When To Call A Professional
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that anyone born between 1945 and 1965 consider getting a one-time blood test for hepatitis C.
High-risk individuals should be tested for hepatitis C. High-risk individuals include anyone who:
- Received transfusions of blood or blood products before 1992
- Received an organ transplant before 1992
- Has ever injected drugs or snorted cocaine
- Has been on long-term hemodialysis
- Has had multiple sexual partners
- Has a long-term sexual partner with hepatitis C
- Lives in the same household as someone with hepatitis C
- Has evidence of liver disease
What Are The Side Effects Of Treatments For Hepatitis C Infection
Side effects of interferon or pegylated interferon
- The most common side effects of interferon or pegylated interferon include fever, flu-like symptoms, and depression. Patients must be monitored closely for depression. Risk of suicide is a reason to avoid interferons.
- Interferons also reduce white blood cell and/or red blood cell counts . This may cause increased susceptibility to infection. Interferons also increase the risk of certain cancers. Death rarely occurs as a result of therapy, but may occur from progression of liver failure in patients with advanced cirrhosis.
Side effects of ribavirin
- Ribavirin most commonly causes anemia due to destruction of red blood cells . This can be severe enough that people with heart disease may suffer a heart attack from insufficient blood flow, so people with heart disease should not receive this drug. Anemia improves with a reduction in the dose of ribavirin. Injected growth factor that stimulates the production of red blood cells often is used to improve the anemia associated with ribavirin. Ribavirin also accumulates in the testicles and ovaries and causes birth defects in animals. Although no birth defects have been reported in humans, both men and women should use contraceptive measures to avoid pregnancy during and for at least six months after ribavirin treatment.
Side effects of DAAs
- The most common and significant side effects of boceprevir , sofosbuvir , and ledipasvir/sofosbuvir include
- fatigue ,
Complications Of Hepatitis C
If the infection is left untreated for many years, some people with hepatitis C will develop scarring of the liver .
Over time, this can cause the liver to stop working properly.
In severe cases, life-threatening problems, such as liver failure, where the liver loses most or all of its functions, or liver cancer, can eventually develop.
Treating hepatitis C as early as possible can help reduce the risk of these problems happening.
Also Check: What Are The Early Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
How Is Acute Hepatitis C Treated
Acute hepatitis C is typically monitored and not treated. Treatment during the acute stage doesnt change the risk that the disease will progress to the chronic form. An acute infection may resolve on its own without treatment. The following treatment may be all thats necessary:
- proper rest
- adequate fluids
- a healthy diet
Some people may need treatment with prescription medication. Your doctor will be able to work with you about what treatment options may be best for you.
Those most at risk for acute and chronic hepatitis C are people who use or share contaminated needles. Mothers can transmit HCV to their babies during childbirth, but not through breastfeeding. Other risk factors for transmission of HCV include:
- healthcare work, especially work around needles
- getting a tattoo or body piercing with unsterile equipment
- undergoing hemodialysis
- living in a household with someone with HCV
- sharing personal hygiene products, such as razors or toothbrushes
- engaging in sexual activity with multiple partners without condoms or dental dams
- having a blood transfusion or organ transplant before July 1992 or receiving clotting factors before 1987
The most serious long-term risk of acute hepatitis C is developing chronic hepatitis C, which can lead to cirrhosis and liver cancer. In 75 to 85 percent of those with acute hepatitis C, the disease will progress to the more serious chronic hepatitis C.
Chronic Hepatitis C Symptoms

There are often no symptoms in the early stages of hepatitis C infection. The symptoms only become apparent when the liver has already been damaged.
The symptoms of liver disease resulting from HCV can include:
- Bleeding and bruising easily
- Itching
Other signs of a hepatitis C infection can include confusion, drowsiness, and slurred speech.
These are the general symptoms of liver disease. Hepatitis C is one of a number of causes of liver disease. A doctor will be able to diagnose whether hepatitis C is causing these symptoms through a blood test.
Read Also: How Do People Catch Hepatitis B
Chronic Hepatitis Cirrhosis Adenoma Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Hepatocyte necrosis and mitosis of chronic hepatitis favor nodular regeneration, which in appropriate circumstances, is followed by hepatocyte dysplasia and carcinoma.
