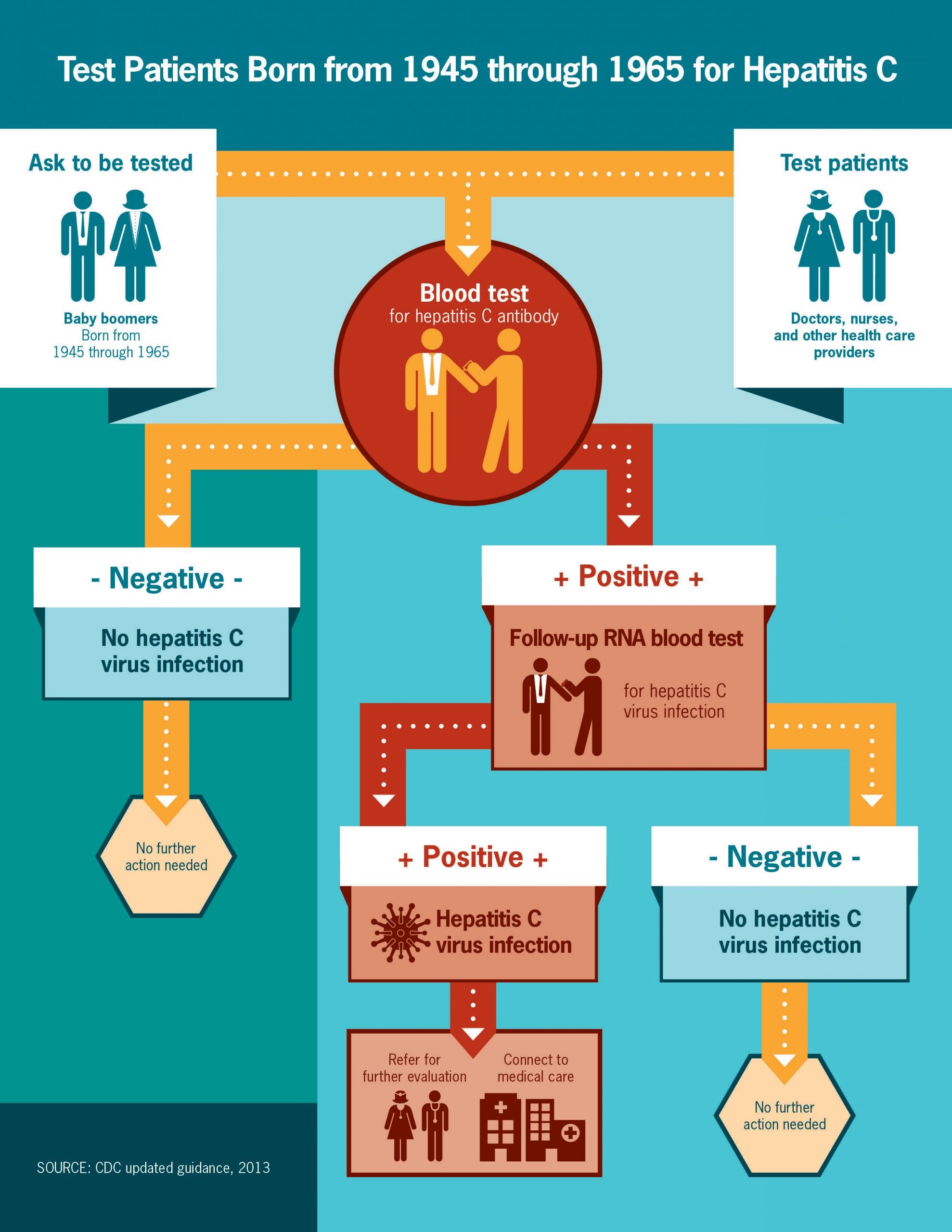
Getting Tested Is The Only Way To Know If You Have Hepatitis C
A blood test called a hepatitis C antibody test can tell if you have been infected with the hepatitis C viruseither recently or in the past. If you have a positive antibody test, another blood test is needed to tell if you are still infected or if you were infected in the past and cleared the virus on your own.
