What Does The Test Measure
Hepatitis C testing identifies antibodies to the hepatitis C virus, detects viral RNA, and/or determines the strain of hepatitis C. Hepatitis C testing may involve several different tests:
- Hepatitis C antibody test: Antibodies are a part of the bodys response to an infection. Testing for hepatitis C antibodies determines whether or not a patient has been exposed to the hepatitis C virus at some point in their life. If this test is positive, the next step is to test for hepatitis C RNA which can tell you if you have a current infection.
- Hepatitis C RNA test: RNA is a type of genetic material from the hepatitis C virus that can be detected in the blood. If test results are positive after a hepatitis C antibody test, doctors use a hepatitis C RNA test to look for and/or measure the amount of the virus in the blood. Qualitative HCV RNA tests can detect the presence of HCV RNA, while quantitative HCV RNA tests measure the amount of HCV RNA. Understanding the amount of HCV in the blood helps to monitor response to treatment.
- Genotype test: There are at least six types of hepatitis C, which are also called strains or genotypes. Treatment for hepatitis C depends on the strain, so genotype testing to guide treatment is performed in patients who are diagnosed with an HCV infection.
Summary Table: Most Common Causes Of Viral Hepatitis
| Virus |
|
PreventionThe incidence of new cases of viral hepatitis has decreased due to use of safer injection and sex practices and the availability of vaccines for hepatitis A and hepatitis B . Screening units of blood for hepatitis B and C has virtually eliminated infections through blood transfusions. A systematic program to screen pregnant mothers for hepatitis B and to vaccinate all newborns has greatly decreased new cases of hepatitis B.
TreatmentHepatitis ASupport and symptom relief are frequently the only treatments required for acute hepatitis A. This usually involves plenty of rest, fluids, and nutritious food. With hepatitis A, most people recover without complications.
Hepatitis BManagement of acute hepatitis B is primarily supportive and usually involves plenty or rest and fluids and good nutrition. For those who progress to the chronic form of hepatitis B, management goals include minimizing further damage to the liver, treating underlying conditions that are causing or exacerbating the condition, and preventing transmission of the virus. There are medications available to treat chronic hepatitis B, but not all people need to be treated. People with chronic hepatitis are closely monitored for the development of liver cirrhosis or cancer.
Questions For Your Doctor After At
Your doctor can help you understand the meaning of your at-home hepatitis C test results and discuss the need for additional testing. Helpful questions for your doctor may include:
- What does my at-home hepatitis C test result mean?
- Do I need follow-up testing to confirm or rule out a hepatitis C infection?
- Should I be tested for hepatitis C again in the future?
- How can I reduce my risk of getting hepatitis C?
