Prevalence Of Hiv In The World
In 2015, the number of HIV-related deaths ranged from 930,000 to 1,300,000 worldwide . According to Global AIDS in 2016, approximately, 37 million people live with HIV and 21 million are under treatment.
The distribution of HIV infection is not equitable in the world, sub-Saharan Africa is the most affected region. In 2015, it alone counted 25,600,000 people living with HIV or nearly 70% of the worlds PLHIV. The overall prevalence in this part of the world is 5.0% , with 1,900,000 new infections per year.
How Is It Spread
Hepatitis A is spread when a person ingests fecal mattereven in microscopic amountsfrom contact with objects, food, or drinks contaminated by feces or stool from an infected person.
Hepatitis B is primarily spread when blood, semen, or certain other body fluids- even in microscopic amounts from a person infected with the hepatitis B virus enters the body of someone who is not infected. The hepatitis B virus can also be transmitted from:
- Birth to an infected mother
- Sex with an infected person
- Sharing equipment that has been contaminated with blood from an infected person, such as needles, syringes, and even medical equipment, such as glucose monitors
- Sharing personal items such as toothbrushes or razors
- Poor infection control has resulted in outbreaks in health care facilities
Hepatitis C is spread when blood from a person infected with the Hepatitis C virus even in microscopic amounts enters the body of someone who is not infected. The hepatitis C virus can also be transmitted from:
- Sharing equipment that has been contaminated with blood from an infected person, such as needles and syringes
- Receiving a blood transfusion or organ transplant before 1992
- Poor infection control has resulted in outbreaks in health care facilities
- Birth to an infected mother
Hbv Infection: Chronic But Preventable Disease
Current treatment strategies do not allow complete viral eradication in HBV infection. Peg-IFN has significant side effects, but it is able to achieve a functional cure in a number of patients and remains a possible therapeutic option . Lifelong nucleoside analog therapy, on the other hand, has few side effects but achieves functional cure only in a small minority of patients .
What makes hepatitis B infection really different from HIV and HCV is the availability of an effective vaccination since the early 1980s. A long-term study of 14 years conducted in The Gambia showed a high effectiveness of vaccination against chronic carriage and new infection among children and young people at different ages . To date, 183 of the 193 WHO member states have initiated an hepatitis B vaccination program . Approximately 84% of children worldwide received three doses of hepatitis B vaccine and are thus probably protected from HBV infection for life. The additional administration of hepatitis B immune globulin at birth can further reduce the risk of MTCT in high-risk deliveries .
Also Check: Can Chronic Hepatitis B Be Cured
Risks Of Contracting Hiv And Stds
Just as HIV and STDs are spread in the same ways, they can also share some of the same risk factors. A risk factor is anything that makes you more likely to contract a condition or disease.
For HIV and some STDs, risk factors include:
- having unprotected sex of any kind
- sharing injection needles
- sharing tattoo or piercing needles
- having sexual encounters under the influence of drugs or alcohol
The risks of contracting HIV or an STD are also higher among some populations and groups. This can be due to a variety of factors, like:
- lack of access to healthcare
- discrimination faced in accessing healthcare
- population size
47 percent of primary and secondary syphilis were among men who have sex with men. But STDs are common among all Americans. Its important for anyone of any gender or sexuality who has one or more risk factors to get tested and treated.
Intervention Strategy Resources: Diagnosis Treatment Prevention And Response
HIV.gov provides an in-depth review of the official federal government response to the HIV/AIDS epidemic titled Ending the HIV Epidemic: A Plan for America.
- The plans goal is to reduce HIV infections in the U.S. by 75% by 2025 and 90% by 2030.
- Early detection and immediate access to care resources improve outcomes for individuals and communities.
- Rapid start treatment programs should be available to all. At the same time, the thousands of HIV-positive people who are aware of their status but arent currently receiving treatment should be encouraged to resume their care programs.
- Interventions such as PrEP and syringe services programs have been shown to reduce HIV infection rates.
- Real-time response systems allow communities to quickly identify and address new outbreaks of HIV infections. The systems are made possible by innovative epidemiological techniques and close links between federal, state and local resources.
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatic Function Panel
Can Hbv Infection Be Prevented
Yes. The best way to prevent HBV is to get the hepatitis B vaccine.
CDC recommends that people with HIV and people who are at risk for HIV get the HBV vaccine . The housemates and sexual partners of people with HBV should get the HBV vaccine, too.
