Managing Fever After Immunisation
Common side effects following immunisation are usually mild and temporary . Specific treatment is not usually required.
There are a number of treatment options that can reduce the side effects of the vaccine such as giving extra fluids to drink and not overdressing if there is a fever.
Although routine use of paracetamol after vaccination is not recommended, if fever is present, paracetamol can be given check the label for the correct dose or speak with your pharmacist, especially when giving paracetamol to children.
Aboriginal And Torres Strait Islander People
Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people are recommended to:
- have their risks and vaccination status for hepatitis B reviewed
- receive testing for previous hepatitis B virus infection
- receive vaccination if non-immune
Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people have a higher risk of acquiring new hepatitis B virus infection than non-Indigenous Australians.2,3
Adult-formulation hepatitis B vaccine should be given in a 3-dose schedule.
Children with HIV are recommended to receive 3 doses of hepatitis B vaccine using an adult formulation. This is double the recommended dose for children. In a limited number of studies, children who were immunocompromised responded better when given higher doses in a 3-dose schedule.4,5
Levels of antibody to hepatitis B surface antigen should be checked after the vaccination course. See Serological testing after hepatitis B vaccination.
Adults with HIV are recommended to receive larger-than-usual doses of hepatitis B vaccine. They should receive 2 injections of the standard adult dose on each occasion at 0, 1, 2 and 6 months. Limited studies in adults with HIV have revealed an improved and accelerated serological response to a schedule that consists of 4 double doses.6,7
A 3-dose schedule at 6, 8 and 12 months after transplant is required using:
Concerns About Immunisation Side Effects
If the side effect following immunisation is unexpected, persistent or severe, or if you are worried about yourself or your child’s condition after a vaccination, see your doctor or immunisation nurse as soon as possible or go directly to a hospital.
It is important to seek medical advice if you are unwell, as this may be due to other illness, rather than because of the vaccination.
Immunisation side effects may be reported to SAEFVIC, the Victorian vaccine safety and reporting service. Discuss with your immunisation provider how to report adverse events in other states or territories.
Recommended Reading: How Many Hepatitis B Shots Are Required
What Hepatitis B Immunisation Involves
Full protection involves having 3 injections of the hepatitis B vaccine at the recommended intervals.
Babies born to mothers with hepatitis B infection will be given 6 doses of hepatitis B-containing vaccine to ensure long-lasting protection.
If you’re a healthcare worker or you have kidney failure, you’ll have a follow-up appointment to see if you have responded to the vaccine.
If you have been vaccinated by your employer’s occupational health service, you can request a blood test to see if you have responded to the vaccine.
How Is Hepatitis B Passed On
The hepatitis B virus is passed from person to person in one of these ways:
- Blood-to-blood contact. For example, drug users sharing needles or other equipment which may be contaminated with infected blood. Healthcare workers can be infected through accidental needlestick injuries.
- Having unprotected sex with an infected person.
- An infected mother passing it to her baby.
- A human bite from an infected person. This is very rare.
Also Check: How Do You Know If You Have Hepatitis
When To Delay Or Avoid Hepb Immunization
Doctors delay giving the vaccine to babies who weigh less than 4 pounds, 7 ounces at birth whose mothers do not have the virus in their blood. The baby will get the first dose at 1 month of age or when the baby is discharged from the hospital.
The vaccine is not recommended if your child:
- is currently sick, although simple colds or other minor illnesses should not prevent immunization
- had a serious allergic reaction after an earlier dose of the vaccine or is allergic to baker’s yeast
How Is The Hepatitis B Vaccine Given
Hepatitis B
The vaccination for hepatitis B is given as 3 injections over a 6-month period–an initial dose, followed by a second dose 1 month later, and a third dose 5 months after the second.
If you need hepatitis A vaccination in addition to hepatitis B, you can do these individually or as a combined vaccine that covers both. The combination vaccine is given as 3 injections over a 6-month period–an initial dose, followed by a second dose 1 month later, and a third dose 5 months after the second.
If you are not able to get the shots on time, it is not necessary to restart the series, but you should continue from the last dose given.
Babies born to mothers who have chronic hepatitis B should get the first shot within 12 hours after birth, followed by a second shot 1 month later, and the third shot 5 months after the second. Babies born to mothers who are not infected with the hepatitis B virus should get the first shot within 1 to 2 months after birth, the second shot a month later, and the third shot 5 months after the second.
You will NOT get hepatitis B from the vaccine.
You will be protected for about 13 years. If it has been many years since you received your hepatitis B vaccination, or if you do not know when you were vaccinated, ask your doctor to check to see if you have antibodies against hepatitis B.
You May Like: What Is Hepatitis C Genotype 1a
Safety Of Hepatitis Vaccines
Hepatitis vaccines have been given to millions of people all across the world without any evidence of serious side effects. “They’re very safe, and they’re extremely effective,” says Poland.
