Who Should Be Vaccinated For Hepatitis B
All newborns should be vaccinated. Also, people who are under 18 who were not vaccinated at birth should also get the vaccine. Other groups who should be sure to be vaccinated are those in certain high-risk categories, such as:
- People who have more than one sexual partner.
- Men who have sex with men.
- Adults with diabetes.
- Sexual partners of infected people and people who share households with infected individuals.
- People who are exposed to blood and other bodily fluids, including healthcare and public safety professionals, and people who work in jails and other places taking care of people who cant take care of themselves.
Is There A Cure For Chronic Hepatitis B
Currently, there is no complete cure for hepatitis B. But when managed properly, those living with the virus can expect to live a normal life. Maintaining a healthy diet and avoiding alcoholic beverages and tobacco products are crucial components in managing the disease.
You should also visit a doctor familiar with hepatitis B at least annuallythough twice a year might be best to monitor your liver through blood tests and medical imaging. As with most diseases, detecting it early leads to a better outcome. If youre exposed to the virus, you should get an antibody injection within 12 hours of exposure.
Can Hepatitis B Be Prevented
The hepatitis B vaccine is one of the best ways to control the disease. It is safe, effective and widely available. More than one billion doses of the vaccine have been administered globally since 1982. The World Health Organization says the vaccine is 98-100% effective in guarding against the virus. Newborns should be vaccinated.
The disease has also been more widely prevented thanks to:
- Widespread global adoption of safe blood-handling practices. WHO says 97% of the blood donated around the world is now screened for HBV and other diseases.
- Safer blood injection practices, using clean needles.
- Safe-sex practices.
You can help prevent hepatitis B infections by:
- Practicing safe sex .
- Never sharing personal care items like toothbrushes or razors.
- Getting tattoos or piercings only at shops that employ safe hygiene practices.
- Not sharing needles to use drugs.
- Asking your healthcare provider for blood tests to determine if you have HBV or if you are immune.
Read Also: Hepatitis B Virus Dna Quantitative
Can I Take The Test At Home
Samples for hepatitis B testing can be collected at home. At-home hepatitis B testing requires a patient to collect a blood sample, typically from a fingerstick using a very small needle provided in the test kit. Once a blood sample is collected, it is prepared according to the instructions contained in the test kit and mailed to a laboratory for testing.
Because there are numerous types of tests for HBV, it is important to look closely at the specific components of any at-home test kit. Many at-home test kits only look for hepatitis B surface antigen .
Who Are Hepatitis B Carriers
Hepatitis B carriers are people who have the hepatitis B virus in their blood, even though they dont feel sick. Between 6% and 10% of those people whove been infected with the virus will become carriers and can infect others without knowing it. There are over 250 million people in the world who are carriers of HBV, with about 10% to 15% of the total located in India. Children are at the highest risk of becoming carriers. About 9 in 10 babies infected at birth become HBV carriers, and about half of children who are infected between birth and age 5 carry the virus. A blood test can tell you if you are a hepatitis B carrier.
Also Check: How Do You Transfer Hepatitis C
What Should You Know About Hepatitis B Before You Travel
Hepatitis B is quite common in China and other Asian countries, where as many as 1 in 12 people have the virus, though many dont know it. Before traveling to those places, you should make sure youve been vaccinated against the virus.
In addition to getting the vaccine, you can take these additional precautions to reduce your risk of contracting the virus:
- Refrain from taking illegal drugs.
- Always use latex or polyurethane condoms during sex.
- Make sure new, sterile needles are used during all piercings, tattoos and acupuncture sessions.
- Avoid direct contact with blood and bodily fluids.
- Know the HBV status of all your sexual partners.
- Ask your doctor about possible vaccination before you travel to a place where hepatitis B is common.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Hepatitis B is a liver disease that can cause serious damage to your health. One reason that is dangerous is that it can easily go undetected for years while damaging your liver. Talk with your healthcare provider about being tested for hepatitis B if you have any reason to believe that you were not vaccinated or if you have engaged in risky behavior. If you do test positive, follow the directions from your healthcare provider so that you can live a longer, healthier and happier life.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 07/09/2020.
References
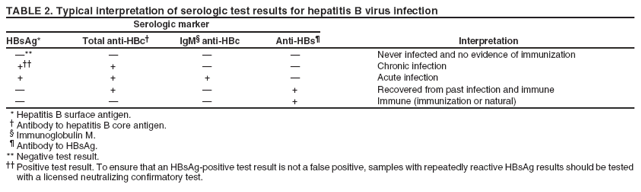
Interpreting The Hepatitis B Serologic Panel
The hepatitis B blood tests are collectively known as the serologic panel. This set of tests can accurately diagnose current and past hepatitis B infection. Since there are a number of markers and at least six interpretations of the various results, determining their meaning can be challenging. To help clarify, below are the six interpretations organized in a table from these hepatitis B markers.
