Who Is More Likely To Get Hepatitis E
Different types of hepatitis E are more likely to affect different groups of people. The types of hepatitis E that are more common in developing countries are more likely to affect adolescents and young adults.26
In contrast, the types of hepatitis E that are more common in developed countries most often affect older men.26
Case Management And Treatment
Acute hepatitis E infection is considered to be a self-limiting disease and no specific treatment is recommended. However, risk groups such pregnant women, people with pre-existing liver disease, or immunosuppressed patients may require antiviral treatment. In some cases, the reduction of immunosuppressive treatment supports the clearance of the virus. Antiviral therapy with Ribavirin and in some cases pegylated interferon alpha is indicated as treatment of chronic infections .
Animal Models For Chronic Hepatitis E
To elucidate the pathogenetic mechanism, the reason behind high severity in pregnant patients associated with genotype-1, chronicity in transplant recipients and to develop an effective vaccine, permissive, and highly efficient cell culture system and/or suitable animal model is the utmost requirement .
Table 2. Animal and cell culture models used for the propagation of different genotypes of Hepatitis E virus.
So far, human lung carcinoma and human Hepatoma cell lines have shown better permissibility for HEV, replicative efficiency, and viral load till seven passages . Suitable animal models are imperative to understand the immunopathogenesis of Chronic HEV.
These unique animal models for chronic HEV infection might greatly improve our ability to study HEV infectivity by understanding transmission dynamics and delineate underlying pathogenic mechanisms causing chronicity which might lead to the development of specific and effective antiviral drugs and therapeutics against chronic hepatitis E.
You May Like: Is Hepatitis A Virus Or Bacteria
Hepatitis E As A Cause Of Acute
As per Asia Pacific Association for Study of Liver , ACLF is defined as acute hepatic insult manifesting as jaundice and coagulopathy , complicated within 4 weeks by ascites and/or hepatic encephalopathy in a patient with previously diagnosed or undiagnosed chronic liver disease . Superadded HEV infection is a common cause of ACLF in India . A study by Gawande et al. , on 208 patients with ACLF showed a 13.94% contribution by viral hepatitis of which 7.2% exclusively with HEV which acts as precipitating factor for ACLF.
In chronic HBV infected patients, HEV super-infection has an enormous contribution toward ACLF progression . Li et al. observed that 34.7% chronic HBV infected patients had developed ACLF following acute HEV infection and 44.8% of them had a poor prognosis. This suggests that HEV super-infection with genotype-3 upon HBV or underlying diseases is a precipitating event to initiate ACLF in patients. Other studies from around the world describing the impact of HEV infection as CLD or/and ACLF manifestations were described in Table 1.
Table 1. Presenting the cases/studies around the world, i.e., India, China, Nepal, Pakistan, United States, France, and Egypt, etc., where HEV manifests as an acute-on-chronic liver failure and/or chronic liver disease .
Hev Infection And Chronicity In Pediatric And Young Population
Hepatitis E virus infection in children and the pediatric population is usually asymptomatic however, the symptoms might mimic with viral hepatitis A which is supposed to be common in children and younger age groups. Symptomatic HEV infection is uncommon in children even during large HEV epidemics. Since it is uncommon in the pediatric age group, so also the ALF which reflects the paucity of data on chronic HEV in Childhood .
The literature showed the positive relationship of HEV seropositivity with advancing age . Few studies available indicate low HEV seropositivity in the pediatric age groups under the 10 years in Turkey and Morocco whereas 4.2% positivity was observed in children between 2 and 18 years in the province of Van, Turkey . Even in a large worldwide survey in early childhood revealed HEV seroprevalence in less than 10% in children up to 10 years of age and less than 5% in European children . The Dutch pediatric study found a seroprevalence of 3.2% in liver/kidney transplant patients in contrast to immunocompetent patients with 7.4% positivity . In a retrospective study from France on 96 children who had undergone liver transplants, eight patients were HEV seropositive with one reported case of chronic cytolysis.
Also Check: How Long Can You Live With Hepatitis C Untreated
Antiviral Medication For Hepatitis B
Doctors may recommend antiviral medication for people with chronic hepatitis B, which occurs when the virus stays in your body for more than six months.
Antiviral medication prevents the virus from replicating, or creating copies of itself, and may prevent progressive liver damage. Currently available medications can treat hepatitis B with a low risk of serious side effects.
NYU Langone hepatologists and infectious disease specialists prescribe medication when they have determined that without treatment, the hepatitis B virus is very likely to damage the liver over time. People with chronic hepatitis B may need to take antiviral medication for the rest of their lives to prevent liver damage.
