Combined Use Of Maoto And Lamivudine Decreases Hepatitis B Virus Replication More Efficiently Than The Individual Use
Considering that maoto suppresses an HBV infection step different from that of lamivudine , i.e., the reverse transcription step, we reasoned that a combined use of 3TC and maoto would suppress HBV replication more effectively. We therefore compared the effect of maoto alone, 3TC alone, and the combined use on HBV replication. Compared to maoto or 3TC alone, the combined use decreased HBV replication more efficiently as expected . These results suggest the potential of maoto for increasing the efficacy of current anti-HBV drugs when used in combination.
Figure 4 Combined use of maoto and 3TC decreases hepatitis B virus replication more efficiently than the individual use. Cells were treated with distilled water , 30 µg/ml maoto alone, 250 nM lamivudine alone, or maoto and 3TC for 9 days with refreshing the medium and drugs every 3 days as shown in Figure 3A. HBV DNA in culture supernatants of the cells after 9 days of maoto treatment was measured by real-time PCR. Values are expressed as the mean percentage + S.E. of three independent experiments. *P< 0.05 **P< 0.01 ****P< 0.001 N.S., no significance.
Advances In New Drugs To For Curing Hepatitis B And Hepatitis D Announced At Ilc 2021
For Immediate Release
Media Release
Advances in new drugs to for curing Hepatitis B and Hepatitis D announced at ILC 2021
Thursday 24 June 2021 Leading hepatology researchers announced important new developments in hepatitis research at the International Liver Congress 2021 today. This includes new data on antivirals to cure Hepatitis B and Hepatitis D and the application of infusion chemotherapy with P-1 inhibitors to treat liver cancer.
Other announcements included a review of the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on efforts to eliminate Hepatitis C in the USA and some encouraging data from a trial of a new liver dialysis device to treat acute on chronic liver failure .
Scientists and advocates have long argued that if we are realistically going to eliminate Hepatitis B, then we will need a functional cure, said Philip Newsome, Secretary General of EASL and Professor of Experimental Hepatology and Director of the Centre for Liver Research at the University of Birmingham in the UK. The results from the trial of RNAi therapeutic drug VIR-2218 are an encouraging example that a cure is possible sooner than later with potential real-world implications for the 300 million people living with the disease.
Todays official press conference highlighted five studies covering treatment and cure research for hepatitis and acute on chronic liver failure selected from over 1500 abstracts being presented at ILC 2021.
Impact of COVID-19 on eliminating Hepatitis in the U.S.
Contact:
What Are The Risk Factors For Getting Hepatitis B
Due to the way that hepatitis B spreads, people most at risk for getting infected include:
- Children whose mothers have been infected with hepatitis B.
- Children who have been adopted from countries with high rates of hepatitis B infection.
- People who have unprotected sex and/or have been diagnosed with a sexually transmitted infection.
- People who live with or work in an institutional setting, such as prisons or group homes.
- Healthcare providers and first responders.
- People who share needles or syringes.
- People who live in close quarters with a person with chronic hepatitis B infection.
- People who are on dialysis.
Also Check: All Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Antiviral Medication For Hepatitis C
For people with hepatitis C, the goal of treatment with antiviral medication is to prevent the virus from replicating, or copying itself, and to eliminate the virus from the bloodstream. If the hepatitis C virus has been in the body for more than six months, the infection is considered chronic. Without treatment, most people with acute hepatitis C develop the chronic form of the disease.
Your doctor decides which antiviral medicationor combination of medicationsto prescribe based on the results of a blood test called a genotype test. There are six genotypes, or strains, of the hepatitis C virus, and people with certain genotypes respond more quickly to medical treatment.
For many years, the standard treatment for chronic hepatitis C consisted of the antiviral medications pegylated interferon and ribavirin. Ribavirin is taken by mouth every day, and interferon is an injection that you or a caregiver can administer once a week at home.
In 2013 and 2014, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved a group of new medications for the treatment of hepatitis C. These medications, which include sofosbuvir, are very effective and have fewer side effects than older medications, particularly interferon.