You May Like: Hepatitis B Treatment Cost In Us
What Causes Hepatitis C
The hepatitis C virus causes hepatitis C. The hepatitis C virus spreads through contact with an infected persons blood. Contact can occur by
- sharing drug needles or other drug materials with an infected person
- getting an accidental stick with a needle that was used on an infected person
- being tattooed or pierced with tools or inks that were not kept sterilefree from all viruses and other microorganismsand were used on an infected person before they were used on you
- having contact with the blood or open sores of an infected person
- using an infected persons razor, toothbrush, or nail clippers
- being born to a mother with hepatitis C
- having unprotected sex with an infected person
You cant get hepatitis C from
- being coughed or sneezed on by an infected person
- drinking water or eating food
- hugging an infected person
- shaking hands or holding hands with an infected person
- sharing spoons, forks, and other eating utensils
- sitting next to an infected person
A baby cant get hepatitis C from breast milk.18
Also Check: How Hepatitis C Affects The Body
Tests After The Diagnosis
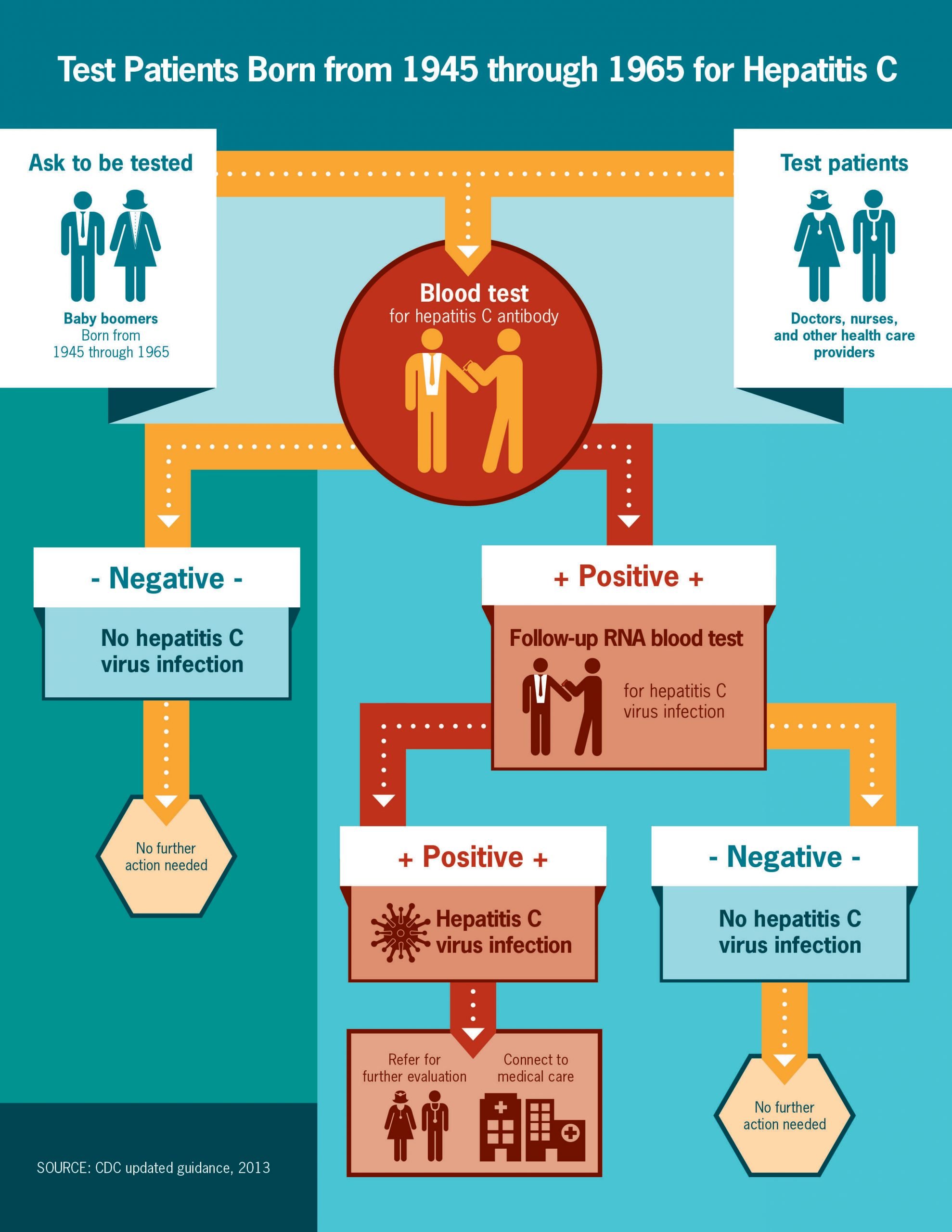
Once the doctor knows you have hep C, theyâll do tests to find out more about your condition. This will help determine your treatment. They could include:
- Genotype tests to find out which of the six kinds of hepatitis C you have.
- Liver function tests. They measure proteins and enzymes levels, which usually rise 7 to 8 weeks after youâre infected. As your liver gets damaged, enzymes leak into your bloodstream. But you can have normal enzyme levels and still have hepatitis C.
- Tests to check for liver damage. You might get:
- Elastography. Doctors use a special ultrasound machine to feel how stiff your liver is.
- Liver biopsy. The doctor inserts a needle into your liver to take a tiny piece to examine in the lab.
- Imaging tests. These use various methods to take pictures or show images of your insides. They include:
Also Check: What Is Hepatitis B Vaccine
Current Hepatitis C Testing Recommendations
Recently, several organizations have issued hepatitis C virus screening recommendations. In general, major guidelines now recommend routine one-time universal HCV testing for adults 18 years of age and older, routine HCV screening of pregnant individuals, screening younger persons at risk of acquiring HCV, and repeat screening for those with ongoing risk for HCV acquisition.
Specific Hcv Rna Assays And Range Of Detectable Virus
HCV RNA tests use target amplification techniques. Several assays exist for HCV RNA testing. Methods include polymerase chain reaction , transcription mediated amplification , and branched chain DNA tests. Results are expressed as international units/mL . The different methods and different commercial assays each have a lower limit of quantification and lower limit of detection , therefore a patient’s results could be reported differently depending on the assay used. HCV RNA tests must have an LLOQ of 25 IU/mL or lower when used to assess treatment response with DAAs.
