department of Medicine, University of Mississippi Medical Center, and the Jackson VA Medical Center, Jackson, MississippiRobert W. McMurrayFootnotes* From the Division of Rheumatology and Molecular Immunology, Department of Medicine, University of Mississippi Medical Center, and the Jackson VA Medical Center, Jackson, Mississippi
- Author Footnotes* From the Division of Rheumatology and Molecular Immunology, Department of Medicine, University of Mississippi Medical Center, and the Jackson VA Medical Center, Jackson, Mississippi
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C And Liver Failure
How Do Doctors Treat Autoimmune Hepatitis
Doctors treat autoimmune hepatitis with medicines that suppress, or decrease the activity of, your immune system, reducing your immune systems attack on your liver. The medicines doctors most often prescribe are corticosteroidsprednisone or prednisolonewith or without another medicine called azathioprine.
Doctors typically start with a relatively high dose of corticosteroids and then gradually lower the dose. Your doctor will try to find the lowest dose that works for you. Your doctor will use blood tests to find out how you are responding to the treatment. A decrease in levels of the liver enzymes alanine transaminase and aspartate transaminase shows a response to treatment. ALT and AST falling to normal levels shows a full response. In some cases, a doctor may repeat a liver biopsy to confirm the response to treatment and find out whether the damage has resolved.
Treatment can relieve symptoms and prevent or reverse liver damage in many people with autoimmune hepatitis. Early treatment of autoimmune hepatitis can lower the chances of developing cirrhosis and other complications. A minority of people who have no symptoms or only a mild form of the disease may or may not need medicines.
Baseline Characteristics Of The Study Population
A total of 15,836 patients were enrolled initially. Among them, 934 and 2,042 patients were excluded because of hepatitis B virus coinfection and unavailable SVR status, respectively 29 patients were excluded because of death during or within 6 months of PR therapy, and 63 patients were excluded because of SLE or RA development before PR therapy. Finally, 12,770 patients were analyzed .
Figure 1
Flowchart of patients enrolled in this study. *2 patients had both HBV infection and unavailable virological outcomes.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Genotype 3 Treatment
Analysing The Immune Systems Complexity
Lead on the study, Niklas Björkström, physician and associate professor at the Department of Medicine, Huddinge, Karolinska Institute, said: Researchers in the field previously focused on analysing individual components but were unable to draw any comprehensive conclusion.
The immune system is extraordinarily complex, incorporating a large number of interacting parts. We adapted new methods in order to assess and analyse that complexity in a fresh manner.
It was found that the overall composition of the bodys defence system was affected by the chronic infection, with significantly reduced diversity among the NK cells. Changes remained long after eradication of the virus.
Hepatitis C Virus And Mixed Cryoglobulinemia
Mixed cryoglobulinemic vasculitis is known to be the most frequently encountered extrahepatic disease that HCV infection can trigger.69,70 MCV is immune complexmediated vasculitis that affects small vessels due to the presence of cryoglobulins.71,72 Cryoglobulins are immunoglobulins that are insoluble below 37ÅãC and soluble after warming.73 Cryoprecipitation was first described among patients with multiple myeloma in 1933 by 2 hematologists, Wintrobe and Buell from Johns Hopkins University. The term cryoglobulin was first used by Lerner and Watson in 1947.74 The clinical triad of MCV, including purpura, arthralgia, and weakness, was initially described by Meltzer and colleagues in 1966.75
According to the Brouet classification, cryoglobulins may be grouped into 3 types. Type 1 cryoglobulinemia includes isolated monoclonal Ig and may account for 10% to 15% of cryoglobulinemia. It is usually associated with lymphoproliferative disorders. The IgG and IgA subtypes exist but are rare.76 Type 2 cryoglobulinemia presents with IgM and polyclonal IgG and is mostly encountered in viral infections and inflammatory disorders.77,78 HCV can potentially induce type 2 cryoglobulinemia in 50% to 60% of cases. Type 3 cryoglobulinemia may present without monoclonal proliferation. Immune complexes are typically formed by polyclonal IgM. Some doctors believe that type 3 cryoglobulinemia may be a transition form between type 1 and type 2.79
You May Like: Fast Track Hepatitis B Vaccine In Houston Tx
Do Patients Recover From Autoimmune Hepatitis Treatment
Autoimmune hepatitis is a chronic condition, and while it can be managed, it usually cannot be cured. It is possible to achieve remission from autoimmune hepatitis with the use of steroids. However, most individuals will require treatment for the rest of their lives. The 10-year survival rate for people being treated for autoimmune hepatitis is between 83.8%94%. Without treatment, the survival rate falls to 50%60%.