If you are not sure whether you should have hepatitis vaccines, talk with your doctor about your specific concerns.
Show Sources
Hepatitis A And B: Diseases Of The Liver
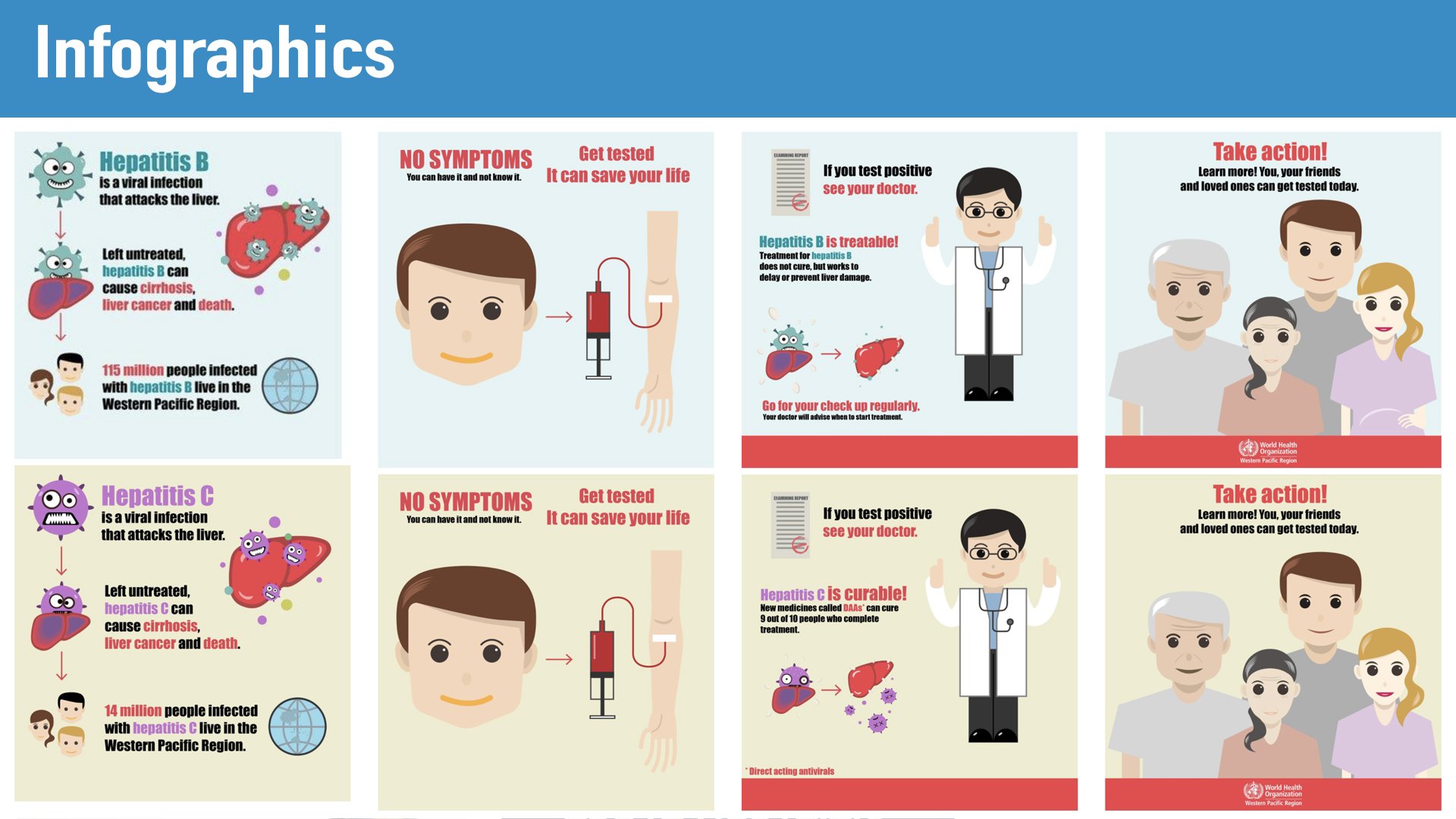
Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver, most often caused by a viral infection. There are three common types of hepatitis caused by viruses: hepatitis A, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C. Vaccines have been developed that protect people from contracting hepatitis A and B. There is no vaccine for hepatitis C.
Hepatitis A and hepatitis B can be spread from person to person, although in different ways. They have similar symptoms, which include abdominal pain, fever, fatigue, joint pain, and jaundice .
Over the last 20 years, there has been a 90% decrease in cases of hepatitis A and an 80% decrease in hepatitis B cases in the U.S. Health experts believe that immunization efforts have led to this drop in rates of infection.