LLOQ = the lowest HCV RNA level that is within the linear and analytically acceptable range of the assay.
LLOD = the lowest level of HCV RNA that is detected 95% of the time.
Read Also: Hepatitis B Blood Test Results
Screening For Hepatitis C
Although most clinicians have extensive experience with the diagnosis and treatment of disease, they have limited experience with screening for disease. Screening is characterized by interventions in a group of individuals with no signs or symptoms of disease to identify unrecognized disease. The hope is that by identifying the disease before the onset of signs or symptoms, morbidity and possibly mortality can be reduced. Screening is not intended to be diagnostic its main purpose is to detect the possibility of disease. The fact that screening is typically performed on healthy individuals can account for some of the limited experience on the part of clinicians.
The 2 most common types of screening are universal screening and selective screening. Universal screening involves screening all individuals in a certain category, such as all individuals above a certain age. Selective screening involves screening individuals who have a high risk for the disease, such as having family members with a known hereditary disease.
The World Health Organization has issued the following guidelines for screening:
Currently, the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the US Preventive Services Task Force recommend screening for hepatitis C for 2 groups of individuals:
Educating Clients About Viral Hepatitis
Clients may believe they know about viral , but their understanding of the disease may not be accurate. It is easy to confuse the three main types of viral , B, and C. Clients may have formed impressions based on limited or incorrect information. Counselors should briefly describe hepatitis A, B, and C, including their prevalence, , and relationship to drug use, as well as to other infections, such as HIV and sexually transmitted diseases. Specific strategies for speaking with clients include:
- Speak clearly and keep the message simple, focused, and brief.
- Use language, examples, and concepts that the client understands.
- Use appropriate visual aids.
- Frame numerical statements in terms that are easy to visualize. Say 5 out of 100 people rather than 5 percent of the population say more than half instead of the majority.
- Repeat the information at different times in different ways. The average client retains only approximately one-third of what he or she is told. Summarize essential points.
- Pay attention to a clients response to the information. For example, if a client stiffens his or her posture, consider saying, I notice that this topic seems to make you uncomfortable. It does for a lot of people. Please tell me what youre feeling right now. Id really like to help you with this.
- Use the opportunity to describe the potential detrimental effects of alcohol and other substance use on the liver of a person who is infected with HCV.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Signs Of Hepatitis C
Limitations Of Screening For Hepatitis C
Barriers to screening for hepatitis C include limited access to healthcare, inadequate health insurance coverage, individuals’ decreasing recall of past risky behaviors, lack of knowledge of hepatitis C prevalence, natural history, and available tests and treatments for hepatitis C at the provider level.- Moreover, nearly 42% of primary care physicians reported being unfamiliar with the CDC guidelines in a survey of community-based physicians.
Who Else Should Get Tested
Anyone who has hepatitis C symptoms should speak with a healthcare professional.
The HCV transmits via contact with blood, and it can pass from person to person through:
- sexual intercourse with someone who has the infection
- sharing personal items that may have come into contact with blood, such as razors
- tattooing in conditions that do not meet health and safety standards
- needle prick accidents in healthcare settings
Anyone who may have come into contact with the HCV should speak with a healthcare professional about having a test.
Recommended Reading: Liver Disease Caused By Hepatitis C
The Treatment Programs Role In The Screening Process
Medical staff members at substance abuse treatment programs might assume the primary role for screening individuals for and explaining the screening process and test results. Opioid treatment programs with medical staff members should screen for and C at intake and periodically as indicated. In programs without onsite medical staff, clients may be referred elsewhere for screening with minimal involvement of the substance abuse treatment program.
Regardless of the type of program, counselors should have a basic understanding of the importance of screening, the screening process, and the meaning of the results. Counselors can encourage clients referred for screening to follow through and complete the screening and evaluation process . Clients might feel anxious about being diagnosed with hepatitis, and they might delay or avoid getting screened.