The Role Of Liver Biopsy In Aih
Liver biopsy is recommended by the American Association for the Study of Liver diseases and the European Association for the Study of the Liver guidelines to help establish the diagnosis, exclude other causes of liver disease, and guide treatment choice ,.
The diagnostic criteria for AIH have been codified in 1993, revised in 1999 by the International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group , and more recently simplified for clinical use . In the simplified system, as in the previous ones, liver histology is included among the parameters required to confirm clinical diagnosis of AIH. Indeed, the system comprises four parameters: autoantibodies, serum IgG, results of viral hepatitis work-up and AIH histology, which is coded as absent, typical or compatible .
You May Like: Is There A Vaccine Available For Hepatitis B
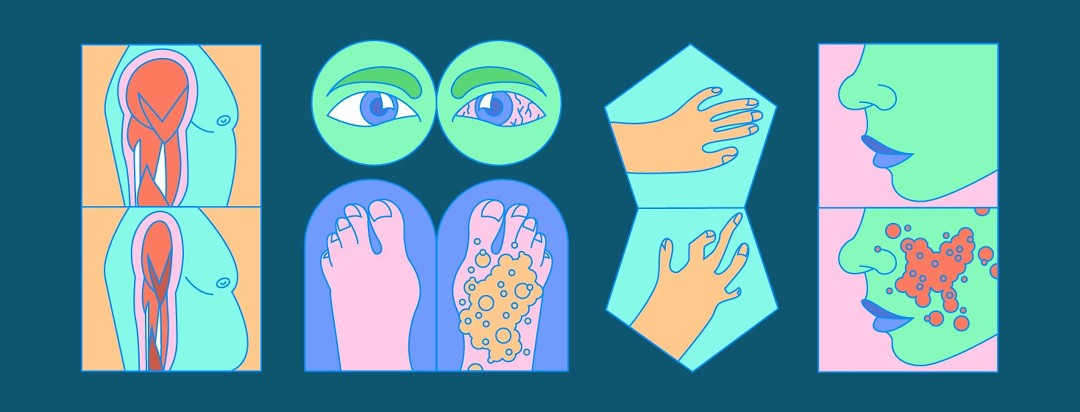
Signs Of Disease To Never Ignore
Lifecareful | Health | 8 Signs of disease to Never Ignore
According to a study published by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, quite 4.5 million Americans were officially diagnosed with a liver-related disease in 2018. And within the same year, liver-related diseases claimed the lives of quite 42,000 individuals.
A separate study published by MarketWatch, a financial information website that gives news, analysis Stock exchange data, shows that the death rate related to chronic liver diseases rose annually since 2000, affecting primarily those between the ages of 45 to 64.
Lets further put this into context. The study ran from 2000 through 2015. Ultimately, it revealed that the death rate among individuals within this age bracket with the disease increased by 31%.
What Causes Autoimmune Hepatitis
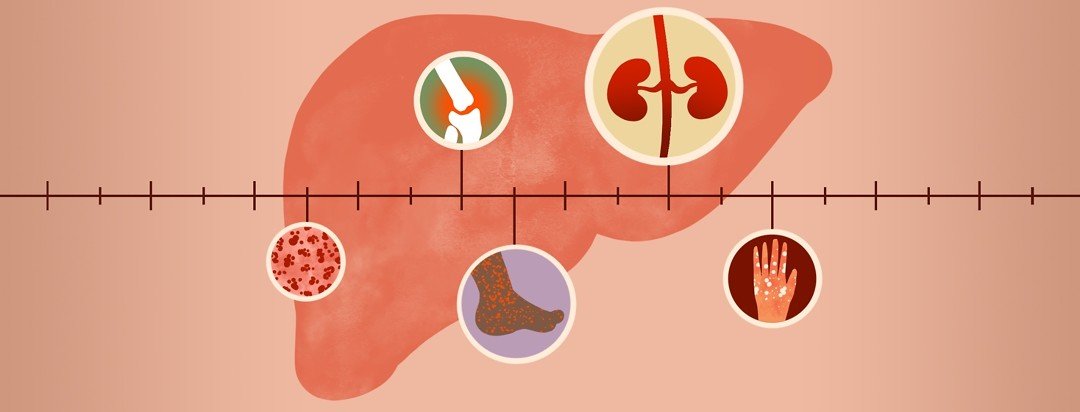
Your immune system normally attacks bacteria, viruses and other invading organisms. It is not supposed to attack your own cells if it does, the response is called autoimmunity. In autoimmune hepatitis, your immune system attacks your liver cells, causing long-term inflammation and liver damage. Scientists dont know why the body attacks itself in this way, although heredity and prior infections may play a role.