- Are 18 years of age and older
- Are pregnant
- Currently inject drugs
- Have ever injected drugs, even if it was just once or many years ago
- Have HIV
- Have abnormal liver tests or liver disease
- Are on hemodialysis
How Is Hepatitis C Treated
Hepatitis C virus is treated with all-oral medications. These pills, calledantiviral medications, are usually taken once per day. These antiviral medications are extremely good at attacking the virus and preventing it from multiplying.
Antiviral medications were not the original treatment for hepatitis C. Before 2014, the only treatment for hepatitis C was called interferon and ribavirin, taken as weekly injections under the skin, plus pills. Interferon treatment caused many unpleasant side effects and was not usually successful. Then a new generation of medications became available. These antiviral treatments are extremely successful at curing the virus and have very minimal side effects.
Ribavirin is still sometimes prescribed to be taken along with the new antiviral medicines, but it has become more and more uncommon that ribavirin is needed at all. Ribavirin has some mild-moderate side effects. Ribavirin is a pill taken twice per day, as 2 or 3 pills in the morning plus 2 or 3 pills at night, depending on the patient’s body weight. Most patients do not need ribavirin.
Hepatitis C Symptoms In Men
Hepatitis C symptoms in men are the same as in women. However, a 2014 study indicated that men may be less likely to clear the virus than women.
Hepatitis C in men may stay in their systems longer. It may also be more likely to cause symptoms in men compared to younger women.
Currently, there isnt a hepatitis C vaccine, though research is underway. However, avoiding contact with the blood of someone who has an HCV infection can help prevent you from acquiring the hepatitis C virus.
You can do this by:
- avoiding using someone elses razor, nail clippers, or toothbrush
- not sharing needles or syringes
- getting tattoos or piercings only at licensed facilities
- practicing safer sex with your partner by using condoms or other barrier methods
If you think you may have been exposed to HCV, its important to get tested as soon as possible.
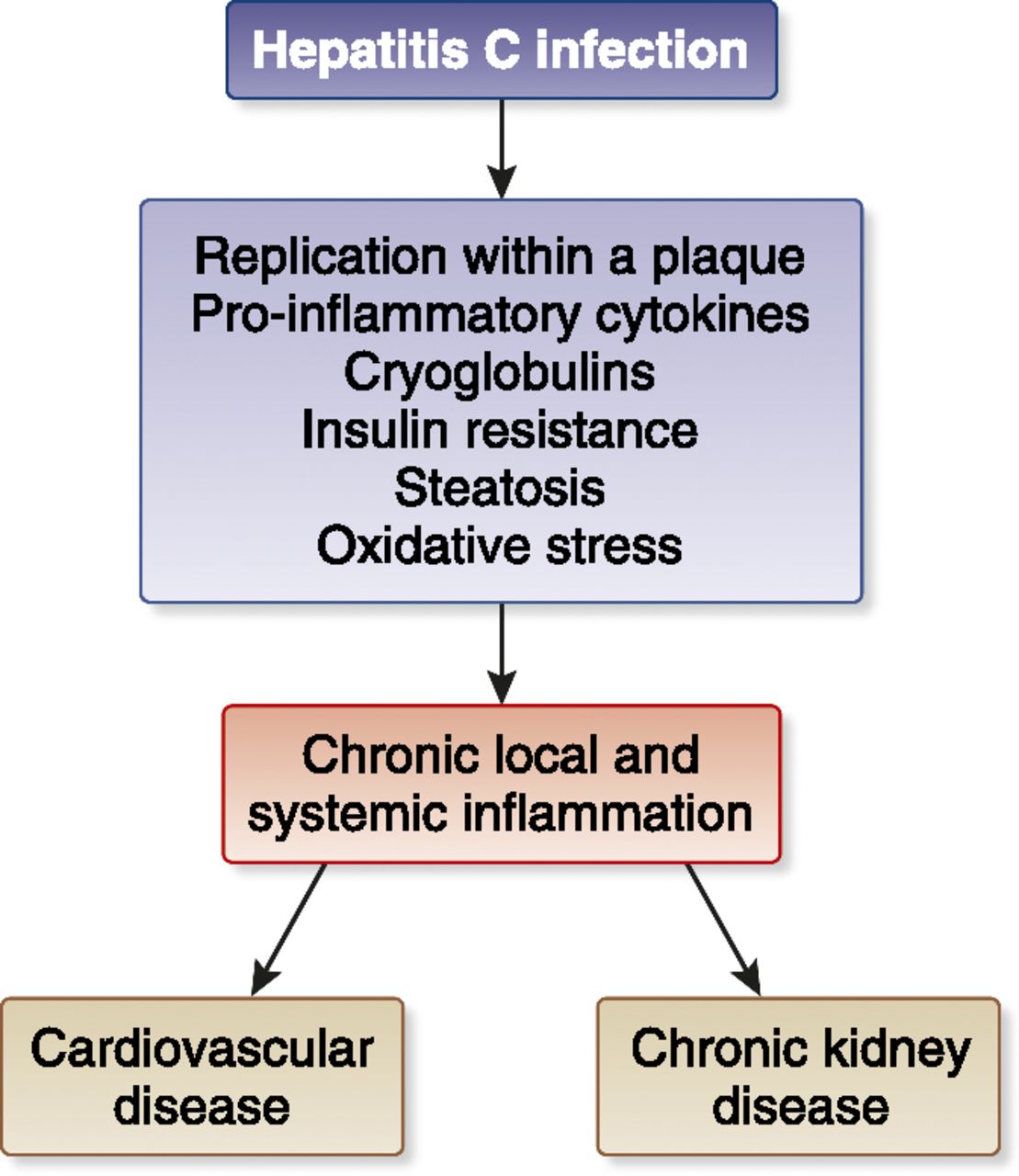
Untreated chronic hepatitis C may eventually lead to complications, which can include severe scarring of the liver, which is called cirrhosis, and liver cancer.
Some people with hepatitis C may need a liver transplant.
If you believe you contracted HCV, the sooner you receive a hepatitis C diagnosis, the sooner your doctor can start a treatment plan to help you avoid complications.