Hepatitis C Testing And Diagnosis
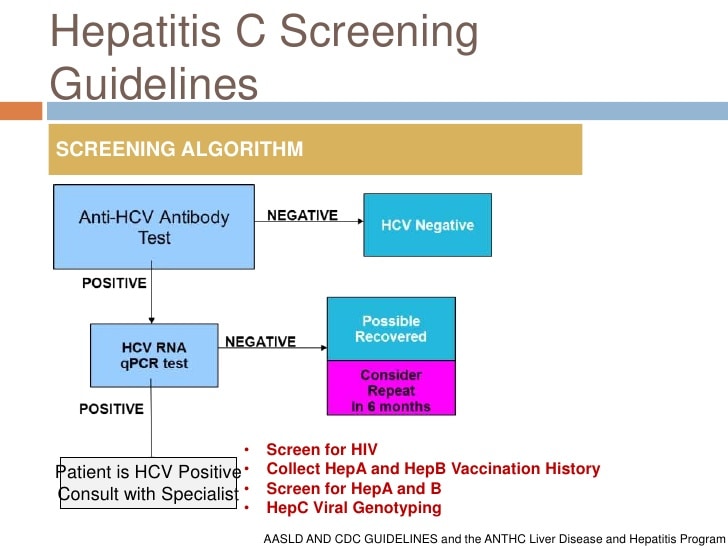
Doctors will start by checking your blood for:
Anti-HCV antibodies: This blood test is the first — and sometimes only — one you may get. Also called the ELISA screen, it checks for antibodies that your body releases to fight the virus. These are proteins your body makes when it finds the hep C virus in your blood. They usually show up about 12 weeks after infection. Your test will be either negative or positive for antibodies. It usually takes a few days to a week to get results, though a rapid test is available in some places.
What the results mean
Negative . This is when your blood shows no signs of HCV antibodies. Most of the time, thatâs because you never came in contact with the virus and you do not have hep C.
Sometimes, your negative result can be false, meaning you have HCV. That may happen if you:
- Took the test too soon after your exposure. This test checks for only HCV antibodies, which can take several months to appear.
- Have HIV, a donated organ, or other conditions that weaken your immune system, which can suppress your antibodies
- Get hemodialysis for kidney problems
If youâve been exposed in the last 6 months, youâll need to be retested.
Positive . This means youâve been infected with HCV. But false positives are surprisingly common. More than 1 in 5 people who test positive donât actually have hepatitis C. Possible reasons include:
What the results mean
You May Like: How Does A Person Get Hepatitis C
What To Expect During An Hcv Test
Initial screening for hepatitis C involves taking the HCV antibody test, which can show whether a person has ever had the infection.
These antibodies are chemicals in the bloodstream that the body makes to combat the HCV. The test checks the blood for these antibodies.
For of people with the infection, the body clears the virus within 6 months without treatment.
Once the body makes these antibodies, they remain detectable, even after the person has cleared the infection. If a test shows that the HCV antibodies are present, the healthcare professional will perform a second test. This is called a nucleic acid test, and it can confirm whether the person still has the infection. If so, it is called a chronic infection.
What Do The Results Mean
A negative result means you probably don’t have a hepatitis infection. A positive result may mean you have or previously had an infection from hepatitis A, hepatitis B, or hepatitis C. You may need more tests to confirm a diagnosis. If you have questions about your results, talk to your health care provider.
Learn more about laboratory tests, reference ranges, and understanding results.
Recommended Reading: How Hepatitis C Is Transmitted Sexually
What Does A Reactive Hcv Antibody Test Result Mean
A reactive or positive antibody test means you have been infected with the hepatitis C virus at some point in time.
Once people have been infected, they will always have antibodies in their blood. This is true if they have cleared the virus, have been cured, or still have the virus in their blood.
A reactive antibody test does not necessarily mean that you currently have hepatitis C and a follow-up test is needed.
Getting Tested For Hepatitis C
A blood test, called an HCV antibody test, is used to find out if someone has ever been infected with the hepatitis C virus. The HCV antibody test, sometimes called the anti-HCV test, looks for antibodies to the hepatitis C virus in blood. Antibodies are chemicals released into the bloodstream when someone gets infected.
Test results can take anywhere from a few days to a few weeks to come back. Rapid anti-HCV tests are available in some health clinics and the results of these tests are available in 20 to 30 minutes.
