How Is Viral Hepatitis Diagnosed
Diagnosis of viral hepatitis is based on symptoms and physical findings as well as blood tests for liver enzymes, viral antibodies, and viral genetic materials.
Symptoms and physical findings
Diagnosis of acute viral hepatitis often is easy, but the diagnosis of chronic hepatitis can be difficult. When a patient reports symptoms of fatigue, nausea, abdominal pain, darkening of urine, and then develops jaundice, the diagnosis of acute viral hepatitis is likely and can be confirmed by blood tests. On the other hand, patients with chronic hepatitis due to HBV and HCV often have no symptoms or only mild nonspecific symptoms such as chronic fatigue. Typically, these patients do not have jaundice until the liver damage is far advanced. Therefore, these patients can remain undiagnosed for years to decades.
Blood tests
There are three types of blood tests for evaluating patients with hepatitis: liver enzymes, antibodies to the hepatitis viruses, and viral proteins or genetic material .
Liver enzymes: Among the most sensitive and widely used blood tests for evaluating patients with hepatitis are liver enzymes, called aminotransferases. They include aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase . These enzymes normally are contained within liver cells. If the liver is injured , the liver cells spill the enzymes into the blood, raising the enzyme levels in the blood and signaling that the liver is damaged.
Examples of tests for viral antibodies are:
History Of Hepatitis E
Hepatitis E was not recognized as a distinct disease until 1980, when waterborne epidemics of hepatitis in India previously thought to have been caused by hepatitis A virus were shown to have occurred in persons who were already immune to HAV.2,3 Three years later the etiologic agent was transmitted to a volunteer following ingestion of a pooled fecal extract from Soviet troops with unexplained hepatitis stationed in Afghanistan.4 The viral genome was cloned and sequenced in 1990,5 and the virus was renamed hepatitis E virus.
In retrospect it is probable that most waterborne clinical hepatitis occurring in developing countries in the first half of the twentieth century or earlier was hepatitis E and not hepatitis A.6 For more than 20 years following its discovery, HEV was thought to be largely restricted to endemic areas in Asia, Africa, and Mexico, where it causes sporadic cases of hepatitis and more dramatic outbreaks involving thousands or tens of thousands of cases. More recently it has become clear that locally acquired hepatitis E is a health issue also in developed countries.7
Sanford H. Feldman, David N. Easton, in, 2006
How Hcv Is Spread
The hepatitis C virus is transmitted primarily through blood to blood contact, meaning that a person can become infected with the virus should the blood of a person who carries the virus be introduced into another person’s bloodstream.
Therefore, as with hepatitis B, blood transfusions , tattooing and body piercing, occupational exposure, medical procedures, and intravenous drug use can all lead to possible exposure to the virus. Unlike hepatitis B, however, sexual contact and childbirth have both been shown to be an inefficient route of exposure to HCV.
The hepatitis G virus is thought to be transmitted in a similar way to HCV.
Don’t Miss: How To Know You Have Hepatitis
How Is Hepatitis E Treated
For people who have severe acute illness and who are not pregnant, treatment with the medication ribavirin for 21 days has resulted in improved liver function in some small studies.
If hepatitis E is suspected and your immune system is not suppressed, you may not need medications. A doctor may advise you to rest, drink plenty of fluids, avoid alcohol, and practice good hygiene until the infection subsides.
Pregnant women, people with suppressed immune systems, or people with acute liver failure will likely be hospitalized and monitored.
Faqs About Hepatitis A And E
What are hepatitis A and E?
Hepatitis A is typically a self-limited, acute viral infection of the liver. It is an RNA virus that can be found in blood, stool and the liver during the acute phase of the disease. The virus is found in the stool of people who are infected. The incidence of hepatitis A in the United States has declined substantially over the last decade since vaccination was recommended for persons at increased risk and universal vaccination of infants was recommended in 2006. The majority of infected people will recover without long-term effects. In rare cases, it can cause liver failure. Like hepatitis A, hepatitis E is both endemic to underdeveloped countries and self-limiting. Recent studies suggest that exposure to hepatitis E is common in the United States, particularly in people who have pets and/or eat liver or other organ meats.
What causes hepatitis A or E?
Hepatitis A and E are spread through contaminated food, water and human waste. Poor personal hygiene, poor sanitation and sexual or intimate contact facilitate viral transmission. Travel to areas with a high incidence of hepatitis A is the greatest risk factor for acquiring hepatitis A in the United States. Intravenous drug use is another risk factor. Developing countries commonly experience water- or food-borne epidemics. Ingestion of contaminated food and water may provide another route of transmission.
