Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Drinking a lot of alcohol damages the liver. When its damaged, the liver cant break down fat properly. This can cause fat to build up, which is known as alcoholic fatty liver.
Alcoholic fatty liver disease is the earliest stage of alcohol-related liver disease.
If theres no inflammation or other complications along with the build-up of fat, the condition is known as simple alcoholic fatty liver.
Characteristics Of The Subjects
A total of 191 patients were enrolled in the study. They were 48.8±9.0years old on average and had mean BMI of 24.8±2.9kg/m2. Among them, males accounted for 67.5% overweight and obesity patients accounted for 60.7% smokers accounted for 40.8% diabetic patients accounted for 13.1% and insulin resistant patients accounted for 18.8% . Table lists the clinical characteristics and laboratory indicators of the studied population.
Table 1 Demographic, laboratory, and clinical characteristics of the enrolled subjects
What Questions Should I Ask My Doctor
- Am I taking any medications that could contribute to fatty liver disease?
- How much damage does my liver have?
- How long will it take to reverse the liver damage?
- What is a healthy weight for me?
- Can I talk to a nutritionist or go to classes to learn about healthy eating?
- How can I get treatment for alcohol use disorder?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Consider fatty liver disease an early warning sign to help you avoid a fatal liver condition, like cirrhosis or liver cancer. Even if you dont have symptoms or any liver function problems at this point, its still important to take steps to stop or reverse fatty liver disease.
Don’t Miss: Antiviral Drugs For Hepatitis A
Nafld And Alcoholic Liver Disease
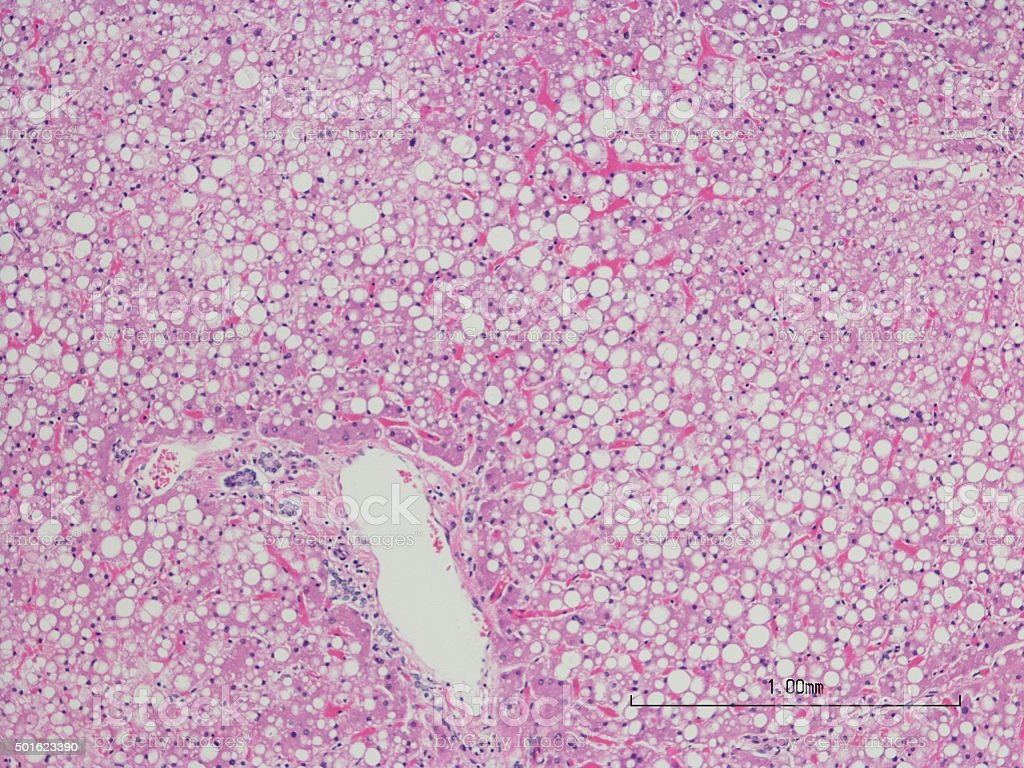
It is often stated in the literature that NASH is histologically identical to ASH, but is that really true? There are several lesions of alcoholic liver disease that, to date, are not known in NAFLD, including sclerosing hyaline necrosis, the veno-occlusive lesion first described by Goodman and Ishak, and alcoholic foamy degeneration. On the other hand, there are several biopsies of fatty liver disease for which the pathologist cannot be sure of the true etiology of liver disease, and cases in which obesity, diabetes and alcohol are all likely contributing factors . In addition, most of the standard literature in liver pathology notes that Mallory hyaline and neutrophilic infiltrates may be more prominent in ALD.