Maoto Suppresses Hepatitis B Virus Production In The Context Of Infection
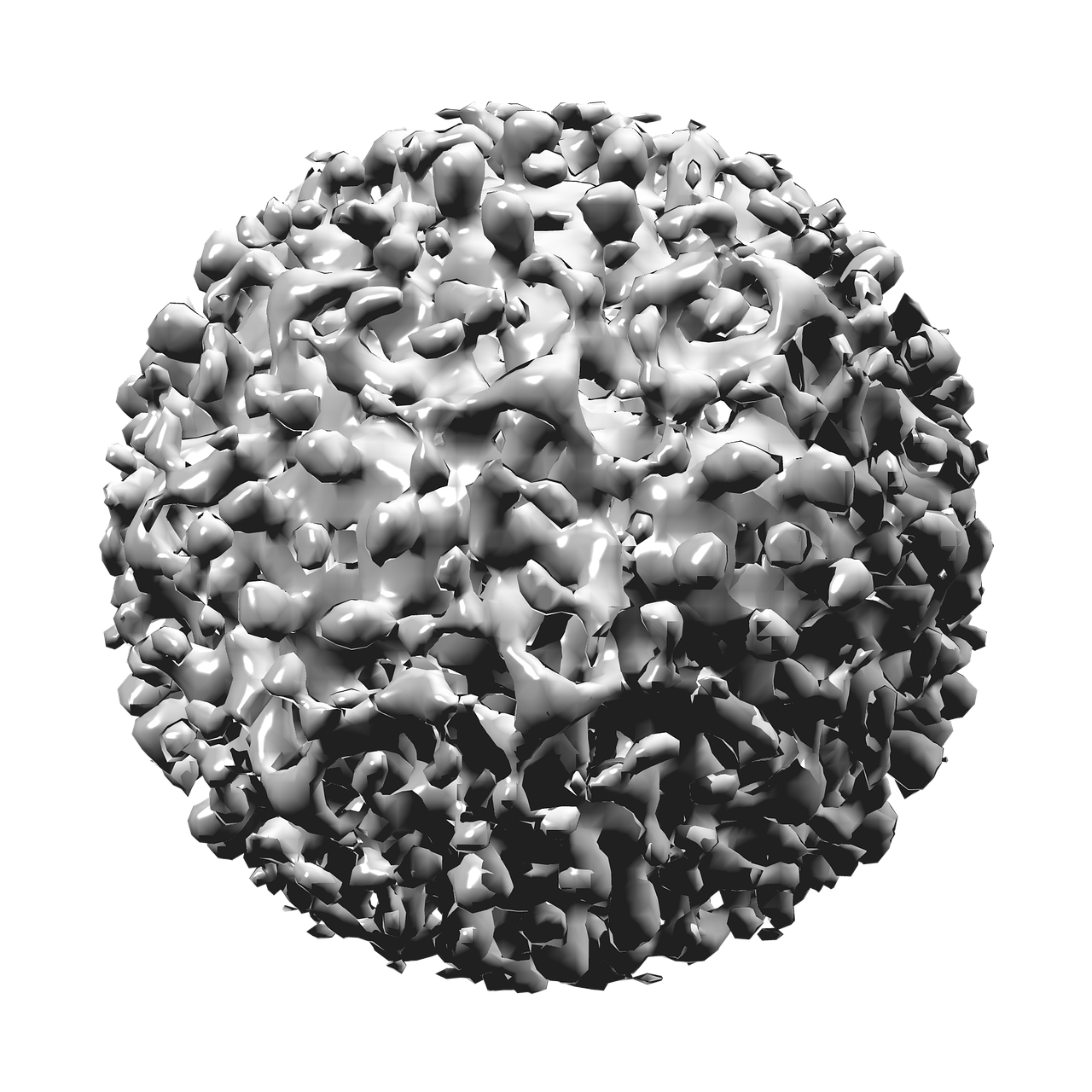
Next, we examined the relevance of the inhibitory effect of maoto on HBV production in the context of HBV infection using HepG2-NTCP cells and primary human hepatocytes isolated from PXB-mice . HepG2-NTCP cells and PXB-cells were infected with HBV at 2×103 GEq/cell and treated with maoto at the indicated concentrations . The effects of maoto on HBV were evaluated at 6 and 9 days of maoto treatment in HepG2-NTCP cells and at 11 days of the treatment in PXB-cells . As shown in Figure 3B and Figure S1B, maoto did not exhibit any cytotoxicity to HepG2-NTCP cells and PXB-cells. We then found that maoto treatment resulted in dose-dependent suppression of extracellular HBV DNA production without affecting HBeAg expression, similar to the effects in HepAD38.7 cells . The IC50 of the maoto extract to inhibit HBV production was 33.2 ± 5.6 µg/ml in HepG2-NTCP cells and 7.5 ± 5.4 µg/ml in PXB-cells . These results confirmed the relevance of the inhibitory effect of maoto on HBV in the context of HBV infection.