Who is at risk for hepatitis A or E?
What are the symptoms of hepatitis A and E?
You May Like: Is There Treatment For Hepatitis B
Can I Drink Alcohol If I Have Hepatitis E
Alcohol is inflammatory to the liver, especially a liver that is already sick. Alcohol worsens liver inflammation from hep E. It can increase the risk of severe hepatitis and liver failure from acute viral hepatitis. Alcohol should be completely avoided when a person has any type of hepatitis or liver disease.
How Is Hepatitis E Virus Transmitted
HEV is the primary cause of enterally transmitted NANB hepatitis. It is transmitted via the fecal-oral route and appears to be endemic in some parts of less-developed countries, where most outbreaks occur. HEV can also be transmitted vertically to the babies of HEV-infected mothers. It is associated with a high neonatal mortality.
In one report, anti-HEV antibodies were found to be present in 29% of urban children and 24% of rural children in northern India. Sporadic infections are observed in persons traveling from Western countries to these regions.
Recommended Reading: Chronic Viral Hepatitis C Contagious
Prevalence Of Hepatitis E
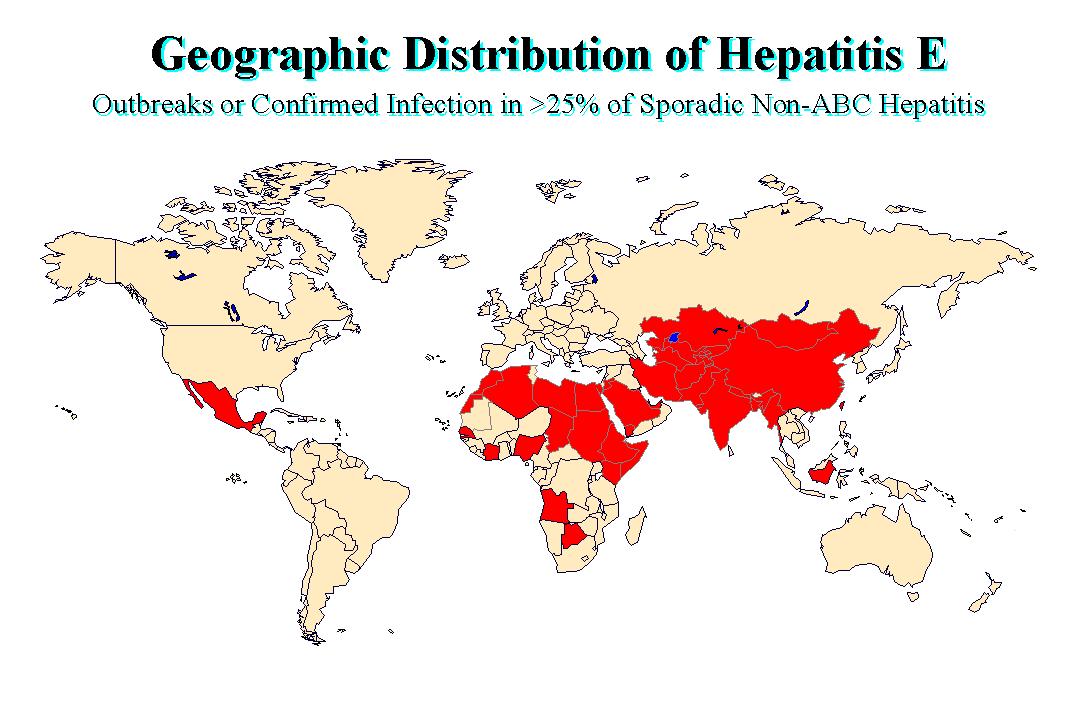
First identified in 1980 as a distinct entity, hepatitis E disproportionately affects certain areas of the globe: Southeast and Central Asia, North and West Africa, and Mexico.
Hepatitis E is most commonly found in those ages 15 to 40 young children may get it, too, but dont usually develop symptoms.
Parenteral Routes: Transmission Of Hepatitis B Hepatitis D And Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B, C, and D viruses are all transmitted by what is known as the parenteral route. Parenteral simply means that these viruses can be introduced by all routes except through the intestinal tract, which leaves the door wide open in terms of possible exposure. Let’s look at the possible transmission routes for each of these types of hepatitis virus more closely.
Recommended Reading: If My Husband Has Hepatitis C Will I Get It
How Is Hepatitis A Spread
Hepatitis A
The hepatitis A virus is usually spread by putting something in your mouth that is contaminated with the virus. The virus is found in the stool of people with hepatitis A and is spread when someone’s stool accidentally contaminates food or water. This can happen when an infected person does not adequately wash their hands after using the bathroom then touches other things such as food. When other people eat that food, they can get infected with hepatitis A. Usually the transmission is between people in very close personal contact.