Read Also: What Does Hepatitis C Mean
How Is Monitoring Done After Treatment For Hepatitis C
Once patients successfully complete treatment, the viral load after treatment determines if there is an SVR or cure. If cure is achieved , no further additional testing is recommended unless the patient has cirrhosis. Those who are not cured will need continued monitoring for progression of liver disease and its complications.
While cure eliminates worsening of fibrosis by hepatitis C, complications may still affect those with cirrhosis. These individuals still need regular screening for liver cancer as well as monitoring for esophageal varices that may bleed.
Because hepatitis B co-infection may reactivate or worsen even after treatment for HCV, monitoring for hepatitis symptoms may be needed after the end of therapy.
New Therapeutic Ideas For Patients Infected With Hepatitis C
Since the number of non-responders or patients with relapse is increasing, many new drugs are being tested briefly. Meta-analysis of several controlled trials for amantadin, for example, showed a significantly better SVR with amantadin and IFN alpha compared to IFN alpha monotherapy. Further, a German study showed an increase of SVR using a triple therapy of INF alpha plus ribavirin plus amantadin compared to INF alpha plus ribavirin plus placebo. Still missing are trials with PEG-INF, ribavirin and amantadin, as well as studies looking at long-term outcomes.
Additional concepts are the use of toll-like receptor agonists and RNA-based therapy, as well as drugs like thymosin-, inosinmonophaphatedehydrogenase inhibitors, anti oxidants, glucosidase inhibitors, cytokines, inhibitors of the internal ribosomal entry site and fusion proteins. Silymarin, which in some cases resulted in a drop of the transaminases, does not produce an effect on HCV-RNA concentration and liver histology in the trials presented to date. Most eagerly, many approaches involve a search to find a vaccine to prevent HCV infection.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B And Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment
How Do Doctors Treat The Complications Of Hepatitis C
If hepatitis C leads to cirrhosis, you should see a doctor who specializes in liver diseases. Doctors can treat the health problems related to cirrhosis with medicines, surgery, and other medical procedures. If you have cirrhosis, you have an increased chance of liver cancer. Your doctor may order an ultrasound test to check for liver cancer.
