What Are The Treatments For Hepatitis B
If you think you may have been exposed to hepatitis B, its important to talk with a healthcare professional as soon as possible.
A doctor or other healthcare professional may administer the first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine and a shot of hepatitis B immunoglobulin. This is a combination of antibodies that provide short-term protection against the virus.
Though both can be given up to a week after exposure, theyre most effective at preventing infection if administered within 48 hours.
If you receive a diagnosis of acute hepatitis B, a doctor may refer you to a specialist. They may advise you to get regular blood tests to ensure you dont develop chronic hepatitis.
Many people with acute hepatitis B dont experience serious symptoms. But if you do, it can help to:
- get plenty of rest
- take over-the-counter pain mediation, like naproxen, when needed
Other lifestyle changes may also be needed to manage your infection, such as:
- eating a nutritious, balanced diet
- avoiding substances that can harm your liver, such as:
- alcohol
- certain herbal supplements or medications, including acetaminophen
If blood tests show you still have an active infection after 6 months, your doctor may recommend further treatment, including medications to help control the virus and prevent liver damage.
Southern Cross Medical Library
The purpose of the Southern Cross Medical Library is to provide information of a general nature to help you better understand certain medical conditions. Always seek specific medical advice for treatment appropriate to you. This information is not intended to relate specifically to insurance or healthcare services provided by Southern Cross. For more articles go to the Medical Library index page.
Hepatitis B Vaccine: Canadian Immunization Guide
For health professionals
Last partial content update : May 2022
The footnotes in and the accompanying text description for the figure have been revised to align with the corresponding figure in Protocole d’immunisation du Québec, 5e édition from which it was adapted.
Last complete chapter revision :
Recommended Reading: How Often Should You Get Hepatitis B Vaccine
What Are The Symptoms And Signs Of Viral Hepatitis
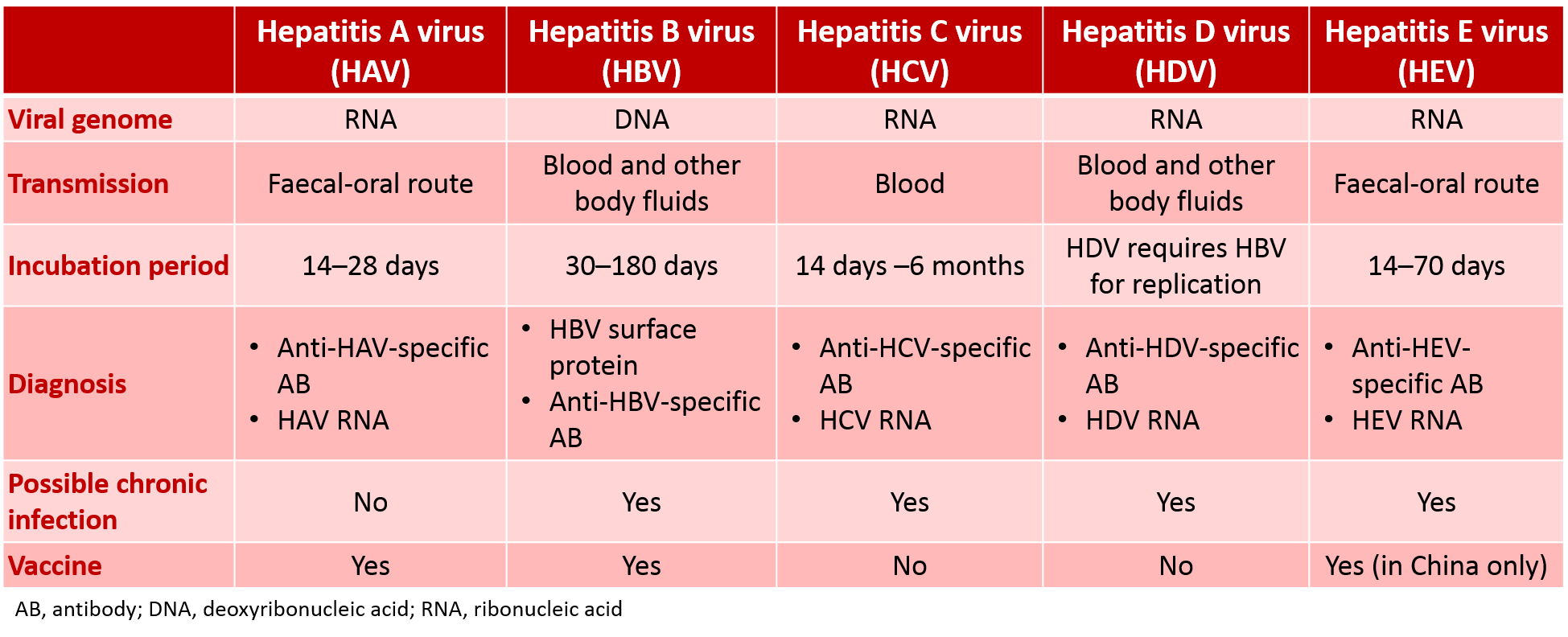
The period of time between exposure to hepatitis and the onset of the illness is called the incubation period. The incubation period varies depending on the specific hepatitis virus. Hepatitis A virus has an incubation period of about 15 to 45 days Hepatitis B virus from 45 to 160 days, and Hepatitis C virus from about 2 weeks to 6 months.