People, including people with HIV, can also take the following steps to reduce their risk of HBV infection:
- Use condoms during sex to reduce the risk of HBV infection and infection with other sexually transmitted diseases, such as gonorrhea and syphilis.
- Do not inject drugs. But if you do, do not share needles, syringes, or other drug injection equipment.
- If you get a tattoo or body piercing, make sure the instruments used are sterile.
What Is The Difference Between An Std And Sti
The term STD is often used interchangeably with the term sexually transmitted infection . But despite this common misconception, STDs and STIs arent exactly the same. Each term has a specific meaning:
- STI. An STI is a sexually transmitted infection and doesnt cause any symptoms. Instead, an STI refers to the presence of the virus, bacteria, or other pathogens in your body.
- STD. An STD is a sexually transmitted disease, which does cause symptoms. It happens when the pathogens in your body have led to the cell damage that produces symptoms.
Put simply, an infection just means the presence of the pathogen is in your body, while a disease means youre having symptoms. A condition is only considered an STD if there are symptoms.
This might seem like a small difference, but the distinction is important. This is especially true for STIs that rarely cause symptoms, like chlamydia or gonorrhea. For many people, these STIs wont ever progress to STDs.
You May Like: Who Should Get Tested For Hepatitis C
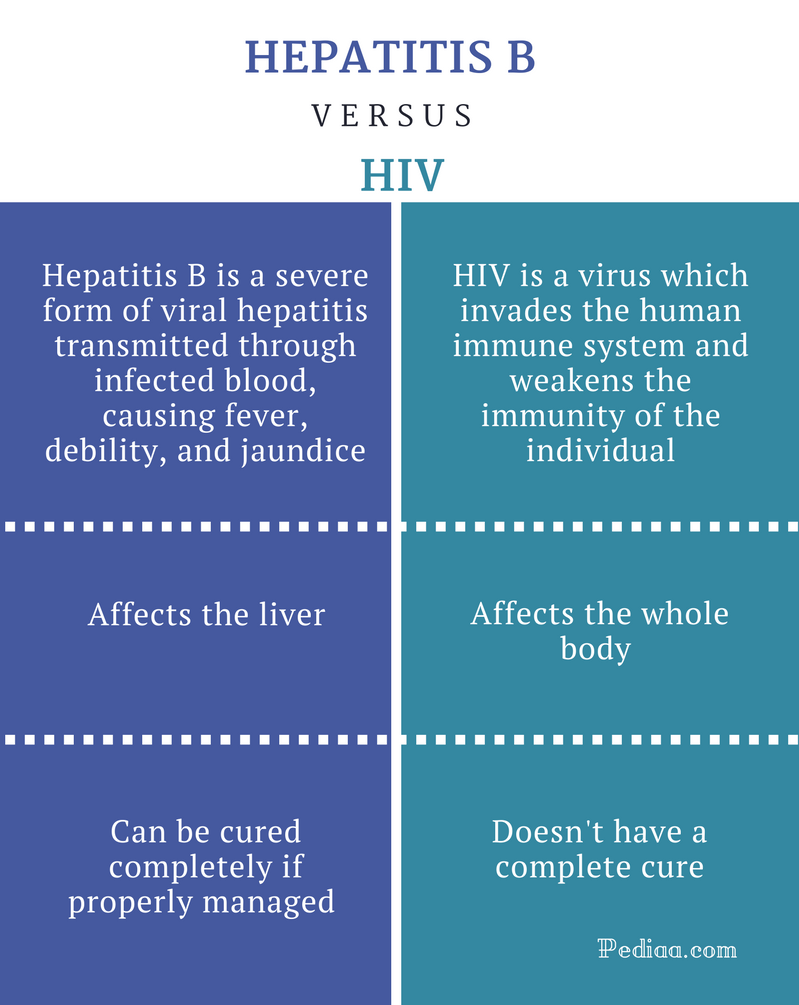
Difference Between Hepatitis B And Hiv
Hepatitis is a disease, affecting the liver which can be caused by several viral entities such as A, B, C, D and E. This condition, in general, is defined as an inflammation of the liver which can either be self-limiting in nature or complicates to fibrosis, scarring, liver cirrhosis or malignancy.
On the other hand, HIV is a virus which invades the human immune system and weakens the immunity of the individual, thus increasing the susceptibility to infections, inflammatory conditions and various other illnesses in the body.
Both Hepatitis and HIV can cause similar signs and symptoms, yet HIV tends to affect the overall body rather than being limited just to the liver.
Hepatitis B, if properly managed can be cured completely.
