Who Is At Risk For Contracting Hepatitis C
The following individuals are at risk for contracting Hepatitis C:
- People who have injected illicit drugs, even if only one time or a few times, including those who have injected only once many years ago
- Healthcare workers who have been exposed to infectious blood on the job or have been stuck by a needle infected with the Hepatitis C virus
- People who were notified that they received blood from a donor who tested positive after they had already donated their blood
- People who received a blood transfusion or had a solid organ transplant before 1992
- People who have HIV
- People who were born to a woman infected with Hepatitis C
- People who live in a household with an infected person
- People who have/had unprotected sex with multiple partners, and/or between males, particularly where there is a history of a sexually transmitted disease
- People who engage or have engaged in anal sex without a condom
- People who have tattoos and body piercing
- People who have signs or symptoms of liver disease such as abnormal liver enzyme tests
- People who have ever worked or been housed in a prison
How Can You Identify What Genotype You Have
With the HCV infection, its important to know which genotype a person has. This will allow a healthcare provider to give the best care by creating a treatment plan specific to the type of HCV.
Overall, this is a relatively new component of HCV treatment. Before 2013, there wasnt a reliable way to distinguish between the different HCV genotypes that may be present in a person with the infection.
In 2013, the Food and Drug Administration approved the first genotyping test for people with HCV.
Various nucleic acid amplification tests can differentiate between the following genotypes:
- 1 and its subtypes
To do this, your doctor firsts obtain a sample of your blood plasma or serum. In the test, genetic material thats present inside the HCV virus is analyzed. During this time, several identical copies of complementary DNA material are produced. This testing can help identify the unique HCV genotype or genotypes present.
This test shouldnt be used as the first diagnostic tool for determining if a person has HCV infection.
However, anyone whos at risk for HCV should at least be tested for the disease with a screening test.
Ns3 Amplification Library Preparation And Ngs
Table 2.
HCV-specific oligonucleotide sequences used for amplification and sequencing of NS3 protease
A threshold value 70% was used to delineate a distinct consensus sequence belonging exclusively to the clade I or clade II genotype . Samples with mapping values below this threshold were considered as mixed samples and 2 different consensus sequences were retrieved . Consensus sequences were called by combining SUPER-CAP and SAMtools programs , and used in MEGA 7 software to create a maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree based on the general time reversible substitution model which was selected by best model search using the Find best DNA Model function implemented in MEGA7 . RASs were analyzed using 1, 5, 10, 15, and 20% cutoffs.
Fig. 1.
Phylogenetic tree showing evolutionary relationships between our HCV subtype 1a sequences and reference isolates included in this study. The evolutionary history was inferred using the maximum likelihood method based on the GTR+G+I as the best-fit model of evolution. Our viral isolates are highlighted with colored circles: red yellow pink blue light blue green violet teal orange . GenBank accession numbers for reference clade I and clade II isolates are also shown.
Don’t Miss: What Is Autoimmune Hepatitis C
How Is Hepatitis C Diagnosed
HCV infection is detected through several blood tests. About 4-10 weeks after exposure, a screening test for the antibody to HCV can be detected by anti-HCV screening test . A positive or reactive test for the HCV antibody could mean you have a current infection, or a past infection that has since resolved or a false positive. If HCV antibody has been detected, the next test would be for HCV RNA which detects the presence or absence of the virus this will determine if you have a current infection. Lastly, if the virus is detected, a quantitative test to detect the amount of virus will be conducted. The Centers for Disease Control provide a chart to help interpret the results of tests for HCV.
It should be noted that when people with early infections have not developed antibody levels high enough that the test can measure, a false negative occurs. In addition, some people may lack the immune response necessary for the test to work well. If you have been recently exposed or have a compromised immune system a PCR may be considered in the event of a nonreactive anti-HCV test.
While lab tests can confirm the presence of HCV, it cannot determine if it has caused any damage to the liver or how severe the damage may be. In order to assess this your doctor will order either a liver biopsy or a non-invasive liver firosis tests.
Why Are Genotypes Important For Treatment
A patient suffering from Hepatitis C should first need to know about Hepatitis C genotype through a blood test so that the doctor can start the hep c treatment accordingly.
Hep c genotype is very important because of that the doctor suggests the appropriate Hep C treatment and decides on the medicine, treatment of duration as per the HCV genotype available in the blood.
