Who Is More Likely To Get Hepatitis B
People are more likely to get hepatitis B if they are born to a mother who has hepatitis B. The virus can spread from mother to child during birth. For this reason, people are more likely to have hepatitis B if they
- were born in a part of the world where 2 percent or more of the population has hepatitis B infection
- were born in the United States, didnt receive the hepatitis B vaccine as an infant, and have parents who were born in an area where 8 percent or more of the population had hepatitis B infection
People are also more likely to have hepatitis B if they
- are infected with HIV, because hepatitis B and HIV spread in similar ways
- have lived with or had sex with someone who has hepatitis B
- have had more than one sex partner in the last 6 months or have a history of sexually transmitted disease
- are men who have sex with men
- are injection drug users
- work in a profession, such as health care, in which they have contact with blood, needles, or body fluids at work
- live or work in a care facility for people with developmental disabilities
- have been on kidney dialysis
- live or work in a prison
- had a blood transfusion or organ transplant before the mid-1980s
In the United States, hepatitis B spreads among adults mainly through contact with infected blood through the skin, such as during injection drug use, and through sexual contact.12
Who Should Be Vaccinated For Hepatitis B
All newborns should be vaccinated. Also, people who are under 18 who were not vaccinated at birth should also get the vaccine. Other groups who should be sure to be vaccinated are those in certain high-risk categories, such as:
- People who have more than one sexual partner.
- Men who have sex with men.
- Adults with diabetes.
- Sexual partners of infected people and people who share households with infected individuals.
- People who are exposed to blood and other bodily fluids, including healthcare and public safety professionals, and people who work in jails and other places taking care of people who cant take care of themselves.
Antiviral Medication For Hepatitis B
Doctors may recommend antiviral medication for people with chronic hepatitis B, which occurs when the virus stays in your body for more than six months.
Antiviral medication prevents the virus from replicating, or creating copies of itself, and may prevent progressive liver damage. Currently available medications can treat hepatitis B with a low risk of serious side effects.
NYU Langone hepatologists and infectious disease specialists prescribe medication when they have determined that without treatment, the hepatitis B virus is very likely to damage the liver over time. People with chronic hepatitis B may need to take antiviral medication for the rest of their lives to prevent liver damage.
There are many different types of antiviral medications available, and your doctor recommends the right type for you based on your symptoms, your overall health, and the results of diagnostic tests. A doctor may take a wait-and-see approach with a person who has a healthy liver and whose blood tests indicate a low viral load, the number of copies of the hepatitis B virus in your bloodstream.
Someone with HIV infection or AIDS may have a weakened immune system and is therefore more likely to develop liver damage. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention strongly recommends that people with HIV infection who are diagnosed with hepatitis B immediately begin treatment with antiviral medication.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Surf Ab Quant
If I Have Hepatitis B And Feel Healthy Do I Need To Keep Going To My Doctor
Chronic hepatitis B is a silent disease because often no symptoms appear until your liver is severely damaged. Although many people with chronic hepatitis B have an inactive disease and will remain healthy, about one in four will have an active disease that may lead to cirrhosis, liver failure, and liver cancer.
Because hepatitis B has no symptoms until your liver is badly damaged, a blood test is the only way for your doctor to find out if your hepatitis B is active or inactive, and to offer treatment, if needed. To help your doctor monitor how your disease behaves over time, you will need lifelong repeat blood tests every six to 12 months. Some tests, such as HBV DNA may need to be done more frequently . No treatment is required while the virus is inactive, but you should continue to get regular blood tests from your doctor to monitor your liver disease.
Medical Treatment For Hepatitis A B & C
Treatment for hepatitis A, B, or C is based on which type of hepatitis is present in the bloodstream and the severity of the resulting liver damage. Depending on the results of diagnostic tests, our specialists at NYU Langone may recommend antiviral medication to stop the virus from replicating and protect your liver from further damage.
