Hepatitis C And Health
How can health-care personnel avoid exposure to HCV?
Avoiding occupational exposure to blood is the primary way to prevent transmission of bloodborne illnesses among health-care personnel. To promote blood safety in the workplace, health-care personnel should consult infectious-disease control guidance from the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health and from CDC. Depending on the medical procedure involved, Standard Precautions may include the appropriate use of personal protective equipment .
What is the risk of acquiring hepatitis C after being accidentally exposed to HCV-contaminated blood or body fluids in the workplace?
Although sharps injuries have decreased in recent decades due to improved prevention measures, they continue to occur, placing health-care personnel at risk for several bloodborne pathogens like hepatitis C. A recent analysis of several studies revealed an overall 0.2% risk for infection among those exposed to HCV-antibody-positive blood through needlestick or sharps injuries . Updated guidelines for management and treatment of hepatitis Cexternal icon are available to provide guidance for health-care personnel who become infected via exposure to contaminated blood at the workplace.
Other than needlesticks, do other exposures place health-care personnel at risk for hepatitis C?
Should HCV-infected health-care personnel be restricted in their work?
Articles On Hepatitis C
If you’ve just been diagnosed with hepatitis C, you may wonder how you got it and worry about passing on the virus to a loved one. If you’ve had the disease for a long time without knowing it, you could dwell on every little incident in the past where you might have accidentally exposed a family member to the disease.
It’s important to remember that hepatitis C isn’t easy to catch. If you take a few precautions, it’s almost impossible to pass on the disease to someone else.
Who Is At Risk
Anyone who has not been vaccinated or previously infected can get infected with the hepatitis A virus. In areas where the virus is widespread , most hepatitis A infections occur during early childhood. Risk factors include:
- poor sanitation
- living in a household with an infected person
- being a sexual partner of someone with acute hepatitis A infection
- use of recreational drugs
- travelling to areas of high endemicity without being immunized.
Also Check: Is There Any Cure For Hepatitis C
What Do Hepatitis C Symptoms Look Like
Hepatitis C infection can go through two stages: acute and chronic. In the early, or acute stage, most people don’t have symptoms. If they do develop symptoms, these can include:
- flu-like symptoms, tiredness, high temperature and aches and pains
- loss of appetite
- tummy pain
- jaundice, meaning your skin and the whites of your eyes turn yellow
While for some people, the infection will clear without treatment, in most cases, acute infection will develop into long-term chronic infection. Chronic infection may not become apparent for a number of years until the liver displays signs of damage. These symptoms can include:
- mental confusion and depression these are specific to hepatitis C
- constantly feeling tired
- nausea, vomiting or tummy pain
- dark urine
- feeling bloated
- joint and muscle pain
Without treatment, chronic hepatitis C can cause scarring of the liver , which can cause the liver to stop working properly. A small number of people with cirrhosis develop liver cancer and these complications can lead to death. Other than a liver transplant, theres no cure for cirrhosis. However, treatments can help relieve some of the symptoms.
Risks Associated With Hepatitis C In Pregnancy
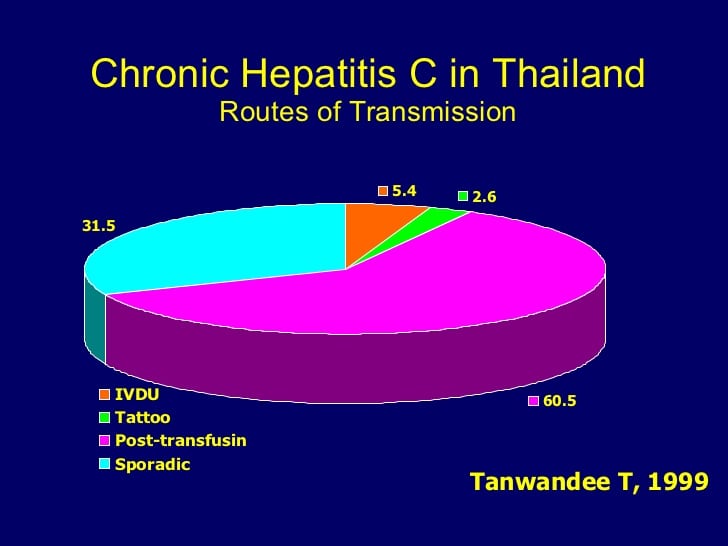
The clearest and most serious risk associated with maternal hepatitis C in pregnancy is transmission of the infection to the baby. There are several factors that influence the risk of mother-to-infant transmission:
- risk of transmission is estimated to be 5.8% among antibodypositive and RNA-positive women
- the highest reported transmission rates occur in infants born to mothers who are both hepatitis C and HIV positive, with rates as high as 36%
- risk of transmission is increased with a higher maternal viral load of hepatitis C
- risk is increased with intrapartum invasive procedures and episiotomy
- transmission does not appear to be influenced by mode of birth or gestational age at birth
- prolonged rupture of membranes may increase the risk of transmission , however this could be related to maternal viral load and length of membrane rupture
- amniocentesis in women infected with hepatitis C does not appear to significantly increase the risk of vertical transmission but very few studies have properly addressed this possibility
- there is no evidence that breastfeeding is associated with an increased risk of hepatitis C transmission to the newborn , unless the nipples are cracked and/or bleeding .
