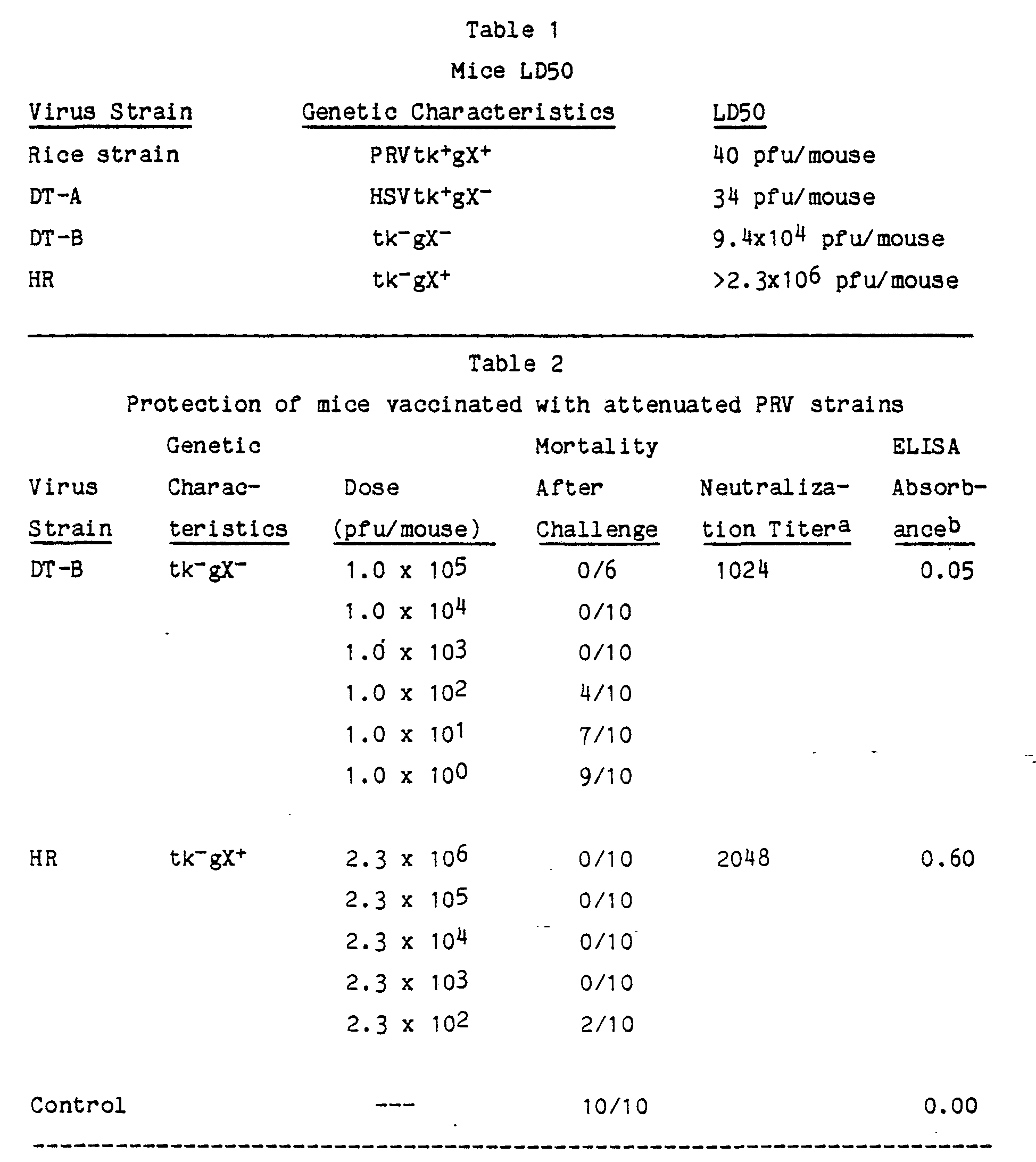
What Is A Titer
A Titer is a blood test that checks your immune status to vaccinations or diseases you may have received in the past. There are two types of immunity a person can have:
1. Active Immunity
- The body’s immune system produces antibodies and cellular immunity which usually lasts for many years to a lifetime.