You May Like: Hepatitis B Treatment Side Effects
Should I Be Screened For Hepatitis B
Screening is testing for a disease in people who have no symptoms. Doctors use blood tests to screen for hepatitis B. Many people who have hepatitis B dont have symptoms and dont know they are infected with hepatitis B. Screening tests can help doctors diagnose and treat hepatitis B, which can lower your chances of developing serious health problems.
Your doctor may recommend screening for hepatitis B if you9,14
- are pregnant
- were born in an area of the world where 2 percent or more of the population has hepatitis B infection, which includes Africa, Asia, and parts of the Middle East, Eastern Europe, and South America
- didnt receive the hepatitis B vaccine as an infant and have parents who were born in an area where 8 percent or more of the population had hepatitis B infection, which includes sub-Saharan Africa and parts of Asia
- are HIV-positive
- are a man who has sex with men
- have lived with or had sex with a person who has hepatitis B
- have an increased chance of infection due to other factors
Hepatitis B Vaccine Side Effects
As with any medication, the hepatitis B vaccine may cause some side effects. Most people dont experience any unwanted effects. The most common symptom is a sore arm from the injection site.
When receiving the vaccination, youll likely receive information or a pamphlet regarding the side effects that you might expect, and others that warrant medical attention.
Mild side effects usually last only . Mild side effects of the vaccine include:
- redness, swelling, or itching at the injection site
- a purple spot or lump at the injection site
You May Like: What Is The Treatment For Autoimmune Hepatitis
Prevalence Of Chronic Hepatitis B
The prevalence of chronic hepatitis B virus infection varies between and within countries:58-61
- < 0.5% among Caucasians in the United States, northern Europe and Australia
- 15% in Mediterranean countries, parts of eastern Europe, Africa, and Central and South America
- > 10% in many sub-Saharan African, East and Southeast Asian, and Pacific island populations
Regions where 2% of the population is positive to hepatitis B surface antigen are considered to have moderate to high prevalence. In these regions, people mainly acquire the infection perinatally or in early childhood.55
Facts About Hepatitis B

- Two billion people, or one in three, have been infected with hepatitis B worldwide. Of these, about 260 million live with chronic hepatitis B.
- Each year about 900,000 people die from hepatitis B worldwide, and about 2,000 of these deaths occur in the United States.
- Hepatitis B is transmitted through blood and is 100 times more infectious than HIV. An estimated one billion infectious viruses are in one-fifth of a teaspoon of blood of an infected person, so exposure to even a minute amount, such as on a shared toothbrush can cause infection.
- Hepatitis B is sometimes referred to as the silent epidemic because most people who are infected do not experience any symptoms.
- Liver cancer is the fourth leading cause of cancer deaths throughout the world, behind lung, colorectal and stomach cancers.
- Almost half of liver cancers are caused by chronic infection with hepatitis B.
- The World Health Organization recommends the inclusion of hepatitis B vaccine in immunization programs of all countries in 2017, about 8 of 10 infants born throughout the world received three doses of hepatitis B vaccine.
Also Check: Is Hepatitis B Curable Or Treatable
Prevent Hepatitis B Infections In Newborns
If you are pregnant and have hepatitis B, talk with your doctor about lowering the risk that the infection will spread to your baby. Your doctor will check your virus levels during pregnancy. If virus levels are high, your doctor may recommend treatment during pregnancy to lower virus levels and reduce the chance that hepatitis B will spread to your baby. Your doctor may refer you to a liver specialist to find out if you need hepatitis B treatment and to check for liver damage.
When it is time to give birth, tell the doctor and staff who deliver your baby that you have hepatitis B. A health care professional should give your baby the hepatitis B vaccine and HBIG right after birth. The vaccine and HBIG will greatly reduce the chance of your baby getting the infection.
Transporting Storing And Handling Vaccines
Transport according to National Vaccine Storage Guidelines: Strive for 5.87 Store at +2°C to +8°C. Do not freeze. Protect from light.
Infanrix hexa must be reconstituted. Add the entire contents of the syringe to the vial and shake until the pellet completely dissolves. Use reconstituted vaccine as soon as practicable. If it must be stored, hold at room temperature for no more than 8 hours.
Don’t Miss: Difference Between Hiv And Hepatitis
Babies And Hepatitis B Vaccination
Pregnant women have a routine blood test for hepatitis B as part of their antenatal care.
Babies born to mothers infected with hepatitis B need to be given a dose of the hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of their birth, followed by further doses at 4, 8, 12 and 16 weeks of age, plus a final dose when they’re 1 year old.
Babies of mothers identified by the blood test as particularly infectious might also be given an injection of HBIG at birth on top of the hepatitis B vaccination to give them rapid protection against infection.
All babies born to mothers infected with hepatitis B should be tested at 1 year of age to check if they have become infected with the virus.
