Tests To Diagnose Hepatitis C
How is Hepatitis C diagnosed?
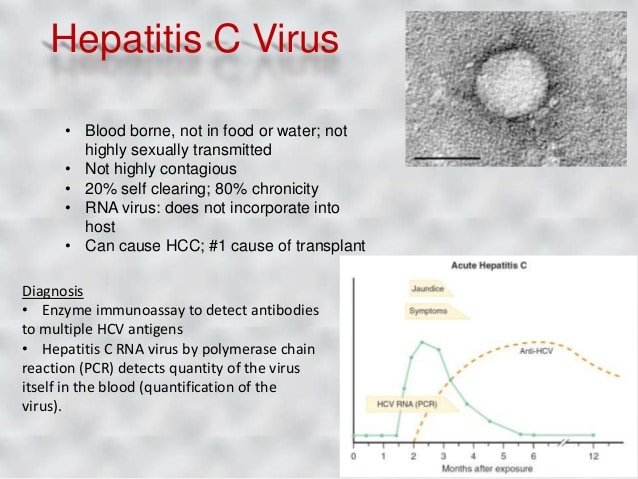
There are two main blood tests typically used to diagnose Hepatitis C. First, youll have a screening test that shows if youve ever had Hepatitis C at some point in your life. If this test is positive, youll have a second test to see if you have Hepatitis C now. These blood tests are described below:
Hepatitis C antibody test
This is the screening test used by doctors to show whether or not you have ever been exposed to Hepatitis C at some time in your life, by detecting antibodies in your blood. Antibodies are substances your body makes to fight off all kinds of infections. If you were ever infected with Hepatitis C, your body would have made antibodies to fight the virus.
If the test result is:
- Negative, it means you have not been exposed to Hepatitis C and further testing is usually not needed.
- Positive, you have had Hepatitis C at some point. However, it does not tell you whether you have it now. Youll need to see your doctor for another test the Hepatitis C RNA test to determine if the virus is still active and present in your blood.
Hepatitis C RNA Qualitative Test
This test will determine whether or not you are currently infected with Hepatitis C. It is often called the PCR test because of the process used . It looks for the genetic material of the Hepatitis C virus in your blood.
If the test result is:
Hepatitis C RNA Quantitative Test
What Do Hepatitis C Symptoms Look Like
Hepatitis C infection can go through two stages: acute and chronic. In the early, or acute stage, most people don’t have symptoms. If they do develop symptoms, these can include:
- flu-like symptoms, tiredness, high temperature and aches and pains
- loss of appetite
- tummy pain
- jaundice, meaning your skin and the whites of your eyes turn yellow
While for some people, the infection will clear without treatment, in most cases, acute infection will develop into long-term chronic infection. Chronic infection may not become apparent for a number of years until the liver displays signs of damage. These symptoms can include:
- mental confusion and depression these are specific to hepatitis C
- constantly feeling tired
- nausea, vomiting or tummy pain
- dark urine
- feeling bloated
- joint and muscle pain
Without treatment, chronic hepatitis C can cause scarring of the liver , which can cause the liver to stop working properly. A small number of people with cirrhosis develop liver cancer and these complications can lead to death. Other than a liver transplant, theres no cure for cirrhosis. However, treatments can help relieve some of the symptoms.
Ask The Expert: From Corinne
Hepatitis C is spread from blood to blood contact generally this happens when blood from a person infected with the Hepatitis C virus enters the body of someone who is not infected. Today, the most common route of HCV transmission is through intravenous or sharing injection drug equipment. Prior to 1992, many people contracted HCV through blood product transfusions. HCV can be transmitted through sexual contact, however, the risk is considered to be low.
According to the National Institutes of Health, for heterosexual discordant couples in monogamous relationships, the risk of HCV transmission is estimated only to be 0 to 0.6 percent. Based on the low risk of transmission, couples in a monogamous relationship do not need to use condoms, although it is important to know that condoms reduce the risk of transmission even more so.
Don’t Miss: Is Hepatitis A Virus Or Bacteria
How Common Is Hepatitis C In The United States
In the United States, hepatitis C is the most common chronic viral infection found in blood and spread through contact with blood.14
Researchers estimate that about 2.7 million to 3.9 million people in the United States have chronic hepatitis C.13 Many people who have hepatitis C dont have symptoms and dont know they have this infection.