Also Check: How Do You Contact Hepatitis A
What Treatments Are Available For Viral Hepatitis
Many medications are available for the treatment of chronic HBV and HCV infection. For chronic HBV infection, there are several antiviral drugs. People who are chronically infected with HBV require consistent medical monitoring to ensure that the medications are keeping the virus in check and that the disease is not progressing to liver damage or cancer.
There are also antiviral medications available for HCV treatment and new treatments have been approved in recent years. Many antiviral HCV treatments can cure more than 90 percent of people who take them within 8 to 12 weeks. HCV treatment dramatically reduces deaths, and people who are cured are much less likely to develop cirrhosis or liver cancer. However, not everyone infected with HCV needs or can benefit from treatment. NIDA researchers have identified genes that are associated with spontaneous clearance of HCV. These genes also enable people who are unable to clear HCV on their own to respond more favorably to treatment medications. This new information can be used to determine which patients can benefit most from HCV treatment. More studies must be done, but this is a first step to personalized medicine for the treatment of HCV.
Whos At Risk For Hepatitis C
You might be more likely to get it if you:
- Inject or have injected street drugs
- Were born between 1945 and 1965
- Got clotting factor concentrates made before 1987
- Received a blood transfusion or solid organ transplants before July 1992
- Got blood or organs from a donor who tested positive for hepatitis C
- Are on dialysis
Recommended Reading: How To Find Out If You Have Hepatitis
Table 2 Indications For Hav Hbv And Hcv Testing19
Suspect acute hepatitis
- Most chronic viral hepatitis infections are asymptomatic.
- ALT may or may not be elevated. No need to routinely test for AST.
- If HBsAg is positive for > 6 months, this confirms chronic HBV infection.
- The presence of anti-HCV can indicate current or past HCV infection. An HCV RNA is needed to confirm active HCV infection. Around 75% of initial HCV infections progress to chronic infection, usually within 6 months.
- If already diagnosed with viral hepatitis, see Appendix 7 Recommended Test for Individuals Already Diagnosed with Viral Hepatitis. Consult with a specialist as needed for HCV infection. Consultation with, or referral to a specialist is strongly recommended for chronic HBV infection.
Illicit drug use current or ever
Persons who are, or were incarcerated
Gay, bisexual and men who have sex with men
* See Appendix 2 for further information on Hepatitis Laboratory Tests and Appendix 3 for Hepatitis B Serology Results and Interpretation.
What Is The Relationship Between Drug Use And Viral Hepatitis
Drug and alcohol use places people at particular risk for contracting viral hepatitis. Engaging in risky sexual behavior that often accompanies drug use increases the risk of contracting HBV and, less frequently, HCV. People who inject drugs are at high risk for contracting HBV and HCV from shared needles and other drug preparation equipment, which exposes them to bodily fluids from other infected people. Because drug use often impairs judgement, PWID repeatedly engage in these unsafe behaviors, which can increase their risk of contracting viral hepatitis. One study reported that each person who injects drugs infected with HCV is likely to infect about 20 others, and that this rapid transmission of the disease occurs within the first 3 years of initial infection.4 Drug and alcohol use can also directly damage the liver, increasing risk for chronic liver disease and cancer among those infected with hepatitis. This underscores that early detection and treatment of hepatitis infections in PWID and other people who use drugs is paramount to protecting both the health of the person and that of the community.
Recommended Reading: Treatment For Liver Cirrhosis Hepatitis B
Hcv In Chronic Kidney Disease
Hepatitis C adversely affects survival in those with chronic kidney disease, especially those on dialysis. In addition, HCV seems to play a role in the rate of progression of kidney disease. Drug metabolism of many of the drugs used for HCV is altered in people with severe renal impairment and those on dialysis. Sufficient data is available for the following statement to be made by the American Association for the Study of Liver Disease and the Infectious Disease Society of America:
No dose adjustment in direct-acting antivirals is required when using recommended regimens
Excellent cure rates have been shown for direct acting agents in chronic kidney disease including those on dialysis.