Read Also: Do I Have Hepatitis B
Whats The Difference Between Acute And Chronic Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B can be either acute or chronic:
- Acute hepatitis B lasts for a short period of time. If you have acute hepatitis B, you may be asymptomatic or have symptoms and develop icteric hepatitis. It can transition into chronic hepatitis B if the virus doesnt naturally go away after 6 months.
- Chronic hepatitis B lasts for at least 6 months. If you have this type of hepatitis, you may carry the hepatitis B virus for the rest of your life. Its possible to have chronic hepatitis B that started as acute, but many people dont have acute hepatitis B first.
Most people with acute hepatitis B make a full recovery. Some may never even show any symptoms. But those with chronic hepatitis B often need treatment to help manage the infection. Chronic hepatitis B also increases your risk of developing cirrhosis and certain types of liver cancer.
Your risk of developing chronic hepatitis B depends on when you first received your diagnosis of the virus. Children who receive a diagnosis of hepatitis B, especially those under the age of 5 years old, have a higher risk of the infection becoming chronic. Adults are less likely to develop chronic hepatitis B. Around 90 percent of adults who develop it will fully recover.
Keep in mind that hepatitis B can be present for years before you start to show any symptoms.
Do Medicines Used To Treat Autoimmune Hepatitis Have Side Effects
Medicines for autoimmune hepatitis can cause side effects. Your doctor will monitor any side effects and help you manage them while you take these medicines. Your doctor also may adjust the doses or change the medicines you take. You may need to stop taking corticosteroids or azathioprine if you have severe side effects.
Side effects of corticosteroids may include
- changes in how you look, which may include weight gain, a fuller face, acne, or more facial hair
Corticosteroids and azathioprine suppress, or decrease the activity of, your immune system, which increases your risk for infections. These medicines can also increase your risk of developing cancers, especially skin cancers.
Read Also: Hepatitis C Is Caused By
Does The Hepatitis B Vaccine Have Side Effects
Some children will develop pain or soreness in the local area of the shot, and low-grade fever.
There is one extremely rare, but serious, side effect. About 1 out of every 600,000 doses of the hepatitis B vaccine will cause a severe allergic reaction, called anaphylaxis, with symptoms including swelling of the mouth, difficulty breathing, low blood pressure or shock. Anaphylaxis usually occurs within 15 minutes of receiving the vaccine. Although anaphylaxis can be treated, it is quite frightening. People should remain at the doctors office for about 15 minutes after getting the vaccine.
Although the hepatitis B vaccine is made in yeast cells, no one has ever been shown to be allergic to the yeast proteins contained in the hepatitis B vaccine .
Hepatitis B Virus Preparation And Infection
HepAD38.7 is a specialized cell line that produces HBV in the absence of tetracycline . The cells were cultured without tetracycline, and the culture supernatant was collected every 3 days for up to 60 days. The culture supernatants were filtered through a 0.22 µm filter, and viruses were purified by polyethylene glycol precipitation. The virus was used to infect HepG2-NTCP cells and PXB-cells at 2 × 103 genome equivalents /cell. Infection was performed in the presence of 2% DMSO and 4% PEG 8000. After 24 h of infection, the cells were washed three times to remove remaining extracellular HBV particles.