Since 2006, the number of new hepatitis C infections has been rising, especially among people younger than age 30 who inject heroin or misuse prescription opioids and inject them.15,16
New screening efforts and more effective hepatitis C treatments are helping doctors identify and cure more people with the disease. With more screening and treatment, hepatitis C may become less common in the future. Researchers estimate that hepatitis C could be a rare disease in the United States by 2036.17
Could I Give It To Other People
Yes. As long as you carry the virus, you can infect others. You may pass it on to your sex partner, to those who live in close contact with you, and to those who share your needles for injecting drugs. All of these contacts should be examined by a doctor. If they are not yet infected, they should be vaccinated.
Pregnant women who are carriers may pass hepatitis B on to their babies around the time of birth. Most infected infants become carriers. A pregnant woman should have a test for hepatitis B at her first visit to a doctor. If she is a carrier, the infant can be vaccinated at birth to protect against infection.
Recommended Reading: Antiviral Drugs For Hepatitis A
What Are The Symptoms And Consequences Of Infection
Approximately 20 percent of persons exposed to the virus develop symptoms which may include jaundice , fatigue, dark-colored urine, stomach pain, loss of appetite and nausea. After the initial infection, 15-25 percent will recover and 75-85 percent will become chronically infected . Approximately 70 percent of persons chronically infected may develop liver disease, sometimes decades after initial infection.
How Hepatitis C Cant Spread
Unlike the flu or common cold, hepatitis isnt airborne. That means it cant be passed through sneezing, coughing, or sharing your food with someone else. Likewise, you cant get it through kissing or hugging someone with the virus.
Theres a small risk of infection if you share personal care items that come in contact with infected blood, like a toothbrush or razor.
The risk of transmission or contraction from sexual contact is very low if both partners are monogamous. However, you should use a condom if you and your partner have had multiple sexual relationships or sex with someone you know has hepatitis C.
As far as traveling, you cant get the virus abroad unless you come into contact with infected blood or receive blood products that contain HCV.
Don’t Miss: Daa Drugs For Hepatitis C
Dendritic Cells In Sexual Transmission Of Hcv
Molecular mechanisms of HCV transmission
Submucosal DCs capture HCV and migrate into the lymphoid tissues to transmit HCV to PBMCs which might lead to further dissemination HCV to the liver. Mucosal LCs capture HCV after immune activation by STIs and either retain HCV in the tissue which could increase the chance of virus to egress into the bloodstream and disseminate to the liver or migrate into the lymphoid tissues thereby allowing HCV dissemination to the liver. DCSIGN, dendritic cellspecific ICAMgrabbing nonintegrin HCV, Hepatitis C virus HIV1, Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 PBMC, peripheral blood mononuclear cells STI, Sexual transmitted infections.
How Can You Prevent Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B: Vaccination is the best way to prevent all of the ways that hepatitis B is transmitted. People with HIV who do not have active HBV infection should be vaccinated against it. In addition to the 3-dose series of hepatitis B vaccine given over 6 months, as of 2017, there is a 2-dose series given over 1 month.
Hepatitis C: No vaccine exists for HCV and no effective pre- or postexposure prophylaxis is available. The best way to prevent hepatitis C infection is to never inject drugs or to stop injecting drugs by getting into and staying in drug treatment. If you continue injecting drugs, always use new, sterile needles or syringes, and never reuse or share needles or syringes, water, or other drug preparation equipment.
You May Like: New Treatment For Hepatitis B
How Can I Cover Medication Costs
New therapies called direct-acting antivirals are effective and can achieve cures of over 90%. Because these new therapies are very new, they remain very expensive. As such, drug coverage from both government and private companies may require that your liver disease has progressed to a certain stage before they are willing to cover the cost of these drugs.
Talk with your healthcare provider about financial support that may be available.
Below are useful resources when looking for financial assistance:Private health insurance or drug plansIf you have private health insurance or a drug plan at work, you may be able to have the medication paid through your plan. Please consult your private health insurance or drug plan provider to see if your drug is covered.
Publicly funded plansEach provincial and territorial government offers a drug benefit plan for eligible groups. Some are income-based universal programs. Most have specific programs for population groups that may require more enhanced coverage for high drug costs. These groups include seniors, recipients of social assistance, and individuals with diseases or conditions that are associated with high drug costs. For more details, please contact your provincial or territorial health care ministry, or click on the appropriate link below.