In many parts of the world HCC is among the leading causes of cancer-related mortality, and the third most common cause of cancer death in the world. Japan, for example, unlike other Asian countries, also has a high proportion of HCC caused by HCV infection accounting for 80 to 90% of all cases, while in the western world hepatocellular carcinoma is known to complicate cirrhosis secondary to hepatitis C in 2-6% per year.
There is currently no evidence that HCV by itself is oncogenic however, HCC may rarely develop in non-cirrhotic HCV-infected individuals, so a direct oncogenic effect cannot be excluded. However, in the pathogenesis of HCC associated with HCV, it remains controversial whether the virus plays a direct or indirect role. Recent studies using transgenic mouse models, in which the core protein of HCV has an oncogenic potential, indicate that HCV is directly involved in hepatocarcinogenesis, albeit other factors such as continued cell death and regeneration associated with inflammation would also play a role.
Almost all HCC occurs in the liver of patients with chronic hepatitis and liver cirrhosis, caused by HBV and HCV. Consequently, eradication of these hepatitis viruses with anti-viral agents and chemoprevention methods may decrease the risk of HCC.
What Are The Complications Of Undiagnosed Hepatitis C
- Hepatitis C is known to be associated with two skin conditions, lichen planus and porphyria cutanea tarda.
- Diabetes, heart disease, and arterial blockage are more common among patients with chronic hepatitis C infection than in the general population. It may be that liver damage and chronic inflammation caused by hepatitis C may affect the levels of blood fats and blood sugar.
- Low platelet counts may occur as a result of the destruction of platelets by antibodies.
Recommended Reading: Chronic Hepatitis C Without Hepatic Coma
Getting Tested Is The Only Way To Know If You Have Hepatitis C
A blood test called a hepatitis C antibody test can tell if you have been infected with the hepatitis C viruseither recently or in the past. If you have a positive antibody test, another blood test is needed to tell if you are still infected or if you were infected in the past and cleared the virus on your own.
- Are 18 years of age and older
- Are pregnant
- Currently inject drugs
- Have ever injected drugs, even if it was just once or many years ago
- Have HIV
- Have abnormal liver tests or liver disease
- Are on hemodialysis
How Do You Treat Hepatitis C
People with acute infection do not always need treatment, because their immune system may clear hepatitis C on its own. If you test positive during the acute stage, your doctor may ask you to come back after a few months to re-test and to see if you need any treatment.
If people develop chronic infection, they will need treatment to help clear the virus. Where available, treatment with drugs called direct-acting antivirals can cure hepatitis in most cases. These are usually taken for 8-12 weeks. Your doctor will also check your liver for any damage.
If youve had hepatitis C in the past, youre not immune to future infections which means you can get it again. You can also still get other types of hepatitis, and having hepatitis C together with another type is more serious.
If youve already had hepatitis C, its advisable to have the vaccination against hepatitis A and B to protect your liver from further damage.
Whether you have symptoms or not, dont have sex until your healthcare professional says you can.
Also Check: How Is Hepatitis A Caused
Is Screening For Hepatitis C Recommended During Pregnancy
There is a 4%-7% risk of transmitting HCV from mother to infant with each pregnancy. Currently, there is no CDC recommendation for routine hepatitis C screening during pregnancy, and there is no currently recommended medicine to prevent transmission from mother to infant . However, CDC is monitoring research findings and may make recommendations in the future as evidence arises.
While data is still limited, a recent study of over 1,000 cases in the United Kingdom found that 11% of infants had been infected at birth, and that these infants were likely to develop cirrhosis in their early 30s. The case for screening for HCV during pregnancy includes the potential to safely treat mothers during pregnancy with direct-acting antiviral agents to treat the mother before cirrhosis develops, prevent infant transmission, and prevent transmission to others. Children born to HCV-infected mothers may also be offered treatment at an early age to prevent cirrhosis, as well as transmission to others. Coordination of care between multiple specialists will be important to accomplish these goals.
Children of HCV-infected mothers may be screened for hepatitis C as early as 1-2 months of age using hepatitis C viral load or PCR testing . Antibodies to hepatitis C passed from the mother to child will be present for up to 18 months, so children should be tested for HCV antibody no earlier than this.