Read Also: What Is The Treatment For Autoimmune Hepatitis
Hepatitis B In The United States
In the United States, about 862,000 people have chronic hepatitis B.6 Asian Americans and African Americans have higher rates of chronic hepatitis B than other U.S. racial and ethnic groups.10 Researchers estimate that about half of the people living with chronic hepatitis B in the United States are Asian Americans and Pacific Islanders.11 Chronic hepatitis B is also more common among people born in other countries than among those born in the United States.7
The hepatitis B vaccine has been available since the 1980s and, in 1991, doctors began recommending that children in the United States receive the hepatitis B vaccine. The annual rate of acute hepatitis B infections went down 88.5 percent between 1982 and 2015.12 In 2017, the annual number of hepatitis B infections rose in some states.13 Experts think the rise was related to increases in injection drug use. Injection drug use increases the risk of hepatitis B infection.
What Will I Need To Do If I Am On Hepatitis B Medications
- Take oral medications every day to avoid developing resistance.
- See your provider on a regular basis
- If you have cirrhosis or high risk of liver cancer, get liver imaging on time as prescribed by your provider
- Have periodic laboratory tests to monitor HBV viral load and liver enzymes to monitor disease activity and response to medications
- You may need blood tests every 3-6 months initially and at least once a year thereafter if virus is undetected in blood.
Read Also: Can I Donate Blood If I Had Hepatitis A
Hepatitis B Treatment: Medication
There are five FDA-approved oral medications and one injection available to treat hepatitis B. The newer oral medications are stronger and less likely to develop viral resistance and have very few side effects.
The medication cannot cure the disease, but can help reduce the number of viruses in the body and the risk of complications. You may undergo periodic blood tests to monitor drug resistance and determine whether the medication is having an effect.
Antiviral Medication For Hepatitis C
For people with hepatitis C, the goal of treatment with antiviral medication is to prevent the virus from replicating, or copying itself, and to eliminate the virus from the bloodstream. If the hepatitis C virus has been in the body for more than six months, the infection is considered chronic. Without treatment, most people with acute hepatitis C develop the chronic form of the disease.
Your doctor decides which antiviral medicationor combination of medicationsto prescribe based on the results of a blood test called a genotype test. There are six genotypes, or strains, of the hepatitis C virus, and people with certain genotypes respond more quickly to medical treatment.
For many years, the standard treatment for chronic hepatitis C consisted of the antiviral medications pegylated interferon and ribavirin. Ribavirin is taken by mouth every day, and interferon is an injection that you or a caregiver can administer once a week at home.
In 2013 and 2014, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved a group of new medications for the treatment of hepatitis C. These medications, which include sofosbuvir, are very effective and have fewer side effects than older medications, particularly interferon.
Recommended Reading: Can Hepatitis B Virus Be Cured
How Is Hepatitis B Diagnosed
There are three main ways to diagnose HBV infection. They include:
- Blood tests: Tests of the blood serum shows how your bodys immune system is responding to the virus. A blood test can also tell you if you are immune to HBV.
- Abdominal ultrasound: An ultrasound uses sound waves to show the size and shape of your liver and how well the blood flows through it.
- Liver biopsy: A small sample of your liver tissue is removed though a tiny incision and sent to a lab for analysis.
The blood test that is used to diagnose hepatitis B is not a test that you get routinely during a medical visit. Often, people whove become infected first learn they have hepatitis B when they go to donate blood. Blood donations are routinely scanned for the infection.
The virus can be detected within 30 to 60 days of infection. About 70% of adults with hepatitis B develop symptoms, which tend to appear an average of 90 days after initial exposure to the virus.
What Are Clinical Trials For Hepatitis B
Clinical trialsand other types of clinical studiesare part of medical research and involve people like you. When you volunteer to take part in a clinical study, you help doctors and researchers learn more about disease and improve health care for people in the future.
Researchers are studying many aspects of hepatitis B, such as
- progression of hepatitis B and long-term outcomes
- new treatments for hepatitis B
- prevention of reactivated or worsening hepatitis B in people receiving cancer treatment
Recommended Reading: Can Hepatitis C Be Passed From Mother To Child
If I Have No Symptoms How Would I Know If I Have Hepatitis B
To confirm whether or not you have hepatitis B, you will need blood tests.
