Hepatitis C And Pregnancy: What You Need To Know
If you have hepatitis C while pregnant, your baby may be at risk of contracting the disease. There is no cure for hepatitis C, but there are treatments available that can help you manage the disease. It is possible to treat symptoms with counseling and/or medication. If you are infected with hepatitis C, you should be tested and treated as soon as possible to reduce your risk of developing serious health problems.
Should All Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B Be On Treatment
Not all patients with chronic hepatitis B need to be on treatment. The decision to treat HBV is based on several factors including blood tests results, the patient’s age, and the risk of developing cirrhosis or liver cancer. Sometimes a liver biopsy is needed to see if there is significant liver damage to make a decision.
Hepatitis B medications are recommended for patients with detected HBV virus on a blood test and evidence of liver damage. Liver damage can be detected with a liver enzyme known as ALT. People with cirrhosis should be considered for treatment even if the liver enzymes appear normal.
Chronic hepatitis B may change over time. Patients can go through different phases with low amounts of virus and normal level of ALT followed by high viral loads and ALT levels. These bursts of virus activity usually don’t cause any symptoms but may cause liver damage overtime. It is important that people with chronic hepatitis B have blood tests on a regular basis to see if treatment is needed.
There are some medications which can cause hepatitis B “reactivation” which can lead to life threatening liver failure. These medications are used to treat some cancers, inflammatory conditions and hepatitis C. Reactivation reactions can be prevented and it is important to let your provider know you have HBV before you start any new medications.
What Are The Risk Factors For Getting Hepatitis B
Due to the way that hepatitis B spreads, people most at risk for getting infected include:
- Children whose mothers have been infected with hepatitis B.
- Children who have been adopted from countries with high rates of hepatitis B infection.
- People who have unprotected sex and/or have been diagnosed with a sexually transmitted infection.
- People who live with or work in an institutional setting, such as prisons or group homes.
- Healthcare providers and first responders.
- People who share needles or syringes.
- People who live in close quarters with a person with chronic hepatitis B infection.
- People who are on dialysis.
You May Like: Symptoms Of Hepatitis C In Females
Unlocking The Power Of The Immune System To Get Ahead Of Hepatitis B
The liver performs over 500 tasks each day that help keep us alive and healthy and has the unique ability to regenerate itself when it becomes damaged. Yet some peoples livers harbour an infection that could impact liver function and may cause the organ to fail: hepatitis B.
Hepatitis B virus infection is caused by a virus that is spread through blood and bodily fluids and localises in the liver. Estimates suggest that one in every three people has been exposed to the hepatitis B virus at some point in their lives, but many of these people will develop natural immunity to the infection. However, up to 10% of adults and nearly all babies infected via their mother during birth will experience an inadequate immune response to the virus causing them to develop chronic, or lifelong, hepatitis B virus infection. The World Health Organization estimates that over 296 million people live with chronic hepatitis B virus infection worldwide, making it a major global health problem.