HIV doesnt have any permanent cure at all except for the treatment with Antiretroviral drugs which is known to control the spread and reduce the incidence of transmitting the disease from infected person to another.
Image Courtesy:
Hepatitis B virus v2 By Original uploader was TimVickers at en.wikipedia via Commons Wikimedia
Symptoms of AIDS By Medical gallery of Mikael Häggström 2014. WikiJournal of Medicine 1 . DOI:10.15347/wjm/2014.008. ISSN 20018762. via Commons Wikimedia
Similarities & Differences Between Hiv & Hepatitis C
Last Updated on June 4, 2020 by Shuvani Sanyal, MD
HIV and the hepatitis C virus share many of the same characteristics, but there are also some very distinct differences in the way they are transmitted, how long each virus lives outside of the body, disease progression, and treatment. This post explores some of the similarities and differences between HIV and HCV.
Recommended Reading: Treatment For Liver Cirrhosis Hepatitis B
Is Hepatitis Testing Recommended For People With Hiv
Yes. Everyone living with HIV should be tested for HBV and HCV when they are first diagnosed with HIV and begin treatment. People living with HIV who have ongoing risk factors for getting hepatitis B or hepatitis C should be tested annually.
In addition, new HCV screening recommendations from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention call for:
- One-time screening for all adults 18 years and older
- Screening of all pregnant women during every pregnancy
- Testing for all persons with risk factors, with testing continued periodic testing those with ongoing risk.
Protecting Everyone Involved In Sport Against Hiv And Hepatitis
Consult your sporting organisations infection control policies. Simple and inexpensive procedures can prevent the spread of HIV, hepatitis B and C, including:
- Remember to cover all pre-existing wounds before starting a game.
- Wear protective gloves when giving first aid to bleeding players.
- If someones eyes have been splashed with blood with the eyes open, rinse the area gently but thoroughly with water or normal saline, rinsing away from the nose.
- If blood gets in your mouth spit it out and rinse your mouth with water several times.
- Standard practice is to stop play if a player is bleeding and allow them to return to play only after bleeding is controlled and the wound is properly covered.
- Bandage any wounds that occur, and properly clean any playing surfaces and change any clothes exposed to blood before play restarts.
- Have your own drink bottle and towel, mouth guard and other personal items, including razors, to reduce the possibility of small amounts of blood-to-blood transmission.
- If you are concerned about potential infection, contact a doctor or health information line for further advice.
If a player is injured while playing sport:
- Remember to wear protective gloves when giving first aid to a player who is bleeding.
- Stop the bleeding from the wound.
- Dress the wound.
- Clean up the blood.
Also Check: Is There A Shot For Hepatitis C
Ebola And Hiv/aids: Similarities And Differences
A strong parallel between HIV and Ebola was drawn by Tom Frieden, M.D., director of the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , at an annual meeting of the World Bank and International Monetary Fund in Washington, D.C.
“In the 30 years I’ve been working in public health, the only thing like this has been AIDS,” he said, as reported by NBC News.
He added, “We have to work now so that this is not the world’s next AIDS.”
HIV and Ebola are both incurable viruses that trigger widespread stigma, and the similarities don’t end there. But there are also significant differences. David Heitz of Healthline News compares and contrasts Ebola and HIV here is a selection from his analysis:
HIV and Ebola are both viruses. Both emerged in Africa neither has a vaccine, and both are fatal if left untreated. Both are carried by host animals and then transmitted to humans, and both may have made that transition when hunters ate bush meat.
Symptoms And Disease Progression
The majority of people do not experience symptoms when they first acquire hepatitis C, a period known as acute infection. Among people living with HIV, routine liver function tests sometimes reveal elevated liver enzymes that can be a sign of liver inflammation due to hepatitis C.
When they do occur, signs and symptoms of acute hepatitis C infection may include the following:
- fatigue
- pain in the upper abdomen or belly
- feeling generally unwell
- yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes .
Around 10 to 25% of people who acquire hepatitis C will clear the virus without treatment. Most people develop chronic hepatitis C that lasts more than six months. People living with HIV appear less likely to spontaneously clear hepatitis C. People with chronic infection will continue to be infectious and can pass on the virus to others, whether or not they have symptoms.
Basic information on how hepatitis C is passed on during sex
Over the longer term, about half of people with chronic hepatitis C will experience some symptoms. The most common include fatigue, loss of appetite, muscle and joint pain, and feeling generally unwell. Some people may experience ‘brain fog’ or depression. Symptoms may worsen or become more numerous over time.
