Recommendations For Frequency Of Repeat Testing In An Asymptomatic Patient
The frequency of testing depends on the history of sexual exposure and number of sexual partners. However, in the case of hepatitis A and B, once the patient has completed a course of vaccination no further repeat testing is required.
For those at continuing risk and who have not received a course of vaccination, the following is recommended.
Symptoms Of Hepatitis A Include Fatigue And Tummy Pain
Hepatitis A is a liver infection caused by the highly contagious Hepatitis A virus. Most people are vaccinated against the virus, and don’t need any treatment if they come in contact with it.
The CDC recommends that unvaccinated people who encounter it to get a hepatitis A shot, and possibly an antibody drug, within two weeks of exposure.
Symptoms usually start within 15 to 50 days of coming into contact with the virus.
For most people, symptoms of hepatitis A include fatigue, loss of appetite, tummy pain, nausea, vomiting, yellow skin, dark urine, and pale poop.
Symptoms range in severity and usually last between a few weeks to about two months, without any long-term liver damage.
But in rare cases, the condition can become chronic and lead to liver failure and death. Older people and those with weakened immune systems are at higher risk of severe illness.
Kids younger than 6 years old with hepatitis A don’t tend to get symptoms.
How Are Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C Spread From Person To Person
Like HIV, the hepatitis B and hepatitis C viruses spread:
- From mother to child: Pregnant women can pass these infections to their infants. HIV-HCV coinfection increases the risk of passing on hepatitis C to the baby.
- Sexually: Both viruses can also be transmitted sexually, but HBV is much more likely than HCV to be transmitted sexually. Sexual transmission of HCV is most likely to happen among gay and bisexual men who are living with HIV.
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatitis And How Do You Get It
How Is Hepatitis B Treated
Your healthcare provider will treat you based on what type of hepatitis B you have, acute or chronic.
Acute hepatitis B infections
If you develop an acute form of the condition, you probably wont need medical treatment. Instead, your doctor will likely suggest that you get plenty of rest, drink lots of fluids and maintain a healthy diet to support your body as it fights off the infection.