Also Check: How Does Hepatitis Affect The Body
Types Of Autoimmune Hepatitis
There are two types of autoimmune hepatitis. Type 1 autoimmune hepatitis is the most common kind in the United States, while type 2 is more commonly seen in Europe and tends to be a more severe disease. The two forms of autoimmune hepatitis are characterized by the presence of different types of antibodies, proteins released by the immune system to fight bacteria and viruses. They are:
- Type 1 is the most common, accounting for 96% of autoimmune hepatitis cases in North America. It usually affects young women who have other autoimmune conditions, such as type 1 diabetes, thyroiditis, and celiac disease. People with this type of autoimmune hepatitis have antinuclear antibodies and antismooth muscle antibody .
- Type 2 is less common in North America, making up only 4% of all autoimmune hepatitis cases. It typically affects females ages 214. Individuals with this type of autoimmune hepatitis have anti-liver kidney microsomal antibody type 1 and/or anti-liver cytosol type 1 autoantibodies.
Hepatitis C Virus And Polyarteritis Nodosa
PAN is a systemic and necrotizing vasculitis of medium and small-sized arteries. This condition, which was previously shown to be associated with hepatitis B virus infection, may also be associated with HCV infection.97,98 The risk of development of HCV-related PAN may be 5% to 12% in chronic HCV infection.99 In a study of 161 patients with chronic HCV infection and HCV-related vasculitis, 31 patients were given a diagnosis of PAN. Compared with HCV-associated MCV, HCV related PAN was associated with more severe symptoms. However, it was also observed that HCV-related PAN was associated with a higher rate of clinical remission.100 Hypocomplementemia is an important marker for the diagnosis of HCV-related PAN. Moreover, cutaneous manifestations are observed more frequently, and C-reactive protein and the erythrocyte sedimentation rate are higher in HCV-related PAN.101
The finding of motor mononeuropathy on clinical examination, which is present in almost 90% of patients, may be more useful.102 Symptoms such as cerebral vasculitis, severe hypertension, and ischemic abdominal pain also may be observed in patients with HCV-related PAN. Antiviral therapies and corticosteroids are the cornerstone treatments for HCV-related PAN. Some specialists also suggest plasma exchange, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab in resistant cases.103
Don’t Miss: How Can You Catch Hepatitis A
Autoimmune Hepatitis Causes And Risk Factors
Doctors aren’t sure exactly what causes your immune system to turn against your liver. Your genes may have something to do with it, since AIH can run in families.
But genes aren’t the whole story. Something you come into contact with may trigger your genes to set autoimmune hepatitis in motion. This could include:
- Medicines such as statins and hydralazine or antibiotics like nitrofurantoin and minocycline
- Infections such as viral hepatitis, herpes, Epstein-Barr, and measles
Willowbrook State School Experiments
A New York University researcher named Saul Krugman continued this research into the 1950s and 1960s, most infamously with his experiments on mentally disabled children at the Willowbrook State School in New York, a crowded urban facility where hepatitis infections were highly endemic to the student body. Krugman injected students with gamma globulin, a type of antibody. After observing the temporary protection against infection this antibody provided, he then tried injected live hepatitis virus into students. Krugman also controversially took feces from infected students, blended it into milkshakes, and fed it to newly admitted children.
You May Like: How Does One Get Hepatitis B And C
How Infections Impact The Immune System
This study comprised 40 patients with chronic HCV of whom researchers followed before, during and after treatment with the new medications in a bid to investigate impact on the composition and diversity of the immune system.
In order for the immune system to have the ability to fight infections, diversity is vital. Particularly important are natural killer cells , which is a type of white blood cells.
The researchers used flow cytometry and a new measurement method to derive the composition of the immune system, as well as the appearance of NK cells and their function in the blood.
