Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection
The aim of treating chronic HBV infection is primarily to prevent complications since cure is often not achievable.
Evaluation to decide if therapy is indicated includes HBeAg and anti-HBe serology, HBV load, transaminases and liver biopsy. Patients with evidence of significant viraemia and chronic inflammation without cirrhosis will benefit the most from therapy. Since HBV has a reverse transcriptase enzyme it is susceptible to a range of nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors: lamivudine, emtricitabin, telbivudine, tenofovir entecavir and adefovir dipivoxil show response rates of between 20% and 40%. These drugs are well-tolerated, but resistance develops, especially to lamivudine and emtricitabine.
The other alternative for chronic HBV therapy is pegylated interferon therapy. Interferon has the advantage of a higher rate of permanent response but has more side effects and adverse effects than the nucleoside analogues .
Janice Main, Howard C. Thomas, in, 2010
Hepatitis A Reactive Means
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
What Foods Increase Cd4 Count
Eat foods high in these vitamins and minerals, which can help boost your immune system:
- Vitamin A and beta-carotene: dark green, yellow, orange, or red vegetables and fruit liver whole eggs milk.
- B vitamins: meat, fish, chicken, grains, nuts, white beans, avocados, broccoli, and green leafy vegetables.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Transmission Routes Cdc
How It Is Done
The health professional taking a sample of your blood will:
- Wrap an elastic band around your upper arm to stop the flow of blood. This makes the veins below the band larger so it is easier to put a needle into the vein.
- Clean the needle site with alcohol.
- Put the needle into the vein. More than one needle stick may be needed.
- Attach a tube to the needle to fill it with blood.
- Remove the band from your arm when enough blood is collected.
- Apply a gauze pad or cotton ball over the needle site as the needle is removed.
- Put pressure on the site and then put on a bandage.
The Fourth Or Reactivation Phase
The previous phase of HBeAg-negative/anti-HBe-positive inactive HBsAg carrier state is not synonymous with permanent termination of HBV replication and of HBV-induced chronic liver damage. Although the majority of patients may remain for life in an inactive HBsAg carrier state, and a number of them may also lose HBsAg and enjoy a complete recovery, others retain or redevelop over time significant HBV replication and progressive liver damage .
This state of HBV-induced liver damage has been first referred to as HBeAg-negative/anti-HBe-positive CHB, and similarly to HBeAg-positive CHB, it also represents an immune active phase in the natural course of chronic HBV infection. It is generally viewed as a fourth phase in the natural history of chronic HBV infection usually developing because of reactivation of HBV replication, though in some patients, it may immediately follow the second phase of HBeAg-positive CHB despite clearance and even seroconversion of HBeAg .
Stephen N.J. Korsman MMed FCPath, … Wolfgang Preiser MRCPath, in, 2012
You May Like: How Does Hepatitis Affect The Body
Getting Tested Is The Only Way To Know If You Have Hepatitis
A blood test called a hepatitis C antibody test can tell if you have been infected with the hepatitis C virus either recently or in the past. If you have a positive antibody test, another blood test is needed to tell if you are still infected or if you were infected in the past and cleared the virus on your own.
Question 3 How Is The Quantitative Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Test Performed
An immunometric technique is used. The anti-HBs binds to HBsAg ad and ay subtypes, which are coated on the test wells. Binding of a horseradish peroxidase-labeled HBsAg conjugate to the anti-HBs completes the sandwich formation. Unbound materials are then washed away. In the next step, the horseradish peroxidase catalyzes oxidation of a luminogenic substrate, producing light. Light signals are detected and quantified. Intensity of the light is proportional to the amount of anti-HBs present in the patient sample. The result is standardized to an international unit system and reported as milliinternational units per milliliter .
Read Also: How Is Hepatitis A Caused
Mutant Viruses And Chronic Infection
Anti-HBe-positive patients in the reactivated phase of the disease are also referred to as the HBeAg-negative viremic group. Genomic analyses has revealed that such patients carry natural mutants of the virus that have either reduced levels or complete abrogation of HBeAg production. These variants are selected at the time of, or soon after, seroconversion, and become dominant during the reactivation phase. The most common precore mutation is the G1896A substitution, which creates a premature stop codon in the precursor protein from which HBeAg is elaborated. This mutation affects the stem of the encapsidation signal, but leads to stronger base pairing with the A1896 change in genotypes with a T at position 1858 of the precore region, such as B, C, D, and E. The double mutation affecting the core promoter region is thought to result in decreased transcription of the precore mRNA, with a knockon effect on HBeAg production, while pgRNA production remains the same or is even upregulated. It is now apparent that additional mutations in this region may contribute to this phenotype.