Chronic hepatitis B infections
If you have chronic hepatitis B, you might be a candidate for drug therapy. Usually, drug therapy is used only if you have active liver disease. There are seven drugs that are approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to treat hepatitis B. Two are injectable forms of interferon, while the five other antivirals are tablets.
You will need to take these medications every day. They help by slowing the viruss ability to multiply in your system. This helps reduce swelling and liver damage. Youll need to be regularly monitored for early signs of liver damage and liver cancer. Your healthcare provider will want to see you once or twice a year.
How Could I Get Hepatitis B
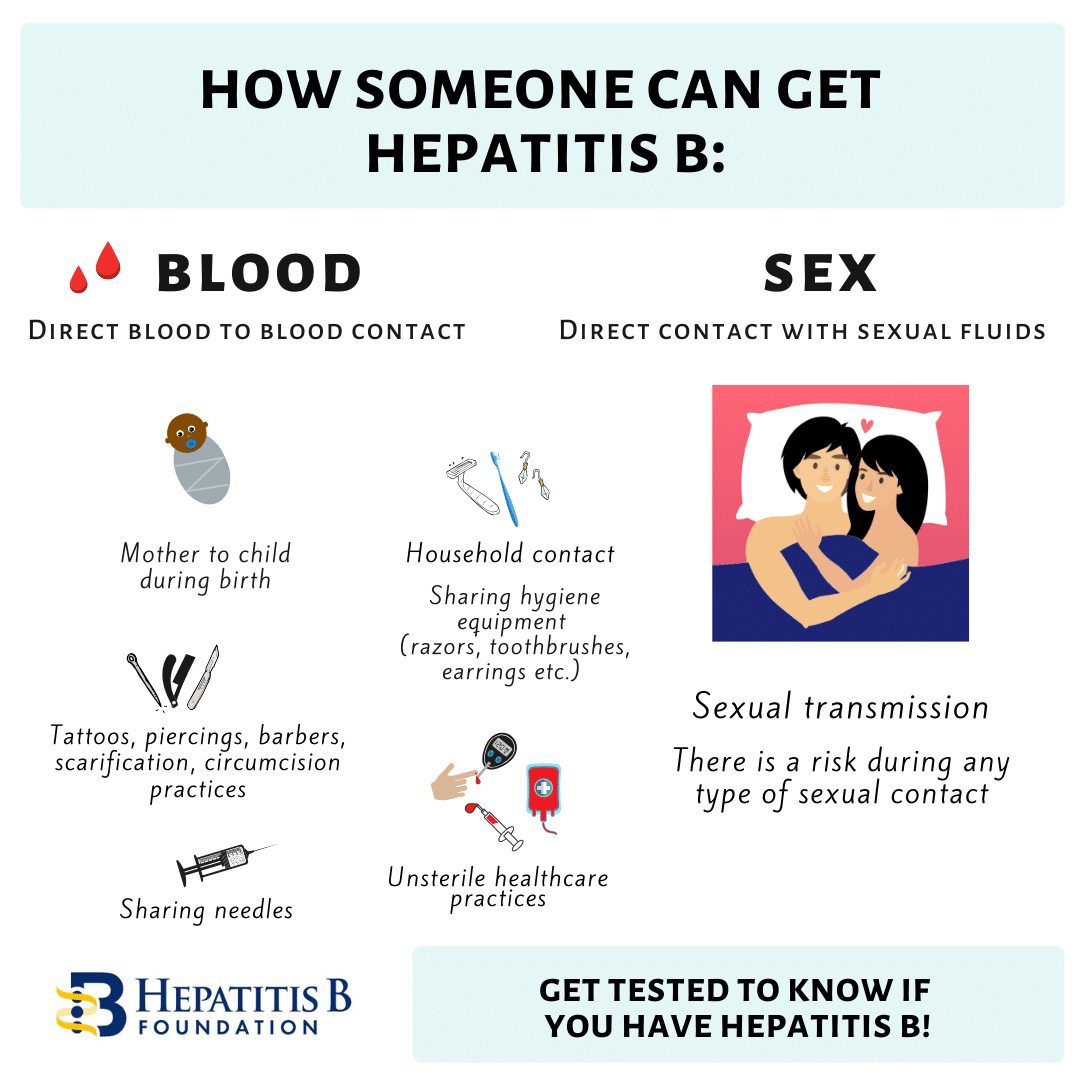
You could get hepatitis B through contact with an infected persons blood, semen, or other body fluid. This contact could occur by
- being born to a mother with hepatitis B
- getting an accidental stick with a needle that was used on an infected person
- having unprotected sex with an infected person
- having contact with blood or open sores of an infected person
- sharing drug needles or other drug materials with an infected person
- being tattooed or pierced with unsterilized tools that were used on an infected person
- using an infected persons razor, toothbrush, or nail clippers
You could get hepatitis B from having unprotected sex with an infected person.
You cannot get hepatitis B from
- shaking hands or holding hands with an infected person
- being coughed or sneezed on by an infected person
- hugging an infected person
- light-colored stools
- yellowish eyes and skin, called jaundice
When symptoms occur, they can begin 2 to 5 months after coming into contact with the virus. See a doctor right away if you or a child in your care has symptoms of hepatitis B.
Dont Miss: Latest Treatment Of Hepatitis C
Don’t Miss: How Is Hepatitis E Transmitted
Hepatitis C: What Happens
About 25% of people who get hepatitis C defeat the virus after a short-term infection. The rest will carry the virus in their body for the long term. Chronic hepatitis C can cause very serious complications, including liver failure and liver cancer. There are effective treatments for the virus, though.
Hepatitis A B And C: What Is The Difference
A, B, C D and E.
