Questions For Your Doctor About Test Results
For support in understanding the results of hepatitis A testing, patients should discuss results with their doctor. Questions about test results may include:
- What is my test result?
- Do I have a hepatitis A infection?
- Does the test result suggest that I have immunity to the hepatitis A virus?
- Would I benefit from hepatitis A vaccination?
- Do I need any follow-up tests based on my hepatitis A test results?
Are Test Results Accurate
While no blood test is accurate all of the time, hepatitis A testing is the standard and accepted method of determining whether or not a person has an active hepatitis A infection or formed immunity.
Although a positive result on an IgM anti-HAV antibody test is considered diagnostic for an acute infection with hepatitis A, this result may be less helpful in patients who arent experiencing symptoms of hepatitis. In patients without symptoms, finding IgM anti-HAV antibodies may reflect a prior hepatitis A infection in which IgM antibodies have remained in the body for longer than usual or an asymptomatic infection.
Hepatitis A Ab Total Reactive
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
You May Like: What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis B Virus
Hbv Dna Hbv Genotype And Hbv Drug Resistance Assays
Specimen: Serum or plasma
Container: Red-top tube, yellow-top tube , gel-barrier tube, plasma preparation tube, or lavender tube
Collection method: Routine venipuncture
The specimen should be transfused to separate plasma/serum from cells within 6 hours and kept frozen when testing cannot be done promptly.
The tests use PCR amplification, DNA probe hybridization, and sequencing method.
What Are Some Of The Tell
The symptoms of HAV may begin all of a sudden. Children can be asymptomatic too along with some adults with no symptoms.
Some adults exhibit very mild symptoms, which may go unnoticed. Yet, such people can also transmit the infection to others. Usually, the older lot exhibits symptoms of HAV as compared to children. Symptoms can be any or all of the following:
- Vomiting
Recommended Reading: How Do You Know If You Have Hepatitis B
Screening Tests For Hepatitis B
Your blood may be screened for HBV for many different reasons. The three tests generally include HBsAg, antibody to HBsAg, and antibody to hepatitis B core antigen. This allows the healthcare provider to know whether you could benefit from vaccination, or if you have active or chronic hepatitis B and need counseling, care, or treatment.
You may be routinely screened if you are pregnant, are donating blood or tissue, need immunosuppressive therapy, or have end-stage renal disease. You will also be screened if you are in groups that are at higher risk for HBV.
What Is Reactive Hepatitis
Looking for an answer to the question: What is reactive hepatitis? On this page, we have gathered for you the most accurate and comprehensive information that will fully answer the question: What is reactive hepatitis?
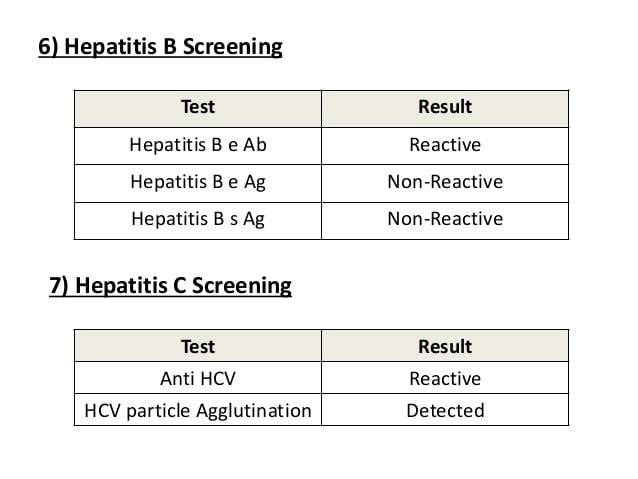
For the hepatitisBcore antibody test,a reactiveor positive resultcan meaneither that a person is currently infected with hepatitisBvirus or have been some time in the test. A reactiveresultfor this testcan also be a false positive,meaningthat the person has never been infected with the virus.
anti-HBs or HBsAb â A âpositiveâ or âreactiveâ anti-HBs test result indicates that a person is protected against the hepatitis B virus. This protection can be the result of receiving the hepatitis B vaccine or successfully recovering from a past hepatitis B infection.