Geoffrey M. Dusheiko, in, 2003
Hepatitis C Can Be Prevented
Although there is no vaccine to prevent hepatitis C, there are ways to reduce the risk of becoming infected.
- Avoid sharing or reusing needles, syringes, or any other equipment used to prepare and inject drugs, steroids, hormones, or other substances.
- Do not use personal items that may have come into contact with an infected persons blood, even in amounts too small to see, such as glucose monitors, razors, nail clippers, or toothbrushes.
- Do not get tattoos or body piercings from an unlicensed facility or in an informal setting.
Read Also: How Do You Get Hepatitis A And B
Explanation Of Test Results:
If this test result is positive, it means your body was exposed to the hepatitis C virus and made antibodies . However, it does not tell you whether you are still infected with hepatitis C. If the antibody test result is positive, you should be tested for hepatitis C RNA , which determines whether you are chronically infected. The lab will perform this RNA test automatically if your hepatitis C antibody test is positive.
If the antibody test result is negative, it means you have not been infected with the hepatitis C virus, and further testing for hepatitis C usually is not needed.
Rna Or Viral Load Test
If you test positively for hepatitis C antibodies, you will need to get a RNA or viral load test. The RNA test is a blood test that checks to see if hepatitis C is active in your body.
- Negative
- If your RNA test result is negative, you do not have hepatitis C.
- Positive
- If your RNA test result is positive, you may have chronic hepatitis C. Talk to your doctor right away about a treatment plan.
Also Check: Can You Cure Hepatitis A
How To Get Tested
Hepatitis B testing is typically prescribed by a doctor and performed in a hospital, lab, or other medical setting. Taking a hepatitis B test requires a blood sample, which can be collected by a health care professional.
For laboratory-based testing, blood is drawn from a patients vein. After blood is collected, the sample is sent to a laboratory for analysis.
What Is The Normal Range For Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
Hepatitis B surface antibodies are measured in blood samples in milli-International Units/milliliter mIU/mL). The ranges for hepatitis B surface antibodies are:
- Anti-HBs greater than 10-12 mIU/mL: Protected against hepatitis B virus infection, either from vaccination or successful recovery from a previous HBV infection.
- Anti-HBs less than 5 mIU/mL: Negative for HBV infection, but susceptible and hence requires vaccination.
- Anti-HBs from 5-12 mIU/mL: Inconclusive results and the test should be repeated.
However, there is no standardization of these values so it is advisable to check the manufacturers values it is the reason values are mainly reported as positive or negative.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Contract Hepatitis B Virus
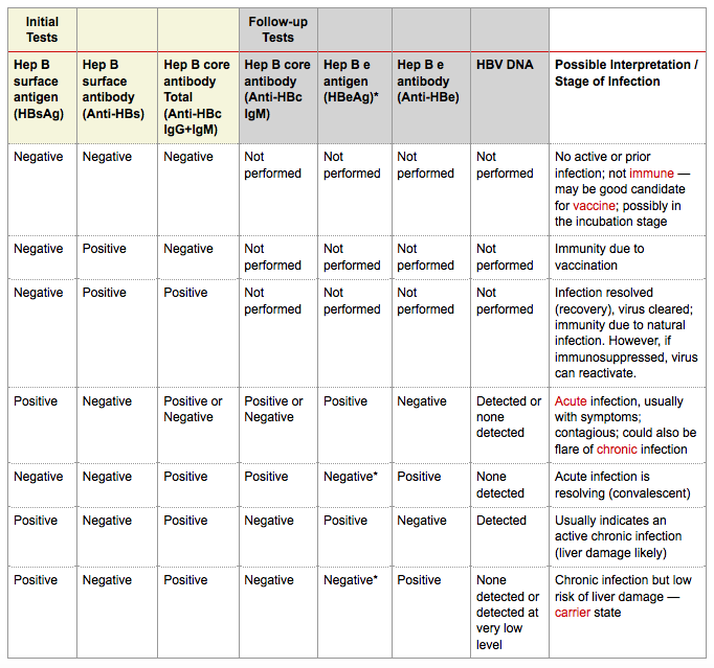
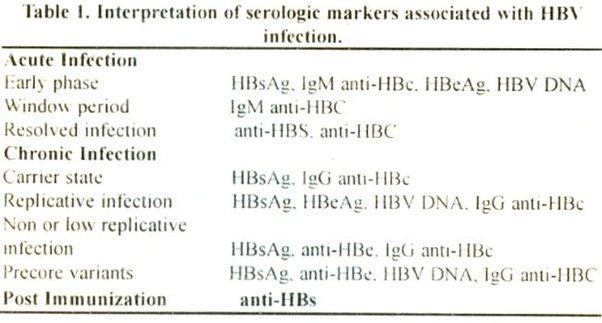
What Do Hepatitis B Test Results Mean
Hepatitis B test results help determine if HBV infection is negative or positive, and if positive, whether the infection is acute or chronic, or if recovery is complete. A combination of results are considered to identify and classify HBV infection status.