- Develops from surviving infection or by vaccination
- Every individual varies in response and production of antibodies
2. Passive Immunity
- Immunity transferred from one to another
- Develops from mother to infant or by blood product such as immune globulin
- This immunity usually only offers temporary protection during a period of weeks to months
Can I Take The Test At Home
Samples for hepatitis B testing can be collected at home. At-home hepatitis B testing requires a patient to collect a blood sample, typically from a fingerstick using a very small needle provided in the test kit. Once a blood sample is collected, it is prepared according to the instructions contained in the test kit and mailed to a laboratory for testing.
Because there are numerous types of tests for HBV, it is important to look closely at the specific components of any at-home test kit. Many at-home test kits only look for hepatitis B surface antigen .
Questions For Your Doctor About Test Results
Patients may find it helpful to ask questions about their hepatitis B test results. Questions that may be helpful include:
- What was my test result?
- Do I have an acute or chronic hepatitis B infection?
- Does the test result suggest that I have immunity for hepatitis B?
- Would I benefit from hepatitis B vaccination?
- Do I need any follow-up tests based on my hepatitis B test results?
Also Check: Hepatitis B And Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment
What Do Hepatitis B Test Results Mean
Hepatitis B test results help determine if HBV infection is negative or positive, and if positive, whether the infection is acute or chronic, or if recovery is complete. A combination of results are considered to identify and classify HBV infection status.
The following are some interpretations of hepatitis B test results:
Table: Hepatitis B test results and interpretations
| Test |
|---|
What Is The Difference Between Hepatitis B Surface Antibody And Antigen
An antigen is a substance that induces antibody production. Hepatitis B surface antigen is a protein on the surface of hepatitis B virus.
Hepatitis B surface antibodies are produced by the bodys immune system in response to HBsAg. The presence of adequate hepatitis B surface antibodies in the blood indicates protection against hepatitis B virus infection.
Also Check: Is There A Cure For Chronic Hepatitis C
How Is It Used
The main uses for hepatitis B virus tests include:
Some of the secondary reasons to perform testing include: to screen for hepatitis B infection in at-risk populations or in blood donors, to determine if someone is a carrier, to detect a resolved infection, and to determine if immunity has developed due to vaccination.