The genotype test can cost around $200 to $300. In order to determine whether the patient has already been cured or his/her infection has become chronic, further blood tests are to be run.
Please note, latest treatment doesnt require genotype test because this medicine is helpful for the treatment of all HCV genotypes between 1 to 6.
Also Check: What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C And Health
How can health-care personnel avoid exposure to HCV?
Avoiding occupational exposure to blood is the primary way to prevent transmission of bloodborne illnesses among health-care personnel. To promote blood safety in the workplace, health-care personnel should consult infectious-disease control guidance from the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health and from CDC. Depending on the medical procedure involved, Standard Precautions may include the appropriate use of personal protective equipment .
What is the risk of acquiring hepatitis C after being accidentally exposed to HCV-contaminated blood or body fluids in the workplace?
Although sharps injuries have decreased in recent decades due to improved prevention measures, they continue to occur, placing health-care personnel at risk for several bloodborne pathogens like hepatitis C. A recent analysis of several studies revealed an overall 0.2% risk for infection among those exposed to HCV-antibody-positive blood through needlestick or sharps injuries . Updated guidelines for management and treatment of hepatitis Cexternal icon are available to provide guidance for health-care personnel who become infected via exposure to contaminated blood at the workplace.
Other than needlesticks, do other exposures place health-care personnel at risk for hepatitis C?
Should HCV-infected health-care personnel be restricted in their work?
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
There are two types of Hepatitis C acute and chronic . Individuals with acute Hepatitis C usually do not manifest symptoms and the small percentage that do will experience symptoms similar to the other cases of acute hepatitis, including flu-like symptoms, joint aches or mild skin rash. Individuals that are particularly likely to experience a severe course of Hepatitis C are those individuals that already have Hepatitis B and become infected with acute Hepatitis C.
Other symptoms which may be experienced by individuals with acute Hepatitis C are:
- Loss of appetite
- Grey colored stool
- Jaundice
As is the case for acute Hepatitis C, most people who have chronic Hepatitis C do not experience symptoms in the early stages or even in the advanced stages of the disease. Therefore, it is not uncommon to find out, by surprise, that one has the virus when donating blood or during a routine blood examination. It is possible to have Hepatitis C for many years and not know it which is the reason why the disease has been referred to as a silent killer.
If symptoms do occur, they will most likely exhibit as:
- Pain and tenderness in the area of the liver
- Fever
- Jaundice
- Fatigue
In those persons who do develop symptoms, the average time period from exposure to symptom onset is 412 weeks .
Recommended Reading: What Does It Mean If You Have Hepatitis C Antibodies
Retreatment Of Persons With Prior Peginterferon And Ribavirin Failure
The latest version of the AASLD-IDSA HCV Guidance no longer provides specific recommendations for retreatment of persons with a history of peginterferon plus ribavirin therapy, with or without an earlier generation direct-acting antiviral agent . The AASLD-IDSA HCV Guidance notes that these individuals respond to retreatment similar to treatment-naïve persons, thus implying the treatment approach should be the same as with treatment-naïve individuals. Although the pool of persons with a history of failure with a peginterferon-based regimen who need retreatment is small and diminishing, there are some individuals with this treatment history who need retreatment and may require special consideration that differs from that of treatment-naïve individuals. The following outlines a few of these key considerations based on available data and previous guidance that should be noted when retreating an individual with a history of prior treatment failure with peginterferon plus ribavirin, with or without an earlier generation DAA . Note that except for the 8-week option of glecaprevir-pibrentasvir , when retreating these individuals with first-line DAA combinations that have pangenotypic activity , the treatment will be the same as their treatment-naïve counterparts.
Genotypes Of Hepatitis C
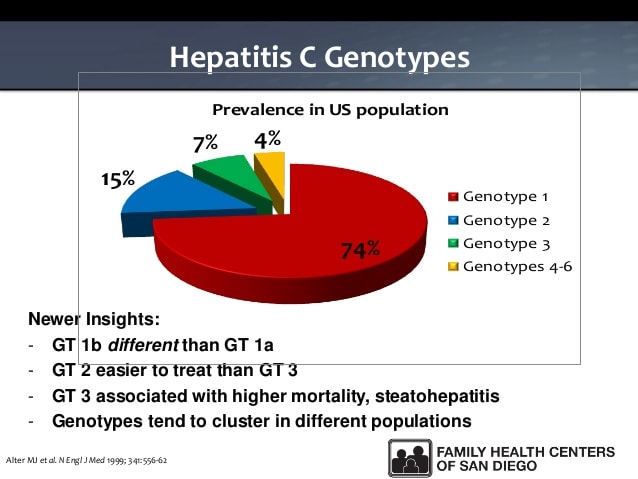
Which genotype of hepatitis C somebody has dictates what treatment is available to them. If you are living with genotype 3, then there is evidence that liver disease might progress more quickly.