The following are some interpretations of hepatitis B test results:
Table: Hepatitis B test results and interpretations
| Test |
|---|
Who Should Get Tested
You should consider getting tested for hepatitis C if you’re worried you could have been infected or you fall into one of the groups at an increased risk of being infected.
Hepatitis C often has no symptoms, so you may still be infected if you feel healthy.
The following groups of people are at an increased risk of hepatitis C:
- ex-drug users and current drug users, particularly users of injected drugs
- people in the UK who received blood transfusions before September 1991
- UK recipients of organ or tissue transplants before 1992
- people who have lived or had medical treatment in an area where hepatitis C is common high-risk areas include north Africa, the Middle East and central and east Asia
- babies and children whose mothers have hepatitis C
- anyone accidentally exposed to the virus, such as health workers
- people who have received a tattoo or piercing where equipment may not have been properly sterilised
- sexual partners of people with hepatitis C
If you continue to engage in high-risk activities, such as injecting drugs frequently, regular testing may be recommended. Your doctor will be able to advise you about this.
Read Also: What Organ Does Hepatitis B Affect
Hepatitis B And Alcohol
Two major types of chronic hepatitis B exist, differing in their HBe antigen and anti-HBe antibody status. HBeAg positive patients more often present with high viral load, elevated transaminases and severe liver damage than HBeAg-negative subjects. HBeAg-positive hepatitis B is frequent among patients who acquired their infection at birth or early childhood and is more common in areas of high endemicity, like South East Asia and Africa. This is also where the largest populations of HCC patients are found. Hepatitis B is not linked to alcohol in the same manner as HCV. HBV infection is less prevalent than HCV among alcoholic patients and the use of alcohol is limited in many countries with a high prevalence of HBV infection. Considering the potentially harmful effect of alcohol on the liver, it is likely to affect the prognosis of any chronic liver disease and some studies have analysed the interplay of alcohol and HBV infection.
Table 4. Prevalence of liver abnormalities according to alcohol consumption in 932 HBsAg carriers and 1704 controls over age 20 years in the Yaeyama District, Okinawa, Japan, 198285
| Alcohol consumption |
|---|
- p& lt 0.001, analysis was done between nondrinkers and light or heavy drinkers among HBsAg carriers.
- **
- p& lt 0.001, analysis was done between nondrinkers and heavy drinkers among controls.
Reprinted with permission from the publisher .
Scott A. Elisofon, Maureen M.F. Jonas, in, 2012
Question 5 What Is The Natural History Of Hepatitis B Surface Antibody During Acute Hepatitis B Infection And Convalescence
HBsAg can be detected in the blood 4 to 10 weeks after exposure. This corresponds to onset of symptoms and viremia detectable by nucleic acid amplification methods. Most hepatitis B infections are self-limited and are associated with disappearance of HBsAg within 4 weeks of onset of symptoms. The anti-HBs then appears and increases to a plateau level that persists indefinitely.2
Recommended Reading: Ok Google How Do You Get Hepatitis C
Diagnosed With Chronic Hepatitis B What Do The Hbe Blood Tests Mean
Your liver specialist has informed you that you have a chronic hepatitis B infection, and that he wants to run additional blood work so he can learn more about your HBV. Some of this blood work may need to be repeated over a period of time, but over the next 6 months or so, your doctor will determine whether or not you are a good candidate for treatment. Regardless, he will definitely want to continue monitoring. Remember, treatment is important, but rarely an emergency, so be patient.