Many patients infected with HAV, HBV, and HCV have few or no symptoms of illness. For those who do develop symptoms of viral hepatitis, the most common are flu-like symptoms including:
Causes Of Hepatitis B

Hepatitis B is spread through contact with blood that contains the hepatitis B virus. If infected blood or body fluids enter another persons bloodstream, that person may become infected.
The time from exposure to the hepatitis B virus to the appearance of the illness is 45 to 180 days.
Risky activities that can cause infection include:
- Sharing unsterile or unclean equipment for injecting drugs.
- Piercing the skin with equipment that is not properly cleaned, disinfected and sterilised.
- Sharing razor blades or toothbrushes.
- Coming into contact with infected blood through open cuts or the mucous membranes of another person.
- Having unprotected sex , especially if there is blood present.
Mothers who have hepatitis B can pass the virus to their babies or children at the time of birth or after birth. If the newborn baby is quickly immunised with 2 vaccines, they can be protected from getting hepatitis B.
All blood and blood products produced for medical purposes in Australia are carefully screened for hepatitis B and other blood-borne viruses. The risk of getting infected with hepatitis B from a blood transfusion is extremely low .
You May Like: Do I Have Hepatitis B
Module 6 Initial Evaluation Of Confirmed Chronic Hbvendnote 2
Baseline clinical evaluation includes:
- History, particularly risk factors for hepatitis acquisition, and family history of liver disease including HCC
- Physical examination to look for signs of liver failure
Initial laboratory evaluation
- Anti-HAV
- HIV-antibody testing, if not already done
- HCV-antibody testing, if not already done
Imaging
All patients with chronic HBV should be referred to a specialist at some point.
There are certain situations where referrals should be expedited.
Indications for urgent referral to a hepatologist:
- Signs of liver failure – acute or chronic
- Pregnant patients
- Imaging results suggestive of HCC
Indications for semi-urgent referral :
- Co-infection with HCV or HIV
- Suspected cirrhosisFootnote
When Should I Contact A Health
Any infant, child, or adult that has not been vaccinated against HBV should be vaccinated especially if they have had any close association with HBV-infected individuals.
An individual with chronic hepatitis B infection is advised to
- have follow-up every 6-12 months to maximize their health,
- get vaccinated against hepatitis A, and
Discuss diet, lifestyle changes, and ways to prevent transmission of their disease to others with your health-care professional.
You May Like: Natural Remedies For Hepatitis C
Who Is Most Affected
In the United States, rates of new HBV infections are highest among adults aged 30-59 years, reflecting low hepatitis B vaccination coverage among adults at risk. The most common risk factor among people with new HBV infections is injecting drugs, related to the opioid crisis.
The highest rates of chronic hepatitis B infection in the United States occur among foreign-born individuals, especially people born in Asia, the Pacific Islands, and Africa. Approximately 70% of cases in the United States are among people who were born outside of the United States. CDC developed this map of the geographic distribution of hepatitis B around the world – PDF. Other groups who have higher rates of chronic HBV infection include people who inject drugs and men who have sex with men.
Immunoglobulin For Contacts Of Hepatitis B Carriers
HBIG can be considered for susceptible household, sexual, percutaneous and mucosal contacts, particularly if the exposure is of recent limited duration and highly significant and the source case is HBeAg positive, has high serum levels of HBV DNA or the sexual contact was non-consensual.
Indications for hepatitis B vaccination are the same as for contacts of acute hepatitis B cases.
Don’t Miss: Ok Google How Do You Get Hepatitis C
When To Get Tested
The timing of testing depends on which STI you may have been exposed to. With some STIs, a test can return an accurate diagnosis within a few weeks. Others may require you to wait for months before the test can accurately detect antibodies and other markers of infection.
The time between the first infection and when a test can reliably detect that infection is known as the window period.
While the incubation period and window period are often closely aligned, a few tests can diagnose an STI well before symptoms appear or when the infection is asymptomatic.
Testing prematurely within the window period can increase the risk of a false-negative result. This means that you have been infected even if the test says you haven’t.