Generally, one set of tests is used as an initial panel of tests to detect HBV infection or to determine the cause of acute symptoms while another set of tests may be used after a diagnosis is made to monitor possible progression of the disease, to detect chronic infection, and/or to determine carrier status.
The following table summarizes the set of tests typically used for initial testing:
The following table summarizes tests that may be used as follow-up after initial tests detect an HBV infection:
What Do I Do If Im A Hepatitis B Vaccine Non
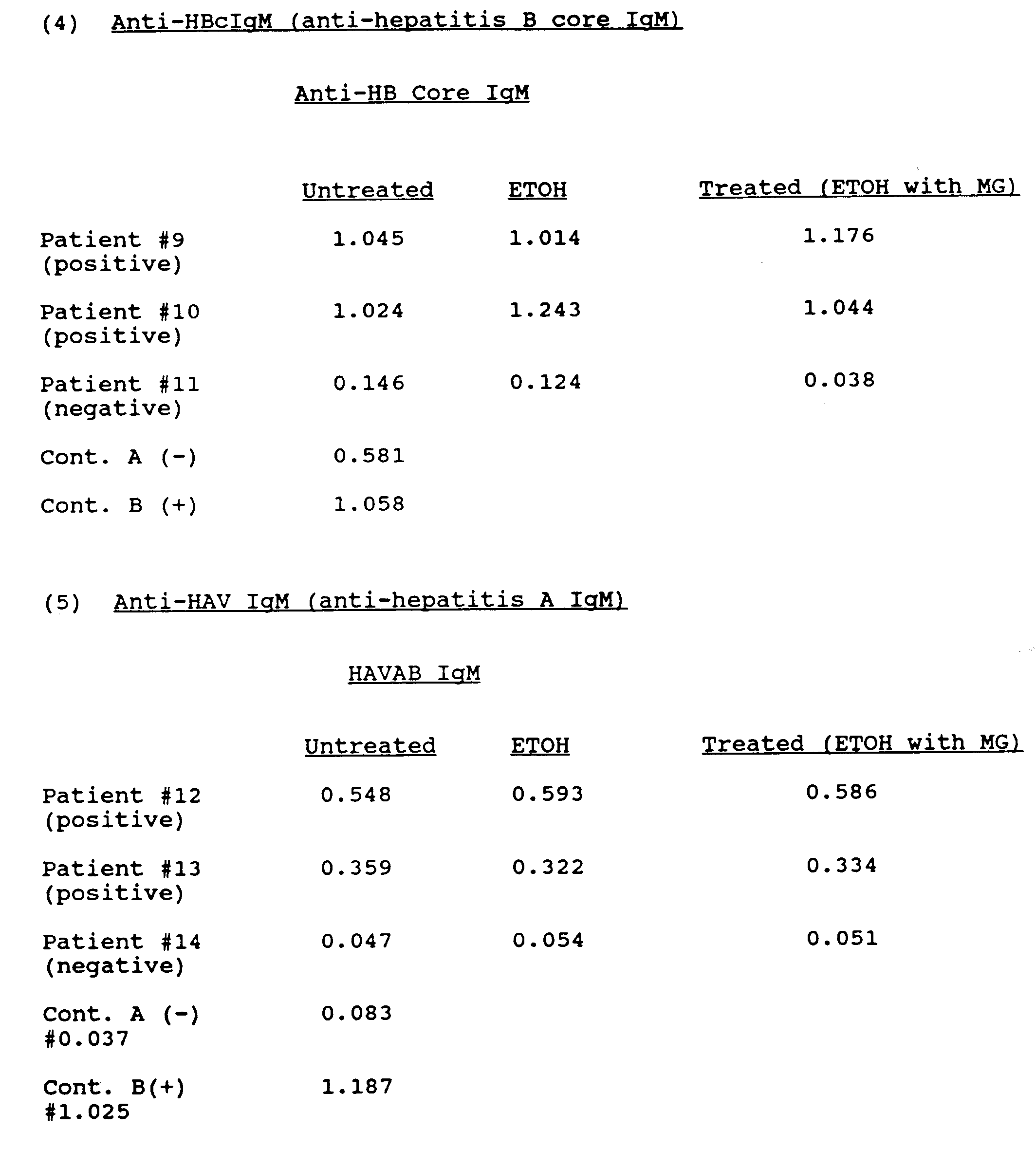
Approximately 5-10% of people do not develop protective antibodies following the completion of the hepatitis B vaccine series. This is confirmed with a blood test called an anti-HBs titer test which is given 4 weeks following the completion of the series. If the test shows the titer is less then 10 mIU/mL the general recommendation is to complete the series again using a different brand of vaccine . A person is considered to be a non-responder if they have completed 2 full vaccination series without producing adequate protective antibodies.
Another vaccine option is the new two-dose hepatitis B vaccine, HEPLISAV-BTM. The new vaccine is expected to increase immunization rates for adults in the United States and is administered over a one-month period. The vaccine provides greater seroprotection, which can mean a greater antibody response especially in adults who may be older, obese or live with type 2 diabetes making it an effective vaccine option.
It is also possible that a person who does not respond to the vaccine may already be infected with hepatitis B. Therefore, testing for the presence of the hepatitis B virus is recommended before diagnosing a person as a vaccine non-responder.
CDC Recommendations for Hepatitis B Vaccine Non-Responders
Check out our previous post on the topic here.
References:
HEPLISAV-B. Retrieved from:
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatitis C Ab
What Is A Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Test
Hepatitis B surface antibody test is part of a panel of blood tests to diagnose HBV infection. Hepatitis B surface antibody test determines the presence and quantity of anti-HBs in the blood serum, which can indicate protection from HBV infection.
Hepatitis B disease affects the liver and commonly spreads through body fluids such as blood, semen, and vaginal secretions.