Now you need additional lab work to determine your HBe status, which will tell you whether or not you are HBeAg and HBeAb negative or positive. This reveals a great deal about your HBV such as whether or not the virus is replicating, and how infectious you are to others.
At this point, it is helpful to have a little background on antigens and antibodies. An antigen is a foreign substance in your body that evokes an immune response. This may include viruses, bacteria or other environmental agents such as pollen or a chemical. In this case, it is the HBV e antigen. Your previous hepatitis B panel tested for the surface antigen, or HBsAg.
Additional blood work ordered by your liver specialist will further clarify your HBeAg and over-all HBV status, and whether or not treatment may benefit you.
More next time
What Is The Difference Between Hepatitis B Surface Antibody And Antigen
An antigen is a substance that induces antibody production. Hepatitis B surface antigen is a protein on the surface of hepatitis B virus.
Hepatitis B surface antibodies are produced by the bodys immune system in response to HBsAg. The presence of adequate hepatitis B surface antibodies in the blood indicates protection against hepatitis B virus infection.
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
Hepatitis B Antibody Reactive Means
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
Question 1 What Is The Clinical Indication For Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Quantitation

Hepatitis B surface antibody quantitation is used to determine hepatitis B immune status, ie, to determine if the patient has developed immunity against the hepatitis B virus. Such immunity may develop following exposure to the hepatitis B virus or its vaccine.
Patients at higher risk of exposure to the virus include:
- Infants born to infected mothers
- Sex partners of infected persons
- People with more than 1 sex partner in the last 6 months
- People with a history of sexually transmitted infection
- Men who have sex with men
- Injection drug users
- Household contacts of an infected person
- Healthcare and safety workers who have contact with blood and body fluids
- People who have lived or traveled in an area in which hepatitis B is common
- People who live or work in a prison
Testing is not recommended routinely following vaccination. It is advised only for people whose subsequent clinical management depends on knowledge of their immune status. These people include:
- Chronic hemodialysis patients
- Immunocompromised people, including those with HIV infection, hematopoietic stem-cell transplant recipients, and people receiving chemotherapy
- Infants born to women who test positive for the hepatitis B surface antigen
- Sex partners of people who test positive for the hepatitis B surface antigen
- Healthcare and public safety workers who have contact with blood or body fluids
You May Like: How Much Cost Hepatitis C Treatment
What Are The Different Types Of Hepatitis B
In most of the adult cases of hepatitis B , the virus is completely cleared from the body upon treatment. However, the remaining 5% can go on to develop chronic forms of the disease. It has been observed that within 6 months of the treatment, most people not only clear the virus but also become immune to the same. In general, there are 3 distinct types of hepatitis B infections seen:Healthy Chronic Carriers These people carry the virus but dont develop any symptoms. They are not infectious to others but have a higher risk of developing hepatic conditions such as cirrhosis. However, if the immune system in such individuals gets suppressed owing to an infection or treatment via immunosuppressant drugs, there are chances that they may develop hepatitis B infection. Chronic Infectious Carriers They are the contagious carriers of the disease as they have virus replicating in their systems. They show signs of hepatitis such as damaged liver that progresses into liver cirrhosis. Only 5% of the cases can show remission of the virus.Chronic Mutant The chronic mutant form is a result of a mutated strain of the virus that causes permanent alteration to the hepatitis B viruss genetic makeup. Those with it have the risk of being infectious to others and it is observed to be more resistant to treatment than other forms of hepatitis B.
Question 7 Is Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Antibody Always Acquired After A Completed Vaccination Protocol
No. After 3 intramuscular doses of vaccine, > 90% of healthy adults and > 95% of those < 19 years of age develop immunity .1 However, there is an age-specific decline in development of immunity. After age 40 years, about 90% of people become immune, but by age 60 years, only 75% of people become immune.1 Larger vaccine doses or an increased number of doses are required to induce immunity in many hemodialysis patients and in other immunocompromised people.1
References
This FAQ is provided for informational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice. A clinicians test selection and interpretation, diagnosis, and patient management decisions should be based on his/her education, clinical expertise, and assessment of the patient.Document FAQS.105 Revision: 0
Don’t Miss: How Is Hepatitis B Contracted