Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Many people with hepatitis C have no symptoms at all. When symptoms do occur they often involve the following:
- tiredness
- stomach problems
- jaundice a yellowing of the skin and eyes.
Some people will clear the virus without treatment, but this is less likely in the case of people living with HIV.
For most people, hepatitis C continues to reproduce in the body long after infection, turning into a chronic infection. This means that they continue to be infectious, although they may not experience any symptoms at all, or not for many years.
Even with a lack of symptoms, the virus may still be damaging the liver, causing fibrosis a hardening of the liver. This can lead to cirrhosis, which is a permanent scarring of the liver. Cirrhosis increases the risk of liver cancer.
How Transmission May Occur
Tattoo artists create their designs by injecting ink into the second layer of a person’s skin, known as the dermis. They do this by using a tattoo machine which punctures the skin with a collection of small, high-speed needles. Body piercing, by contrast, uses a single needle to puncture the skin.
As a result of the broken skin, certain infections can theoretically be passed from one customer to the next if the gun or needles aren’t properly disinfected. But do they?
What’s The Relationship Between Drug Use And Viral Infections
People who engage in drug use or high-risk behaviors associated with drug use put themselves at risk for contracting or transmitting viral infections such as human immunodeficiency virus , acquired immune deficiency syndrome , or hepatitis. This is because viruses spread through blood or other body fluids. It happens primarily in two ways: when people inject drugs and share needles or other drug equipment and when drugs impair judgment and people have unprotected sex with an infected partner. This can happen with both men and women.
Drug use and addiction have been inseparably linked with HIV/AIDS since AIDS was first identified as a disease. According to the CDC, one in 10 HIV diagnoses occur among people who inject drugs.1 In 2016, injection drug use contributed to nearly 20 percent of recorded HIV cases among menmore than 150,000 patients. Among females, 21 percent of HIV cases were attributed to IDU.2 Additionally, women who become infected with a virus can pass it to their baby during pregnancy, regardless of their drug use. They can also pass HIV to the baby through breastmilk.
Don’t Miss: How Did I Get Hepatitis C
What Is Viral Hepatitis
Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. The liver is a vital organ that processes nutrients, filters the blood, and fights infections. When the liver is inflamed or damaged, its function can be affected. Heavy alcohol use, toxins, some medications, and certain medical conditions can cause hepatitis. However, hepatitis is often caused by a virus. In the United States, the most common types of viral hepatitis are hepatitis A, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C.
How Does Hcv Spread From Person To Person

HCV is spread mainly through contact with the blood of a person who has HCV. In the United States, HCV is spread mainly by sharing needles or other injection drug equipment with someone who has HCV. HCV can also be spread through sexual contact. While the risk of transmission through sexual contact is low, the risk is increased in people with HIV.
Don’t Miss: Liver Disease Caused By Hepatitis C
Who Is At Risk
Some specific populations are at increased risk of hepatitis A : people who inject drugs, men who have sex with men , and children in daycare .
Individuals at increased risk of hepatitis A infection include those with close household or sexual contact with an infected person or those who travel to regions that have high prevalence rates of hepatitis A .2,4,5
The Epidemiology Of Hiv/hepatitis C Co
It is estimated that 6.2% of people living with HIV also show signs of past or present hepatitis C infection. This equates to 2.3 million people living with HIV, over half of whom are .7 Injection drug use accounts for 23% of new hepatitis C infections while 8% of people living with chronic hepatitis C currently inject drugs.8
Among people living with HIV, the prevalence of hepatitis C is highest in people who inject drugs , followed by and pregnant women .9 Studies also show very high rates among living with HIV, although less data has been collected.
As a result, developing models of care that meet the needs of people from these key populations is a vital first step to providing an effective co-infection treatment programme. However, the proportion of people living with HIV and hepatitis C co-infection varies considerably, according to risk group and world region.
In 2016, low- and middle-income countries accounted for about 75% of people living with hepatitis C. China has the largest hepatitis C epidemic , followed by Pakistan , India and Egypt . These four countries account for almost 40% of all people living with hepatitis C.10
Eastern Europe is home to the greatest number of people living with HIV-hepatitis C co-infection, estimated to be around 600,000 people.11 Around 400,000 people in sub-Saharan Africa are also living with HIV/hepatitis C co-infection.12
Read Also: What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis C Virus
What Is The Treatment For Individuals With Hiv And Hepatitis
Doctors primarily treat HIV with antiretroviral therapy. This effective treatment helps stop HIV from progressing to a later stage disease called AIDS.