Recommended Reading: Does Hepatitis C Go Away
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis B
After the virus enters the body, there is an incubation period lasting 1.5 to 6 months until illness begins. During the acute phase most persons have no symptoms or might experience a mild illness. Symptoms of acute HBV infection, when present, may include:
- Jaundice
- Dark-colored urine, light-colored stools
- Fever
During the chronic phase hepatitis B usually progresses silently, with no symptoms at all during the first 10-20 years. Signs of severe liver scarring may include:
- Ascites
- Star-shaped vein pattern developing on the swollen belly
- Jaundice
- Easy bruising and bleeding
Chronic HBV infection can lead to serious liver disease, liver scarring , and hepatocellular cancer.
Because symptoms of hepatitis B are usually absent, persons with risk for HBV infection should be tested. If you think you have hepatitis B, or are at risk for hepatitis B, you should contact your doctor.
What Other Tests Might I Have Along With This Test
Your healthcare provider may order other blood tests to look for HBV. These tests can look for antigens on the surface, envelope, and core of the virus, as well as the antibodies to these antigens. Because the symptoms of all 5 hepatitis infections are much the same, this blood test is often done along with other hepatitis blood tests to tell your provider which type of virus you may have.
Also Check: Hepatitis A Vaccine San Diego Free
Hepatitis B Immune Globulin
Hepatitis B immune globulin is prepared from plasma containing high concentrations of anti-HBs and provides short-term protection from infection. Before hepatitis B vaccines were available, HBIG was the only product available for post-exposure prophylaxis. Currently, HBIG, administered in conjunction with hepatitis B vaccine, is recommended for: infants born to HBsAg-positive mothers unvaccinated sexual contacts of a person known or at high risk to be HBsAg-positive and unvaccinated persons with a percutaneous exposure to someone who is known or at high risk to be HBsAg positive. HBIG administration alone is the primary means of protection after exposure to HBV in known nonresponders to hepatitis B vaccination.92
When used for post-exposure prophylaxis, HBIG should be given as soon as possible after exposure, ideally within 12 hours after birth for infants born to HBsAg-positive mothers or within 24 hours after other exposures. Limited data suggest that the efficacy of HBIG is reduced if administered more than 7 days after a percutaneous exposure or 14 days after a sexual exposure.92
J. Peter R. Pelletier MD, FCAP, FASCP, Faisal Mukhtar MBBS, MD, FCAP, FASCP, in, 2020
Common And Local Adverse Events
HB vaccine
HB vaccine is well tolerated. Reactions are generally mild and transient, and include: irritability, headache, fatigue and injection site reactions in 10% or more of recipients.
HAHB vaccine
There is no increase in adverse events when HAHB vaccine is compared with HA vaccine given alone or concomitantly with HB vaccine at a different injection site. When the adult formulation of HAHB vaccine is given to children in the 2 dose schedule, there is no increase in adverse events compared with those occurring after administration of the pediatric formulation of HAHB vaccine.
DTaP-HB-IPV-Hib vaccine
Reactions are usually mild and transient, and include fever, irritability, restlessness and injection site reactions .
HBIg
Headache, diarrhea, fever, urticaria, angioedema and injection site reactions may occur.
Also Check: Hepatitis A Symptoms And Treatment
What Do The Hepatitis B Immunity Results Mean
If an individual is positive for both surface and core antibodies, it can indicate that they had a natural HBV infection and recovered. If only surface antibodies are positive, it can indicate that the individual was vaccinated. In both of these cases, immunity is confirmed, meaning that further vaccination is not generally required.
Identifying Patterns Of Risky Behavior
Screening is an opportunity to draw attention to the clients behaviors that put him or her at risk for contracting :
- Ask for the clients perception of his or her risk for having contracted : How likely do you think it is that the test will be positive?
- Listen for and identify behaviors that put the client at risk for contracting , B, and C and HIV, especially unprotected sex and sharing injection drug paraphernalia.
- Assess the clients alcohol consumption.
You May Like: Does Hepatitis Cause Stomach Pain
Hepatitis B Vaccine And Surface Antibody Titer Faqs
PLEASE NOTE: This is program specific some programs require 3 Hepatitis B vaccines AND a positive Hepatitis B Surface Antibody titer while others will accept 3 vaccines OR a titer. Please read the information in your CastleBranch account carefully so that you know exactly what you need to meet your programs requirements. If you have any questions, please email and a team member will respond.
What Is The Purpose Of A Hepatitis B Test
Hepatitis B test is performed to detect, classify, and treat hepatitis B virus infection.