If hepatitis C leads to liver failure or liver cancer, you may need a liver transplant.
What’s Involved With An Hcv Diagnosis
Discuss your risk factors for hepatitis C infection with your healthcare provider. Drug abuse and having a blood transfusion prior to 1992 may have put you at risk, but there are other risks factors, too.
Hepatitis C screening starts with a blood test to look for viral antibodies. HCV antibodies can be detected in the blood within 2 to 3 months after infection. If this test is positive, a confirmatory blood test would be ordered.
An HCV viral load may be ordered to determine your chances for responding to treatment. In addition, HCV genotyping can help to guide the best treatment option and duration.
Your doctor may also order liver function tests – known as AST, ALT and GGT tests – to monitor the health of your liver.
A liver biopsy, usually performed as an outpatient surgical procedure, may be needed to determine the level of liver damage.
Don’t Miss: What Does Hepatitis C Cause
Current Antiviral Treatment Strategies
The introduction of DAA revolutionized the field of antiviral therapy for patients chronically infected with HCV. Antiviral therapy usually consists of at least two antiviral substances from different drug classes with different modes of action . Treatment decisions are based on genotype , presence of cirrhosis and response to prior treatments . Typical treatment regimens for patients with and without compensated cirrhosis are depicted in Tables 1 and 2. All different recommended regimens achieve SVR rates of more than 95% if administered correctly .
Table 1.
Treatment of patients with chronic hepatitis C without cirrhosis
Table 2.
Treatment of patients with chronic hepatitis C with compensated cirrhosis
Fig. 1.
The replication cycle of the hepatitis C virus and modes of action of direct-acting antivirals are displayed .
The pangenotypic drug combinations sofosbuvir/velpatasvir and glecaprevir/pibrentasvir show high antiviral efficacy against all HCV genotypes. Treatment duration differs from 8 weeks for glecaprevir/pibrentasvir in noncirrhotic treatment-naive patients to 12 weeks for patients with liver cirrhosis or 16 weeks for GT 3 patients with liver cirrhosis and/or prior treatment failure. Sofosbuvir/velpatasvir has to be administered for 12 weeks independently of fibrosis level . Treatment with grazoprevir/elbasvir is possible in patients with GT 1 or 4 infection and has to be administered for 1216 weeks depending on GT, fibrosis stage and viral load .
Treatment And Medication For Hepatitis C
If you have acute hepatitis C, there is no recommended treatment. If your hepatitis C turns into a chronic hepatitis C infection, there are several medications available.
Interferon, peginterferon, and ribavirin used to be the main treatments for hepatitis C. They can have side effects like fatigue, flu-like symptoms, anemia, skin rash, mild anxiety, depression, nausea, and diarrhea.
Now youâre more likely to get one of these medications:
Find out more on treatment options for hepatitis C.
You May Like: What Does Non Reactive Hepatitis B Mean
Treatment Of Patients With Decompensated Cirrhosis
Treatment of patients with decompensated cirrhosis ) is limited to regimens containing sofosbuvir and NS5A inhibitors. Protease inhibitors are not recommended due to the hepatic metabolization and subsequently significantly higher drug exposure in this group of patients. Thus, grazoprevir/elbasvir, glecaprevir/pibrentasvir or SOF/VEL/VOX should not be administered. To improve efficacy the remaining combination of sofosbuvir and NS5A inhibitor should be combined with RBV . Many studies and real-world data have shown that IFN-free antiviral therapy is safe in patients with advanced liver disease. However, patients are still at risk of hospitalization during therapy, mainly because of complications from liver disease . The efficacy of sofosbuvir/ledipasvir plus RBV was studied in the SOLAR-1 and -2 study. In GT 1 patients, SVR rates ranged between 87 and 96% and between 72 and 85% in CPS B and CPS C patients, respectively . The ASTRAL-4 study evaluated the use of sofosbuvir/velpatasvir in patients with CPS B, but not CPS C. Treatment duration of 12 weeks showed high rates of SVR for patients with GT 1, 2, 4 and 6 infection. SVR rates of GT 3 were low at 50% but could be increased to 85% by the addition of RBV . Even though the rate of treatment discontinuations is higher in patients treated with RBV, the additional antiviral substance significantly increases SVR rates .