Aside from the letters associated with it, how much do you know about hepatitis? Whats the difference between the types? And if get a vaccination for hepatitis, which are you protected from?
We spoke with Moises Ilan Nevah, MD, a transplant hepatologist/gastroenterologist and medical director of the Liver Transplant Program at Banner University Medical Center Phoenix, to help better understand the similarities and differences between the various types of hepatitis, who is at risk and when to get vaccinated.
Recommended Reading: How Can A Person Get Hepatitis
Screening And Prevention Of Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B testing in asymptomatic patients should be considered in:
- Men who have sex with men.
- Sex workers .
- People from countries where hepatitis B is common.
- Needlestick victims.
- Sexual partners of people who either have or who are at high risk of having hepatitis B.
- Workers with occupational risk eg, healthcare workers.
If non-immune, consider hepatitis B vaccination. If found to be chronic carriers, consider referral for therapy. See also the separate Hepatitis B Vaccination and Prevention article.
- Vaccination may be universal or just for high-risk groups.
- The current recombinant vaccine is one of the safest available but, being grown in yeast cells, it should not be given to those allergic to yeast.
- Passive immunisation with specific hepatitis B immunoglobulin may be given to non-immune contacts after high-risk exposure.
Read Also: What Does Hepatitis Look Like
What Happens With Hepatitis B
A majority of adults who contract hepatitis B have between mild symptoms and no symptoms at all, and then the virus resolves spontaneously however, about 5% of people are not able to eliminate the hepatitis B virus and develop chronic infection. If a chronically infected mother gives birth, 90% of the time her infant will be infected and develop chronic hepatitis B, usually for life. This may give rise to serious complications of liver disease later in life such as liver damage, liver failure, and liver cancer.
Also Check: When Do You Get Hepatitis B Vaccine
Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Most people with hepatitis C don’t have any symptoms when they acquire the hepatitis C virus infection, however, about 1/4th of those infected will have symptoms like
- abdominal pain,
Infectious causes of hepatitis usually are, but not always, contagious. For example, hepatitis caused by viruses usually is contagious, although many types of hepatitis are transferred mainly from person to person by blood-to-blood transfer, for example, individual sharing needles, acupuncture, sexual contact, and organ transplantation.
Some infectious parasites cause hepatitis in individuals, but are not contagious person to person.
Most noninfectious causes of hepatitis are not contagious. Hepatitis caused by alcohol poisoning, medications, or toxins or poisons are not transmitted from person to person.
Therefore, the answer to the question “Is hepatitis contagious?” depends upon the type of hepatitis.
Prevent Infection After Contact With The Virus
If you think you have been in contact with the hepatitis B virus, see your doctor right away. Doctors typically recommend a dose of the hepatitis B vaccine to prevent infection. In some cases, doctors may also recommend a medicine called hepatitis B immune globulin to help prevent infection. You must get the vaccine dose and, if needed, HBIG shortly after coming into contact with the virus, preferably within 24 hours.
You May Like: If You Have Hepatitis B Do You Have Hiv
Who Are Hepatitis B Carriers
Hepatitis B carriers are people who have the hepatitis B virus in their blood, even though they dont feel sick. Between 6% and 10% of those people whove been infected with the virus will become carriers and can infect others without knowing it. There are over 250 million people in the world who are carriers of HBV, with about 10% to 15% of the total located in India. Children are at the highest risk of becoming carriers. About 9 in 10 babies infected at birth become HBV carriers, and about half of children who are infected between birth and age 5 carry the virus. A blood test can tell you if you are a hepatitis B carrier.
How Long Does It Take Before Symptoms Of Hepatitis Begin

In general, the incubation period from time of initial viral infection to development of symptoms ranges widely from about two weeks to six months.
