How To Prevent Hepatitis C
There is currently no vaccine for hepatitis C. Avoiding contact with infected blood is the only way to prevent the condition.
The most common way for people to contract hepatitis C is by injecting street drugs. Because of this, the best way to prevent hepatitis C is to avoid injecting.
Treatments can help many people quit. People in the U.S. can call the National Helpline for help with finding treatments.
If a person finds it difficult to stop, they can reduce the risk of contracting hepatitis C by never sharing drug equipment, ensuring a clean, hygienic environment, and always using new equipment, including syringes, ties, alcohol swabs, cottons, and cookers.
People who may come into contact with infected blood, such as healthcare workers and caretakers, should always wash the hands thoroughly with soap and water after any contact, or suspected contact, with blood. They should also wear gloves when touching another persons blood or open wounds.
People can also reduce their risk by making sure that any tattoo artist or body piercer they visit uses fresh, sterile needles and unopened ink.
The risk of contracting hepatitis C through sexual contact is low. Using barrier protection, such as condoms, reduces the risk of most sexually transmitted infections.
People who have hepatitis C can reduce the risk of transmitting it to others by:
There are many misconceptions about how hepatitis C spreads. People cannot transmit or contract the virus through:
How Hcv Is Spread
The hepatitis C virus is transmitted primarily through blood to blood contact, meaning that a person can become infected with the virus should the blood of a person who carries the virus be introduced into another personâs bloodstream.
Therefore, as with hepatitis B, blood transfusions , tattooing and body piercing, occupational exposure, medical procedures, and intravenous drug use can all lead to possible exposure to the virus. Unlike hepatitis B, however, sexual contact and childbirth have both been shown to be an inefficient route of exposure to HCV.
The hepatitis G virus is thought to be transmitted in a similar way to HCV.
Read Also: Tenofovir Hepatitis B Side Effects
How Is Hepatitis C Spread
Hepatitis C spreads through contact with the blood of someone who has HCV. This contact may be through:
- Sharing drug needles or other drug materials with someone who has HCV. In the United States, this is the most common way that people get hepatitis C.
- Getting an accidental stick with a needle that was used on someone who has HCV. This can happen in health care settings.
- Being tattooed or pierced with tools or inks that were not sterilized after being used on someone who has HCV
- Having contact with the blood or open sores of someone who has HCV
- Sharing personal care items that may have come in contact with another person’s blood, such as razors or toothbrushes
- Being born to a mother with HCV
- Having unprotected sex with someone who has HCV
Before 1992, hepatitis C was also commonly spread through blood transfusions and organ transplants. Since then, there has been routine testing of the U.S. blood supply for HCV. It is now very rare for someone to get HCV this way.
Read Also: Hepatitis C Can It Be Cured
Is Everyone Around Me Now At Risk
The hepatitis C infection can only occur if the blood of an infected person is able to enter another persons body. It is the blood that is infectious, not the person. The virus cannot be transmitted by touching, kissing, hugging or by sharing cutlery.
Am I sexually infectious?
The risk of sexual transmission is debated, but it is generally accepted as being very low much lower than many other identified transmission routes for hepatitis C.
Choices about sexual behaviour are personal and some couples decide that such a low risk is acceptable and continue to have unprotected sex. Other couples, however, decide to use protection.
Unprotected sexual intercourse could be a risk but the likelihood of transmitting the virus without any blood contact is considered very small.
The risk of sexual transmission is increased if blood is present, if you have multiple sexual partners, or if you have other sexually transmitted infections.
In addition, the risk of sexual transmission is increased if the person also has HIV.
Can I transmit hepatitis C in other ways?
Sharing things such as razor blades, nail scissors, toothbrushes and hair clippers poses a risk. If your blood gets onto one of these things, someone else using them might become infected if they also cut themselves.
It seems that HCV can live outside the body in dried blood for varying levels of time. This can vary between sixteen hours to four days.