How Can I Prevent Spreading Hepatitis C To Others
If you have hepatitis C, follow the steps above to avoid spreading the infection. Tell your sex partner you have hepatitis C, and talk with your doctor about safe sex practices. In addition, you can protect others from infection by telling your doctor, dentist, and other health care providers that you have hepatitis C. Dont donate blood or blood products, semen, organs, or tissue.
Also Check: Hepatitis A Vaccine Cost Walmart
Hepatitis C Virus Infection: How Do You Get It
HCV is transmitted through contact with infected blood — mainly by:
- sharing needles or devices during drug abuse
- from an accidental needle stick
- renal dialysis
- from mother to child during childbirth
- less commonly from contaminated tattoo or body piercing equipment
- less commonly from haring personal care items comtaminated with HCV+ blood, such as razors or toothbrushes
- less commonly from from unprotected sexual intercourse or blood transfusions.
Hepatitis C is not spread through food or water. You also don’t get it from sharing food utensils, breastfeeding your baby, kissing, holding hands, coughing or sneezing.
If you were born from 1945 through 1965, or otherwise are at increased risk for HCV infection, speak to your doctor about being tested for HCV.
Hepatitis C Testing And Diagnosis
Doctors will start by checking your blood for:
Anti-HCV antibodies: These are proteins your body makes when it finds the hep C virus in your blood. They usually show up about 12 weeks after infection.
It usually takes a few days to a week to get results, though a rapid test is available in some places.
The results can be:
- Nonreactive, or negative:
- That may mean you donât have hep C.
- If youâve been exposed in the last 6 months, youâll need to be retested.
If your antibody test is positive, youâll get this test:
HCV RNA: It measures the number of viral RNA particles in your blood. They usually show up 1-2 weeks after youâre infected.
- The results can be:
- Negative: You donât have hep C.
- Positive: You currently have hep C.
You might also get:
Liver function tests: They measure proteins and enzyme levels, which usually rise 7 to 8 weeks after youâre infected. As your liver gets damaged, enzymes leak into your bloodstream. But you can have normal enzyme levels and still have hepatitis C. Learn the reasons why you should get tested for hepatitis C.
Also Check: How Common Is Hepatitis B
How Serious Is It
- People can be sick for a few weeks to a few months
- Most recover with no lasting liver damage
- Although very rare, death can occur
- 15%25% of chronically infected people develop chronic liver disease, including cirrhosis, liver failure, or liver cancer
- More than 50% of people who get infected with the hepatitis C virus develop a chronic infection
- 5%-25% of people with chronic hepatitis C develop cirrhosis over 1020 years
Stages Of Hepatitis C
The hepatitis C virus affects people in different ways and has several stages:
- Incubation period. This is the time between first exposure to the start of the disease. It can last anywhere from 14 to 80 days, but the average is 45
- Acute hepatitis C. This is a short-term illness that lasts for the first 6 months after the virus enters your body. After that, some people who have it will get rid of, or clear, the virus on their own.
- Chronic hepatitis C. For most people who get hepatitis C — up to 85% — the illness moves into a long-lasting stage . This is called a chronic hepatitis C infection and can lead to serious health problems like liver cancer or cirrhosis.
- Cirrhosis. This disease leads to inflammation that, over time, replaces your healthy liver cells with scar tissue. It usually takes about 20 to 30 years for this to happen, though it can be faster if you drink alcohol or have HIV.