Figure 4
Sclerosing hyaline necrosis. The terminal hepatic venule is obliterated and only visualized on special stains, which may highlight the remnants of the vein wall. Many of the surrounding hepatocytes have undergone necrosis, and several of the remaining hepatocytes are ballooned and/or have Mallorys hyaline with surrounding neutrophils, a lesion known as satellitosis.
Molecular Sieves And Desiccants
Apart from distillation, ethanol may be dried by addition of a , such as , , or . The desiccants can be dried and reused. can be used to selectively absorb the water from the 95.6% ethanol solution. Molecular sieves of pore-size 3 , a type of , effectively sequester water molecules while excluding ethanol molecules. Heating the wet sieves drives out the water, allowing regeneration of their dessicant capability.
Recommended Reading: How Does A Person Contract Hepatitis
Is Mild Hepatomegaly Dangerous
The extent to which a slightly enlarged liver is dangerous depends on the reason for the enlargement.
For people with NAFLD, a slightly enlarged liver is unlikely to pose a major threat to health. However, it could be an indication that a person should consider making some lifestyle changes.
That said, certain conditions can cause a slightly enlarged liver to become a significantly enlarged and damaged liver without treatment. Such conditions include:
- alcohol use disorder
- hepatitis B, C, and D
- cancer
In general, mild hepatomegaly indicates that it is time to visit a doctor for a full physical evaluation.
Hepatomegaly usually does not cause any symptoms. In fact, the liver conditions that lead to hepatomegaly can progress significantly without causing any symptoms at all.
Because of this, a person should see a doctor if they:
- experience any symptoms of an enlarged liver
- develop any other symptoms of liver disease
- have any conditions that increase their risk of developing liver disease
The outlook for people with hepatomegaly depends on the cause of the hepatomegaly and the extent of the liver damage.
People with hepatitis A and acute hepatitis B usually recover without treatment.
People with the early stages of NAFLD may also have a positive outlook. A mildly damaged liver can often repair itself if a person makes the necessary lifestyle changes early on.
People who have other forms of liver damage will need to ask their doctor about their individual outlook.
Prolong Exposure To Excess Carbohydrates Energy Drives Systemic Metabolic Derangements Primarily Promoting Insulin Resistance
The continued ad libitum consumption of the HC diet sustained a sufficient substrate influx for gluconeogenesis to induce steady hyperglycemia throughout the 4 months of the experimental duration. Along with the hyperglycemia, the over-nourished lambs had also developed hyperinsulinemia, excess body fat, dyslipidemia, insulin resistance and increased expression of proinflammatory markers. Humans presenting with these metabolic abnormalities would probably be diagnosed with metabolic syndrome. Of notice, the HC lambs may not be classified as diabetic, at least not during the course of the experimental period, since their final fasting glucose levels were relatively low and statistically non-different from those of the LC lambs .
Also Check: What’s The Difference Between Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C
Types Of Fatty Liver Disease
There are two main types of fatty liver disease: nonalcoholic and alcoholic.
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease includes simple nonalcoholic fatty liver, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis , and acute fatty liver of pregnancy .
Alcoholic fatty liver disease includes simple AFLD and alcoholic steatohepatitis .
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
There are two different types of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease:
Simple fatty liver: This means you have fat in your liver, but you may not have any inflammation in your liver or damage to your liver cells. It usually doesnât get worse or cause problems with your liver. Most people with NAFLD have simple fatty liver.
Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis : This is much more serious than a simple fatty liver. NASH means you have inflammation in your liver. The inflammation and liver cell damage that happen with NASH can cause serious problems such as fibrosis and cirrhosis, which are types of liver scarring, and liver cancer. About 20% of people with NAFLD have NASH.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedule For Adults
Aasld/acg/aga Guidelines For Workup Of Nafld
Recommendations from a 2018 practice guideline from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases , the American College of Gastroenterology , and the American Gastroenterological Association regarding the workup of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease are below , with the updated 2018 AASLD recommendations incorporated.
The 2018 ACG guidelines on alcoholic liver disease provided the following guidance :
-
Liver function tests and ultrasonography are recommended for patients with harmful alcohol use and/or alcohol disorders.
-
Liver biopsy is not routinely recommended for diagnosis of alcoholic fatty liver disease, but it and noninvasive tools of fibrosis may be considered for diagnosis of steatohepatitis and/or liver fibrosis.
-
The Alcohol Use Disorders Inventory Test is validated for identifying individuals with alcohol use and dependence.