Here is a general overview of window periods for some of the more common STIs:
| Infection |
|---|
How Do You Know If You Have Hepatitis B
Signs and symptoms can vary, in particular by the age of the individual. Many individuals may not show symptoms . When symptoms develop, they include fever, joint pain, abdominal pain, fatigue, lack of appetite, nausea, vomiting, dark urine, clay-coloured bowel movements, or jaundice.
Most infections are asymptomatic or mild. Occasionally, people with serious cases of hepatitis B require hospitalization. A very small proportion of these patients develop a critical form of the disease called “fulminant” hepatitis B. This condition results from a sudden breakdown of liver function.
Also Check: How To Contract Hepatitis B And C
Resolution Time And Clinical Course Of Infection
The majority of immunocompetent adults will recover within 6 months and develop lifelong immunity the remainder will be chronically infected. Immunocompromised adults are at a particular risk of developing chronic infection. The risk of developing chronic infection is also much higher for those who acquired the infection in infancy or before 7 years of age .Endnote 3, Endnote 13, Endnote 14
Acute HBV does not require antiviral treatment. Management should focus on relief of symptoms, monitoring and prevention of hepatic complications, as well as counselling aimed at preventing transmission. Persistence of HBsAg for 6 months indicates chronic infection.
Baseline laboratory testing to assess liver function and screen for other infections:
- Bilirubin , albumin, INR , creatinine
- ALT, AST, ALP
- anti-HBc IgM
- Testing for STIs, including HIV, and for HCV, where appropriate
- Repeat HBsAg at least 6 months after baseline, to confirm / rule out chronic infection. . See Module 6 for additional testing recommendations for those with confirmed chronic HBV
What Is Hepatitis
Viral hepatitis is a condition that causes inflammation of your liver. When a hepatitis virus enters your body, it travels to the liver. It can then enter liver cells and begin to replicate, making more of itself.
The activity of the virus can cause damage to your liver cells. Immune cells begin to travel to your liver to fight the infection. This can also contribute to inflammation.
Liver damage and inflammation can affect your livers ability to function, which can in turn affect your overall health. This is because your liver has several important functions for your body, including:
- breaking down or filtering various substances in the body, such as drugs and toxins
- producing bile, which is important for digestion
- making important blood proteins, including those that help your blood to clot
- storing additional blood sugar as glycogen, which can be used for energy later
- synthesizing immune system factors that are important for fighting infections
- Eastern Europe
Recommended Reading: Can You Get Hepatitis A After Vaccination
How Is It Treated
Hepatitis A is treated using supportive methods. These can include things like rest, fluids, and healthy foods. Medications can also help to ease some symptoms like fever, aches, and pains.
Theres a vaccine available to protect against infection with HAV. This is typically recommended for children as well as for people at an increased risk for contracting the virus.
Also, receiving a single dose of the hepatitis A vaccine may prevent you from becoming ill if youve been exposed to HAV. For it to be effective, the vaccine needs to be given of exposure.
Complications Of Hepatitis B
A small proportion of people who become infected with the hepatitis B virus develop a long-term hepatitis B infection. They may have the virus in their bloodstream for most of their life without realising they are infected.
People with chronic hepatitis B infection may not notice any health problems until they develop liver problems such as liver disease or liver cancer later in life. Treatment for hepatitis B is essential because it is not possible to be a healthy carrier of the hepatitis B virus. Chronic hepatitis B infection occurs more commonly in some communities, including:
- Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander communities.
- In people from parts of the world where hepatitis B is more common, such as:
- North-East Asia
- Sub-Saharan Africa.
You May Like: What Is Hepatitis B Infection
How Is Hepatitis B Prevented
Testing & Vaccination
- The hepatitis B vaccine offers excellent protection against HBV. The vaccine is safe and highly effective. Vaccination consists of 3 doses of vaccine over the course of 6 months. Protection lasts for 20 years to life.
- The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that all children should receive hepatitis B vaccine starting at birth. .
- The CDC recommends hepatitis B vaccine for persons traveling to countries where HBV is common .
- If you have one or more risk factors for hepatitis B infection, you should get a simple HBV blood test. The blood test will determine whether you are:
- immune to hepatitis B or
- susceptible to hepatitis B and need vaccination or
- infected with hepatitis B and need further evaluation by a physician
Perinatal Hepatitis
- California law requires testing of all pregnant women for hepatitis B infection
- If the mother is HBV-infected, she will pass the infection to the baby during the birth process, unless the baby gets immunized within hours of birth
- Giving the infant HBIG and HBV vaccine right away will reliably prevent infection of the infant
- Other family members should best tested for hepatitis B too, and given vaccine if they are not already infected or immune
Healthy Habits
After Exposure to Hepatitis B
Signs And Symptoms Of Chronic Hbv
People with CHB often do not have symptoms, so those with the disease may have no way of knowing that they are infected. However, some complain of fatigue, aches and pains, fever, loss of appetite, nausea and abdominal pain.