These symptoms can have a negative impact on work, family life, social life and sex life. If this is the case for you, be sure to tell your doctor about the problems the symptoms cause you.
Don’t Miss: How Contagious Is Hepatitis C
Incorporating Hiv And Aids Education In Community Outreach
The National HIV/AIDS Strategy for the United States: Federal Action Plan, which the federal government originally published in 2015, was updated in 2020. The plan highlights the important role played by community-based organizations , healthcare providers and informal networks of people who have HIV in achieving the goal of making new infections rare and ultimately nonexistent.
Another important goal of the federal strategy is to ensure that everyone whos living with HIV has access to quality care and has the opportunity to live a full, healthy life free of discrimination and stigma. The plan calls for the CDC to support community mobilization efforts to strengthen CBOs social network strategies. It also recommends national campaigns targeting segments of the population who are at the greatest risk of contracting HIV.
How Serious Is It
- People can be sick for a few weeks to a few months
- Most recover with no lasting liver damage
- Although very rare, death can occur
- 15%25% of chronically infected people develop chronic liver disease, including cirrhosis, liver failure, or liver cancer
- More than 50% of people who get infected with the hepatitis C virus develop a chronic infection
- 5%-25% of people with chronic hepatitis C develop cirrhosis over 1020 years
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Symptoms Mayo Clinic
How Is It Treated
Hepatitis A is treated using supportive methods. These can include things like rest, fluids, and healthy foods. Medications can also help to ease some symptoms like fever, aches, and pains.
Theres a vaccine available to protect against infection with HAV. This is typically recommended for children as well as for people at an increased risk for contracting the virus.
Also, receiving a single dose of the hepatitis A vaccine may prevent you from becoming ill if youve been exposed to HAV. For it to be effective, the vaccine needs to be given of exposure.
Difference Between A Virus And A Syndrome
The National Human Genome Research Institute describes a virus as a small bundle of genetic code, whether DNA or RNA, wrapped in a coat of protein. Viruses are unable to replicate on their own, so they depend on parts within the cells they infect to create copies of themselves. The replication process typically destroys the host cell and damages the host organism.
The Cambridge Dictionary defines a syndrome as a group of medical problems that result from a single disease or mental condition. With AIDS, the group of medical problems that HIV causes all result from the viruss slow destruction of the persons immune system.
HIV.gov identifies AIDS as the most advanced stage of HIV infection. AIDS is diagnosed in two ways:
- When a person with HIV exhibits a condition associated with AIDS .
- When a person with HIV has a cluster of differentiation 4 thats less than 200 cells for every cubic millimeter CD4 is a glycoprotein thats found on the surface of T-helper cells and other immune system cells.
You May Like: How Do You Get Hepatitis A B C
Resources For Hiv And Aids Education And Prevention
Education is central to the goal of treating, preventing, and ultimately eradicating HIV and AIDS. The strategy for achieving that goal unites community organizations with research and social services agencies at all strata of government. The organizations are among the HIV and AIDS resources available to public health educators and the public.
Living With Hepatitis C: Your Lifestyle
People living with HIV and hepatitis C can benefit from adopting a healthy lifestyle, including eating a balanced diet. Try to maintain a healthy weight. Being overweight is linked to fatty liver disease, which can worsen liver damage.
Since people living with HIV and hepatitis may have an increased risk of cardiovascular disease and diabetes, your clinic should regularly monitor your blood fats or lipids and blood sugar .
People living with hepatitis C should limit how much alcohol they drink, and those with liver damage should avoid alcohol altogether. Not smoking and cutting down or stopping recreational drug use are also important for overall health.
- Eat a balanced diet including vegetables, fruit and wholegrains.
- Get regular moderate exercise.
Read Also: Hep C Without Hepatic Coma
Who Should Be Tested
Testing for hepatitis A is not routinely recommended.
CDC recommends hepatitis B testing for:
- Men who have sex with men
- People who inject drugs
- Household and sexual contacts of people with hepatitis B
- People requiring immunosuppressive therapy
- People with end-stage renal disease
- People with hepatitis C
- People with elevated ALT levels
- Pregnant women
- Infants born to HBV-infected mothers
CDC recommends hepatitis C testing for:
- All adults aged 18 years and older
- All pregnant women during each pregnancy
- About 24,900 new infections each year
- About 22,600 new infections in 2018
- Estimated 862,000 people living with hepatitis B
- About 50,300 new infections in 2018
- Estimated 2.4 million people living with hepatitis C