What Can I Do If I Think I Have Hepatitis C
A doctor or sexual health clinician can test you to see if you have hepatitis C. If you do, effective treatment with fewer side effects than the older medicine is available and you can discuss how to avoid infecting your sexual partners or people you live with.
It can take three to six months before the blood test for hepatitis C will be able to detect signs of infection in your blood. For people with HIV who may be immunocompromised, the antibody may not be detectable and it may be necessary to request an RNA test which detects the virus.
You May Like: What Does Hepatitis B Non Reactive Mean
Diagnosis Of Hepatitis C
If you are at risk of hepatitis C infection, or think you may have been exposed to hepatitis C in the past, see your doctor for an assessment of your liver health. This will include blood tests and possibly a non-invasive test for liver damage .
There are 2 blood tests used to diagnose hepatitis C. Usually these can be done at the same time but sometimes they will be done separately.
The first test known as a hepatitis C antibody test can tell you whether you have ever been exposed to hepatitis C.
It may take 2 to 3 months from the time of infection until a blood test can detect antibodies to hepatitis C, so there is a window period during which you cannot tell if you are or have been infected. In this time, take precautions to prevent the potential spread of the virus.
The second test is called hepatitis C PCR, which will be done if the antibody test is positive. This determines if the virus is still present in your blood or liver or if you have already cleared the infection.
If you have cleared the virus or had successful treatment to cure it, the PCR test will be negative.
A liver ultrasound or Fibroscan can also be performed to assess if you have any liver damage.
If your doctor is inexperienced in diagnosing hepatitis C you can call the LiverLine on for information, and to find a GP who can help you.
Who Is More Likely To Get Hepatitis C
People more likely to get hepatitis C are those who
- have injected drugs
- had a blood transfusion or organ transplant before July 1992
- have hemophilia and received clotting factor before 1987
- have been on kidney dialysis
- have been in contact with blood or infected needles at work
- have had tattoos or body piercings
- have worked or lived in a prison
- were born to a mother with hepatitis C
- are infected with HIV
- have had more than one sex partner in the last 6 months or have a history of sexually transmitted disease
- are men who have or had sex with men
In the United States, injecting drugs is the most common way that people get hepatitis C.13
You May Like: How Can I Get Hepatitis
Can Hepatitis C Be Prevented
There is no vaccine for hepatitis C. But you can help protect yourself from hepatitis C infection by:
- Not sharing drug needles or other drug materials
- Wearing gloves if you have to touch another person’s blood or open sores
- Making sure your tattoo artist or body piercer uses sterile tools and unopened ink
- Not sharing personal items such toothbrushes, razors, or nail clippers
- Using a latex condom during sex. If your or your partner is allergic to latex, you can use polyurethane condoms.
NIH: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
What Are The Symptoms
Most people have no symptoms when they are first infected with the hepatitis C virus. If you do develop symptoms, they may include:
- Feeling very tired.
- Sore muscles.
- Dark urine.
- Yellowish eyes and skin . Jaundice usually appears only after other symptoms have started to go away.
Most people go on to develop chronic hepatitis C but still don’t have symptoms. This makes it common for people to have hepatitis C for 15 years or longer before it is diagnosed.
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatitis C Genotype 1a
Eat Regular Nutritious Meals
Sometimes people with hepatitis C have a hard time eating. You may have no appetite, feel nauseated, or have different tastes than you are used to. Even if you don’t feel like eating, it’s very important to eat small meals throughout the day. Some people have nausea in the afternoon. If this happens to you, try to eat a big, nutritious meal in the morning.
If you have cirrhosis, it may not be a good idea to eat salty foods or foods that are high in protein. If you want to know more about which foods to avoid and which foods are good to eat, ask your doctor about meeting with a registered dietitian to discuss a healthy eating plan.
Contagious And Incubation Periods
The incubation periodthe time it takes for symptoms to appear after the hepatitis C virus has entered your bodyis from 2 weeks to 6 months. But not all people have symptoms when they are first infected.
You can spread the virus to someone else at any time after you are infected, even if you don’t have symptoms.
