No Identifiable Source Of Infection
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, injection drug use accounts for approximately 60% of all HCV infections in the United States, while other known exposures account for 20-30%. Approximately 10% of patients in most epidemiological studies, however, have no identifiable source of infection. HCV exposure in these patients may be from a number of uncommon modes of transmission, including vertical transmission, and parenteral transmission from medical or dental procedures prior to the availability of HCV testing. There are no conclusive data to show that persons with a history of exposures such as intranasal cocaine use, tattooing or body piercing are at an increased risk for HCV infection based on these exposures solely. It is believed, however, that these are potential modes of HCV acquisition in the absence of adequate sterilization techniques.
Diagnosing Hepatitis C In People Living With Hiv
Everyone with HIV should be tested to see if they also have hepatitis C. A blood test for antibodies to hepatitis C is used to see whether you have been exposed to the virus. You might be given a PCR test to confirm infection.
In people living with HIV, the diagnosis of hepatitis C can be more difficult, as the infection may not show up on their antibody tests.
If you think you may be at risk of hepatitis C infection, you should have regular tests to see if you have been infected with the virus.
Biology And Genetics Of Perinatal Hcv Transmission
Other authors attributed the biology of perinatal transmission of HCV to the infection of maternal peripheral blood mononuclear cells by the virus and to the presence of the negative strand of HCV inside the PBMC, which is a sign of viral replicative activity .
It was noted that HLA antigen class II diversity between the mother and the baby induces rapid clearance of infected maternal cells through the newborn alloimmune anti-major histocompatibility complex response this was demonstrated to be protective for perinatal transmission of HCV . A biologically reasonable explanation has been provided for these apparently contradictory results involving the important role of the interaction between HLA antigen class II molecules and CD4+ T lymphocytes in the immune response and in allo-recognition .
With regard to single nucleotide polymorphisms of interleukin -28B that have been demonstrated to be important in determining spontaneous and treatment-induced clearance of HCV in children and in adults recently, neither the mothers nor the childrens IL-28B status was associated with an increased risk of perinatal transmission .
High levels of NK cells in the placenta of HCV-positive mothers were detected by some researchers . These cells had greater cytotoxicity in the HCV-positive mothers. This may be an explanation for the relatively low rates of vertical transmission, though the increased cytotoxicity of the NK cells may also lead to a higher risk of preterm delivery .
Also Check: Is Hepatitis C Contagious Mayo Clinic
What Are The Chances Of Getting Hepatitis C From Sex
Hepatitis C can spread through sexual intercourse, but it’s rare. And it’s extremely rare among monogamous couples. In fact, the CDC considers the risk of sexual transmission between monogamous couples so low that it doesn’t even recommend using condoms. Also, there’s no evidence that hepatitis C is spread by oral sex. But you should avoid sharing razors, toothbrushes, and nail clippers, and sex during menstruation.
If you have HIV or if you have multiple partners, you should take precautions. Using condoms will protect you and your partners.