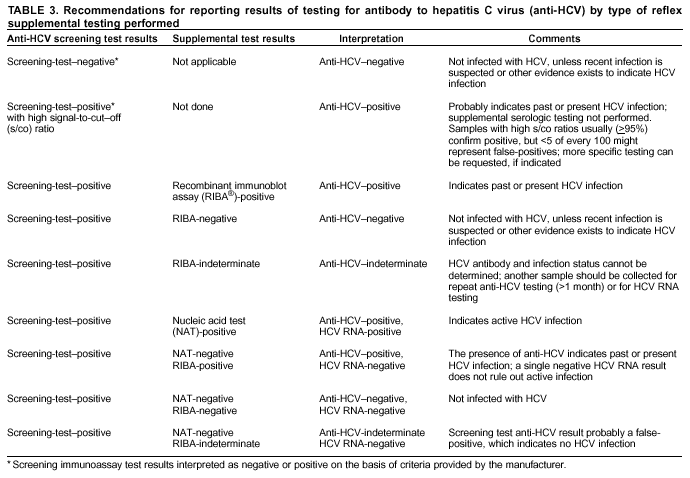
A âreactiveâ HCV antibody test could mean you were exposed to the HCV virus at some point in the past . However, there is a significant chance this was a false positive test. Additionally, about 20% of patients who are indeed exposed will clear the virus with their own immune response in the acute phase of infection.
A âreactiveâ result from your finger prick test indicates that HIV antibodies may be present. However,this is NOT definite and reactive results can occur and a subsequent negative HIV result be determined. If the test result is âreactiveâ additional laboratory testing is required before a definitive HIV result can be confirmed.
Don’t Miss: What Is Hepatitis B And C
What Do The Hepatitis A Test Results Mean
The test may indicate the following:
- Positive IgM results indicate that the antibody was found in your blood, meaning you may have an acute or recent HAV infection.
- Negative IgM results indicate the antibody was not found in your blood, meaning there is no active infection.
- Positive AB/IgG results indicate that the antibody was found in your blood, which means that you have been exposed to the virus in the past and have either developed immunity to HAV or have been vaccinated for it.
- Negative AB/IgG results indicate that the antibody was not found in your blood, meaning that you have not had a past HAV infection nor have been vaccinated or immunized to the virus.
Negative But Other Hepatitis Tests Are Positive
Your HBsAb test may be negative even when other hepatitis B tests are positive, showing active or chronic infection. Further testing is necessary, especially for the hepatitis B surface antigen , which shows that the virus itself is circulating in your bloodstream and that you have an active or chronic infection.
You May Like: Treatment To Cure Hepatitis C
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis E Causes And Treatment
Demographic Characteristics And Clinical Status
The analytic samples drawn from 294 patients with HBsAg/anti-HBs+serostatus at baseline, comprised 23 cases and 311 matched controls Table shows their demographic and clinical characteristics. Mean age and rheumatic disease types were similar between case and control groups. No patients with HBsAg/anti-HBs+serostatus had detectable HBV DNA at enrolment. Compared with controls, cases had lower baseline serum anti-HBs titers, more prevalent comorbidities , and relatively higher accumulated doses of sulfasalazine, leflunomide, and prednisolone. Most people in both groups used anti-TNF agents . No study subjects were kidney transplant recipients.
Table 1 Baseline characteristics of cases and controls treated with biologic DMARDs
No cases had clinical HBV reactivation during follow-up , and no cases developed alanine transaminase elevation, or received any anti-viral treatment during median follow-up of 30months after anti-HBs loss. Only one of the 16/23 cases whose serum HBV DNA was monitored after anti-HBs loss ever had a detectable viral load , which was observed only once, with no recurrence as of August 2020.
Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Non Reactive
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â itâs anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â itâs anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
Recommended Reading: How Can You Get Rid Of Hepatitis C
You May Like: Does Hepatitis C Affect The Brain
Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Quantitative
The hepatitis B surface antibody is the antibody that is produced in response to hepatitis B surface antigen , a protein present on the surface of the hepatitis B virus. Anti-HBs appears after convalescence from acute infection and lasts for many years. It can also be produced in response to hepatitis B vaccination.
Provider Education And Case Investigation
Providers should be educated about the importance of reporting all cases of hepatitis A to their respective health department. A common risk factor identified in persons with acute hepatitis A infection is contact with a previously identified case-patient. Aggressive case investigations of persons with acute disease provide the best opportunity for post-exposure prophylaxis of contacts and for reducing further transmission.
Surveillance and epidemiology staff should routinely investigate suspected cases of viral hepatitis. Basic information that should be routinely collected in the course of a hepatitis A case investigation is described below. Each jurisdiction may have their own protocols for conducting these investigations, and CDC is available to provide support as needed.
Don’t Miss: How Would You Know If You Have Hepatitis C
Does Hepatitis B Show Up In Routine Blood Tests
Routine blood tests do not detect hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatitis B tests are specifically done if blood tests show abnormal liver function results, or if a person experiences symptoms or falls into the high-risk category for HBV infection.