You May Like: Can You Catch Hepatitis C From Your Own Blood
What Is The Connection Between Hiv And Hcv
Because both HIV and HCV can spread in blood, a major risk factor for both HIV and HCV infection is injection drug use. Sharing needles or other drug injection equipment increases the risk of contact with HIV- or HCV-infected blood.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , approximately 21% of people with HIV in the United States also have HCV. Infection with both HIV and HCV is called HIV/HCV coinfection.
In people with HIV/HCV coinfection, HIV may cause chronic HCV to advance faster. Whether HCV causes HIV to advance faster is unclear.
Sharing Toothbrushes Scissors And Razors

There’s a potential risk that hepatitis C may be passed on through sharing items such as toothbrushes, razors and scissors, as they can become contaminated with infected blood.
Equipment used by hairdressers, such as scissors and clippers, can pose a risk if it has been contaminated with infected blood and not sterilised or cleaned between customers. However, most salons operate to high standards, so this risk is low.
Don’t Miss: Lactulose Dose For Hepatic Encephalopathy
What Are The Different Types Of Hepatitis C
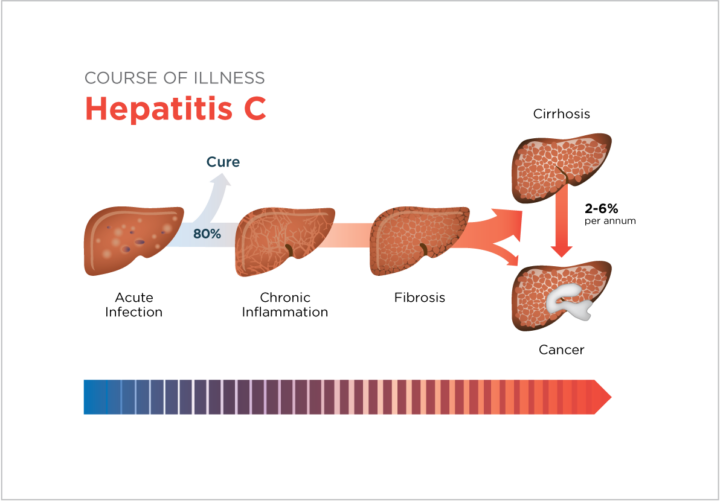
Hepatitis C can be acute or chronic. How long you experience symptoms will depend on the type you have.
Acute hepatitis C involves more short-term symptoms that typically last 6 months or less but acute hepatitis often leads to chronic hepatitis. When hepatitis C lasts longer than 6 months, its considered chronic.
Without treatment, you may have chronic hepatitis your whole life, since your body often cant get rid of the virus easily. Some people do get better without treatment, although treatment can go a long way toward improving the outlook.
Hepatitis C wont necessarily become chronic.
As a matter of fact, for anywhere from 15 to 45 percent of people with acute hepatitis C, the virus will clear up without treatment. In other words, if you dont have any symptoms, hepatitis C could improve on its own before you ever know you have it.
However, if your body cant get rid of the hepatitis C virus, the infection wont go away. Instead, it will become chronic, or long-term.
Experts arent sure why some people develop the chronic form of the disease and others dont. But more than half of all people with the hepatitis C virus will eventually develop the chronic form, according to the
Since hepatitis C symptoms can resemble those of other health conditions, your symptoms alone if you have any may not make it clear that you have hepatitis C.
A doctor or other healthcare professional may recommend getting tested if you:
- daclatasvir
Need More Proof Viruses Are Fragile
The hepatitis viruses are very picky about what they infect and where they can survive. They really like livers, and mosquitoes donât have livers! This means that the mosquitoes arenât really a good home and the viruses wouldnât survive long enough to be spread, even if they could be.
Also, people who study mosquitoes have noticed they usually donât bite two people consecutively. After they bite, they will fly away to let their food digest and then after a period of time, they will feed again. Because the hepatitis viruses donât last long in a harsh environment, they wouldnât survive long enough to infect.