Eat Lots Of Fruits And Vegetables
Fruits and veggies are a critical component of the fatty liver disease diet plan. Both fruits and vegetables are chock-full of anti-inflammatory components like polyphenols, carotenoids, and other antioxidants that can fight liver damage. Reach for foods like broccoli, spinach, apples, blueberries, and raspberries for a liver-friendly diet.
You May Like: Hepatitis C Causes Symptoms And Treatment
Causes Of Fatty Liver Disease
Eating excess calories causes fat to build up in the liver. When the liver does not process and break down fats as it normally should, too much fat will accumulate. People tend to develop fatty liver if they have certain other conditions, such as obesity, diabetes or high triglycerides.Alcohol abuse, rapid weight loss and malnutrition may also lead to fatty liver. However, some people develop fatty liver even if they have none of these conditions.
Formation And Secretion Of Vldl
In the fed state, -oxidation of fatty acids is not required as an energy source, and fatty acids delivered to the liver are mainly converted to TAG. Insulin regulates the metabolic path that fatty acids take in the liver. Without insulin, creatinine palmitoyl transferase-I commit fatty acids to mitochondrial -oxidation when insulin levels are high, glycerol-3-phosphate acetyltransferase commits fatty acids to the formation of TAG. This bulk of acetyl CoA entering the citric acid cycle, results in delivery of electrons to the respiratory chain, where they generate ROS.
Read Also: Signs You Have Hepatitis B
What Gets Stored In A Cookie
This site stores nothing other than an automatically generated session ID in the cookie no other information is captured.
In general, only the information that you provide, or the choices you make while visiting a web site, can be stored in a cookie. For example, the site cannot determine your email name unless you choose to type it. Allowing a website to create a cookie does not give that or any other site access to the rest of your computer, and only the site that created the cookie can read it.
Things You Can Do If You Have Non
Adopting a healthy lifestyle is the main way of managing NAFLD.
For example, it can help to:
- lose weight you should aim for a BMI of 18.5 to 24.9 losing more than 10% of your weight can remove some fat from the liver and improve NASH if you have it
- eat a healthy diet try to have a balanced diet high in fruits, vegetables, protein and carbohydrates, but low in fat, sugar and salt eating smaller portions of food can help, too
- exercise regularly aim to do at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity activity, such as walking or cycling, a week all types of exercise can help improve NAFLD, even if you do not lose weight
- stop smoking if you smoke, stopping can help reduce your risk of problems such as heart attacks and strokes
NAFLD is not caused by alcohol, but drinking may make it worse. It’s therefore advisable to cut down or stop drinking alcohol.
Page last reviewed: 19 November 2018 Next review due: 19 November 2021
Also Check: New Cure For Hepatitis B
Delivery Of Fatty Acids From Peripheral Stores To The Liver
Triglycerides are stored in adipose tissue and released as FFAs into the circulation through the actions of lipoprotein lipase. FFAs released from peripheral stores are hydrophobic and are strongly bound to circulating albumin. FFAs are transported by albumin to the liver where they can then be used as a substitute for -oxidation, stored as TAG, or exported as VLDL.
Excess glucose is converted to the liver, the backbone of most amino acids, can be converted to pyruvate and then to acetyl-coenzyme A , which feeds directly into cytosolic fatty acid synthesis.
Processes that can lead to excessive FFAs delivery or impaired -oxidation or secretion can lead to hepatic steatosis, increased mitochondrial reactive oxygen species and lipid peroxidation products.
What You Need To Know About Fatty Liver Disease
If a fatty liver disease diagnosis is made, your doctor will perform a series of tests to identify the cause of the condition. These may include a CT scan, blood test, liver enzymes test, albumin level, serum creatinine, and urine test. Blood tests may also reveal symptoms such as high calcium, low albumin, or polydipsia. Once these symptoms are present, your doctor will evaluate them to determine if you do have fatty liver disease and what course of treatment is appropriate.
Some factors that are known to cause fatty liver disease include being overweight or obese, being a woman, and being over 50 years of age. People who smoke cigarettes or use other tobacco products are at increased risk of developing this condition. There are also other risk factors that are not well understood but include genetic tendencies toward obesity and polydipsia. Other risk factors that are associated with this disease include being older than 50 years of age and having an unhealthy body mass index. Obese people are at greater risk than thinner people for developing fatty liver disease because obese people have excess fat deposits around their bellies, hips, and thighs.
About one of every five Americans has a fatty liver, which is also called steatosis. In fact, up to 9 of every 10 diabetics and people with obesity have fatty liver.
Here are the details of each of these disorders:
Don’t Miss: What Is Hepatic Metastatic Disease
Lose Weight If Needed
Losing weight can help you reverse fatty liver disease. When you lose fatty tissue, this also means that you are losing fat from your liver.