At GSK, we have been working hard to get ahead of hepatitis B for decades. Vaccines that help prevent hepatitis B virus infection now exist, and antiviral therapies are available to help control the infection. Yet the burden for many remains. We are using our expertise to advance research to help reduce this burden.
Does Hepatitis Spread Through Water
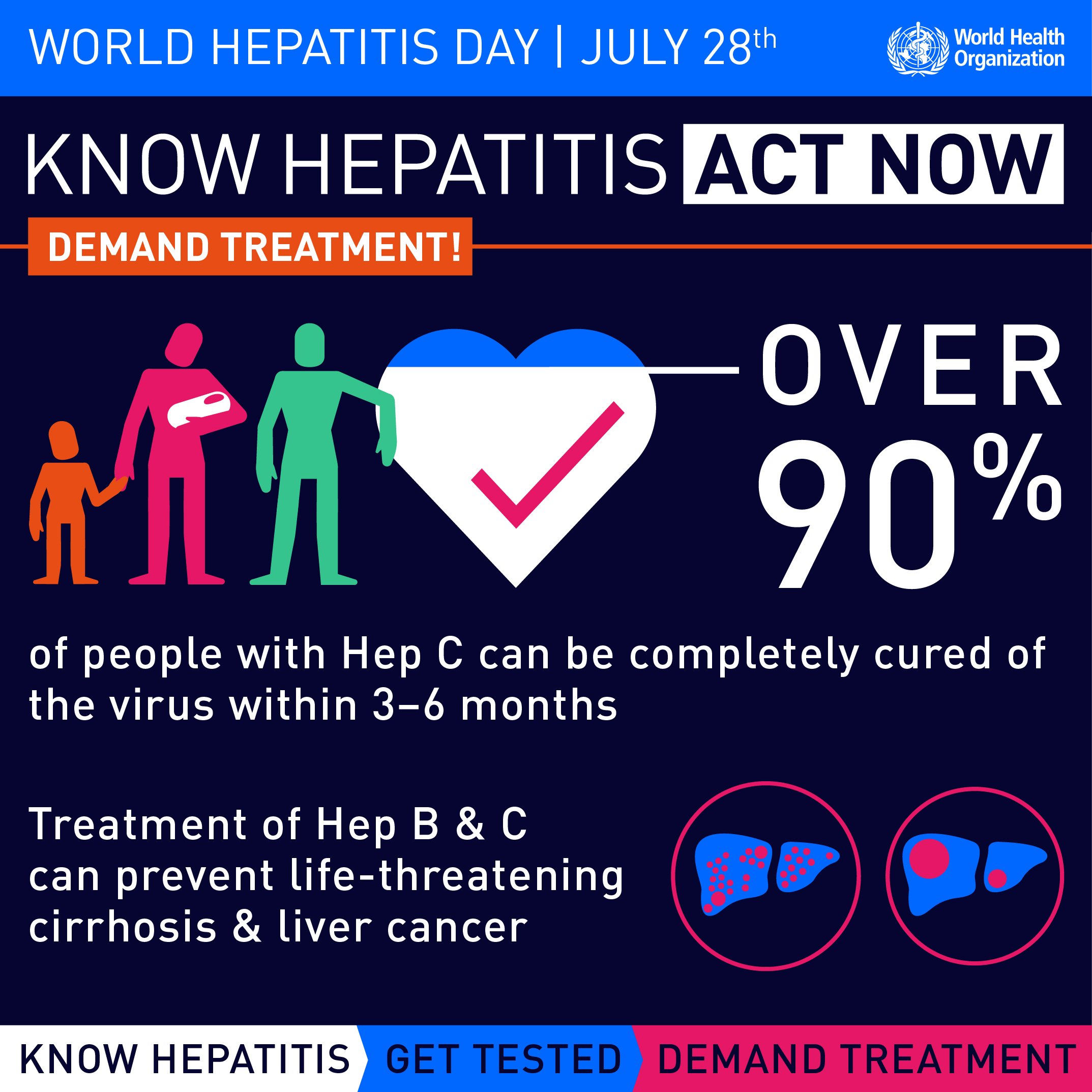
A person who has been infected with the Hepatitis A virus can also spread the disease by eating or drinking contaminated food or drinks. Waterborne outbreaks are uncommon and usually occur when sewage-contaminated or inadequately treated water is released into the environment.
The virus that causes Hepatitis A is found throughout the world and in the United States. A virus can be introduced into water supplies through sewage overflows or by faulty sewage treatment plants. Because children can get stool on their hands and then touch objects, hepatitis A is uncommon among children in daycare facilities. In three out of every four adults who are infected with HAV, symptoms will appear for several days. Symptoms typically appear between 2 and 6 weeks after the virus has been exposed. Hepatitis A vaccines are available to provide long-term protection against the disease. After 1 minute of boiling water, it is possible to kill or inactivate the hepatitis A virus.
How can I get hepatitis A from drinking uncontaminated water? If that water has been contaminated by someone who has the disease, it is not a source of water. Washing your hands thoroughly after going to the bathroom, before preparing food, and after eating can all help to prevent infections. It is also possible to prevent infection by immunizing yourself before international travel, and by avoiding drinking tap/well water and uncooked foods in countries or regions where Hepatitis A is common.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Effects On Liver
How Common Is Hepatitis B
The number of people who get this disease is down, the CDC says. Rates have dropped from an average of 200,000 per year in the 1980s to around 20,000 in 2016. People between the ages of 20 and 49 are most likely to get it.
About 90% of infants and 25-50% of children between the ages of 1-5 will become chronically infected. In adults, approximately 95% will recover completely and will not go on to have a chronic infection.
As many as 1.2 million people in the U.S. are carriers of the virus.
European Commission And Thervacb Join Forces
The role of viral hepatitis as a public health threat has long been underestimated. Only very recently, the United Nations in their 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development called for international action to combat viral hepatitis and reduce the disease burden. The major killer is the hepatitis B virus causing liver cirrhosis and liver cancer. Worldwide 880,000 humans die each year from the consequences of an HBV infection.
A prophylactic vaccine is available to prevent HBV infection, but more than 3% of the worlds population are chronically infected and do not profit from that vaccine anymore. For those suffering from chronic hepatitis B, until today no curative treatment option exists.