Recommended Reading: What Does Hepatitis Rash Look Like
Can I Drink Alcohol If I Have Hepatitis C
The combination of any cause of hepatitis, such as alcohol on top of HCV, adds to and accelerates liver damage. Both hepatitis B and C can cause chronic hepatitis and progression to cirrhosis and liver cancer, although the disease is much more likely to become chronic in the U.S. Therefore, people with chronic HCV should not drink alcohol and should talk to a doctor about vaccines for other hepatitis viruses.
Data Collection And Follow
Demographic data, medical history, clinical parameters, including vital signs and radiology, laboratory, microbiology, and treatment data, were collected when the diagnosis of HBV-ACLF was made and patients were free of BIs then. The lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio , neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio , disseminated intravascular coagulation score, transplant-free survival probability, and cumulative incidence of BIs were then calculated. The patients were followed 90 days after their first diagnosis of HBV-ACLF. A 90-day transplant-free survival was considered the primary endpoint. Information on prognosis was confirmed through medical records and telephone contact.
Also Check: What Is Hepatitis A And B
New Zealand Case Reports
The Centre for Adverse Reactions Monitoring has received a total of 360 reports of liver injury associated with the use of non-tuberculosis antibiotics since January 2000. Most reports were in adults aged over 50 years , with 13 reports in patients aged less than 20 years. Seven reports involved a fatality.
The majority of CARM reports of liver injury were associated with -lactam penicillins . Amoxicillin/clavulanic acid, flucloxacillin and erythromycin were the antibiotics most often implicated in the development of liver injury in New Zealand.
Figure 1: Classes of non-tuberculosis antibiotics associated with liver injury in New Zealand
Key Messages
- Antibiotics are a common cause of drug-induced liver injury.
- Most cases of antibiotic-induced liver injury are idiosyncratic, unpredictable and largely dose-independent.
- In New Zealand, the antibiotics most often implicated with liver injury are amoxicillin/clavulanic acid, flucloxacillin and erythromycin.
- Withdrawal of the causative antibiotic is the most effective treatment.
References
How You Can Get Hepatitis B
You can get hepatitis B from:
- injecting drugs using shared needles
- being injured by a used needle
- having a tattoo or piercing with unsterilised equipment
- having a blood transfusion in a country that does not check blood for hepatitis B. Blood transfusions in the UK are checked for hepatitis B.
If you’re pregnant and have hepatitis B, you can also pass it onto your baby during pregnancy or birth.
Don’t Miss: Hep C Without Hepatic Coma Meaning
Immunisation For Hepatitis B
Immunisation is the best protection against hepatitis B infection. A course of vaccination is recommended for all babies and people in high-risk groups.
Immunisation can be with a vaccine against hepatitis B alone or with a combination vaccine. To be immunised, contact your doctor or local council.
Protection against hepatitis B is available free of charge under the National Immunisation Program Schedule. In Victoria, immunisation against hepatitis B is free for:
- Babies at birth immunisation against hepatitis B alone as soon as possible after birth.
- Babies at 2, 4 and 6 months combination immunisation in the form of a diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough, hepatitis B, polio and Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine .
- Premature babies at 12 months premature babies born under 32 weeks gestation or under 2,000g birth weight receive a single booster dose.
- Children up to and including 9 years of age.
- People aged less than 20 years having a catch-up immunisation.
- Refugees and humanitarian entrants aged 20 years and above.
In Victoria, free hepatitis B vaccine is provided for people who are at increased risk of infection, including:
Immunisation is also recommended, but not necessarily free, for people who are at increased risk of infection, including:
The Sex Superbug: Gonorrhoea
Gonorrhoea may be on the verge of becoming an untreatable disease. Gonorrhoea is caused by a bacteria, and it is treated with two drugs but resistance is already developing to one of the drugs. Soon we may have no treatment options remaining for multi-drug resistant gonorrhoea infections.