Foods themselves can be contaminated with hepatitis A virus, such as raw oysters harvested from sewage-contaminated water. When people eat food contaminated with hepatitis A virus, they can get infected with the virus.
Hepatitis A is usually spread through:
- household contact with an infected person
- sexual contact with an infected person
- eating or drinking contaminated food or water
- sharing eating utensils that are contaminated
- touching contaminated surfaces and then placing your hands near or in the mouth
How Hbv Is Spread
It is possible for the hepatitis B virus to be spread through the bodily fluids of an infected person, which is to say that the virus can be transmitted through the blood, sweat, tears, saliva, semen, vaginal secretions, menstrual blood, and breast milk of an infected person. That said, having hepatitis B does not necessarily mean that you are infectious only some people with HBV are actually contagious.
Opportunities for exposure can include sharing a syringe or getting tattoos or body piercings with infected tools. But it also means that it is possible to be exposed during childbirth as well as sexual contact and intercourse. In fact, nearly two-thirds of acute cases of hepatitis B in the United States are caused by sexual exposure.
Though HBV can be spread through blood, there is generally very little risk of contracting the virus through blood transfusions as most countries began screening for it by 1975.
Read Also: How You Get Hepatitis C
Hepatitis E Virus Aetiology
Hepatitis E is a hepatotropic virus and the causative agent of hepatitis E, an acute viral hepatitis in humans it is a single-strand positive-sense RNA virus. The infection may vary in severity from inapparent infection to fulminant liver failure and death. Although considered acute, chronic infections have been observed in liver and kidney transplant and chronic liver disease patients. The mortality rate is between 1% and 4% , higher than hepatitis A virus HAV, a Picornavirus and in people with CLD and in pregnant women it can reach 2530%.
Hepatitis E is an important public health concern and a major contributor to enterically transmitted hepatitis worldwide . Based on seroprevalence data, it is estimated that one-third of the worlds population has been infected with HEV .
Fig. 19.1. Hepatitis E virus endemic areas and global seroprevalence. Dark areas on the map indicate regions of the world that are endemic for hepatitis E and where & gt 25% of acute viral hepatitis is due to HEV infection. Superimposed on the map are seroprevalence rates of HEV from various countries, determined in different studies. Image taken from Chandra et al., 2008.
In endemic regions, hepatitis E occurs in epidemic forms, while in developed regions HEV occurs sporadically .
X.J. Meng, in, 2008
How Can Hepatitis A Be Prevented
The hepatitis A vaccine offers immunity to adults and children older than age 1. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends routine hepatitis A vaccination for children aged 12 to 23 months and for adults who are at high risk for infection. Treatment with immune globulin can provide short-term immunity to hepatitis A when given before exposure or within 2 weeks of exposure to the virus. Avoiding tap water when traveling internationally and practicing good hygiene and sanitation also help prevent hepatitis A.
Also Check: Hepatitis C And Liver Damage
How Is Viral Hepatitis Prevented
Prevention of hepatitis involves measures to avoid exposure to the viruses, using immunoglobulin in the event of exposure, and vaccines. Administration of immunoglobulin is called passive protection because antibodies from patients who have had viral hepatitis are given to the patient. Vaccination is called active protection because killed viruses or non-infectious components of viruses are given to stimulate the body to produce its own antibodies.
Avoidance of exposure to viruses
Prevention of viral hepatitis, like any other illness, is preferable to reliance upon treatment. Taking precautions to prevent exposure to another individual’s blood , semen , and other bodily secretions and waste will help prevent the spread of all of these viruses.
Use of immunoglobulins
Immune serum globulin is human serum that contains antibodies to hepatitis A. ISG can be administered to prevent infection in individuals who have been exposed to hepatitis A. ISG works immediately upon administration, and the duration of protection is several months. ISG usually is given to travelers to regions of the world where there are high rates of hepatitis A infection and to close or household contacts of patients with hepatitis A infection. ISG is safe with few side effects.
Hepatitis A
Individuals at increased risk of acquiring hepatitis A are:
Some local health authorities or private companies may require hepatitis A vaccination for food handlers.
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B vaccine is recommended for:
How Can You Reduce Your Risk Of Hepatitis E
Currently there is no vaccine available for hepatitis E and, because of this, it is sensible to take precautions when you travel to endemic areas or areas where the virus is known to occur. You should practice good hygiene always wash your hands properly after using the bathroom and before preparing or eating food. Use alcohol hand gel or baby-wipes for cleaning hands if soap and water are not available.