Why Getting Tested Is Important
A blood test is one of the only ways to confirm a diagnosis of hepatitis C. Additionally, hepatitis C often has no visible symptoms for many years.
Because of this, its important to be tested if you believe youve been exposed to the virus. Getting a timely diagnosis can help ensure you receive treatment before permanent liver damage occurs.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Get Hepatitis A And B
Sexual Transmission And Viral Hepatitis
Certain adults who are sexually active should be vaccinated against hepatitis B.
CDC and the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices recommend hepatitis B vaccination for
- sexually active people with more than one sex partner during the previous 6 months
- people seeking evaluation or treatment for a sexually transmitted disease
- sex partners of people with hepatitis B and
- men who have sex with men .
CDC recommends one-time hepatitis C testing of all adults and regular testing for people with risk factors.
Contaminated Needles And Infected Blood
You can get hepatitis C from sharing contaminated needles, syringes and other injecting equipment during recreational drug use. Banknotes and straws used for snorting may also pass the virus on.
Being exposed to unsterilised tattoo and body piercing equipment can also pass hepatitis C on. Occasionally, you can get it from sharing a towel, razor blades or a toothbrush if there is infected blood on them.
Hepatitis C infection is also passed on in healthcare settings, from needle stick injuries or from medical and dental equipment that has not been properly sterilised. In countries where blood products are not routinely screened, you can also get hepatitis C by receiving a transfusion of unscreened blood and blood products.
You can prevent hepatitis C by:
- never sharing needles and syringes or other items that may be contaminated with infected blood
- only having tattoos, body piercings or acupuncture in a professional setting, where new, sterile needles are used
- following the standard infection control precautions, if youre working in a healthcare setting.
Read Also: Hepatitis A Vaccine At Cvs
Hcv Transmission By Blood
HCV transmission has considerably changed, reflecting both the evolution of medicine, in particular the cloning of the HCV, and health and social changes. The main modes of HCV transmission are parenteral exposure, unapparent parenteral transmission and occupational exposure. Blood transfusion was the main risk factor for HCV infection before donor screening for surrogate marker testing for non-A and non-B hepatitis which began in the mid-1980s, followed by screening for antibodies to HCV in 1990 . After 1985, the incidence of post-transfusion HCV infection has been halved by excluding HIV-positive people in developed countries . Moreover, since 1993, the availability of more sensitive tests has further reduced this prevalence. However, given that anti-HCV antibodies are not detectable for several weeks or months in recently infected donors blood, in some countries, all donations are tested by nucleic acid amplification tests for the presence of HCV RNA. The WHO reports that 39 countries do not routinely screen blood transfusions for blood-borne viruses . The generalised epidemic of HCV infection in Egypt is an example of health careassociated transmission originating from unsafe injection practices, where, in 2015, HCV RNA prevalence was 7.7% in some regions .
In Italy, in 2013, the prevalence was 80.8/100,000 in first time donors and the incidence rate was 2.5/100,000 in first time donors .
Side Effects And Drugdrug Interactions
The directacting antivirals have an excellent side effect profile and are generally well tolerated. The most common side effects of are headache , fatigue , nausea , asthenia
A major drug interaction with both of these drugs occurs with amiodarone. Serious symptomatic bradycardia has been associated with velpatasvirsofosbuvir and amiodarone, especially in those with advanced liver disease or underlying heart disease. Therefore, co-administration of velpatasvirsofosbuvir or amiodarone is not recommended for people without alternative treatment options.
In addition, drugs that are inducers of Pglycoprotein and/or inducers of certain cytochrome P enzymes may decrease the serum concentrations of sofosbuvir and/or velpatasvir resulting in a decreased potency of the combination. Certain established clinically significant drug interactions have also been described. Statins and proton pump inhibitors are generally held during treatment of hepatitis C.
Don’t Miss: What Are The First Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis Bhepatitis C Coinfection
The clinical course of HCV is thought to be worsened by HBV coinfection. Those with chronic HCV and active HBV coinfection have a more severe degree of liver fibrosis and a higher risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma than with HCV alone. Some studies, however, have suggested that an active HBV infection, but not previous infection, actually suppresses the replication of H. One study in antiHCV positive subjects found a significantly lower prevalence of HCV RNA in those with active HBV infection than in those who had recovered from HBV infection .