The European Commission therefore selected the project TherVacB led by Helmholtz Zentrum München for a five-year funding within the Horizon 2020 program. A consortium of leading virologists, immunologists and physicians specialized in treating viral hepatitis, will use a newly designed therapeutic vaccine, TherVacB, as an immunotherapy to cure HBV. TherVacB will be evaluated in a three-year clinical trial starting in 2022 conducted in Europe and in Africa. Integration of a partner site in Tanzania shall help building local capacities for diagnosing and treating hepatitis B and support an important goal of the consortium to raise awareness for hepatitis B.
Read Also: How Do People Contract Hepatitis C
Panel : Immediate And Future Actions Required To Achieve Hbv Curethe Ice
- INCREASE funding for individual and collaborative cure-related research projects by governmental and private funding agencies and philanthropic benefactors. Consideration should be given to establishing international research consortia, similar to the Martin Delaney Collaboration for HIV research managed by the National Institutes of Health in the USA. HBV cure research investment strategies should be prioritised in national HBV plans globally. We also believe the WHO hepatitis elimination strategy19 should be funded in full, with particular focus on delivery of birth dose vaccines and substantially increased investments in HBV research. We support recent calls from the Hepatitis B Foundation for increased HBV cure research funding125,126
- CONCENTRATE on the discovery of interventional strategies that will permanently reduce the number of productively infected cells or permanently silence the cccDNA in those cells and also stimulate HBV-specific T cells and the production of neutralising antibodies that will prevent viral spread to uninfected cells, mimicking spontaneous resolution of acute HBV infection
- ESTABLISH repositories of standardised HBV reagents and protocols, facilitate access to all researchers across the world, and support the development of new animal models of HBV infection
Panel : Definitions Of Curative Hbv Treatment Outcomes
- Cure of infectioncomplete sterilising cure with undetectable HBsAg in serum and eradication of HBV DNA including intrahepatic cccDNA and integrated HBV DNA31
- Functional cure of HBV infectionsustained, undetectable HBsAg and HBV DNA in serum with or without seroconversion to hepatitis B surface antibody , with the persistence of low levels of intrahepatic cccDNA31
- Remission of liver diseaseresolution of residual liver injury including reversal of fibrosis, prevention of fibrosis progression, remission of disease, and reducing risk of hepatocellular carcinoma
Read Also: Hepatitis C Virus Can Cause
Hiv And Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C Coinfection
Hepatitis B and hepatitis C are liver infections caused by a virus. Because these infections can be spread in the same ways as HIV, people with HIV in the United States are often also affected by chronic viral hepatitis.
Viral hepatitis progresses faster and causes more liver-related health problems among people with HIV than among those who do not have HIV. Liver disease, much of which is related to HBV or HCV, is a major cause of non-AIDS-related deaths among people with HIV.
Given the risks of hepatitis B or hepatitis C coinfection to the health of people living with HIV, it is important to understand these risks, take steps to prevent infection, know your status, and, if necessary, get medical care from someone who is experienced in treating people who are coinfected with HIV and HBV, or HIV and HCV.
Closing In On A Cure For Hepatitis B
For Thomas Tu, eliminating hepatitis B is a deeply personal goal.
Tu, a molecular virologist at the Westmead Institute for Medical Research in Sydney, Australia, learnt he had chronic hepatitis B as a teenager. A blood test revealed telltale signs of the infectious liver disease, which Tu had probably acquired at birth.
In his late 20s, Tu started taking a medication to limit the viruss replication and prevent collateral damage to his liver cells. Now 36, he has been on that daily treatment a pill known as a nucleoside analogue ever since.
Yet, even with a therapy that keeps his infection well under control, Tu remains at heightened risk for liver disease. He must juggle visits to specialist doctors and bear prescription-drug costs. And he knows that many others racked by the financial instability, emotional toil and stigma that the lifelong infection can bring have it much worse.
Im in this quite privileged space to be able to be on therapy and not have any side effects or feel any burden from taking daily medicines, Tu says. Thats not the same for the majority of people living with hepatitis B.
We are using all our weapons to tackle every single step of the virus, says Man Fung Yuen, a hepatologist at the University of Hong Kong.
Don’t Miss: Symptoms Of Active Hepatitis C
How You Can Get Hepatitis B
You can get hepatitis B from:
- injecting drugs using shared needles
- being injured by a used needle
- having a tattoo or piercing with unsterilised equipment
- having a blood transfusion in a country that does not check blood for hepatitis B. Blood transfusions in the UK are checked for hepatitis B.
If you’re pregnant and have hepatitis B, you can also pass it onto your baby during pregnancy or birth.
Can Hep C Survive Outside Body
According to a recent study conducted by Yale School of Medicine and Public Health researchers, the hepatitis C virus can remain infectious on surfaces for up to six weeks, significantly longer than previously thought.