Living With Hepatitis C Infection
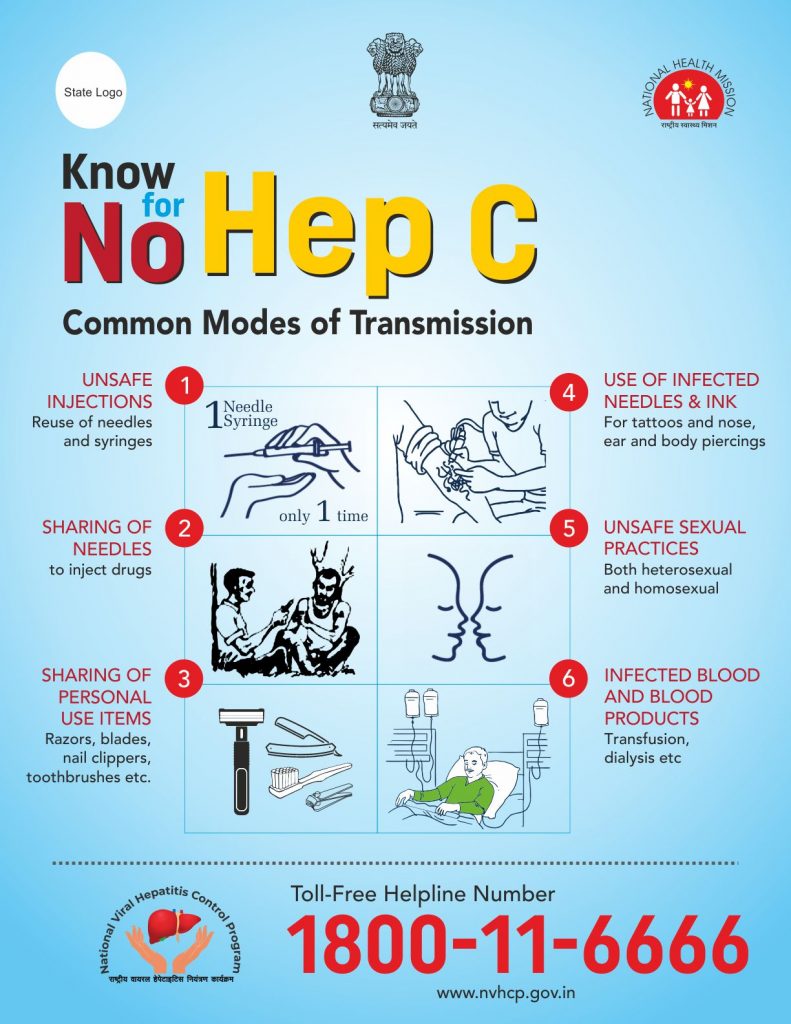
Many people are living with hepatitis C. If you have hepatitis C, there are several important things that you can do to help yourself and others such as:
- Eat a healthy diet and get plenty of rest.
- To avoid further liver damage:
- Do not drink alcohol.
- Do not take medicine that can cause liver damage .
- Get vaccinated against hepatitis A & B if you are not already immune.
- Do not to pass the infection to anyone else by taking the following precautions, such as:
- Do not share toothbrushes or razors with others.
- Do not to let anyone else come into contact with your blood, urine or feces.
- Use condoms during sexual activity.
- Limit the number of sex partners you have.
- If you use injection drugs, do not share needles or syringes with anyone else.
- It is best to not get tattoos or body piercings.
Although often uncomfortable, you should notify your partner of your hepatitis C prior to having sex. You also must notify all your health care professionals of your infection, so they can take precautions.
Recommended Reading: How To Get Rid Of Hepatitis C
How To Prevent Hepatitis C
There is currently no vaccine for hepatitis C. Avoiding contact with infected blood is the only way to prevent the condition.
The most common way for people to contract hepatitis C is by injecting street drugs. Because of this, the best way to prevent hepatitis C is to avoid injecting.
Treatments can help many people quit. People in the U.S. can call the National Helpline for help with finding treatments.
If a person finds it difficult to stop, they can reduce the risk of contracting hepatitis C by never sharing drug equipment, ensuring a clean, hygienic environment, and always using new equipment, including syringes, ties, alcohol swabs, cottons, and cookers.
People who may come into contact with infected blood, such as healthcare workers and caretakers, should always wash the hands thoroughly with soap and water after any contact, or suspected contact, with blood. They should also wear gloves when touching another persons blood or open wounds.
People can also reduce their risk by making sure that any tattoo artist or body piercer they visit uses fresh, sterile needles and unopened ink.
The risk of contracting hepatitis C through sexual contact is low. Using barrier protection, such as condoms, reduces the risk of most sexually transmitted infections.
People who have hepatitis C can reduce the risk of transmitting it to others by:
There are many misconceptions about how hepatitis C spreads. People cannot transmit or contract the virus through:
Viral Hepatitis Definition And Overview
Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. Many illnesses and conditions can cause inflammation of the liver, for example, drugs, alcohol, chemicals, and autoimmune diseases. Many viruses, for example, the virus causing mononucleosis and the cytomegalovirus, can inflame the liver. Most viruses, however, do not attack primarily the liver the liver is just one of several organs that the viruses affect. When most doctors speak of viral hepatitis, they are using the definition that means hepatitis caused by a few specific viruses that primarily attack the liver and are responsible for about half of all human hepatitis. There are several hepatitis viruses they have been named types A, B, C, D, E, F , and G. As our knowledge of hepatitis viruses grows, it is likely that this alphabetical list will become longer. The most common hepatitis viruses are types A, B, and C. Reference to the hepatitis viruses often occurs in an abbreviated form The focus of this article is on these viruses that cause the majority of human viral hepatitis.