Hepatitis B blood tests involve the measurement of several HBV-specific antigens and antibodies. In addition, HBV blood tests also include liver enzymes and liver function tests to assess and monitor the condition of the liver and provide appropriate treatment.
The HBV specific tests include the following:
- HBsAg: HBsAg is an antigen found on the surface of hepatitis B virus. HBsAg may be detected in the blood any time after 1 week post-exposure to HB virus, but usually appears after 4 weeks.
- Anti-HBs: Anti-HBs are antibodies produced by the bodys immune system to fight HBsAg. Anti-HBs from a prior infection or vaccination provides immunity against further infection.
- Hepatitis B core antigen : HBcAg is an antigen found in the core layer which covers the hepatitis B viral DNA.
- Hepatitis B core antibody : Anti-HBc is the antibody that fights HBcAg. Anti-HBc is the first detectable antibody after HBV infection. There are two kinds of Anti-HBc:
- Immunoglobulin M hepatitis B core antibody : IgM anti-HBc indicates acute or reactivated recent infection within the previous 6 months.
- Immunoglobulin G hepatitis B core antibody : IgG anti-HBc may indicate previous or chronic infection. Once present, IgG anti-HBc persists for a lifetime.
Read Also: Best Food For Hepatitis C
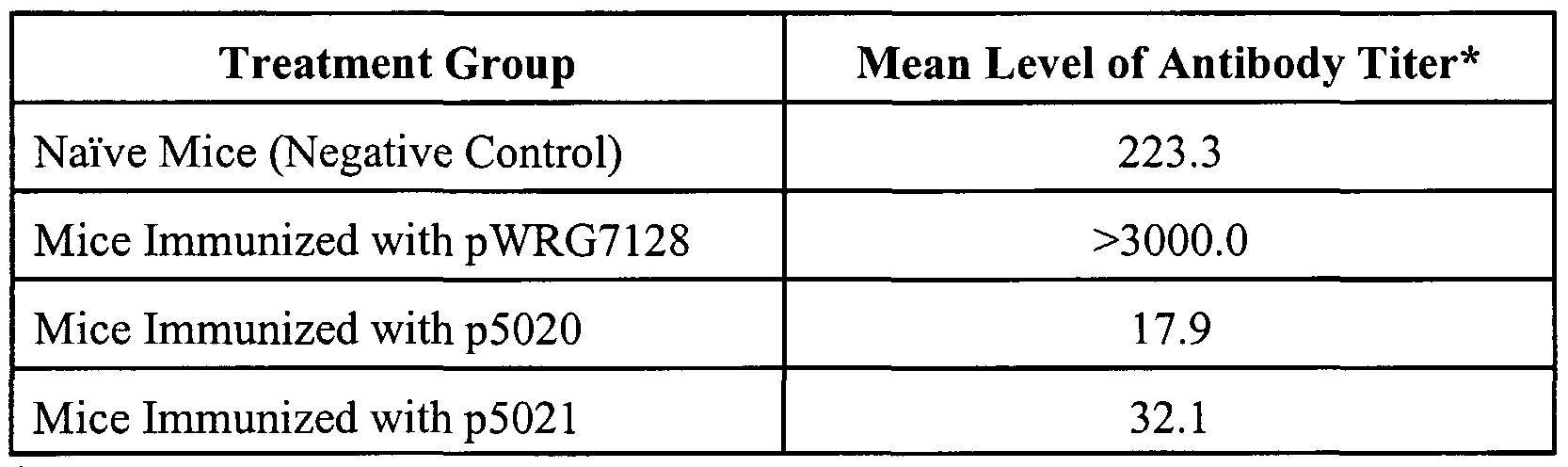
Comparison Of Responses To A Hepatitis B Vaccine Challenge Dose Among Students With < 10 Iu/liter At The Baseline: Baseline Anti
Of the 153 students who completed the study, 131 had an anti-HBsAg level of < 10 IU/liter at the baseline 73 had a level of 0 IU/liter, and 58 had levels of 1 to 9 IU/liter . Thirty-six of 73 with a level of 0 IU/liter and 48 of 58 with levels of 1 to 9 IU/liter responded to the challenge dose . Relative to those with a baseline anti-HBsAg level of 0 IU/liter, students with levels of 1 to 9 IU/liter were more likely to respond to the challenge dose . The anti-HBsAg GMCs after the challenge dose among students whose baseline anti-HBsAg level was 0 IU/liter versus those with baseline anti-HBsAg levels of 1 to 9 IU/liter were 9.8 IU/liter and 99.8 IU/liter , respectively . Among the 58 students with anti-HBsAg levels at the baseline ranging from 1 to 9 IU/liter, 21 had a level of 3 IU/liter of these 21 students, 20 responded to the challenge dose.