The majority of acute HBV infections are also asymptomatic but around 30% of adults will present with jaundice, fatigue, poor appetite, weight loss, nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, pyrexia, dark urine and light stools .
Diagnosis
HBV is diagnosed with a blood test to detect hepatitis B surface antigen . The different HBV serological markers may be used collectively to determine a persons HBV status. These are shown in Table 4.
HBV testing
Since 2000, all pregnant women have been tested for HBV. The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence has published a new guideline to promote HBV and hepatitis C virus testing. The guideline recommends that the at-risk groups listed in Box 1 are tested for HBV, and given counselling before and afterwards.
Box 1. Who to screen
The following at-risk groups should be tested for HBV:
All those who test positive for HBV surface antigen should be referred to a specialist centre within six weeks. Pregnant women should be assessed by a specialist within six weeks of receiving the screening test result so treatment can be offered in the third trimester if necessary .
Read Also: How Do You Contact Hepatitis
Other Reported Adverse Events And Conditions
While serious events and chronic illnesses such as chronic fatigue syndrome, multiple sclerosis, Guillain-Barré syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis and sudden infant death syndrome have been alleged or reported following HB vaccination, no evidence of a causal association has been demonstrated in a number of studies.
What Causes Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is caused by the hepatitis B virus. It can happen through exposure to infected blood and other bodily fluids in the following situations:
- sharing needles and other injecting drug equipment
- sharing razors, toothbrushes or nail clippers
- sexual contact
- tattooing with unsterilised needles and equipment
- close family contact with someone who has hepatitis B
- being born to a mother with hepatitis B
- accidental exposure such as a needle stick injury or being splashed with infected blood or body fluid
- blood transfusion this is now very rare as blood in Australia is screened for hepatitis B
You cannot catch hepatitis B through being coughed or sneezed on by infected people or by consuming contaminated food and drink. You cannot catch the virus from saliva, breast milk or tears.
You May Like: Autoimmune Hepatitis Primary Biliary Cholangitis
Is Hepatitis B Curable
Theres currently no known cure for hepatitis B, but there are many ways you can prevent infection and avoid transmitting the virus to others.
The most effective and safe way to prevent hepatitis B is to get vaccinated. You can also use barrier methods, like condoms, when having sex and avoid sharing needles.
What Should You Know About Hepatitis B Before You Travel
Hepatitis B is quite common in China and other Asian countries, where as many as 1 in 12 people have the virus, though many dont know it. Before traveling to those places, you should make sure youve been vaccinated against the virus.
In addition to getting the vaccine, you can take these additional precautions to reduce your risk of contracting the virus:
- Refrain from taking illegal drugs.
- Always use latex or polyurethane condoms during sex.
- Make sure new, sterile needles are used during all piercings, tattoos and acupuncture sessions.
- Avoid direct contact with blood and bodily fluids.
- Know the HBV status of all your sexual partners.
- Ask your doctor about possible vaccination before you travel to a place where hepatitis B is common.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Hepatitis B is a liver disease that can cause serious damage to your health. One reason that is dangerous is that it can easily go undetected for years while damaging your liver. Talk with your healthcare provider about being tested for hepatitis B if you have any reason to believe that you were not vaccinated or if you have engaged in risky behavior. If you do test positive, follow the directions from your healthcare provider so that you can live a longer, healthier and happier life.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 07/09/2020.
References
Recommended Reading: What Do You Get Hepatitis C From
Reducing The Risk Of Hepatitis B
Simple steps that everyone can take to protect themselves against hepatitis B include:
- Making sure you and your children are immunised this is the best protection.
- Using condoms every time you have anal or vaginal sex with new partners until you both get a check-up .
- Avoiding oral sex if you or your partner have herpes, ulcers or bleeding gums it is unlikely that you will contract hepatitis through oral sex unless blood is present.
- Choosing to have any body piercing or tattooing done by an experienced practitioner who follows good sterilisation and hygiene practices, and who works at premises registered by the local council.
- Wearing single-use gloves if you give someone first aid or need to clean up blood or body fluids.
- Never sharing needles and syringes or other equipment , if you inject drugs. Always use sterile needles and syringes. These are available from needle and syringe programs and some pharmacists. Always wash your hands before and after injecting.
If you have hepatitis B:
If you think you have been exposed to hepatitis B, see a doctor immediately. Your doctor can give you treatment in some instances, which greatly reduces the risk of you becoming infected with hepatitis B.