To facilitate weight loss, aim to create a calorie deficit, meaning you are burning more energy than you consume. Eating healthy foods, controlling portion sizes, and exercising help encourage weight loss.
Make sure that you follow a balanced diet to lose weight, instead of following extreme diet plans. In addition to losing fat, its essential to also maintain muscle mass.
Who Is At Risk For Fatty Liver Disease
The cause of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is unknown. Researchers do know that it is more common in people who
- Are middle aged or older
- Are Hispanic, followed by non-Hispanic whites. It is less common in African Americans.
- Have high levels of fats in the blood, such as cholesterol and triglycerides
- Have certain infections, such as hepatitis C
- Have been exposed to some toxins
NAFLD affects about 25% of people in the world. As the rates of obesity, type 2 diabetes, and high cholesterol are rising in the United States, so is the rate of NAFLD. NAFLD is the most common chronic liver disorder in the United States.
Alcoholic fatty liver disease only happens in people who are heavy drinkers, especially those who have been drinking for a long period of time. The risk is higher for heavy drinkers who are women, have obesity, or have certain genetic mutations.
Recommended Reading: Can A Hepatitis B Carrier Get Vaccinated
Ultrasonography Ct Scanning And Mri
Noninvasive studies such as ultrasonography , computed tomography scanning, and magnetic resonance imaging are useful in helping to establish a diagnosis of steatosis, as well as in finding evidence for portal hypertension these imaging tests are also helpful in ruling out biliary dilation in patients with a cholestatic pattern of liver test result abnormalities.
However, these imaging modalities can neither define the cause of steatosis nor reliably distinguish between benign steatosis and steatohepatitis. Benign steatosis may be focal or diffuse, whereas steatohepatitis is usually diffuse.
In patients with alcoholic steatosis, the liver appears diffusely echogenic on US. In patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease , the liver is hyperechogenic or bright. Steatosis is detected only when substantial fatty change is present. Studies in patients who are about to undergo gastric bypass surgery indicate that US has a 93% predictive value for NAFLD, with an accuracy of 76%. Patients with steatosis on US have a higher incidence of coronary artery disease and should undergo cardiac evaluation if suspicious symptoms are present.
The mean CT count is lower in the liver than in the spleen. CT scans may be used to monitor the course of the disease on successive scans. Focal fatty lesions may be identified by dual-energy CT scans that demonstrate increased attenuation with increasing energy.
Recommended Reading: Who Should Get Tested For Hepatitis C
Metabolic Syndrome And Fatty Liver Disease
Many researchers now believe that metabolic syndrome a cluster of disorders that increase the risk of diabetes, heart disease and stroke plays an important role in the development of fatty liver.Signs and symptoms of metabolic syndrome include:
- obesity, particularly around the waist
- high blood pressure
- one or more abnormal cholesterol levels high levels of triglycerides, a type of blood fat, or low levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, the good cholesterol
- resistance to insulin, a hormone that helps to regulate the amount of sugar in the blood.
Of these, insulin resistance may be the most important trigger of NASH. Because the condition can remain stable for many years, causing little harm, researchers have proposed that a second hit to the liver, such as a bacterial infection or hormonal abnormality, may lead to cirrhosis.
Read Also: What Are The Signs Of Hepatitis
Treatment For Fatty Liver Disease
There are no medications approved for NAFLD, though some are in clinical trials.
Usually the first line of treatment is to lose weight. It helps reduce fat, inflammation, and scarring in your liver. Losing just 3% to 5% of your body weight can cut down on how much fat is in your liver. Weight loss surgery is also an option if you have a lot to lose.
Youâll also need to quit drinking. Itâs the only way you can keep liver damage from getting worse. You may even be able to undo some of the liver damage thatâs already happened. Talk to your doctor about how you can get help. You may need a medically supervised detox program to safely quit drinking and manage withdrawal symptoms.
If you have complications due to NASH, such as cirrhosis or liver failure, you may need to have a liver transplant. In general, people with NASH who get a liver transplant do very well.
Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
NAFLD is usually seen in people who are overweight or obese.
According to the WHO , obesity is defined as an excess of weight by increasing the fat mass of an individual.1
However, it has been found in people of a normal weight whose diets are very high in fat and/or sugar content. A healthy liver should contain little or no fat and for most people, carrying a small amount of fat in the liver causes no major problems. Having high levels of fat in your liver is also associated with an increased risk of problems such as diabetes, heart attacks and strokes.2
If fat has been in the liver for a prolonged amount of time, the liver cells can become inflamed and the term NASH is then used. NASH may progress, like many liver diseases, to cirrhosis and liver cancer. See the diagram below:
Do not hesitate to read our article about FATTY LIVER DISEASE
References:
Don’t Miss: How To Know If I Have Hepatitis