Yukon
Available Patient Assistance Programs for Hepatitis C treatment Holkira Pak Maviret
MerckCare Hepatitis C Program 1 872-5773 Zepatier
What Is Hepatitis C
The term hepatitis means an inflammation of the liver. The inflammation may damage the liver, which is the largest internal organ in the body. The liver filters the blood and breaks down harmful substances.
Infection with a virus is the most common cause of hepatitis. If a person contracts HCV, the disease is called hepatitis C, or hep C for short.
Hepatitis A and hepatitis B are other types of hepatitis that result from viral infection. Hepatitis A, B, and C differ in the way they spread, their effect on the liver, and their method of treatment, according to the
HCV causes hepatitis C. A person may contract HCV by coming into contact with the blood of someone else who has the condition. Even microscopic amounts of blood may be enough to spread the virus.
In the United States, the way for someone to contract hepatitis C is by sharing drug-injection equipment, such as needles or syringes.
According to the , other ways a person may contract hepatitis C include:
- coming into contact with the open sores or blood of a person with the condition
- using the toothbrush, nail clippers, or razor of a person with the condition
- getting a tattoo or piercing with non-sterile instruments or inks
- getting an accidental stick with a needle from someone with hepatitis C
About 6% of babies born to people with hepatitis C will develop hepatitis C.
Sometimes an individual will experience symptoms 13 months after contracting HCV, according to
Also Check: How Is Hepatitis C Test Done
Hepatitis C Symptoms & Treatment
FAST FACTS:
-
Hepatitis C is found in infected blood. It is also rarely found in semen and vaginal fluids.
-
Hepatitis C is mainly passed on through using contaminated needles and syringes or sharing other items with infected blood on them. It can also be passed on through unprotected sex, especially when blood is present.
-
You can prevent hepatitis C by never sharing needles and syringes, practising safer sex, and avoiding unlicensed tattoo parlours and acupuncturists.
-
Hepatitis C will often not have any noticeable symptoms, but a simple blood test carried out by a healthcare professional will show whether you have hepatitis C.
-
In the early stages, some peoples bodies can clear a hepatitis C infection on their own, others may develop chronic hepatitis C and will need to take antiviral treatment to cure the infection.
-
Without treatment, chronic hepatitis C can lead to permanent liver damage.
Hepatitis C is part of a group of hepatitis viruses that attack the liver.
Its mainly passed on through contaminated needles, either from injecting drugs or from needle stick injuries in healthcare settings. It can also be transmitted sexually, especially during anal sex or other types of sex that may involve blood.
Some groups are more at risk of getting hepatitis C than others, including people who use drugs, people in prisons, men who have sex with men, health workers and people living with HIV.
More Ways To Reduce The Risk Of Infection

If you arent sure whether you have hepatitis C, get tested. Testing is especially important if you have sex with more than one person or if you have other risk factors for hepatitis C, including being born being 1945 and 1965, having had a blood transfusion prior to 1992, and injecting drugs .
Talk to your partner about getting tested as well, for hepatitis C and other STDs, so you know the risks before having sex. People who are at risk for hepatitis C are also at risk for HIV and other STDs, emphasizes Talal.
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
For Safer Sex Treat Hepatitis C
If you have chronic hepatitis C, of the best strategies for preventing transmission of the virus is to get medical treatment. More than 90 percent cases of hepatitis C can be cured within 8 to 12 weeks of treatment, according to the CDC. Newer hepatitis C treatments are not only effective but generally have fewer and much less severe side effects than previous drugs.
Just be aware that during treatment, transmission can still occur. And a cure doesnt grant you protection against the virus for life. If you continue to engage in high-risk behavior, you can get re-infected, warns Kenneth Sherman, MD, PhD, a professor of medicine and the director of the division of digestive diseases at UC Health in Cincinnati, Ohio.
Contaminated Needles And Infected Blood
You can get hepatitis C from sharing contaminated needles, syringes and other injecting equipment during recreational drug use. Banknotes and straws used for snorting may also pass the virus on.
Being exposed to unsterilised tattoo and body piercing equipment can also pass hepatitis C on. Occasionally, you can get it from sharing a towel, razor blades or a toothbrush if there is infected blood on them.