Treatments for contagious hepatitis types vary according to the underlying cause and type of hepatitis. Most individuals are contagious about one to two weeks before symptoms appear. Depending upon the type of hepatitis, they can remain contagious for an extended length of time. For example, people with hepatitis A are contagious for at least two weeks after the onset of symptoms, but for hepatitis C and other types of hepatitis, individuals may not be cured of hepatitis and are contagious unless specific treatments occur.
In general, it takes about six months for the liver to recover from “cured”hepatitis A in most individuals. With other hepatitis types, patients may not be cured for many years.
With noncontagious hepatitis, again the “cure” is dependent upon treatment of the underlying cause. If the underlying cause is “cured,” the liver function may or may not improve.
Also Check: What Are The Different Types Of Hepatitis
Where Is The Hepatitis B Virus Found And How Is It Transmitted
Blood is the major source of the hepatitis B virus in the workplace. It can also be found in other tissues and body fluids, but in much lower concentrations. The risk of transmission varies according to the specific source. The virus can survive outside the body for at least 7 days and still be able to cause infection.
What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis
Each type of hepatitis is treated differently.
Hepatitis A often goes away on its own and home treatment is all that is needed to help the liver recover, such as:
- Rest
- Avoiding alcohol
- Avoiding certain medicines that can be harmful to the liver
Hepatitis B often goes away on its own in about 6 months, and can also be treated at home with the above remedies. Other treatments for hepatitis B include:
- Antiviral medications
- Liver transplant in severe cases
Treatment for hepatitis C is effective on certain forms of the hepatitis C virus. The choice of medications depends on the type of hepatitis C you have, whether you have been treated for the illness before, how much liver damage has occurred, any other underlying medical issues, and other medicines you take. Treatment for hepatitis C usually involves 8 to 12 weeks of oral antiviral medications, such as:
- Elbasvir-grazoprevir
- Sofosbuvir-velpatasvir-voxilaprevir
Read Also: Difference Between Hepatitis A And B
Treatment: Chronic Hepatitis C
The latest drug to be approved by the FDA is glecaprevir and pibrentasvir . This medication offers a shorter treatment cycle of 8 weeks for adult patients with all types of HCV who donât have cirrhosis and who have not been previously treated. The length of treatment is longer for those who are in a different disease stage. The prescribed dosage for this medicine is 3 tablets daily.
There are several other combination drugs available, as well as some single drugs that may be used in combination. Your doctor will choose the right one for you depending on the type of hepatitis C you have, how well your liver is functioning and any other medical problems you may have. Also be sure to discuss your insurance coverage since these medications are expensive.
The Difference Between Hepatitis A B C
Hepatitis A, B, and C all cause liver infection and inflammation but are different viruses.
Hepatitis A tends to be a short-term infection that doesn’t become chronic in the majority of cases, while hepatitis B and C are more likely to remain in the body and cause chronic disease and long-term liver damage.
Hepatitis A is most commonly spread via close contact for example during sex with an infected person, or while caring for someone who is unwell with the virus. People can also ingest hepatitis A unknowingly via contaminated food and drink or items that have been contaminated with an infected person’s poop.
Hepatitis B is spread via infected blood, semen, and other body fluids, and hepatitis C is caught from infected blood.
There are vaccines to prevent hepatitis A and hepatitis B, but not hepatitis C.
You May Like: Where To Get A Hepatitis B Shot
How Is Hepatitis B Transmitted
Hepatitis B is spread in several distinct ways: sexual contact sharing needles, syringes, or other drug-injection equipment or from mother-to-child at birth.
In the United States, in 2018, injection drug use was the most common risk factor reported among people with an acute HBV infection, followed by having multiple sex partners. Less commonly reported risk factors included accidental needle sticks, surgery, transfusions, and household contact with a person with HBV infection. In the United States, healthcare-related transmission of HBV is rare.