- Liver cancer. Cirrhosis makes liver cancer more likely. Your doctor will make sure you get regular tests because there are usually no symptoms in the early stages.
Learn more about the stages and progression of hepatitis C.
You May Like: How Can Hepatitis C Be Transmitted
Exacerbation Of Chronic Viral Hepatitis
In the treatment of chronic hepatitis B, HBe seroconversion was sometimes preceded by transient and moderate worsening of serum transaminases, but severe exacerbation of chronic hepatitis B infection and fatal liver failure can occur. Such fatalities were reported in under 0.5% of patients with hepatitis B . Patients with active cirrhosis or a previous history of decompensated cirrhosis are particularly susceptible to these complications .
Acute exacerbation of hepatitis is an extremely rare complication of chronic hepatitis C treatment. An exaggerated immune response to hepatitis virus was supposedly the cause of acute icteric hepatitis in two patients .
-
A 43-year-old man had a moderate rise in hepatic transaminase activities after 4 weeks of interferon alfa treatment. His liver tests normalized after withdrawal, but the aspartate transaminase activity increased dramatically shortly after treatment was restarted. His condition rapidly deteriorated, with a diagnosis of hepatorenal failure, and he finally required liver transplantation. Histological examination of the liver showed advanced micronodular cirrhosis, a feature not found on pretreatment liver biopsy.
In another study, only four of 11 241 patients treated with interferon alfa died of fulminant liver failure .
Talia B. Baker, Juan Carlos Caicedo, in, 2017
Treatment Of Patients With Prior Daa Treatment Failure
After failure of DAA treatment, the development of RAS is very likely. RAS linked to the NS5A gene are more likely to persist for a longer time at a significant level than those connected to the NS3/4 gene. RAS relevant for the NS5B inhibitor sofosbuvir are usually rapidly suppressed after treatment cessation due to a significantly impaired viral fitness. Resistance testing and the adaptation of antiviral regimes according to RAS is one possible option for retreatment . Currently, the only approved drug combination for the retreatment of patients with prior DAA failure is the combination of sofosbuvir, velpatasvir and voxilaprevir . This combination is not only well tolerated, but also highly effective, and SVR rates > 95% can be achieved in pretreated patients independently from the initial treatment regimen . The recommended treatment duration for DAA-experienced patients is 12 weeks . Preliminary real-world data confirmed the high efficacy of the SOF/VEL/VOX in previous DAA failures. All of the first 110 patients who had completed SOF/VEL/VOX in the German Hepatitis C Registry achieved SVR . Excellent results have also been reported from French and US cohorts . Due to its effectiveness this combination should be reserved for the retreatment of patients with prior DAA failure and is usually not recommended for the initial treatment of therapy-naive patients .
You May Like: Treatment For Liver Cirrhosis Hepatitis B
Does Svr Mean Cured
If blood tests canât detect hep C 12 weeks or more after you finish treatment, in 99% of cases you’ll stay free of the virus for the rest of your life.
Once you reach SVR, you canât pass the virus on to other people. You still canât give blood, though. Some doctors might test for hep C one more time, 6-12 months after you reach SVR. But you’re most likely cured at this point.
Your doctor may continue to watch your liver damage and function, especially if your hepatitis was far along or if you have other serious health issues.
You can also reinfect yourself with hep C. And it can be harder to treat the second time around. Common ways you can get infected again include:
- Sexual partners, especially for IV drug users
- Shared razors or toothbrushes
What Health Professionals Need To Know About Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is not a vaccine-preventable disease.
Hepatitis C is reportable by laboratories and clinicians to local public health authorities in all provinces and territories.
In Canada:
- hepatitis C antibody and nucleic acid amplification testing methods for screening the blood supply were implemented in 1992
- prior to this implementation, thousands were infected with the hepatitis C virus after receiving blood or blood products
Consult the national case definition for additional information.
You May Like: Can Hepatitis C Spread Through Saliva