You May Like: Can You Get Hepatitis C From Your Own Blood
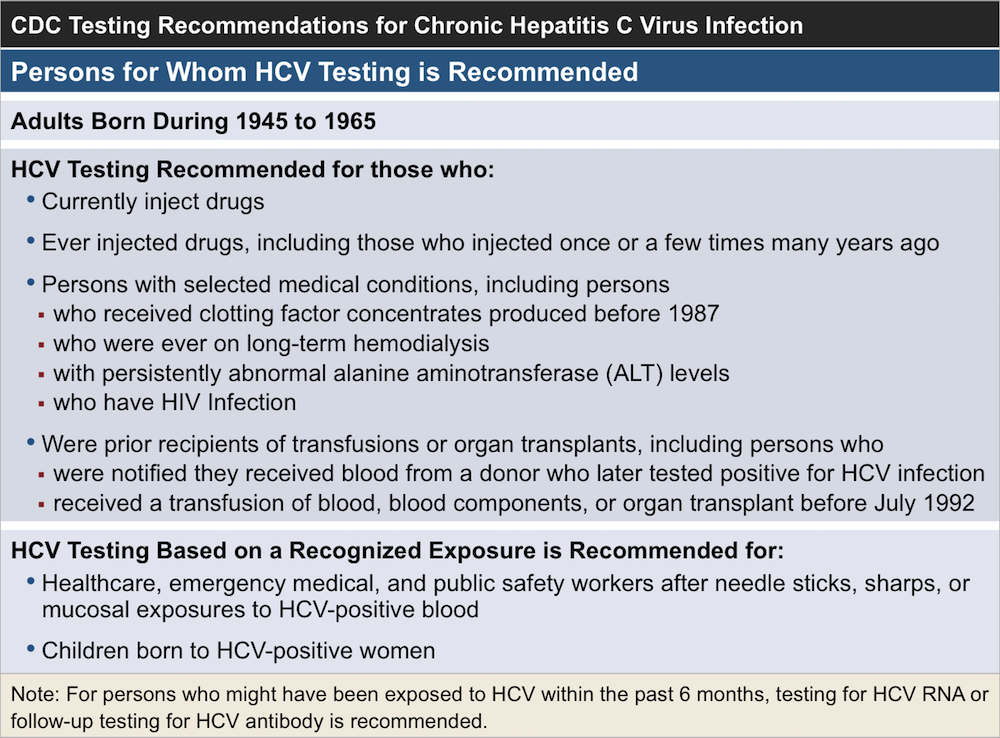
Who Should Get Tested For Hepatitis C
The CDC recommends that you get tested at least once no matter what. Definitely get screened if any of these things apply to you:
- You were born between 1945 and 1965.
- You use or inject drugs.
- You have ever injected drugs — even if it was just once or a long time ago.
- Youâre on kidney dialysis.
- You have abnormal alanine aminotransferase levels .
- You had a blood transfusion, blood components, or an organ transplant before July 1992.
- Youâve ever gotten clotting factor concentrates made before 1987.
- You received blood from a donor who later tested positive for hepatitis C virus.
- Youâre a health care worker, first responder, or have another job that exposes you to HCV-infected needles.
- You were born to a mother with HCV.
How To Test For Hep C
If you suspect you may have a hepatitis C infection, taking a hepatitis C test can be a great start in addition to consulting your healthcare provider for next steps. Our at-home hepatitis C test is a convenient way to check for this virus. To check for hepatitis C with this test, you just collect a small sample of blood with a simple finger prick, then ship the sample to a lab for testing with the prepaid shipping label that comes with the kit.
If your results from our hepatitis C test indicate that you do have this viral infection, share your results with your healthcare provider right away so you can take the next steps they recommend.
Don’t Miss: What Happens If You Have Hepatitis
When To Get Tested
For screening: at least once when you are age 18 years or older when you are pregnant when you have risk factors for HCV infection, regardless of age
For diagnosis: when you may have been exposed to the hepatitis C virus, such as through injection drug use, or when you have signs and symptoms associated with liver disease
For monitoring: before, during, and after hepatitis C treatment
Read Also: Can Hepatitis C Spread Through Saliva
What Is A Hepatitis C Screening
Testing for hepatitis C involves a blood test called an HCV antibody test . This test determines if youve ever had a hepatitis C infection by checking your blood for HCV-specific antibodies.
If you test positive for HCV antibodies, youll need to undergo follow-up testing. Having antibodies doesnt mean you currently have an active infection. It may simply mean that you have had a prior exposure that your immune system cleared.
To check whether you have an active infection, a doctor will order a nucleic acid test . A positive result means the virus is currently active in your bloodstream. If you get a negative result, the virus was once in your body, but its not anymore.
- have HIV
- have ever had a needle-stick injury or potentially been exposed to HCV-positive blood
- have had a tattoo or piercing done outside of a professional sterile environment
According to the , HCV may be passed through sexual activity, though this isnt common. The agency notes that your risk may be increased if you:
- have a sexually transmitted infection
- have sex with multiple partners
- have anal sex
Read Also: Interpretation Of Hepatitis A Serologic Test Results