There are many different types of antiviral medications available, and your doctor recommends the right type for you based on your symptoms, your overall health, and the results of diagnostic tests. A doctor may take a wait-and-see approach with a person who has a healthy liver and whose blood tests indicate a low viral load, the number of copies of the hepatitis B virus in your bloodstream.
Someone with HIV infection or AIDS may have a weakened immune system and is therefore more likely to develop liver damage. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention strongly recommends that people with HIV infection who are diagnosed with hepatitis B immediately begin treatment with antiviral medication.
Clinical Features And Sequelae
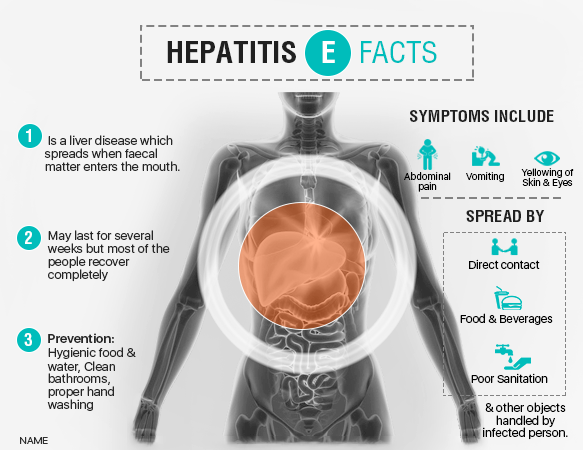
HEV infection in humans is mostly an asymptomatic infection. The majority of cases do not develop any symptoms but seroconvert. The incubation period is estimated to be between two and six weeks . In acute cases the infection causes a self-limiting hepatitis initially with fatigue, asthenia, nausea, fever and jaundice. Other signs can be elevated liver enzyme levels and abnormal liver function tests, abdominal pain and hepatosplenomegaly. Most people with an acute infection recover completely within one to five weeks. In a few cases the acute infection can result in fulminant hepatitis with acute liver failure. Patients with pre-existing chronic liver disease are at risk of severe disease progression with liver failure.
HEV-1 and -2, endemic in African and Asian countries, can cause severe disease and fulminant hepatitis particularly in pregnant women, with up to 21% mortality . In Europe, where HEV-3 is endemic, the infection is not associated with severe disease in pregnant women and thus they are not considered as risk group .
Also Check: What Does Hepatitis Feel Like
How Is Hepatitis E Diagnosed
Hepatitis E is not clinically distinguishable from other types of acute viral hepatitis especially hepatitis A but blood tests are carried out to check for the presence of specific lgM antibodies to the virus in a patientâs blood sample.
Reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction is another test that is used to detect the presence of HEV in the blood or stool of a patient. A test that can detect the presence of hepatitis virus in the serum has already been developed.
Prevention Of Hepatitis E Infection
Currently, there is no licensed vaccine for hepatitis E. Prevent infections by:
- cooking meat and meat products thoroughly
- avoid eating raw or undercooked meat and shellfish
- washing hands thoroughly before preparing, serving and eating food
When travelling to countries with poor sanitation:
- boil all drinking water, including water for brushing teeth
- avoid eating raw or undercooked meat and shellfish
Recommended Reading: How Is Hepatitis C Spread
What Are The Causes
The hepatitis E virus occurs most often when people consume food or drink that is contaminated with feces.
Hepatitis E mainly spreads through contaminated water in areas with poor water quality.
Fecal matter from humans or farm animals may contaminate the water, which may then carry the virus.
This is more common in developing countries with poor water quality and control, especially in highly populated areas. Traveling to or living in these areas may increase the risk of getting the infection in this way.
In developed countries such as the U.S., the virus tends to spread from animals to humans. Humans may eat undercooked meats, such as pork or venison, that carry the virus. Eating shellfish from tainted waters may be another risk factor.
People who are pregnant and have hepatitis E may also spread the virus to their baby. Apart from in these cases, it is uncommon for people to spread the hepatitis E infection to other people.
That said, in very rare cases, a person may get hepatitis E from a blood transfusion, according to the NIDDK.