Who Should Not Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine
Generally seen as a safe vaccine, there are some circumstances in which doctors advise against receiving the HBV vaccine. You shouldnt have the hepatitis B vaccine if:
- youve had a serious allergic reaction to a previous dose of the hepatitis B vaccine
- you have a history of hypersensitivity to yeast or to any other vaccine components
- youre experiencing a moderate or severe acute illness
If youre currently experiencing an illness, you should postpone receiving the vaccine until your condition has improved.
Recommended Reading: How To Cure Alcoholic Hepatitis
What Are Clinical Trials For Hepatitis B
Clinical trialsand other types of clinical studiesare part of medical research and involve people like you. When you volunteer to take part in a clinical study, you help doctors and researchers learn more about disease and improve health care for people in the future.
Researchers are studying many aspects of hepatitis B, such as
- progression of hepatitis B and long-term outcomes
- new treatments for hepatitis B
- prevention of reactivated or worsening hepatitis B in people receiving cancer treatment
Safety Checks Before Immunization
For Children being immunized at the public health office:
Your nurse will talk to you about your childs health history before giving your child any vaccines. This will include questions about any medicines your child is taking, health conditions your child has or is experiencing, as well as any allergies your child may have. Your nurse will guide you on what is safe for your child, based on your childs health history.
When your nurse talks to you about your childs health history, it is important that you inform your nurse if your child:
- is sick or has a fever greater than 38.5 C
- has allergies to any part of the vaccine
- is allergic to any foods, drugs, bee stings, etc.
- has a weakened immune system
- has had an allergic reaction or other severe or unusual reaction to this or other vaccines in the past
Your nurse will guide you on what is safe for your child, based on your childs health history.
For Children being immunized at school:
If you have additional questions about the in-school immunization, you can dial for Health Link, or contact the Public Health Nurse who provides immunizations in your school at the number included in the information package.
Also Check: How Does A Person Contract Hepatitis
Do The Benefits Of The Hepatitis B Vaccine Outweigh Its Risks
Every year in the United States about 2,000 people die following an overwhelming hepatitis B virus infection. In addition, every year about 22,000 people are infected with hepatitis B. Some of them will remain chronically infected, putting them at high risk of the long-term consequences of hepatitis B virus infection: cirrhosis and liver cancer. In fact, with the exception of influenza virus, hepatitis B virus causes more severe disease and death in the United States than any other vaccine-preventable disease. On the other hand, the hepatitis B vaccine is an extremely rare cause of a severe allergic reaction called anaphylaxis. To date, no one has died from this reaction, but it is theoretically possible that this could occur.
Because hepatitis B virus is a common cause of severe disease and death in the United States, and because the hepatitis B vaccine does not cause permanent damage or death, the benefits of the hepatitis B vaccine clearly outweigh its risks.
Eating Diet And Nutrition For Hepatitis B
If you have hepatitis B, you should eat a balanced, healthy diet. Obesity can increase the chance of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease , and NAFLD can increase liver damage in people who have hepatitis B. Talk with your doctor about healthy eating and maintaining a healthy weight.
You should also avoid alcohol because it can cause more liver damage.
Read Also: Can Your Body Heal Itself From Hepatitis C
What Might My Child Experience After Immunization
The side effects your child may have after immunization depend on which vaccine they received. To find this information, click on the vaccine name in the Routine Immunization Schedule or from the list of Vaccine Information Sheets.
It is rare to have a serious side effect. Call Health Link at 811 to report any serious or unusual side effects.
Hepatitis B Vaccination In Pregnancy
Hepatitis B infection in pregnant women may result in severe disease for the mother and chronic infection for the baby.
This is why the hepatitis B vaccine is recommended for pregnant women who are in a high-risk category.
There’s no evidence of any risk from vaccinating pregnant or breastfeeding women against hepatitis B.
And, as it’s an inactivated vaccine, the risk to the unborn baby is likely to be negligible .
Read Also: Hepatitis C And Fatty Liver
Hepatitis B In The United States
In the United States, about 862,000 people have chronic hepatitis B.6 Asian Americans and African Americans have higher rates of chronic hepatitis B than other U.S. racial and ethnic groups.10 Researchers estimate that about half of the people living with chronic hepatitis B in the United States are Asian Americans and Pacific Islanders.11 Chronic hepatitis B is also more common among people born in other countries than among those born in the United States.7
The hepatitis B vaccine has been available since the 1980s and, in 1991, doctors began recommending that children in the United States receive the hepatitis B vaccine. The annual rate of acute hepatitis B infections went down 88.5 percent between 1982 and 2015.12 In 2017, the annual number of hepatitis B infections rose in some states.13 Experts think the rise was related to increases in injection drug use. Injection drug use increases the risk of hepatitis B infection.