Hepatitis viruses replicate primarily in the liver cells. This can cause the liver to be unable to perform its functions. The following is a list of major functions of the liver:
Don’t Miss: What Is Hepatic Luciferase Expression
Effect Of Pregnancy On Hbv Infection
During pregnancy there are several modifications in the maternal immune system, namely, a shift in the Th1-Th2 balance towards a Th2 response, increased amounts of regulatory T cells, etc., that contribute to a depressed immune response against HBV. The aim of these modifications is to prevent the rejection of the fetus who is partially allogenic for the mothers immune system. These modifications result in an increase of HBV DNA and a reduction of aminotransferase levels. After delivery the immune system is restored thereby causing opposite consequences namely, there is a significant increase in alanine aminotransferase and a reduction of HBV DNA in this period.
ter Borg et al studied the course of the liver disease in 38 HBV-positive pregnancies before, during and after delivery. In 13 pregnancies, antiviral therapy with lamivudine was started during the last trimester of pregnancy due to high viremia to reduce the risk of mother-to-child transmission and was stopped immediately after delivery. Forty-five per cent of untreated women experienced a flare within 6 mo after delivery, compared to 62% of women who received lamivudine. No clinical decompensation occurred in these women. However, the authors recommend monitoring closely and, if necessary, administering treatment to women with chronic HBV shortly after delivery.
How Common Is Hepatitis C
There are approximately 30,000 new cases of acute hepatitis C every year in the United States as estimated by the CDC. In 2015, it was estimated that approximately 3.5 million Americans were infected with hepatitis C.
On a global scale, the prevalence of hepatitis C is greatest in Central and East Asia, North Africa, and the Middle East. In 2016, it was estimated that 177 million people worldwide had antibodies to hepatitis C virus.
- exposure to other people who do or might have hepatitis C.
Recommended Reading: What Do You Get Hepatitis C From
Is Liver Transplantation An Option For A Person With Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is the leading reason for 40% to 45% of liver transplants in the U.S. Hepatitis C usually recurs after transplantation and infects the new liver. Approximately 25% of these patients with recurrent hepatitis will develop cirrhosis within five years of transplantation. Despite this, the five-year survival rate for patients with hepatitis C is similar to that of patients who are transplanted for other types of liver disease.
Most transplant centers delay therapy until recurrent hepatitis C in the transplanted liver is confirmed. Oral, highly effective, direct-acting antivirals have shown encouraging results in patients who have undergone liver transplantation for hepatitis C infection and have recurrent hepatitis C. The choice of therapy needs to be individualized and is rapidly evolving.
What Are The Risk Factors For Hepatitis C
In the United States, having been born between 1945 and 1965, and the use of illicit injection drugs are the two most common factors associated with hepatitis C. Other risk factors include
- having received blood transfusions prior to 1990,
- hemodialysis, and
- having greater than 10-lifetime sex partners.
Population studies show that hepatitis C is more common among males, non-Hispanic blacks, those with low income, and those with less than a high school education.
People who have HIV/AIDS have an increased risk for hepatitis C, because both these diseases are transmitted in the same ways, through blood and body fluids. If someone has both infections, that person is said to be co-infected with HIV and HCV.
Read Also: Hepatitis B Shot Side Effects
Prevention Of Hepatitis C
There are effective ways to prevent hepatitis and unnecessary measures. For example, kissing, hugging, and holding hands does not spread the infection, and avoiding this type of contact does nothing to prevent the spread of the disease. Breastfeeding is also safe in these cases, and it does not spread through sneezing or coughing.
There is not a vaccine currently available to prevent hepatitis C. However, we can reduce the chance of infection by adopting safety measures against transmission modes mentioned above. Do not share needles and avoid sharing personal items such as razors or a toothbrush. Get tested if youre pregnant, and make sure that youre with a licensed technician if you ever get a tattoo or a body piercing.