Emerging Hev Genotypes And Predilection Toward Chronicity
Hepatitis E virus is a positive-sense, single-stranded RNA virus with a 7.2 kb genome, divided into three open reading frames except genotype-1 having an additional ORF4 . The 5 non-coding region is capped with 7-methylguanosine and 3 is polyadenylated . Open reading frame 1 encodes for a polyprotein of 190 KDa comprising of non-structural proteins including regions of unknown function and methyltransferase , cysteine protease , helicase and RNA polymerase . ORF2 and ORF3 are translated from a subgenomic RNA of 2.2 Kb where ORF2 encodes for capsid protein which becomes N-glycosylated at three sites. The unique ORF4 encodes a protein that stimulates viral RNA-dependent RNA-polymerase and promotes viral replication. The life cycle of HEV includes various crucial steps that initiate from the attachment of HEV to the heparin sulfate proteoglycans followed by clathrin-mediated endocytosis and release of viral RNA into the cytoplasm. The viral RNA encodes for ORF1 protein followed by replication via negative-strand RNA intermediated, synthesis of full-length and subgenomic RNAs. Subgenomic RNAs undergo translation that yields ORF2 and ORF3 proteins followed by packaging, assembly, and release of the newly generated virus. Pieces of evidence are suggesting that ORF3 is associated with the release of HEV into the bloodstream .
Key factors which might be the player in the causation of chronic infection are as follows:
Don’t Miss: How Do I Know If I Have Hepatitis B
Hepatitis E: Causes Symptoms And Treatments
Hepatitis is a liver disease that is characterized by an inflamed liver it is of five main types namely hepatitis A, B, C, D and E. A different virus is responsible for each type and in this article we will be focusing mainly on hepatitis E.
Before we look at hepatitis E, we need to know the importance and functions of the liver which is the target organ of the hepatitis viruses.
Clinical Spectrum Of Genotype 1 Disease
Manifestations of HEV infection are quite diverse and include asymptomatic infection, nonspecific viral syndrome, elevation of liver enzymes without any jaundice , icteric hepatitis, and ALF. Overall, asymptomatic infection and anicteric hepatitis appear to be more common than icteric hepatitis the latter is more frequent in adults than in children. Most of those affected have complete resolution with no residual liver damage, except for some persons with ALF who succumb.
The clinical patterns of GT1 infection in India are different from those seen in low-endemic, developed countries in Europe and North America with GT3 dominance . The main differences relate to the following: a particular propensity for severe disease in pregnant women, lack of persistent HEV infection and chronic hepatitis E, and lack of transfusion-related hepatitis E. In addition, extrahepatic manifestations of HEV infection other than pancreatitis, such as neurological manifestations, have been infrequent in the Indian population despite a high incidence of hepatic disease.
| Feature |
|---|
In a systematic review of 23 studies, including 18 from India, that examined the outcomes of hepatitis E in pregnant women, maternal mortality rate varied from 3.2% to 70%, with a median of 26%. In a study of 144 pregnant Indian women with HEV infection and acute hepatitis or ALF, HEV RNA was detected in the cord blood in 46% of infants, indicating vertical transmission.
Don’t Miss: How Often Should You Be Tested For Hepatitis C
The Virus And Its Epidemiology
HepevirusHepeviridaeJ Hepatol.
J Med Virol.
- Opriessnig T.
- et al.
J Virol.N Engl J Med.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.
- Opriessnig T.
- et al.
J Virol.Virus Res.
scaleRed squaresHepatology.
- Torian U.
- et al.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.
- Rahman S.A.
- et al.
J Virol.
J Hepatol.J Hepatol.Anim Health Res Rev.J Viral Hepat.Vet Microbiol.J Viral Hepat.Emerg Infect Dis.Anim Health Res Rev.J Clin Microbiol.
- Schemmerer M.
- et al.
J Clin Virol.J Infect Dis.
- Hjort C.
- et al.
Clin Infect Dis.Lancet.
- Osawa Y.
- et al.
J Viral Hepat.J Infect Dis.Liver Transpl.Zoonoses Public Health.
- Geng J.
- et al.
Hepatol Res.
- Antonis A.F.
- et al.
PLoS One.J Infect Dis.Virol J.
Vox Sang.Transfus Med.Transfusion.Transfus Med.
- Nick S.
- et al.
Vox Sang.Vox Sang.
- Neuhaus R.
- et al.
J Hepatol.
- Hofmann J.
- et al.
Gut.Transpl Infect Dis.Emerg Infect Dis.
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis D
Symptoms of hepatitis D are similar to hepatitis B, so it can be difficult to determine which disease is causing your symptoms. In some cases, hepatitis D can make the symptoms of hepatitis B worse. Symptoms of hepatitis D include:
- Yellow skin and eye
Whos at risk of getting affected with hepatitis D?
People are at risk of getting hepatitis D if they have
- Had hepatitis B infection in the past
- not received the hepatitis B vaccine at the time of birth or later
- Had unprotected sex
- taken drugs or toxic supplements
How is hepatitis D diagnosed?
If you have any of those above-mentioned symptoms of hepatitis D, then you should immediately consult with your doctor. To diagnose hepatitis D, your doctor will perform a hepatitis test that can detect hepatitis D antibodies in your blood. If antibodies are found, it implies youve been infected with the virus. Although it is a liver affecting disease, your doctor may order a full-body health checkup or liver function test to know the condition of your liver.