If you have at least one risk factor , you should ask your health care provider to be tested for hepatitis B. Also, you should be tested for hepatitis B if:
- you were born in a region where hepatitis B is more common, including Asia, Africa, southern and eastern Europe, the Pacific Islands, the Middle East, and the Arctic
- one or both of your parents immigrated from a region where hepatitis B is more common
- you live or travel to regions where hepatitis B is more common
- you have a family history of liver disease or liver cancer
- you have been in prison
- you are pregnant
- you have ever used injection drugs, even just once
- you have unexplained abnormal liver enzymes or if
- you receive medicines that suppress the immune system.
How Can I Prevent Spreading Hepatitis B To Others
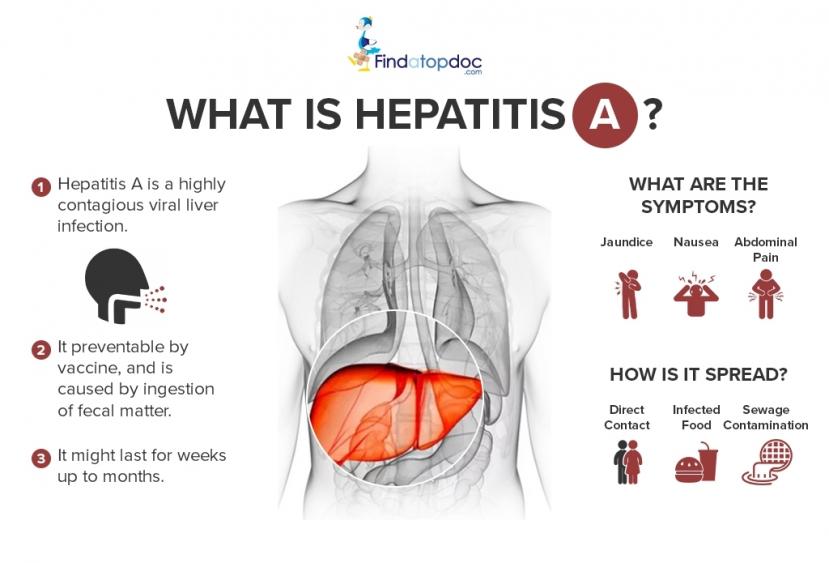
If you have hepatitis B, follow the steps above to avoid spreading the infection. Your sex partners should get a hepatitis B test and, if they arent infected, get the hepatitis B vaccine. You can protect others from getting infected by telling your doctor, dentist, and other health care professionals that you have hepatitis B. Dont donate blood or blood products, semen, organs, or tissue.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Antibody Reactive Meaning
Closing In On A Cure For Hepatitis B
For Thomas Tu, eliminating hepatitis B is a deeply personal goal.
Tu, a molecular virologist at the Westmead Institute for Medical Research in Sydney, Australia, learnt he had chronic hepatitis B as a teenager. A blood test revealed telltale signs of the infectious liver disease, which Tu had probably acquired at birth.
In his late 20s, Tu started taking a medication to limit the viruss replication and prevent collateral damage to his liver cells. Now 36, he has been on that daily treatment a pill known as a nucleoside analogue ever since.
Yet, even with a therapy that keeps his infection well under control, Tu remains at heightened risk for liver disease. He must juggle visits to specialist doctors and bear prescription-drug costs. And he knows that many others racked by the financial instability, emotional toil and stigma that the lifelong infection can bring have it much worse.
Im in this quite privileged space to be able to be on therapy and not have any side effects or feel any burden from taking daily medicines, Tu says. Thats not the same for the majority of people living with hepatitis B.
We are using all our weapons to tackle every single step of the virus, says Man Fung Yuen, a hepatologist at the University of Hong Kong.
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis B
After the virus enters the body, there is an incubation period lasting 1.5 to 6 months until illness begins. During the acute phase most persons have no symptoms or might experience a mild illness. Symptoms of acute HBV infection, when present, may include:
- Jaundice
- Dark-colored urine, light-colored stools
- Fever
During the chronic phase hepatitis B usually progresses silently, with no symptoms at all during the first 10-20 years. Signs of severe liver scarring may include:
- Ascites
- Star-shaped vein pattern developing on the swollen belly
- Jaundice
- Easy bruising and bleeding
Chronic HBV infection can lead to serious liver disease, liver scarring , and hepatocellular cancer.