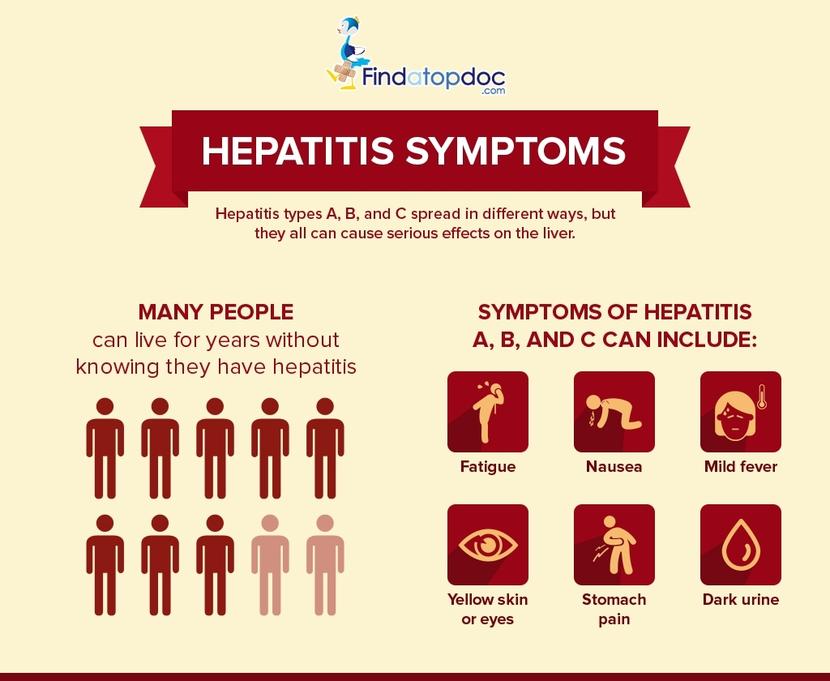
Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
The problem with hep C is that most people will live with the virus without showing any signs. Not only does this place them at risk of not getting treatment, but during this time, they can also spread the virus without knowing. However, after someone gets infected with HCV, usually two weeks to 6 months after the virus enters the bloodstream, theyll experience some symptoms that last for 2 to 12 weeks. The most common symptoms include:
- Clay-colored poop
- Weight loss
- Fluid buildup in the abdominal cavity or legs
Many people eventually develop chronic liver disease, ranging from mild to severe, including cirrhosis and liver cancer. Chronic liver disease in people with hepatitis C usually happens slowly, without any signs or symptoms, over several decades. However, for alcohol abusers, this can happen sooner.
Also Check: What Is Hepatitis B Vaccine For
What Causes Hepatitis C In The First Place
When your blood is exposed to a hep-C infected persons blood, the virus beelines to your liver and rapidly reproduces. As this happens, the virus sends your immune system into overdrive as it works to eliminate those infected liver cells.
Over time, the way in which your immune system goes about destroying those infected cells can ultimately lead to your liver scarring, which can affect its ability to function properly.
Youre at a higher risk of getting hep C if you:
People With Hepatitis C Should Not Eat
- Calories : Increasing calories means gaining weight or being obese, while increasing the risk of diabetes. To cut calories, limit foods: high in fat, processed, canned, and fast foods.
- Salt: Salty foods can lead to water retention, thus increasing blood pressure, which is extremely dangerous for people with cirrhosis.
- Sugar : Foods that contain sugar are often high in fat, which can easily cause weight gain.
- Raw or unpasteurized products: Sushi or other raw foods may contain bacteria that aggravate hepatitis C. You should also avoid raw eggs, unpasteurized milk and cheese.
Recommended Reading: Antiviral Drugs For Hepatitis A
Whats The Difference Between Acute And Chronic Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a contagious disease caused by HCV, which is spread through contact with blood and bodily fluids that contain HCV. This disease damages your liver. There are two types of hepatitis C infection: acute and chronic.
Acute hepatitis C is a short-term viral infection. People with acute hepatitis C carry the infection for a small window of time, often just several months . Most people with the acute form of hepatitis C will experience illness and mild symptoms such as fatigue and vomiting within the first six months after exposure. In many cases, the disease causes no symptoms at all.
Acute hepatitis C may improve or resolve without treatment. It leads to chronic infection in 75 to 85 percent of cases. The chronic form may cause long-term problems in your liver, including liver damage and liver cancer.