Read Also: Doctors Who Treat Hepatitis C
Blood Transfusion/receipt Of Blood Products
Early case-control studies of patients with newly acquired, symptomatic non-A, non-B hepatitis found a significant association between disease acquisition and a history six months prior to illness of blood transfusions, injection drug use, health care employment with frequent exposure to blood, personal contact with others who had hepatitis, multiple sexual partners or low socioeconomic status. Today, HCV is rarely transmitted by blood transfusion or transplantation of organs due to thorough screening of the blood supply for the presence of the virus and inactivation procedures that destroy bloodborne viruses. In the last several years, blood banks have instituted techniques that utilize nucleic acid amplification of the hepatitis C virus, which will detect the presence of virus even in newly-infected patients who are still hepatitis C antibody-negative. These techniques are estimated to have prevented 56 transfusion-associated HCV infections per year in the U.S. since 1999, and have lowered the current risk of acquiring HCV via transfused blood products to 1 in 2 million.
What Is Hepatitis
Hepatitis is the swelling of the liver and is mainly caused due to viruses. The other causes of hepatitis include:
- Autoimmune reactions
- Medications, drugs, or toxins
- Drinking alcohol in more than recommended amounts for a long time
Viral hepatitis is caused by a virus and can be of two types:
- Acute
- Chronic
The most common type of viral hepatitis includes:
- Hepatitis A: It is caused by the hepatitis A virus . This form of hepatitis heals on its own and does not lead to a chronic infection. It generally does not have any complications. Hepatitis A can be prevented by vaccination.
- Hepatitis B: Most of the patients with hepatitis B recover from it and do not become chronically infected. It can be prevented by a vaccine.
- Hepatitis C:Hepatitis C is the most common cause of liver disease. Most of the cases can lead to chronic liver infection. It cannot be prevented using a vaccine.
- Hepatitis D: Hepatitis D happens to people infected with the hepatitis B virus. Vaccination against hepatitis B virus gives protection from hepatitis D virus.
- Hepatitis E: This infection is common throughout the world. Vaccines are not available everywhere.
Also Check: Can Hepatitis Cause Heart Problems
How Is It Spread
Hepatitis C virus is mostly spread by blood from aninfected person when:
- Sharing needles or other equipment to inject drugs. This is the most common way people get hepatitis C in the U.S.
- Getting a needle stick with a needle that was used on an infected person
- Sharing items that may have come in contact with another person’s blood, such as razors, nail clippers, pierced earrings, toothbrushes
- Being tattooed or pierced with tools that were used on an infected person
- Having sexual contact with a person infected with the hepatitis C virus. The risk of getting hepatitis C from sexual contact is thought to be low.
Hepatitis C is rarely spread from a blood transfusion because:
- Hepatitis C tests are done on all donated blood.
- Blood and blood products that test positive for hepatitis C are safely destroyed. None are used for transfusions.
- There is no risk of getting hepatitis C when donating or giving blood.
Hepatitis C is not spread by kissing,hugging, coughing, or sharing food and eating utensils.
Hiv And Hepatitis C Coinfection
HCV infection is common among people with HIV who also inject drugs. Nearly 75% of people living with HIV who report a history of injection drug use are co-infected with HCV. All people who are diagnosed with HIV are recommended to be tested for HCV at least once. People living with HIV are at greater risk for complications and death from HCV infection. Fortunately, direct acting antivirals that are used to treat HCV work equally well in people with and without HIV infection. For more information about HIV and HCV coinfection, visit the HIV.govs pages about hepatitis C and HIV coinfection.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Know When You Have Hepatitis
Sexual Transmission And Hepatitis A
Transmission of hepatitis A virus can occur from any sexual activity with an infected person and is not limited to fecal-oral contact. People who are sexually active are considered at risk for hepatitis A if they are MSM, live with or are having sex with an infected person, or inject drugs. Vaccination is the most effective means of preventing hepatitis A transmission among people at risk for infection. CDC has published recommendations for prevention of hepatitis A that identify all groups recommended for vaccination, including hepatitis A vaccination for MSM.
Read Also: Symptoms Of Hepatitis C Flare Up