Those diagnosed with gonorrhoea are at risk of serious complications and untreated, the disease can cause inflammation of the womb and infertility. The infection can also be passed from a pregnant woman to her baby.
Infection in pregnant women can lead to early labour and delivery or permanent blindness in a newborn baby.
There were 87 million new cases gonorrhoea amount men and women aged 15-49 years in 2016.
WHO/Yoshi Shimizu. Testing for sexually transmitted infections in Mongolia.
Read Also: How Do You Get Viral Hepatitis C
Transmission Symptoms And Treatment
How is HBV transmitted?
HBV is transmitted through activities that involve percutaneous or mucosal contact with infectious blood or body fluids , including
- sex with a partner who has HBV infection
- injection drug use that involves sharing needles, syringes, or drug-preparation equipment
- birth to a person who has HBV infection
- contact with blood from or open sores on a person who has HBV infection
- exposures to needle sticks or sharp instruments and
- sharing certain items with a person who has HBV infection that can break the skin or mucous membranes , potentially resulting in exposure to blood.
How long does HBV survive outside the body?
HBV can survive outside the body and remains infectious for at least 7 days .
What should be used to clean environmental surfaces potentially contaminated with HBV?
Any blood spills should be disinfected using a 1:10 dilution of one part household bleach to 9 parts water. Gloves should be worn when cleaning up any blood spills.
Who is at risk for HBV infection?
The following populations are at increased risk for becoming infected with HBV:
- Infants born to people with HBV infection
- Sex partners of people with HBV infection
- Men who have sex with men
- People who inject drugs
- Household contacts or sexual partners of known people with chronic HBV infection
- Health care and public safety workers at risk for occupational exposure to blood or blood-contaminated body fluids
- Patients on hemodialysis
Who should be screened for HBV?
Extrahepatic Manifestations Of Hepatitis B
Extrahepatic manifestations of HBV infection includes various forms of vasculitis, renal disease, and arthritis, typically associated with circulating immune complexes within the host . Polyarteritis nodosa as well as glomerulonephritis, including membranoproliferative, membranous, and mesangial proliferative variants, appear to be associated with immune complex deposition and may improve with antiviral therapy, although data are limited. Essential mixed cryoglobulinemia can also occur in association with HBV infection, initially presenting with purpura, recurrent arthritis, and weakness, but can then progress to advanced disease characterized by features of vasculitis, glomerulonephritis, and pulmonary involvement. Additional extrahepatic manifestations of HBV may include palpable purpura and generalized arthralgias, which can appear at the time of acute infection or once chronic infection is established.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Virus Ab 0.1
Read Also: Initial Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
What If I Am Pregnant
Its recommended that all pregnant women have a blood test for hepatitis B in early pregnancy.
If you have hepatitis B and are pregnant, treatments can reduce the risk of transmission of hepatitis B to the baby.
If you have hepatitis B, it is important to protect others from infection.
Important ways to prevent the spread of hepatitis B include:
- vaccination of all your close contacts
- practise safe sex until your sexual contacts are fully vaccinated and immune
- do not donate blood, organs or body tissue
- do not allow your blood to contact another person
- inform healthcare workers
- if your work involves potential for your blood or other body fluid to spread to other people, discuss your situation with your doctor
The hepatitis B vaccine is safe and effective in protecting against hepatitis B infection, providing protection in 95 in 100 vaccinated people.
In Australia, hepatitis B vaccination is part of the standard immunisation schedule for all newborn babies and infants. Its also recommended for adults who are at high risk of exposure, people who are immunosuppressed or have other liver disease. People in these risk groups should be vaccinated against hepatitis B. Talk to your doctor about your level of risk and whether hepatitis B vaccination is recommended for you.
If you werent vaccinated against hepatitis B as a child, or if youre not sure whether you are vaccinated, talk to your doctor about whether you need a catch-up vaccine.