The ability of the virus to mutate has resulted in the existence of different genetic variations of HCV. These are called genotypes. The different genotypes are often, but not exclusively, related to different parts of the world.
Genotypes 1, 2 and 3 have a worldwide distribution. Types 1a and 1b are the most common, accounting for about 60% of global infections. They predominate in Northern Europe and North America and in Southern and Eastern Europe and Japan. Genotype 2 is less frequently represented than type 1. Genotype 3 is endemic in south-east Asia. Genotype 4 is principally found in the Middle East, Egypt, and central Africa. Type 5 is almost exclusively found in South Africa. The most common genotypes found in the UK are 1 and 3.
It is still unclear whether or not the type of virus affects the progression of the disease. If it does it is not thought to present any real cause for concern. However, HCV genotype does influence response to treatment. If you are considering treatment it is very important to know which genotype you are actually infected with.
Don’t Miss: Is Hepatitis C An Std
What Is The Long Term Prognosis For Hepatitis C
The future looks promising for those with Hepatitis C. Fortunately, scientific advances and intense research and development have led to the development of many oral antiviral drugs. In addition, research shows that combining specific supplements such as milk thistle shows promise in assisting the liver of patients with Hepatitis C.
The odds of living well with Hepatitis C rather than dying from Hepatitis C are very good. By maintaining a positive attitude, working closely with ones physician after diagnosis, getting support from as many areas as possible , and making positive lifestyle changes, Hepatitis C doesnt have to be the death sentence it was once believed to be.
What Is The Conventional Medical Treatment For Hepatitis C
Not all people who have been diagnosed with Hepatitis C need treatment, especially in the case of acute Hepatitis. Medication may be prescribed, however, bed rest, drinking plenty of fluids, avoidance of alcohol and eating a healthy diet will be recommended by the doctor. It is important to work closely with ones doctor and follow up with tests to make sure the virus has cleared the body.
Some people wont be treated because they dont know they have the Hepatitis C virus.
Individuals who have been diagnosed with chronic Hepatitis C will probably be treated with various combinations of medication. The type of treatment as well as the length of treatment for Hepatitis C depends on the genotype of the virus. Working closely with ones physician, using an open line of communication will help in determining the best course of action.
For various medications used for the treatment of Hepatitis C, please visit our Medications to Treat Hepatitis C Timeline.
Further studies are needed to develop better strategies to prevent recurrence of infection after a liver transplant as well as better treatment protocols after reinfection of the liver has occurred.
Read Also: Can You Get Hepatitis C From Alcohol
Are There Different Types Of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is divided into six distinct genotypes throughout the world with multiple subtypes in each genotype class. A genotype is a classification of a virus based on the genetic material in the RNA strands of the virus. Generally, patients are only infected with one genotype, but each genotype is actually a mixture of closely-related viruses called quasi-species. These quasi-species have the ability to mutate very quickly and become immune to current treatments, which explains why chronic Hepatitis C is so difficult to treat.
In 2014, HCV genotypes and subtypes wer expanded. There are now 7 different HCV genotypes and 67 subtypes. Following is a list of the different genotypes of chronic Hepatitis C:
Genotype 1a, 1b, 1c, 1e, 1g, 1hGenotype 2a, 2b, 2c, 2d, 2e, 2i, 2j, 2k, 2m, 2q, & 2rGenotype 3a, 3b, 3h, 3h, 3i, & 3kGenotype 4a, 4b, 4c, 4d, 4f, 4g, 4k, 4l, 4m, 4n, 4o, 4p, 4q, 4r, 4t, 4v, & 4wGenotype 5aGenotype 6a, 6b, 6c, 6d, 6e, 6f, 6g, 6h, 6i, 6j, 6k, 61, 6m, 6n, 6o, 6p, 6q, 6r, 6s, 6t, 6u, 6v, 6w, & 6xaGenotype 7a
Genotype 1 is the most common type of Hepatitis C genotype in the United States. For physicians, knowing the genotype of Hepatitis C is helpful in making a treatment recommendations as well as treatment duration. Once the genotype is identified, it need not be tested again as genotypes do not change during the course of infection.