After a new patient is detected with the hepatitis C virus, secondary prevention aims to reduce the chance of disease progression in cirrhosis and liver cancer. These patients should abstain from alcoholic beverages. They should understand that, even if the transmission rate from sexual intercourse is low, there is always a risk of passing down the disease to their sexual partners. Thus, safe sex is recommended, and any sharing of personal items should be avoided. These patients are not candidates for blood or organ donations, except if the transplant recipient also has hepatitis C.
Mode Of Delivery And Hcv Perinatal Transmission
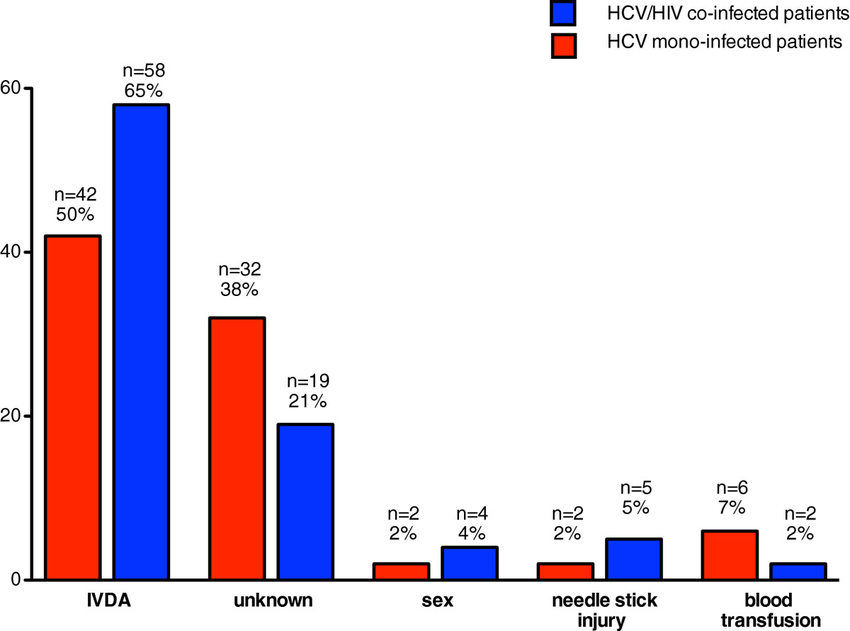
The effect of the mode of delivery on HCV perinatal transmission is controversial. Some authors suggested that with vaginal delivery, there is increased risk of HCV transmission to the baby due to increased risk of exposure to virus-contaminated maternal blood. Consequently, cesarean section may hypothetically be a better option .
Four large studies were carried out on 2,080 mothers and their infants, comparing the HCV transmission risk with elective cesarean versus vaginal or emergency cesarean section , where three of them reported higher transmission risk with group 2, which was statistically significant in only 1 one of them.
On the other hand, other studies, including the European Pediatric Hepatitis C Virus Network study on 1,758 mothers and their infants, reported that delivery mode does not appear to influence the risk of transmission .
Also Check: Home Remedies For Hepatitis C In Urdu
Other Risks Can Include:
- Sharing personal care items that may have come in contact with another persons blood, such as razors, toothbrushes or nail clippers
- Inoculation practices involving multiple use needles or immunization air guns
- Exposure of broken skin to HCV infected blood
- HIV infected persons
People with current or past risk behaviors should consider HCV testing and consult with a physician. HCV testing is currently not available at most public health clinics in Missouri. For information about HCV testing that is available, call the HCV Program Coordinator at 573-751-6439.
Differences Between Acute Hepatitis And Chronic Hepatitis
The main difference between Acute and Chronic Hepatitis is the period of time the infection has been in the body. If the infection has been for less than 6 months, it is said to be an Acute Hepatitis infection In contrast, Chronic Hepatitis infection means there is persistence of infection by the Hepatitis Virus for more than 6 months. The Hepatitis Core antigen shows whether there is Chronic hepatitis or not.