Influenza A & B Antibody Titer Blood Test
This test measures antibodies to Influenza, commonly known as the flu. Influenza is a respiratory viral infection which affects millions of people every year. Many flu cases are mild but some can lead to serious health complications if not identified and treated. The highest risk from the flu is to those whose immune systems are weakened. either due to age or other health conditions. Common symptoms of the flu include headache, fever, chills, muscle pain, stuffy nose, sore throat, and a cough. Testing for influenza antibodies can help determine if a person is actually suffering from the flu or a different condition with similar symptoms. This test looks for two types of antibodies to different forms of the flu virus. Differentiating what form of the flu a person has can help ensure they receive the correct treatment as well as help to identify when a large community is suffering from the same flu strain.
The Influenza Antibodies titer is typically ordered when a person displays symptoms of the flu, especially if they are at higher risk.
Turnaround for this test is typically 2-5 business days.
Note: Result turn around times are an estimate and are not guaranteed. Our reference lab may need additional time due to weather, holidays, confirmation/repeat testing, or equipment maintenance.
Categories:
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Virus Symptoms And Treatment
Should I Get The Hbv Vaccine
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that adults in high-risk groups get vaccinated. Some of these groups include people:
- In close contact with someone who has hepatitis B
- Who undergo dialysis
- With chronic liver or kidney disease
- With HIV or who seek treatment for other sexually transmitted diseases or drug treatment
- Who travel to countries where hepatitis B is common
- Who are healthcare workers with potential exposure to HBV
Unless there is something in your medical history to the contrary, it is prudent to get the series of vaccinations. Babies, children and adolescents are routinely given the series of shots if you have already been vaccinated, you probably are protected for many years, perhaps for life, and will not usually need to get the vaccine again.
Who Is At Risk For Hepatitis B
Anyone can contract hepatitis B. However, certain groups are at greater risk. According to the CDC, the following groups are at highest risk for contracting hepatitis B:
- Infants born to infected mothers
- People who inject drugs or share needles
- Sexual partners of people infected with hepatitis B
- Men who have sex with men
- People living in close proximity to a person with hepatitis B
- Health care workers or others exposed to blood in their work environments
- Hemodialysis patients
You May Like: Can You Get Hepatitis C From Drinking
Why Get Tested For Hepatitis B Immunity
Schools, workplaces, or other entities may require proof of immunity to hepatitis B within their requirements. Additionally, if you are unsure if you have previously been vaccinated for, or been infected by, hepatitis B, a screening will allow you to confirm your status.
*It is solely your responsibility to promptly discuss all laboratory test results with a physician. Neither Sonora Quest Laboratories nor its Medical Director will provide interpretation, counseling, consulting, or care recommendations on the basis of any laboratory results provided to you.
Order Your Own Hepatitis B Immune Status Screening
Order a Hepatitis B Immune Status screening for $30 & pay for your test in 3 easy steps.
- 1Select Tests
Why It Is Done
You may need testing if:
- You have symptoms of hepatitis.
- You may have been exposed to the hepatitis B virus. You are more likely to have been exposed to the virus if you inject drugs, have many sex partners, or are likely to be exposed to body fluids .
- You’ve had other tests that show you have liver problems.
- You are pregnant.
- You or your doctor wants to know if you are protected from getting the disease.
The tests also are done to help your doctor decide about your treatment and see how well it’s working.
Recommended Reading: Is Hepatitis C A Disease
How Is Hepatitis B Treated
There is no specific treatment for acute hepatitis B infections. Symptoms are usually treated with supportive care. This usually involves making sure that you are getting plenty of rest and enough fluids and nutrition by eating and drinking small amounts several times a day.
Chronic forms of hepatitis B may be treated with antiviral medications such as interferon, entecavir, tenofovir, lamivudine, and adefovir. However, some antiviral drugs can have serious side effects and not all people need to be treated. Often, people with chronic hepatitis will be closely monitored to see if they develop cirrhosis or liver cancer. It is important to talk to your healthcare provider about your treatment options and the risks and benefits of those currently available.