HCV is spread through direct contact with blood or certain bodily fluids that contain HCV. Its safe to engage in the following activities without worry of transmission:
- hugging
- light, clay-colored bowel movements
- jaundice, or yellowing of the skin and eyes
If your doctor suspects that you have hepatitis C, they will draw blood to check for HCV antibodies. Antibodies are substances your body produces when its fighting an infection. If you have them, your doctor may order a second test to confirm that the virus is still present.
North America And Western Europe
The most common malignant tumors in the liver represent metastases from tumors which originate elsewhere in the body. Among cancers that originate from liver tissue, HCC is the most common primary liver cancer. In the United States, the US surveillance, epidemiology, and end results database program, shows that HCC accounts for 65% of all cases of liver cancers. As screening programs are in place for high-risk persons with chronic liver disease, HCC is often discovered much earlier in Western countries than in developing regions such as sub-Saharan Africa.
Acute and chronic hepatic porphyrias and tyrosinemia type I are risk factors for hepatocellular carcinoma. The diagnosis of an acute hepatic porphyria should be sought in patients with HCC without typical risk factors of hepatitis B or C, alcoholic liver cirrhosis, or hemochromatosis. Both active and latent genetic carriers of acute hepatic porphyriasare at risk for this cancer, although latent genetic carriers have developed the cancer at a later age than those with classic symptoms. Patients with acute hepatic porphyrias should be monitored for HCC.
The incidence of HCC is relatively lower in the Western Hemisphere than in Eastern Asia. However, despite the statistics being low, the diagnosis of HCC has increased since the 1980s and it is continuing to increase, making it one of the rising causes of death due to cancer. The common risk factor for HCC is hepatitis C, along with other health issues.
You May Like: What Is Autoimmune Hepatitis C
Alcohol And Other Toxins
Excessive alcohol consumption can cause liver damage and inflammation. This is sometimes referred to as alcoholic hepatitis. The alcohol directly injures the cells of your liver. Over time, it can cause permanent damage and lead to liver failure and cirrhosis, a thickening and scarring of the liver.
Other toxic causes of hepatitis include overuse or overdose of medications and exposure to poisons.
What Laboratory Tests Diagnose Hepatitis C
Laboratory blood tests will be done to evaluate the patient’s liver function and to look for hepatitis C antibodies . If these tests indicate that the person has hepatitis C, a hepatitis C “viral load” test will be done. This looks for genetic material from the hepatitis C virus and measures the quantity of hepatitis C virus that is circulating in the patient’s blood. This is helpful in determining if treatment is appropriate and to monitor the success of the treatment .
Individuals who had hepatitis C in the past and cleared the virus on their own will have a positive HCV antibody test, but there will be no hepatitis C virus genetic material in the blood. If a person is immunosuppressed due to an immunological condition, cancer chemotherapy, immunotherapy or HIV/AIDS, the test results may be different and need to be evaluated accordingly.
Recommended Reading: Hepato Support For Dogs Side Effects
Top Hep C Instagrammers And Bloggers
-
Karen Hoyt, , ihelpc.com
Follow because: As an author, health writer, and speaker, shes become pretty dang comfortable talking about her life with hep C. So much so that she turned her experience with hep C into help for anyone else living with the disease. Her website I Help C is your best friends guide to hepatitis C and cirrhosis, and its chock-full of health and nutrition tips to fuel your liver, and stories of her own experiences that are sure to leave you nodding along.
Acute Vs Chronic Hepatitis C Infection
Acute hepatitis C infection refers to symptoms that appear within 6 months of newly acquiring the virus. About 20% to 30% of those who acquire hepatitis C experience acute illness. After this, the body either clears the virus or goes on to develop chronic infection. Chronic hepatitis C infection refers to long-lasting infection. The majority of people who have acute hepatitis C infection go on to develop the chronic form of the illness.
You May Like: What Are The Symptoms To Hepatitis C
How Does The Hepatitis C Virus Spread
Hepatitis C is a blood-borne infection. It means that its risk increases when you get in contact with blood contaminated with the virus.
These are a few common ways of hepatitis C transmission:
- Sharing needles, syringes, or any equipment to inject drugs.
- An infected mother passing the virus to the child at the time of birth.
- Healthcare professionals not following proper hygiene practices.
- Getting tattoos or piercing in informal settings or with non-sterile instruments.
- Sharing personal items like razors, nail clippers, or toothbrushes.
- Through blood transfusion or organ transplants, especially which are before 1992.
- Having sex, especially if you have HIV.