Also Check: How Soon Do Hepatitis C Symptoms Appear
Diagnosis And Treatment Of Hcv Infection
Hepatitis C is rarely diagnosed at the time of infection, since few individuals are symptomatic. Asymptomatic cases may be detected, however, through recommended screening in high-risk populations, such as intravenous drug users and recipients of blood transfusions or organ transplants in which the tissues were not initially tested for HCV. Diagnostic testing and screening for hepatitis C centres on the detection of circulating antibodies and RNA specific to HCV. HCV RNA is detectable within 1 to 3 weeks of infection, and the antibodies are usually detectable within 8 to 12 weeks.
Treatment of hepatitis C is focused on the elimination of viral infection, improvement of liver function, and the prevention of cirrhosis and liver cancer. Liver function may be improved with the use of interferon, which reduces HCV replication and stimulates the immune system to fight HCV infection. Interferon is often given in combination with ribavirin, an antiviral drug that mimics nucleosides and thereby interferes with viral reproduction. Ribavirin may also be used in combination with agents known as sofosbuvir and velpatasvir, which inhibit key molecules involved in HCV RNA replication. Treatment of end-stage or advanced liver disease and cirrhosis caused by HCV infection is also possible with liver transplantation, though recurrence of detectable HCV infection is almost universal after transplantation.
Is Hepatitis C Sexually Transmitted
Can hepatitis C be spread through sexual contact?
Hepatitis C is a contagious liver disease caused by the hepatitis C virus . The disease can be passed from person to person.
As with many infections, HCV lives in blood and bodily fluids. You can contract hepatitis C by coming into direct contact with an infected persons blood. It can also be transmitted by contact with bodily fluids including saliva or semen of an infected person, but this is rare.
Researchers in found that 1 out of every 190,000 instances of heterosexual sexual contact led to HCV transmission. Participants in the study were in monogamous sexual relationships.
HCV may be more likely to spread through sexual contact if you:
- have multiple sexual partners
- participate in rough sex, which is more likely to result in broken skin or bleeding
- dont use barrier protection, such as condoms or dental dams
- dont use barrier protection properly
- have a sexually transmitted infection or HIV
Theres no evidence that HCV can be spread through oral sex. However, it may still be possible if blood is present from either the person giving or receiving oral sex.
For example, a slight risk may exist if any of the following are present:
- menstrual blood
- genital warts
- any other breaks in the skin in the involved areas
Though sexual transmission is rare overall, HCV may be more likely to spread through anal sex than oral sex. This is because rectal tissue is more likely to tear during intercourse.
Also Check: Is Hepatitis A Sexually Transmitted Disease
How Is The Health Of Your Liver Monitored
Everyone living with HIV should have regular tests to monitor the health of their liver as part of the routine check-ups carried out by their HIV clinic. These tests are especially important if you have hepatitis C.
These include liver function tests that monitor levels of liver enzymes. Ultrasounds and scans are also important monitoring tools which may be used if more information is needed.
Sometimes its necessary to have a liver biopsy. This involves the removal of a small amount of the liver, under a local anaesthetic, for further tests on the health of your liver.
What Are The Side Effects Of Treatments For Hepatitis C Infection
Side effects of interferon or pegylated interferon
- The most common side effects of interferon or pegylated interferon include fever, flu-like symptoms, and depression. Patients must be monitored closely for depression. Risk of suicide is a reason to avoid interferons.
- Interferons also reduce white blood cell and/or red blood cell counts . This may cause increased susceptibility to infection. Interferons also increase the risk of certain cancers. Death rarely occurs as a result of therapy, but may occur from progression of liver failure in patients with advanced cirrhosis.
Side effects of ribavirin
- Ribavirin most commonly causes anemia due to destruction of red blood cells . This can be severe enough that people with heart disease may suffer a heart attack from insufficient blood flow, so people with heart disease should not receive this drug. Anemia improves with a reduction in the dose of ribavirin. Injected growth factor that stimulates the production of red blood cells often is used to improve the anemia associated with ribavirin. Ribavirin also accumulates in the testicles and ovaries and causes birth defects in animals. Although no birth defects have been reported in humans, both men and women should use contraceptive measures to avoid pregnancy during and for at least six months after ribavirin treatment.
Side effects of DAAs
- The most common and significant side effects of boceprevir , sofosbuvir , and ledipasvir/sofosbuvir include
- fatigue ,
Don’t Miss: How Do You Get Hepatitis A B C