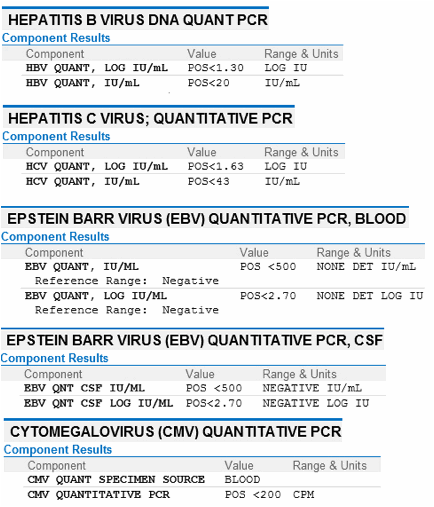
Question 5 What Is The Natural History Of Hepatitis B Surface Antibody During Acute Hepatitis B Infection And Convalescence
HBsAg can be detected in the blood 4 to 10 weeks after exposure. This corresponds to onset of symptoms and viremia detectable by nucleic acid amplification methods. Most hepatitis B infections are self-limited and are associated with disappearance of HBsAg within 4 weeks of onset of symptoms. The anti-HBs then appears and increases to a plateau level that persists indefinitely.2
You May Like: How Contagious Is Hepatitis C
Hbv Dna Hbv Genotype And Hbv Drug Resistance Assays
Specimen: Serum or plasma
Container: Red-top tube, yellow-top tube , gel-barrier tube, plasma preparation tube, or lavender tube
Collection method: Routine venipuncture
The specimen should be transfused to separate plasma/serum from cells within 6 hours and kept frozen when testing cannot be done promptly.
The tests use PCR amplification, DNA probe hybridization, and sequencing method.
What Does The Test Result Mean
The tests for hepatitis B may be ordered individually but are often ordered in some combination, depending on the reason for testing. Results of the tests are typically evaluated together. Sometimes the meaning of one result depends on the result of another test. However, not all tests are performed for all people.
The table below summarizes possible interpretations of some common patterns of results.
| Initial Tests | |
| None detected or detected at very low level | Chronic infection but low risk of liver damage carrier state |
*Note: There are some types of HBV that do not make e-antigen. In areas where these strains of HBV are common , testing for HBeAg is not very useful. In these cases, a negative HbeAg result does not necessarily mean that the person is not infectious it may be that the person is infected with a strain that does not make the e-antigen.
Monitoring treatment of chronic infection: If the results from initial and follow-up testing indicate that a person has chronic hepatitis B, then the individual may be treated with medication and the effectiveness of that treatment may be monitored using the tests for HBe and HBs antigen and antibody and HBV DNA:
You May Like: Where Do I Get A Hepatitis A Vaccine
When To Get Tested
When you have risk factors for HBV infection or when you have signs and symptoms of hepatitis, such as jaundice or unexplained elevated blood levels of alanine aminotransferase , a liver-associated enzyme when you have a condition that requires chemotherapy or drugs that suppress your immune system when you are being treated for HBV or hepatitis C when it is unclear whether you have immunity and your healthcare practitioner is considering giving you the hepatitis B vaccine
When And How To Perform Post
Which test to use: If testing is needed following vaccination, use quantitated HBsAb only
- Post-vaccination testing is needed for certain groups who are at especially high risk for HBV infection
- The purpose of post-vaccination testing is to confirm if patients have achieved adequate immune response as measured by hepatitis B surface antibody
- Perform testing 1-2 months after final dose of the HBV vaccine series
- Persons with HBsAb concentrations of > 10 mIU/ml are considered immune
- Post-vaccination testing is recommended for some patients:
- Infants born to HBsAg+ women
- Infants born to women whose HBSAg status remains unknown
- Health care personnel and public safety workers at risk for blood or body fluid exposure
- Hemodialysis patients
- Other immunocompromised persons such as hematopoietic stem-cell transplant patients or persons receiving chemotherapy
- Sex partners of HBSAg+ persons
Also Check: Side Effects Of Having Hepatitis C
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis B
Not all individuals infected with acute hepatitis B will experience symptoms. In fact, the CDC estimates that only about 30-50% of infected people age 5 and older will have symptoms. When symptoms are present, they will develop about 3 months after exposure and will include the following:
- Fever
- Joint pain
- Jaundice
Individuals with chronic hepatitis B will generally not have any symptoms. When symptoms are present, they are generally very similar to the symptoms of acute hepatitis B. Given the serious nature of hepatitis B and the effects it can have on your liver and overall health, it is important to talk to your doctor about hepatitis B if you believe you may have been exposed to the disease.