A panel of HBV-specific blood tests are required to detect HBV infection.
Serologic Testing And Cdc Laboratory Special Studies
Diagnostic tests used to confirm hepatitis A virus infection include serologic testing, and occasionally, PCR-based assays to amplify and sequence viral genomes. Refer to Chapter 22, Laboratory Support for Surveillance of Vaccine-Preventable Diseases for detailed information on laboratory testing for hepatitis A and for specific information on specimen collection and shipment.
Read Also: Is A Vaccine Available For Hepatitis B
How Is Hepatitis A Transmitted
Hepatitis A can be acquired or spread when an unvaccinated, or not immune, person consumes infected fecal matter. This is most commonly done by eating or drinking contaminated food or water.
Hepatitis A can also be spread through sexual scenarios where there is oral-anal contact with someone carrying the virus.
Risk factors for hepatitis A:4)
- Live with or are caregivers to someone with hepatitis A
- Have eaten contaminated food or drank contaminated water
- Travel to areas of low/poor sanitation
- Have had sexual contact with someone who has the virus
- Have eaten food prepared by someone with the virus who doesn’t thoroughly wash their hands after using the restroom
Hbc Antibody Positive/hbs Antigen Negative/hbs Antibody Negative
The HBc antibody positive/HBs antigen negative serotype is further divided into naïve and occult types . However, since HBV reactivation is often observed in HBc antibody positive/HBs antigen negative cases, it may be preferable to divide HBc antibody positive/HBs antigen negative cases based on whether they are positive or negative for HBs antibodies. For HBc antibody positive patients, perhaps HBV reactivation is induced by rituximab. Although Hui et al reported a 3%-25% reactivation rate, prophylactic treatment may be desirable since the mortality is relatively high after reactivation occurs. In 2013, Huang et al conducted a randomized controlled trial to evaluate the effect of the prophylactic administration of entecavir on the frequency of HBV reactivation in HBc antibody positive patients. In their report, unlike in retrospective analyses, the prophylactic administration of entecavir was the most important factor, at least for HBc antibody positive patients. Furthermore, Seto et al recently reported frequent reactivation of HBV in patients with 10 mIU/mL HBs antibody prior to rituximab treatment. In HBc antibody positive patients, prophylactic treatment is necessary, at least for those who are antibody negative prior to rituximab treatment . We believe that the prophylactic administration of a nucleic acid analog is preferable in HBc antibody positive/HBs antigen negative/HBs antibody negative cases.
Don’t Miss: How Can You Transfer Hepatitis C
What Is Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Reactive Mean Clfeax
Reactive results from the hepatitis B surface antibody test means that people are now immune to the virus because they have been infected in the past and their immune systems produced antibodies to fight the infection, This protection can be the result of receiving the hepatitis B vaccine or successfully recovering from a past hepatitis B â¦
Epidemiology Of Hbv Reactivation
When combined with chemotherapy, the HBV reactivation rate during rituximab treatment has been reported to be 20%-55% overall and 3% in hepatitis B surface antigen negative patients. HBV reactivation can be caused by chemotherapy alone. However, rituximab more easily induces HBV reactivation independently upon combined treatment with chemotherapy or steroid treatment. The frequency of HBV reactivation is also higher with combination treatments including rituximab compared to chemotherapy alone or a combination chemotherapy and steroid treatment. Risk factors for HBV reactivation in patients receiving chemotherapy include being male, lack of HBs antibody, HBs antigen positivity, presence of a precore mutant, HBV-DNA level, anthracycline/steroid use, transplantation, second/third line treatment, youth, and the presence of lymphoma. However, when rituximab is used, the risk factors for HBV reactivation are narrowed to a lack of HBs antibody, youth, and being male. All the above reports are retrospective analyses of patients who were HBs antigen positive and who therefore were subject to prophylactic nucleoside analog therapy. In the future, patient groups must be identified who tend to experience reactivation even when receiving such therapy.
Read Also: How Did You Get Hepatitis C
Read Also: How To Test For Hepatitis C Virus
What Is A Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Test
Hepatitis B surface antibody test is part of a panel of blood tests to diagnose HBV infection. Hepatitis B surface antibody test determines the presence and quantity of anti-HBs in the blood serum, which can indicate protection from HBV infection.
Hepatitis B disease affects theliver and commonly spreads through body fluids such as blood, semen, and vaginal secretions.