When travelling to an area where hepatitis E is common you are advised to avoid12,15:
- drinking tap water
- having ice cubes in your drinks
- cleaning your teeth with tap water
- drinking unpasteurised milk
You May Like: What Do You Get Hepatitis C From
What Home Remedies And Lifestyle Changes Are Used For The Treatment Hepatitis E
A person with hepatitis E should listen to their body’s signals of fatigue and get plenty of rest. The infected person should be encouraged to at least drink plenty of liquids every day. This is especially important if they have been vomiting, have fevers, or do not feel like taking much by mouth. Alcohol must be eliminated completely with all types of hepatitis until the liver has fully healed.
If you are pregnant with hepatitis E, eat and keep hydrated, and keep in close contact with your OB/GYN or midwife. He or she may want to monitor you frequently. You may need to be hospitalization to ensure the well-being of you and your baby if you cannot keep up fluids, or if you lose weight at home.
The liver’s most important job is to process chemicals , toxins, and waste products. This job is weakened during acute hepatitis. Consult your doctor before taking any over-the-counter medications. For example, usually acetaminophen and NSAIDs like ibuprofen are safe when used for fevers and body aches, but it may need to be limited while the liver is inflamed. The normal dose might create too much damage to the liver to handle and may even cause overdose or more liver damage.
What Is Hepatitis E
Hepatitis E, also known as Enteric non-A, non-B is a virus that attacks the liver and causes liver inflammation. Hepatitis E virus is transmitted by contaminated stool . People infected with hepatitis E excrete the virus in their stools, and the virus is spread by coming in contact with contaminated food and water.
When people come in contact with infected stool and do not wash their hands properly with soap and water, they can become infected with hepatitis E. The hepatitis E virus is easily spread in areas that have poor sanitation or poor personal hygiene.
In the United States, hepatitis E virus is relatively uncommon because the water and sewage treatment facilities in this country are effective in killing any hepatitis E virus that may enter the water supply. However, many countries in the world do not have effective facilities to kill the virus and they have many people with hepatitis E virus infection.
In industrialized countries, undercooked contaminated meat, particularly pork, has been associated with hepatitis E infection.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Get Hepatitis C
Diagnosis Of Hepatitis E
-
IgM antibody test
-
IgM antibody to hepatitis A virus
-
Hepatitis B surface antigen
-
IgM antibody to hepatitis B core
-
Antibody to hepatitis C virus and hepatitis C RNA PCR
If tests for hepatitis A, B, and C are negative but the patient has typical manifestations of viral hepatitis and has recently traveled to an endemic area, IgM antibody to HEV should be measured if the test is available.
Transmission Of Hepatitis E
Hepatitis E infection occurs after ingesting food or water that has been contaminated with feces infected with the virus.
For example, a person may unknowingly drink contaminated tap water when traveling in an area with poor sanitation.
Natural disasters can also contribute to the spread of hepatitis E.
Monsoons and flood waters can cause sewers to overflow and mix with drinking water, leading to contamination.
People may also be at risk of contracting hepatitis E from animals cows, pigs, rodents, sheep, and others can harbor the infection.
As for whether hepatitis E can be spread through sexual contact, the answer remains unclear: The World Health Organization states it cant, while the U.S. National Institutes of Health state that it can.
Further research is needed to clarify this issue.
Also Check: How Do You Catch Hepatitis C
Looking After Yourself When You Have Hepatitis E
AlcoholAlcohol is processed by your liver and, as a result, it can be dangerous for anyone with liver problems. If you have hepatitis E it is important that you stop drinking alcohol for the duration of infection as it can make your symptoms worse11.
Alcohol can accelerate the rate of liver damage in those with hepatitis B and C, and can limit the effectiveness of anti-viral treatment30. Therefore, it is recommended to avoid alcohol in these circumstances.
SmokingSmoking is dangerous to everyones health31, 32, 33. Smoking can increase the severity of liver damage34. People with liver disease are more vulnerable to infection and to general poor health, so smoking or exposure to passive smoking is not advisable. If you smoke, speak to your doctor about what help is available for cutting down and giving up.
Diet Being overweight or obese can affect the progression, or treatment of, your liver condition. If you have a liver condition, there may be some special considerations you need to make in your diet to stay nutritionally well and to help manage your condition. Some of these are specific to certain liver diseases, others relate to how advanced your liver disease is .
For most people with hepatitis E there is no special diet, however, eating a good, balanced diet is one of the most important things you can do to keep yourself well. Regular low calorie meals containing protein , starch and vitamins is the best approach.