Question 3 How Is The Quantitative Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Test Performed
An immunometric technique is used. The anti-HBs binds to HBsAg ad and ay subtypes, which are coated on the test wells. Binding of a horseradish peroxidase-labeled HBsAg conjugate to the anti-HBs completes the sandwich formation. Unbound materials are then washed away. In the next step, the horseradish peroxidase catalyzes oxidation of a luminogenic substrate, producing light. Light signals are detected and quantified. Intensity of the light is proportional to the amount of anti-HBs present in the patient sample. The result is standardized to an international unit system and reported as milliinternational units per milliliter .
Don’t Miss: How Do You Know If You Have Alcoholic Hepatitis
Hepatitis B Immunity Test
Use this to test your immunity to hepatitis B. The kit contains all you need to prick your finger, produce a small blood sample at home and send it to our lab. Confidential results come back in 2-3 working days.
- A reliable test for hepatitis B immunity
- Results available in 2-3 days of the lab receiving your test
When Should I Get Hepatitis B Testing
Using hepatitis B tests to screen for HBV is recommended for certain groups that are at an increased risk of infection. Groups that may benefit from hepatitis B screening include:
- Pregnant people
- People born in parts of the world where hepatitis B is more common, including Africa, Asia, Eastern Europe, South America, and parts of the Middle East
- People who didnât receive a hepatitis B vaccine
- HIV-positive people
- Pain in the joints or abdomen
- Loss of appetite, nausea, or vomiting
- Yellowish skin and eyes
Using hepatitis B testing to assess immunity to HBV may be used before or after vaccination. Pre-vaccination testing is not always needed but may be performed if there is a chance that a patient has previously been infected with HBV or has already been vaccinated. Post-vaccination testing is used in certain groups of people who are at an especially elevated risk for HBV infection, including infants born to mothers with a hepatitis B infection.
Don’t Miss: Doctors And Medical Specialists For Hepatitis B
Taking A Hepatitis B Test
Testing for hepatitis B is performed on a sample of blood. A doctor, nurse, or other health care provider can obtain a blood sample using a small needle to draw blood from a vein.
At-home hepatitis B testing requires that users carefully follow instructions provided in the test kit to collect a small sample of blood, package the sample, and mail it to a lab for testing.
Question 1 What Is The Clinical Indication For Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Quantitation
Hepatitis B surface antibody quantitation is used to determine hepatitis B immune status, ie, to determine if the patient has developed immunity against the hepatitis B virus. Such immunity may develop following exposure to the hepatitis B virus or its vaccine.
Patients at higher risk of exposure to the virus include:
- Infants born to infected mothers
- Sex partners of infected persons
- People with more than 1 sex partner in the last 6 months
- People with a history of sexually transmitted infection
- Men who have sex with men
- Injection drug users
- Household contacts of an infected person
- Healthcare and safety workers who have contact with blood and body fluids
- People who have lived or traveled in an area in which hepatitis B is common
- People who live or work in a prison
Testing is not recommended routinely following vaccination. It is advised only for people whose subsequent clinical management depends on knowledge of their immune status. These people include:
- Chronic hemodialysis patients
- Immunocompromised people, including those with HIV infection, hematopoietic stem-cell transplant recipients, and people receiving chemotherapy
- Infants born to women who test positive for the hepatitis B surface antigen
- Sex partners of people who test positive for the hepatitis B surface antigen
- Healthcare and public safety workers who have contact with blood or body fluids
Recommended Reading: What Is Included In A Hepatitis Panel