Read Also: Hepatitis C And Treatment Options
Hbcab Or The Hepatitis B Core Antibody Test
The hepatitis B core antibody is produced by your immune system after infection by the hepatitis B virus, and it can persist for life. It is a sign that you either have an new, active hepatitis B infection or that you acquired hepatitis B in the past.
HBcAb is an immune system response to a protein in the core of the virus, and it is only present if you have been infected, rather than immunized against the virus. It is part of a routine screening panel of tests for hepatitis B. If your rest results turn out to be positive, your healthcare provider will order further tests to determine the stage of the infection, acute or chronic .
Also Known As: anti-HBc, HBcAb
Recommended Reading: Cure For Chronic Hepatitis B
Hepatitis A Infection Is Typically Diagnosed Through Blood Tests
The various human hepatitis viruses cause very similar symptoms. Therefore, neither the individual nor the healthcare provider can tell by symptoms or signs if a given individual is suffering from hepatitis A unless laboratory tests are performed.
Fortunately, blood tests are widely available to accurately diagnose hepatitis A, including tests for antibodies, or the affected persons immune response to hepatitis A proteins. This immune response is conclusively demonstrated by the presence of Immunoglobulin M antibodies, indicating acute disease, and immunoglobulin G , indicating a past infection or vaccination. The IgG antibodies are present for life, indicating immunity.
HAV RNA is present in blood and feces soon after infection , until 1 to 2 weeks after the onset of symptoms. Longer shedding in feces can occur in children and those infected with HIV. HAV is also shed in saliva and urine, but no assays are available to detect this.
Following is some guidance for the interpretation of the test results:
Previous Chapter
What Does A Reactive Result To A Hepatitis B Test Mean
The meaning of a reactive result for a hepatitis B test depends on the type of test performed, according to the Hepatitis B Foundation. The three most common blood tests detect the presence of hepatitis B surface antigens, hepatitis B surface antibodies or hepatitis B core antibodies.
In the hepatitis B surface antigen test, a reactive or positive result means that a person is currently infected with the hepatitis B virus, explains the Hepatitis B Foundation. Reactive results from the hepatitis B surface antibody test means that people are now immune to the virus because they have been infected in the past and their immune systems produced antibodies to fight the infection. For the hepatitis B core antibody test, a reactive or positive result can mean either that a person is currently infected with hepatitis B virus or have been some time in the test. A reactive result for this test can also be a false positive, meaning that the person has never been infected with the virus.
Don’t Miss: What Are The Early Signs Of Hepatitis C
Discussing Screening Results With Clients
The medical personnel who ordered or arranged the screening test, not counselors, usually explain the results. Hepatitis screening should be part of the intake physical examination in an opioid treatment program, and medical personnel may report the results. However, the client may want to discuss the results with the counselor or ask the counselor questions.
Anxiety might interfere with some clients ability to comprehend or retain information, which might need to be repeated.
Suggestions for conversations with clients when the test results are negative include the following:
- Explain results clearly and simply: So the HCV screening result was negative? This means that, as of 6 months ago, you did not have .
- Emphasize that a negative result to an HCV test does not indicate to and that the client should take precautions to avoid . If a relapse to drug use occurs, advise clients to avoid sharing any drug paraphernalia or equipment. Specify that this includes cookers, cotton, water, needles, syringes, pipes, and straws.
- Emphasize the importance of getting HAV and HBV vaccinations. Provide information about the availability of low- or no-cost vaccinations.
Clients whose screening test results are positive for will need additional tests and examinationsusually with doctors who specialize in diseases of the liver to get accurate diagnoses and to determine their health status and the extent of liver damage. These tests are described in .
What Is Hepatitis A Virus
Hepatitis A happens to be one of the three most common hepatitis viruses in the world. As the body begins to be infected with the hepatitis A virus, the immune system produces antibodies in response to the infection.
The body at first produces hepatitis A IgM antibodies when the patient is first exposed to the HAV. It takes about 2 to 3 weeks for the IgM antibodies to develop after the initial infection sets in and can be detected before the symptoms of Hepatitis A begin. Victims complain of symptoms usually anywhere from 14 to 50 days from the start of the infection. The IgM antibodies show up in the blood tests usually about 5 to 10 days before patients experience symptoms. The IgM antibodies can be found in the blood for about 3 to 6 months post HAV infection.
Hepatitis A IgG antibodies are produced by the immune system in the body after about one or two weeks following the production of IgM antibodies. The IgG antibodies remain in the system for a lifetime, providing lifelong immunity against HAV.
Also Check: How To Get Rid Of Hepatitis C