Several cases of reactivation of dormant hepatitis B have been reported when treatment of HCV is undertaken, including a few with severe liver injury requiring urgent liver transplantation. Those who are antiHBc positive are at risk. Because of this, we recommend referral of these people to a specialist for HCV treatment whenever antiHBc or HBsAg is present.
Definition Of Hbv Prevalence
The prevalence of hepatitis B infection is defined as the number of persons living with chronic HBV infection in the total population. Although research studies often use HBsAg carrier status as a marker for chronic infection, the CDC defines chronic HBV infection as the presence of HBsAg, HBeAg, or HBV DNA in the absence of IgM antibodies to hepatitis B core antigen , which are seen in acute infection. The HBV prevalence in the United States is impacted by the number of acute HBV infections, the rate of progression from acute to chronic infection, the number of individuals with chronic HBV infection migrating into or out of the country, the number of persons who have spontaneous resolution of HBV or are cured with therapy, and the rate of death among chronically infected individuals.
Read Also: Where To Get Hepatitis B Test
What Do I Do If I Find Out I Have Viral Hepatitis
After learning from your doctor that you have hepatitis, your first step will be to learn more about the virus. Read government resources, like the websites listed below, to find current, scientific information. Adopting a healthy lifestyle is important to prevent the virus from becoming serious. Dont drink or misuse drugs because they are hard on your liver. Get plenty of rest, eat healthy foods, and exercise. Work to protect others by not donating blood or participating in risky behaviors, including sharing needles when using drugs or having unprotected sex.
Getting Tested Is The Only Way To Know If You Have Hepatitis C
A blood test called a hepatitis C antibody test can tell if you have been infected with the hepatitis C viruseither recently or in the past. If you have a positive antibody test, another blood test is needed to tell if you are still infected or if you were infected in the past and cleared the virus on your own.
- Are 18 years of age and older
- Are pregnant
- Currently inject drugs
- Have ever injected drugs, even if it was just once or many years ago
- Have HIV
- Have abnormal liver tests or liver disease
- Are on hemodialysis
Read Also: What Is Hepatitis C From
Clinical Utility Of Testing
The clinical utility of testing for hepatitis C in pregnancy is limited by the lack of effective treatment options to avoid mother-to-child transmission during pregnancy or childbirth .
However, new treatment options for people living with hepatitis C have become available and were recently listed on the Australian Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme . While these treatments have not been proven to be safe in pregnancy or during breastfeeding , women who are diagnosed with hepatitis C during pregnancy could commence such curative treatment after completion of breastfeeding , thus reducing their risk of significant liver disease and the risk of perinatal infection for subsequent pregnancies.
In addition, knowledge of a womans hepatitis C status means interventions that may increase the risk of mother-to-baby transmission can be avoided.
Targeted Versus Universal Testing
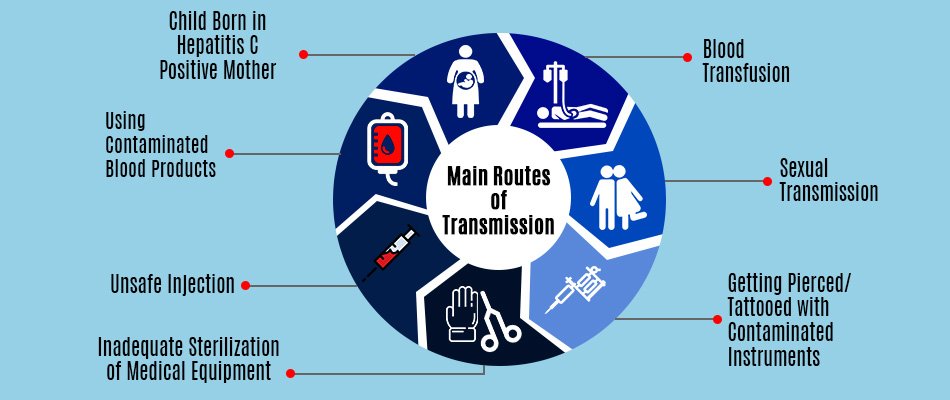
Studies were largely consistent in finding that hepatitis C seropositivity was associated with the following risk factors:
- injecting drug use
- receipt of blood transfusion or organ transplant
- history of tattooing or body piercing
- use of intranasal cocaine
- incarceration
- origin from a country of high prevalence these include Africa and central and east Asia .
Additional findings were:
- only high severity risk factors were significantly associated with testing positive for hepatitis C antibodies
- age, history of prior pregnancy and healthcare employment were additional considerations .
However, studies have estimated that, compared to universal testing, targeted testing would fail to identify 2.5 to 27% of seropositive women .
Read Also: Can Hepatitis C Turn Into Hiv