Outlook For Hepatitis B
The vast majority of people infected with hepatitis B in adulthood are able to fight off the virus and fully recover within 1 to 3 months.
Most will then be immune to the infection for life.
Babies and children with hepatitis B are more likely to develop a chronic infection.
Chronic hepatitis B affects around:
- 90% of babies with hepatitis B
- 20% of older children with hepatitis B
- 5% of adults with hepatitis B
Although treatment can help, there’s a risk that people with chronic hepatitis B could eventually develop life-threatening problems, such as scarring of the liver or liver cancer.
Page last reviewed: 30 January 2019 Next review due: 30 January 2022
Read Also: Hepatitis E Causes And Treatment
Sequence Following An Initial Negative Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Titer
As you obtain documentation, please submit documentation of each step to CastleBranch
- Initial Hepatitis B titer negative for immunity
- Receive Hepatitis B challenge dose/booster
- Repeat Hepatitis B titer 4-6 weeks after challenge/booster vaccine
Counseling Practices That Educate Support And Motivate Clients Undergoing Screening
Clients might need help deciding whether to get screened, understanding the test results, and determining their next steps. Even when services offered through the substance abuse treatment program are limited, discussing testing with clients presents an opportunity for counselors to motivate clients for change by confronting substance use and by making choices that improve their overall health. However, this may also be true when services are offered on-site through substance abuse treatment programs. A study at one methadone clinic that offered hepatitis screening and vaccination revealed that although the majority of clients completed screening , only 54.7 percent of clients who lacked for hepatitis A received vaccinations and only 2.9 percent of clients who lacked immunity for received vaccinations .
The Consensus Panel makes the following general recommendations while recognizing that, in some programs, the counselors role may be limited:
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Non Reactive Test Result
Is Hepatitis B Contagious
Hepatitis B is highly contagious. It spreads through contact with infected blood and certain other bodily fluids. Although the virus can be found in saliva, its not spread through sharing utensils or kissing. It also doesnt spread through sneezing, coughing, or breastfeeding. Symptoms of hepatitis B may not appear for 3 months after exposure and can last for 212 weeks. However, you are still contagious, even
To screen for hepatitis B, your doctor will perform a series of blood tests.
Preparation Prior To Transport
Label the specimen container with the patients full name, date of collection and one other unique identifier such as the patients date of birth or Health Card Number. Failure to provide this information may result in rejection or testing delay.
Centrifuge if using SST. Place specimen in biohazard bag and seal. Specimens should be stored at 2-8°C following collection.
Specimens more than the following number of days post collection will not be tested:
- > 6 days for Hepatitis B surface antigen
- > 7 days for Hepatitis B e Antigen and Hepatitis B e Antibody
- > 10 days for Hepatitis B core Antigen and Hepatitis B surface Antibody
Also Check: What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis A
Question 7 Is Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Antibody Always Acquired After A Completed Vaccination Protocol
No. After 3 intramuscular doses of vaccine, > 90% of healthy adults and > 95% of those < 19 years of age develop immunity .1 However, there is an age-specific decline in development of immunity. After age 40 years, about 90% of people become immune, but by age 60 years, only 75% of people become immune.1 Larger vaccine doses or an increased number of doses are required to induce immunity in many hemodialysis patients and in other immunocompromised people.1
References
This FAQ is provided for informational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice. A clinicians test selection and interpretation, diagnosis, and patient management decisions should be based on his/her education, clinical expertise, and assessment of the patient.Document FAQS.105 Revision: 0
Chronic Hepatitis Cinfected Patients
Of the 5328 CHC-infected patients identified, 75% were aged 5069 years, 61% were male, and 63% were white. There was documented decompensated cirrhosis in 27% and compensated cirrhosis in 8%. Of the 5328 patients, 2998 had immunity or vaccination against hepatitis A, whereas 659 tested negative and were unvaccinated and 1671 were neither tested for nor vaccinated against hepatitis A infection . Among 3393 unvaccinated participants, 1722 had an anti-HA test, and of these, 1063 were positive. Of the 1935 vaccinated, 1355 received the complete hepatitis A vaccine series of 2 doses.
In univariate analysis , immunity or vaccination against hepatitis A varied between 41% and 58% by 10-year age strata, and those with immunity or vaccination had longer member coverage . Patients with an income of < $30 000 had less immunity or vaccination than those $30 000. Non-Hispanic patients were less likely to be protected than Hispanic patients . Black patients were least likely and Asian patients were most likely to have immunity or vaccination. Patients with compensated cirrhosis also had significantly more immunity or vaccination than those with no documented cirrhosis . After multivariable adjustment, compensated cirrhosis , increased time of member coverage , and increased FIB-4 score were significantly associated with immunity or vaccination.
Also Check: Can You Get Hepatitis From Donating Plasma