With the exception of HAV, most hepatitis infections are treated with medications called antivirals. Treating HBV and HCV early is important in preventing liver diseases and cancers, some of which may be fatal.
HCV is treated with antiviral medications taken over the course of 8 to 12 weeks. The HHS says that this treatment has a 97 percent cure rate, including in people with HIV.
While HBV is also treatable, medications work to suppress the virus. They cant get rid of it entirely. Similar to HIV, treatment for HBV may be lifelong.
HAV is an acute infection. It can resolve on its own, or it can last up to 6 months, according to the . Rest and fluids are standard treatments, but more severe cases may require hospitalization.
HIV-hepatitis coinfections are treatable when detected early, according to the HHS.
Some people may take separate medications for HIV and hepatitis, like in the case of HCV. However, you can sometimes treat both viruses at the same time with the same medications. It may be helpful to find a doctor whos also experienced with treating both viruses.
Risk factors for contracting HIV or hepatitis may include:
- sharing needles, razors, or syringes
- having sex without a condom or other type of barrier method
- transmission during childbirth
Hiv And Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C Coinfection
Hepatitis B and hepatitis C are liver infections caused by a virus. Because these infections can be spread in the same ways as HIV, people with HIV in the United States are often also affected by chronic viral hepatitis.
Viral hepatitis progresses faster and causes more liver-related health problems among people with HIV than among those who do not have HIV. Liver disease, much of which is related to HBV or HCV, is a major cause of non-AIDS-related deaths among people with HIV.
Given the risks of hepatitis B or hepatitis C coinfection to the health of people living with HIV, it is important to understand these risks, take steps to prevent infection, know your status, and, if necessary, get medical care from someone who is experienced in treating people who are coinfected with HIV and HBV, or HIV and HCV.
Read Also: What Does Hepatic Steatosis Mean
Keep Personal Items Personal
Any tools or implements that may have a bit of blood on them from infected people are potential sources of hepatitis B or C transmission. Toothbrushes, nail clippers, razors, needles, and washcloths may all contain trace amounts of blood that can transmit infection. Keep personal items such as these to yourself and never use personal items that belong to others.
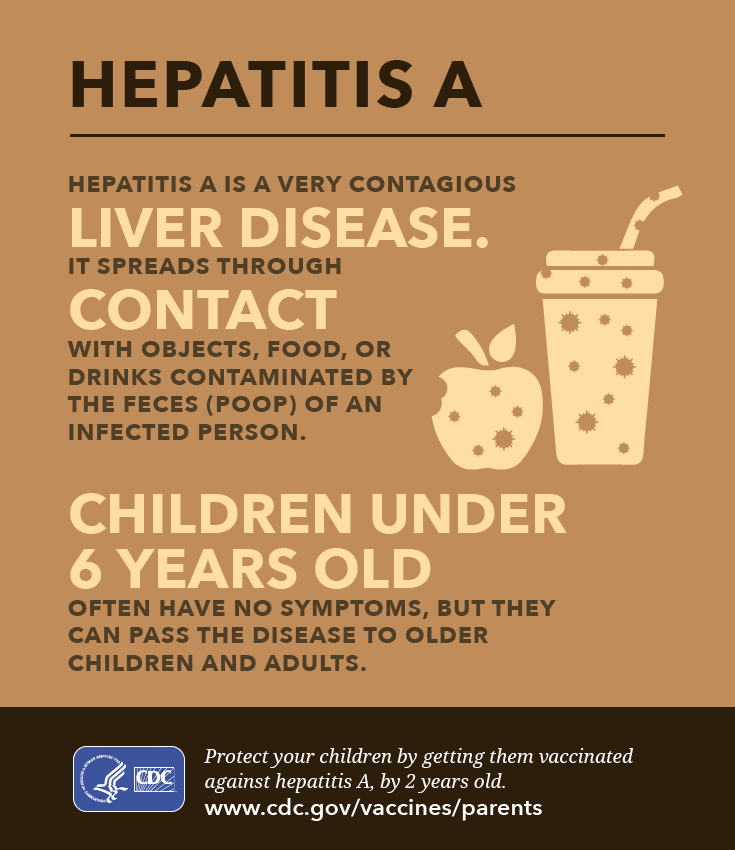
How Do You Get Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A can be spread by sexual contact with an infected person or close personal contact . However, it is most often spread by what scientists call the fecal-oral route. This happens when one person eats or drinks something that has small amounts of fecal matter from another person who has hepatitis A. This can happen by touching something that has the virus on it and then putting your hands in your mouth. It can happen when food is grown, picked, processed or served. Water can also be contaminated.