We will be able to find solutions. Despite the fact that the disease cannot be cured, there are some medications that can help to control it. Antiviral drugs, which prevent the virus from replicating, and immune systemboosting therapies, which aid in the bodys ability to fight the virus more effectively, are two examples of drugs that help the body fight the virus. It is not necessary to avoid people with hepatitis C, because they are only likely to become infected through blood contact. Washing and rinsing the washing machine and dishes as usual is not required, and boiling is not. To combat the disease, an antiviral drug and a immunosuppressive therapy are used.
You May Like: What Hepatitis Is Sexually Transmitted
What Should You Know About Pregnancy And Hepatitis B
A pregnant woman who has hepatitis B can pass the infection to her baby at delivery. This is true for both vaginal and cesarean deliveries.
You should ask your healthcare provider to test you for hepatitis B when you find out you are pregnant. However, while it is important for you and your healthcare provider to know if you do have hepatitis B, the condition should not affect the way that your pregnancy progresses.
If you do test positive, your provider may suggest that you contact another healthcare provider, a liver doctor, who is skilled in managing people with hepatitis B infections. You may have a high viral load and may need treatment during the last 3 months of your pregnancy. A viral load is the term for how much of the infection you have inside of you.
You can prevent your infant from getting hepatitis B infection by making sure that your baby gets the hepatitis B vaccine in the hours after they are born along with the hepatitis B immunoglobulin. These two shots are given in two different locations on the baby. They are the first shots needed.
Depending on the type of vaccine used, two or three more doses must be given, usually when the baby is 1 month old and then 6 months old, with the last by the time the baby is 1 year old. It is critical that all newborns get the hepatitis B vaccination, but even more important if you have hepatitis B yourself.
What If I Am Pregnant
It’s recommended that all pregnant women have a blood test for hepatitis B in early pregnancy.
If you have hepatitis B and are pregnant, treatments can reduce the risk of transmission of hepatitis B to the baby.
If you have hepatitis B, it is important to protect others from infection.
Important ways to prevent the spread of hepatitis B include:
- vaccination of all your close contacts
- practise safe sex until your sexual contacts are fully vaccinated and immune
- do not donate blood, organs or body tissue
- do not allow your blood to contact another person
- inform healthcare workers
- if your work involves potential for your blood or other body fluid to spread to other people, discuss your situation with your doctor
The hepatitis B vaccine is safe and effective in protecting against hepatitis B infection, providing protection in 95 in 100 vaccinated people.
In Australia, hepatitis B vaccination is part of the standard immunisation schedule for all newborn babies and infants. It’s also recommended for adults who are at high risk of exposure, people who are immunosuppressed or have other liver disease. People in these risk groups should be vaccinated against hepatitis B. Talk to your doctor about your level of risk and whether hepatitis B vaccination is recommended for you.
If you werent vaccinated against hepatitis B as a child, or if youre not sure whether you are vaccinated, talk to your doctor about whether you need a catch-up vaccine.
You May Like: What Does Hepatitis C Non Reactive Mean
Chronic Hepatitis B And Resolution Of Infection
In the absence of vaccination, over 90% of individuals infected in infancy will progress from acute hepatitis to lifelong chronic infection. By contrast, over 90% of people infected in adulthood will resolve the infection, due to robust immune responses that eliminate infected cells and produce neutralising antibodies that provide lifelong protection. Once chronic infection is established, patients are exposed to significant risk of liver disease including chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma. The natural history of chronic HBV infection usually consists of up to five stages,13 which differ in the level of viral replication, viral antigen expression, and inflammatory activity in the liver.
What Is The Outlook For People With Hepatitis B
The outlook for people with HBV is better now than ever before. You are certainly able to live a full life and help yourself stay healthy. You should make sure to have regular check-ups with a healthcare provider who is qualified to treat hepatitis B, possibly a liver doctor.
Make sure you are vaccinated against hepatitis A. Check with your healthcare provider or pharmacist before taking other medications or over-the-counter products, including supplements and natural products. These could interfere with your medication or damage your liver. For instance, taking acetaminophen in large doses may harm your liver.
Follow the usual guidelines for living a healthy life:
- Eat nutritious foods, choosing from a variety of vegetables, fruits and healthy proteins. It is said that cruciferous vegetables are especially good at protecting the liver.
- Exercise regularly.
- Dont smoke and dont drink. Both tobacco and alcohol are bad for your liver.
- Do things that help you cope with stress, like journaling, talking with others, meditating and doing yoga.
- Avoid inhaling toxic fumes.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Flu Like Symptoms