Is there any vaccine available for hepatitis D?
No, there is no vaccine to prevent hepatitis D. If the hepatitis B vaccine is taken then it can provide protection against future infection of hepatitis D.
How is hepatitis D treated?
How can hepatitis D be prevented?
We know that the only way to prevent hepatitis D is to prevent hepatitis B first. So, you should take these precautions to prevent hepatitis B.
You May Like: What Is Hepatic Flexure Cancer
Chronic Hev Infection In Hematological Patients
No studies have systematically assessed the prevalence or incidence of chronic HEV infection among hematological patients receiving chemotherapy, and only a small number of patients have been found to have chronic HEV infection in this situation. These cases include a patient with untreated hairy cell leukemia, a patient with idiopathic CD4 T lymphopenia, and patients treated for lymphoma, chronic myelomonocytic leukemia, and B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia . The clinical and biological presentation is quite similar to that observed in SOT patients.
Hev Infection In Developed Countries
Over the last 15 years, it has become evident that hepatitis E is not a disease confined to developing countries or travelers returning from such locations. Numerous studies show that autochthonous hepatitis E is a problem across Europe, North America, New Zealand, and Japan . In contrast to the case in developing countries, autochthonous hepatitis E is a zoonotic infection caused by HEV genotypes 3 and 4, and an important route of infection is by consumption of uncooked or poorly cooked pork or game meat .
In developed countries, anti-HEV IgG seroprevalence studies are problematic . Many of the earlier studies showed very low seroprevalences, in the 1 to 2% range . Most of these studies used anti-HEV assays of poor sensitivity and almost certainly significantly underestimated the true seroprevalence .
Read Also: What Are The First Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Extrahepatic Manifestations Of Hev
In addition to the classical hepatic manifestations, HEV is responsible for extrahepatic disorders. These include a range of neurological syndromes, renal injury, pancreatitis, and hematological problems.
Neurological disorders.
Neurological symptoms have been described for HEV1 and acute and chronic HEV3 infections . The neurological manifestations observed in HEV patients are Guillain-Barré syndrome , Bell’s palsy , neuralgic amyotrophy , acute transverse myelitis , and acute meningoencephalitis . In a retrospective analysis of 126 patients with HEV infection, neurological symptoms were observed in 7 patients , including 3 immunocompetent patients with acute HEV3 infection, 3 solid organ transplant recipients, and 1 HIV-positive individual with chronic infection . Recently, Guillain-Barré syndrome associated with necrotizing myositis was described for a liver transplant recipient . It is interesting that HEV RNA in the cerebrospinal fluid was documented for all patients with chronic HEV infection presenting with neurological syndromes . Clonal sequences in the CSF and serum of a kidney transplant recipient with chronic HEV and neurological symptoms demonstrated quasispecies compartmentalization. This suggests that HEV-associated neurological injury might be linked to the emergence of neurotropic variants . More recently, cases of anti-ganglioside GM1-positive and anti-GM2-positive Guillain-Barré syndrome associated with HEV infection have been described .
Kidney injury.
Prevention Of Hev Infection
HEV1 infection can be prevented by providing clean drinking water and improving the sanitary infrastructure in developing countries. HEV3 infection may be prevented by avoiding eating undercooked meat, especially pork products. Note that it has been shown that HEV is completely inactivated when heated above 70°C .
Read Also: How To Get Hepatitis A Virus
Treatment Of Chronic Hev Infection
In transplant recipients with chronic HEV infection, viral clearance is desirable. The first step is to reduce the immunosuppressive therapy, as reduction of immunosuppression results in viral clearance in 30% of patients. Calcineurin inhibitor and mTOR inhibitors have an in vitro effect of stimulation of HEV replication. However, mycophenolic acid inhibits the HEV replication in vitro. Steroids were found not to influence HEV replication in vitro.
Antiviral therapy should be considered for patients for whom immunosuppressive therapy cannot be reduced and for those who do not achieve viral clearance after reducing immunosuppression. Although data are limited, ribavirin monotherapy for at least 3 months seems to be the first treatment option for patients with chronic hepatitis E who are not able to clear HEV after immunosuppression is reduced. However, the presence of G1634 mutation in the RdRp domain of HEV ORF1 protein was reported to be associated with ribavirin treatment failure. In this situation, pegylated interferon alfa may be used as an alternative treatment option if there is no contraindication. It appears that ribavirin causes HEV mutagenesis in treated patients, and distinct mutants within the viral population occur during ribavirin therapy.