Mothers do not pass on hepatitis A in breast milk. You cannot be infected with HAV by sitting near to or hugging someone with hepatitis A. It does not spread through coughs or sneezes.
You May Like: Does The Hpv Vaccine Protect Against Hepatitis B
Living With Hepatitis B: Your Lifestyle
People living with HIV and hepatitis B can benefit from adopting a healthy lifestyle, including eating a balanced diet. Try to maintain a healthy weight. Being overweight is linked to fatty liver disease which can worsen liver damage.
Since people living with HIV and hepatitis may have an increased risk of cardiovascular disease and diabetes, your clinic should regularly monitor your blood fats or lipids and blood sugar .
People living with hepatitis B should limit how much alcohol they drink, and those with liver damage should avoid alcohol altogether. Not smoking and cutting down or stopping recreational drug use are also important for overall health.
- Eat a balanced diet including vegetables, fruit and wholegrains.
- Get regular moderate exercise.
Hiv Treatment And Prevention

Simple, effective treatments for HIV are widely available in Australia. In addition to protecting the health and wellbeing of people living with HIV, these treatments significantly reduce the risk of HIV transmission. Almost all people on HIV treatments have very low levels of virus in their body. This is called having an undetectable viral load. There is no risk of HIV transmission from a person with an undetectable viral load. This is sometimes referred to as undetectable equals untransmissible, or U=U.
For people who do not have HIV, but may be at higher risk of it, affordable medication is available that is more than 99 per cent effective at preventing HIV. Known as PrEP , this medication is available through the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme from your regular GP.
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatic Metastatic Disease
Sport And Transmission Of Hiv And Hepatitis
The risk of transmission of HIV or hepatitis B or C from an infected player is:
- negligible for other athletes and players involved in contact sports
- negligible for first aid officers who follow infection control guidelines
- zero for coaches, trainers, officials and spectators.
HIV and hepatitis B and C cannot spread through:
- sweat or saliva from other sportspeople
- sharing drink bottles with team members
- hugging or shaking hands.
How Can You Prevent Hepatitis A
There is a vaccine, made from an inactivateddeadvirus to prevent hepatitis A. If you are not sure you have had the vaccine, you can ask your doctor to test you to see if you have been vaccinated.
You can also practice good hand washing hygiene. Make sure you use soap and warm water to wash your hands for at least 15 to 30 seconds after you use the toilet, change diapers, and before and after touching food.
If you are traveling in another country, especially a developing country, drink only bottled water and use only bottled water to brush your teeth, wash your produce, and freeze for ice cubes.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Cdc Fact Sheet
How Can You Prevent Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B: Vaccination is the best way to prevent all of the ways that hepatitis B is transmitted. People with HIV who do not have active HBV infection should be vaccinated against it. In addition to the 3-dose series of hepatitis B vaccine given over 6 months, as of 2017, there is a 2-dose series given over 1 month.
Hepatitis C: No vaccine exists for HCV and no effective pre- or postexposure prophylaxis is available. The best way to prevent hepatitis C infection is to never inject drugs or to stop injecting drugs by getting into and staying in drug treatment. If you continue injecting drugs, always use new, sterile needles or syringes, and never reuse or share needles or syringes, water, or other drug preparation equipment.
How Is Hepatitis Diagnosed
Getting tested for hepatitis is important to help detect infection early. Tests may even detect hepatitis before symptoms begin. In people with HIV, this is especially important so that they may receive treatment early. Testing for hepatitis may also reduce transmission to others.