Because symptoms of hepatitis B are usually absent, persons with risk for HBV infection should be tested. If you think you have hepatitis B, or are at risk for hepatitis B, you should contact your doctor.
Read Also: Is Hepatitis C An Autoimmune Disease
With The Momentum Growing Around Hepatitis B Drug Discovery Research We Are Closer Than Ever To A Cure
From the Spring 2016 B Informed Newsletter
With the momentum growing around hepatitis B drug discovery research, how far are we from a cure?
Closer than ever, according to Timothy Block, PhD, president and co-founder of the Hepatitis B Foundation and its research arm, the Baruch S. Blumberg Institute. He points out that hepatitis C, initially thought to be incurable, can now be cured with new combination treatments.
Hepatitis B is in a similar position, Block believes. And the need for a cure has never been greater, with over 240 million people living with chronic hepatitis B infection worldwide, resulting in 1 million deaths per year from related liver failure and liver cancer.
Treatments are available, explains Block, but we have become a little too comfortable with the seven medications that are currently approved for use. While these drugs are effective, the interferons have many side effects and the oral antivirals require lifelong use. Moreover, they work in only about half of the infected population, and reduce the rate of death due to liver disease by only about 40 to 70 percent.
For those who benefit from treatment, the antiviral drugs prove that medications can be effective. However, there are millions who do not benefit and are still left vulnerable. We should not accept that a significant number of people will still die from hepatitis B-related complications despite taking the current drugs, Block declares.
What would a cure look like?
cccDNA Inhibitors
How Can You Prevent Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B: Vaccination is the best way to prevent all of the ways that hepatitis B is transmitted. People with HIV who do not have active HBV infection should be vaccinated against it. In addition to the 3-dose series of hepatitis B vaccine given over 6 months, as of 2017, there is a 2-dose series given over 1 month.
Hepatitis C: No vaccine exists for HCV and no effective pre- or postexposure prophylaxis is available. The best way to prevent hepatitis C infection is to never inject drugs or to stop injecting drugs by getting into and staying in drug treatment. If you continue injecting drugs, always use new, sterile needles or syringes, and never reuse or share needles or syringes, water, or other drug preparation equipment.
Recommended Reading: What Happens When You Have Hepatitis
Is The Vaccine Safe
The vaccine is safe. It’s been used in Canada for many years and it’s one of the safest vaccines around. It might cause minor side effects – maybe redness, warmth or slight swelling where the needle went in, maybe tiredness or slight fever for a day or so. More serious reactions occurring within 15 days should be reported to your doctor or local health unit. These include breathing trouble, swelling of face or mouth, a fever over 39°C, hives or rashes.
The risk from hepatitis B is much greater than the risk from the vaccine, however, some people should not have this vaccine.
You won’t be vaccinated if you have a fever or anything more serious than a minor cold. Tell your doctor if you’ve had a past allergic reaction to a vaccine. You should always discuss the benefits and risks of any vaccine with your doctor.
Who Should Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine
All newborn babies should get vaccinated. You should also get the shot if you:
- Come in contact with infected blood or body fluids of friends or family members
- Use needles to take recreational drugs
- Have sex with more than one person
- Are a health care worker
- Work in a day-care center, school, or jail
Read Also: Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedule For Child
Clearing Acute Hepatitis B
Some studies suggest that up to 95% of adults with acute HBV infection will spontaneously clear the virus, usually within six months, with no lasting repercussions.
Chronic hepatitis B occurs when the immune system does not clear the virus. Around one of every 20 people acutely infected with HBV will progress to this persistent stage of infection.
Chronic hepatitis B is a slowly progressive disease in which ongoing inflammation causes the gradual scarring of the liver. This can lead to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma .
However, the course of chronic HBV infection is not set. Some people may progress faster than others, while others may never develop overt symptoms.
Statistically speaking:
- The risk of cirrhosis in people with chronic hepatitis B is approximately 10% to 20% over 20 years, increasing to 40% after 30 years.
- The risk of hepatocellular carcinoma increases by 2% and 3% per year in people with HBV and cirrhosis. People without cirrhosis can also get it, but the annual risk drops to around 0.02%.