Why Do People Have Different Genotypes
A person of any racial or ethnic group can carry any genotype or subtype. However, some may be more prevalent in some racial or ethnic groups than others. In the United States, over 90% of African Americans, compared to 67% of Caucasians, carry genotype 1.
People who travel between regions where different genotypes are more common can be exposed to different HCV genotypes, leading to a mixed infection. HCV is transmitted through contact with blood, such as through contaminated blood products or medical equipment, blood transfusions, kidney dialysis, or the sharing of drug injection equipment, such as syringes, or non-injection equipment, such as pipes, spoons, cotton balls, or straws for snorting drugs.
Read Also: What Happens To Your Body When You Have Hepatitis C
What Are The Most Common Hepatitis C Virus Genotypes
HCV genomic analysis by means of an arduous gene sequencing of many viruses has led to the division of HCV into six genotypes based on homology. Numerous subtypes have also been identified. Arabic numerals denote the genotype, and lower-case letters denote the subtypes for lesser homology within each genotype.
Molecular differences between genotypes are relatively large, and they have a difference of at least 30% at the nucleotide level. The major HCV genotype worldwide is genotype 1, which accounts for 40%-80% of all isolates. Genotype 1 also may be associated with more severe liver disease and a higher risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. Genotypes 1a and 1b are prevalent in the United States, whereas in other countries, genotype 1a is less frequent. Genotype details are as follows:
Within a region, a specific genotype may also be associated with a specific mode of transmission, such as genotype 3 among persons in Scotland who abuse injection drugs.
References
World Health Organization. Hepatitis C: fact sheet. Available at . Updated: October 2017 Accessed: January 23, 2018.
Frank C, Mohamed MK, Strickland GT, et al. The role of parenteral antischistosomal therapy in the spread of hepatitis C virus in Egypt. Lancet. 2000 Mar 11. 355:887-91. .
Kim A. Hepatitis C virus. Ann Intern Med. 2016 Sep 6. 165 :ITC33-ITC48. .
Bonkovsky HL, Mehta S. Hepatitis C: a review and update. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001 Feb. 44:159-82. .
Cautions Discusses Conditions That May Cause Diagnostic Confusion Including Improper Specimen Collection And Handling Inappropriate Test Selection And Interfering Substances
An “Undetected” or “Indeterminate” hepatitis C virus genotype result does not rule-out active HCV infection. Test results should be correlated with routine serologic and molecular-based testing, as well as clinical presentation. Specimens with indeterminate results will be automatically evaluated with the subsequent test HCVGR / Hepatitis C Virus Genotype Resolution, Serum.
Known cross-reactivity between the assay probes and various HCV genotypes limits the ability of this assay to identify multiple HCV genotypes present in a given specimen. Such cross-reactivity or the actual presence of multiple HCV genotypes in the same specimen may result in an “Indeterminate” or multiple/mixed genotype result.
You May Like: Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedule For Adults
What Is The Current Research Into Genotypes And Treatments For Each Type
The most widely used anti-HCV therapy, PEG/ribavirin, doesnt target the virus itself. This treatment regimen primarily affects the persons immune system. Its goal is to rally the immune system to recognize and eliminate cells infected with HCV.
However, variations of HCV in a single person wont necessarily look the same to the immune system. This is one of the reasons that HCV infections persist and become chronic infections.
Even with this genetic diversity, researchers have identified proteins that are required for the reproduction of HCV in the body. These proteins are present in essentially all of the many HCV variants.
The new treatments for HCV target these proteins. That means they target the virus. Direct-acting antiviral therapy uses small molecules designed to specifically inhibit these viral proteins.
Many DAA drugs have been under development during the past decade. Each drug targets one of the handful of essential HCV proteins.
The first two DAA drugs, boceprevir and telaprevir, got approval for use in the United States in 2011. Both target a particular type of HCV enzyme known as protease. These drugs are used in combination with PEG/ribavirin.
Both of these new medications are most effective for HCV genotype 1. Theyre moderately effective for genotype 2, and not effective for genotype 3.
Initially, they were only approved for use in people with genotype 1 HCV in combination with PEG/ribavirin.