Hepatitis is diagnosed with blood testing. This may involve:
- antibody testing for HAV
- hepatitis B surface antigen, to detect either acute or chronic infections of HBV
- hepatitis C antibody test if antibodies are found in the blood, your doctor may order a follow-up test to confirm HCV
- liver function tests, which may find chronic hepatitis infections
Read Also: Is There Any Cure For Hepatitis C
What Is The Risk Of Coinfection
A coinfection is when someone has two or more infections at the same time. People living with HIV are at risk of developing coinfections such as hepatitis C because HIV weakens the immune system, which leaves the body more vulnerable to other infections and illnesses.
HIV and HCV are also transmitted in similar ways, which means that people who have HIV may be at higher risk of exposure to HCV. In the United States, over a third of people living with HIV also have hepatitis C.
Coinfection of HCV and HIV is higher among those who use injected drugs. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , HCV coinfection occurs in between 62 and 80 percent of people with HIV who use injected drugs.
A systematic review of 783 studies concluded that people living with HIV were six times more likely to have hepatitis C than people without HIV.
Hepatitis C infections are more serious in people with HIV and can lead to more severe damage of the liver. HIV and HCV coinfections can increase the risk of:
- liver fibrosis and cirrhosis, which is a buildup of scar tissue in the liver
- end-stage liver disease
A person can contract HCV through direct contact with blood or other body fluids that contain the virus. Possible modes of transmission include:
Ways to prevent hepatitis C include:
- not sharing needles
How Are Hepatitis C And Hiv Connected
People living with HIV are at higher risk for hepatitis C. Of the 1.2 million people living with HIV in the U.S., about 1 in 4 also have hepatitis C.
Having both HIV and hepatitis C means increased risk for liver disease, liver failure and liver-related death from hepatitis C. Because hepatitis is often serious in people living with HIV and may lead to liver damage more quickly, the CDC recommends people living with, or at risk for HIV, also get tested for hepatitis C.
You May Like: What Is A Hepatitis Panel
Treating Hepatitis C In People With Hiv Co
DAAs have good outcomes for people previously considered hard-to-treat. This includes people with HIV co-infection. The outcomes of treatment in people with co-infection are comparable to those in people with hepatitis C alone – rates of sustained virological response are over 95%, even in individuals who have not responded to previous treatment and people with cirrhosis.38There is no longer a need to consider HIV/HCV- co-infected patients as a special, difficult-to treat patient population, WHO states in its 2016 guidance.39
The key issue that remains, WHO emphasises, is the potential for drug-drug interactions between medications for HIV and hepatitis C. When these may occur, the regimens for either infection may need to be altered.40 However, modern HIV medications rarely have the harmful effects on the liver that characterised some older drugs. Hepatitis C treatment is generally provided to people who are already taking HIV treatment.41
Is Hepatitis Testing Recommended For People With Hiv
Yes. Everyone living with HIV should be tested for HBV and HCV when they are first diagnosed with HIV and begin treatment. People living with HIV who have ongoing risk factors for getting hepatitis B or hepatitis C should be tested annually.
In addition, new HCV screening recommendations from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention call for:
- One-time screening for all adults 18 years and older
- Screening of all pregnant women during every pregnancy
- Testing for all persons with risk factors, with testing continued periodic testing those with ongoing risk.
Recommended Reading: Symptoms Of Advanced Hepatitis C
How Long Does The Hepatitis A Vaccine Last
We dont know exactly how long the protection of the vaccine lasts, but studies have indicated that it lasts at least 20 years in some people and it could last as long as 40 years or more. Having only one dose of the recommended two-dose vaccine has shown to provide protection for at least 10 years.
Does Hiv Viral Load Affect Getting Or Transmitting Hiv
Yes. Viral load is the amount of HIV in the blood of someone who has HIV. Taking HIV medicine daily as prescribed can make the viral load very lowso low that a test cant detect it .
People with HIV who take HIV medicine daily as prescribed and get and keep an undetectable viral load have effectively no risk of transmitting HIV to an HIV-negative partner through sex.
HIV medicine is a powerful tool for preventing sexual transmission of HIV. But it works only as long as the HIV-positive partner gets and keeps an undetectable viral load. Not everyone taking HIV medicine has an undetectable viral load. To stay undetectable, people with HIV must take HIV medicine every day as prescribed and visit their healthcare provider regularly to get a viral load test. Learn more.
Read Also: How Did You Get Hepatitis C