Hepatitis C infection is also passed on in healthcare settings, from needle stick injuries or from medical and dental equipment that has not been properly sterilised. In countries where blood products are not routinely screened, you can also get hepatitis C by receiving a transfusion of unscreened blood and blood products.
You can prevent hepatitis C by:
- never sharing needles and syringes or other items that may be contaminated with infected blood
- only having tattoos, body piercings or acupuncture in a professional setting, where new, sterile needles are used
- following the standard infection control precautions, if youre working in a healthcare setting.
Read Also: How To Get Rid Of Hepatitis C
How Is Hepatitis C Infection Prevented
Unfortunately, there is no vaccine to prevent hepatitis C. To reduce your risk of getting hepatitis C:
- Injection drug use is the most common way people get hepatitis C. Avoid injecting drugs to reduce your risk. If you do inject drugs, use sterile injection equipment. Avoid reusing or sharing.
- Avoid sharing personal care items that might have blood on them
- If you are a health care or public safety worker, follow universal blood/body fluid precautions and safely handle needles and other sharps
- Consider the risks if you are thinking about tattooing, body piercing, or acupuncture are the instruments properly sterilized?
- If youre having sex with more than one partner, use latex condoms correctly and every time to prevent the spread of sexually transmitted diseases, including hepatitis C.
Sexual Transmission And Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B can be transmitted through sexual activity. Unvaccinated adults who have multiple sex partners, along with sex partners of people with chronic hepatitis B infection, are at increased risk for transmission. Injection-drug use and sexual contact are other common modes of hepatitis B transmission in the United States.
Among adults seeking treatment in STD clinics, as many as 10%40% have evidence of past or current hepatitis B virus infection. Many of these infections could have been prevented through universal vaccination during delivery of STD prevention or treatment services. Offering vaccination to all adults as part of routine prevention services in STD treatment facilities has been demonstrated to increase vaccination coverage among adults at risk for hepatitis B infection, as the behavioral risk factors for STDs and hepatitis B are similar.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Get Hepatitis Ab And C
Activities That Present A Very Low Risk Of Hepatitis C Transmission:
- Saliva transfer Sharing a toothbrush or open-mouth kissing facilitates the sharing of saliva. The likelihood of transmitting Hepatitis C through saliva is very rare, but microscopic bits of blood can present a small risk.
- Sharing certain personal hygiene items The likelihood of transmitting Hepatitis C within your household is very low, but it is possible if personal hygiene items are shared. Anything that could be contaminated with blood, like toothbrushes, razors, cuticle scissors, and nail clippers have the potential to be a contagion vehicle.
- Can hepatitis c be transmitted through sex? Although sex will often find itself on a list of potential routes for Hepatitis C transmission, this is extremely rare. Factors increasing the risk of sexual transmission of Hepatitis C include co-infection with HIV, sexual techniques that damage mucosa, acute Hepatitis C infection, high Hepatitis C viral load, and those with multiple sexual partners. There is also a small a risk of transmitting Hepatitis C via oral sex when there is any blood or breaks in the affected skin. Every single potential scenario of how Hepatitis C can be transmitted may not be covered in the examples listed above. This is because there are many possible ways for infected blood to make contact with someones bloodstream.
Ask The Expert: From Sue
Hepatitis C virus is not considered a sexually transmitted disease. In order for hepatitis C to be contracted, blood from an infected partner must enter the bloodstream of a non-infected person. Unlike hepatitis B or HIV, the virus is not found in infective amounts in sexual body fluids.
On the rare occasion that someone is infected through sex, it is usually due to the person having a sexually transmitted infection that causes lesions or cuts in the genital tract or the female partner is menstruating. It is also transmitted more frequently between men who have sex with men, and in people who have sex with prostitutes, and in sex between couples who have more than 5 sexual partners. Anal sex puts a person at higher risk than the people who engage in vaginal sex. Rough sex increases risk of transmission, as well. In long term monogamous couples the rate of transmission is less than 2%. In fact, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention does not recommend the use of barrier protection in long term monogamous couples. Some of that 2% statistic may actually be because married couples take care of each when there is illness or an accident and blood may be exchanged during those times.
Ultimately, it’s always beneficial to talk with your doctor or counselor about any concerns or ways to stay safe.
Also Check: What Happens To Your Body When You Have Hepatitis C