Mother-to-child transmission of HBV is especially concerning, because it is preventable. An estimated 25,000 infants are born to mothers diagnosed with HBV each year in the United States, and approximately 1,000 mothers transmit HBV to their infants. Without appropriate medical care and vaccinations, 90% of HBV-infected newborns will develop chronic infection, remaining infected throughout their lives. Up to 25% of people infected at birth will die prematurely of HBV-related causes. For this reason, the standard of care for pregnant women includes an HBV test during each pregnancy so that the appropriate steps can be taken to prevent HBV-positive mothers from transmitting the disease to her infant.
What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis B
Prevention is recommended by receiving a vaccine for HBV.
Receiving an injection of the hepatitis B immune globulin within 12 hours of coming in contact with the virus may help prevent the development of the disease.
At present, there is no specific treatment for patients with acute hepatitis B. Acute infection is usually short and will often resolve on its own. Your health care provider may recommend rest, and adequate nutrition and fluids to help your body fight the infection. Hospitalization may be required for patients who suffer from severe vomiting and who are unable to maintain adequate nutritional levels. It may also be required to prevent the development of complications.
While chronic infection cannot be cured, there are two standard treatments in Canada that may control the virus and prevent further damage to the liver.
- Antiviral medications can fight the virus and slow damage to the liver.
- Interferon which may be given for short periods and if effective, results in suppression of the virus.
You May Like: Hepatitis C Quant Rna Pcr
What Are The Chances Of Getting Hepatitis C From Sex
Hepatitis C can spread through sexual intercourse, but it’s rare. And it’s extremely rare among monogamous couples. In fact, the CDC considers the risk of sexual transmission between monogamous couples so low that it doesn’t even recommend using condoms. Also, there’s no evidence that hepatitis C is spread by oral sex. But you should avoid sharing razors, toothbrushes, and nail clippers, and sex during menstruation.
If you have HIV or if you have multiple partners, you should take precautions. Using condoms will protect you and your partners.
Is Hepatitis B Curable

Theres no cure for hepatitis B. The good news is it usually goes away by itself in 4 to 8 weeks. More than 9 out of 10 adults who get hepatitis B totally recover.
However, about 1 in 20 people who get hepatitis B as adults become carriers, which means they have a chronic hepatitis B infection. Carriers are more likely to pass hepatitis B to other people. Most carriers are contagious meaning they can spread hepatitis B for the rest of their lives.
Hepatitis B infections that last a long time may lead to serious liver diseases like cirrhosis and liver cancer. About 1 in 5 people with chronic hepatitis B die from it. There are medicines that can help treat chronic hepatitis B infections.
Most babies who get hepatitis B during birth develop chronic infection, unless they get treated right away. But treatments are almost always effective if your baby gets them quickly. Thats why its important for pregnant people to get tested for hepatitis B.
Also Check: How Can I Tell If I Have Hepatitis
Read Also: Does Hepatitis B Have A Cure
What Should You Know About Hepatitis B Before You Travel
Hepatitis B is quite common in China and other Asian countries, where as many as 1 in 12 people have the virus, though many dont know it. Before traveling to those places, you should make sure youve been vaccinated against the virus.
In addition to getting the vaccine, you can take these additional precautions to reduce your risk of contracting the virus:
- Refrain from taking illegal drugs.
- Always use latex or polyurethane condoms during sex.
- Make sure new, sterile needles are used during all piercings, tattoos and acupuncture sessions.
- Avoid direct contact with blood and bodily fluids.
- Know the HBV status of all your sexual partners.
- Ask your doctor about possible vaccination before you travel to a place where hepatitis B is common.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Hepatitis B is a liver disease that can cause serious damage to your health. One reason that is dangerous is that it can easily go undetected for years while damaging your liver. Talk with your healthcare provider about being tested for hepatitis B if you have any reason to believe that you were not vaccinated or if you have engaged in risky behavior. If you do test positive, follow the directions from your healthcare provider so that you can live a longer, healthier and happier life.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 07/09/2020.
References