Hepatitis C Virus And Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis is a systemic inflammatory disease characterized by the formation of noncaseating epithelioid cell granulomas in the organs. The etiology of the disease is still not well understood.104 The relationship between chronic HCV infection and sarcoidosis was first described in 1993.104 This relationship can be IFN-related or completely unrelated to IFN treatment. IFN-related sarcoidosis is rare but well defined in the literature. Studies have shown that the incidence of sarcoidosis may vary between 0.09% and 0.2% in HCV-infected patients undergoing IFN treatment. The incidence rate seems low, but it is higher than the rate seen in the general population.105,106 Symptoms of sarcoidosis develop in almost two-thirds of patients during the first 6 months of IFN treatment.105
However, data also demonstrate that the disease may occur toward the end of treatment. IFN-related sarcoidosis presents mostly with lung and cutaneous findings. Thus, HCV infected patients treated with IFN therapy should be carefully evaluated for development of sarcoidosis.106 Although rare, non-IFNrelated sarcoidosis has been reported in chronic HCV infection. IFN-related sarcoidosis clinically progresses in a benign fashion. Patients with mild symptoms may continue with IFN treatment. However, IFN treatment should be stopped in patients whose symptoms do not regress. In such cases, corticosteroids and hydroxychloroquine can be considered as possible treatment options.105-107
Also Check: What Happens If You Have Hepatitis
Screening For Viral Hepatitis
The purpose of screening for viral hepatitis is to identify people infected with the disease as early as possible, even before symptoms and transaminase elevations may be present. This allows for early treatment, which can both prevent disease progression and decrease the likelihood of transmission to others.
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A causes an acute illness that does not progress to chronic liver disease. Therefore, the role of screening is to assess immune status in people who are at high risk of contracting the virus, as well as in people with known liver disease for whom hepatitis A infection could lead to liver failure. People in these groups who are not already immune can receive the hepatitis A vaccine.
Those at high risk and in need of screening include:
- People with poor sanitary habits such as not washing hands after using the restroom or changing diapers
- People who do not have access to clean water
- People in close contact with someone who has hepatitis A
- People who use illicit drugs
- People with liver disease
- People traveling to an area with endemic hepatitis A
The presence of anti-hepatitis A IgG in the blood indicates past infection with the virus or prior vaccination.
Hepatitis B
The CDC, WHO, USPSTF, and ACOG recommend routine hepatitis B screening for certain high-risk populations. Specifically, these populations include people who are:
Other
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis B and C
Hepatitis D
Hepatitis E
Alcoholic hepatitis
Hepatitis C Virus And Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
SLE is a common connective tissue disease, and its prevalence is estimated to be 15 to 200 per 100,000.47,48 Articular, mucocutaneous, renal, hematologic, central nervous system, liver, and lung involvement are well documented in this disease. The pathophysiology of SLE is multifactorial and includes environmental triggers, such as viral infections49 with HCV considered to be among the suspected viruses.50 HCV infection and SLE may share common clinical and serologic features. The extrahepatic manifestations of HCV may mimic SLE, with associated symptoms such as arthralgia, myalgia, sicca syndrome, and antinuclear antibody positivity.51,52 One study has shown that the prevalence of HCV infection in patients with SLE was greater than that of the general population.53 In another study, the prevalence of HCV among patients evaluated for SLE was found to be 10%.54 In a study from Egypt, the frequency of HCV infection among patients in a rheumatologic clinic was found to be 18.5%. Only 7% had clinical symptoms of HCV infection.55
In summary, extrahepatic manifestations of HCV infection may mimic features that resemble SLE. Further testing of anti-Smith antibody, anti-dsDNA, and antinucleosome antibodies may help clinicians establish the diagnosis of SLE. Although the association between HCV and SLE is still uncertain, it has been suggested that HCV may play a role in triggering SLE.
Recommended Reading: How Contagious Is Hepatitis B
How Can I Cover Medication Costs
New therapies called direct-acting antivirals are effective and can achieve cures of over 90%. Because these new therapies are very new, they remain very expensive. As such, drug coverage from both government and private companies may require that your liver disease has progressed to a certain stage before they are willing to cover the cost of these drugs.
Talk with your healthcare provider about financial support that may be available.
Below are useful resources when looking for financial assistance:Private health insurance or drug plansIf you have private health insurance or a drug plan at work, you may be able to have the medication paid through your plan. Please consult your private health insurance or drug plan provider to see if your drug is covered.
Publicly funded plansEach provincial and territorial government offers a drug benefit plan for eligible groups. Some are income-based universal programs. Most have specific programs for population groups that may require more enhanced coverage for high drug costs. These groups include seniors, recipients of social assistance, and individuals with diseases or conditions that are associated with high drug costs. For more details, please contact your provincial or territorial health care ministry, or click on the appropriate link below.
Yukon
Available Patient Assistance Programs for Hepatitis C treatment Holkira Pak Maviret
MerckCare Hepatitis C Program 1 872-5773 Zepatier