Accessibility And Hbsag Clearance Rate
HBsAg clearance occurs spontaneously or via antiviral treatment in CHB patients. The most commonly used drugs are nucleoside analogue and pegylated interferon . NA drugs include entecavir , tenofovir disoproxil fumarate and tenofovir alafenamide fumarate . The 2018 AASLD guidelines recommend Peg-IFN, ETV, or TDF as the preferred initial therapy for adults with immune-active CHB. It also suggests that alanine transaminase levels be tested at least every 6 months for adults with immune-tolerant CHB to monitor for potential transition to immune-active or immune-inactive CHB . The 2017 EASL guideline recommends ETV, TDF and TAF as the preferred monotherapy regimens, and the extension of the duration of Peg-IFN therapy beyond week 48 may be beneficial in selected HBeAg-negative CHB patients . The potential side effects of NAs include lactic acidosis for ETV and nephropathy, osteomalacia, lactic acidosis for TDF. CHB patients should be clinically monitored. The most frequently reported side effects for Peg-IFN are flu-like syndrome, myalgia, fatigue, mood disturbances, weight loss, hair loss and local reactions at the site of injection, and these side effects may be partially managed with dose reduction . Currently, the clearance of HBsAg is based primarily on sequential or combined treatment with NA and Peg-IFN.
You May Like: Hepatitis B Surface Ab Immunity
Who Is Most At Risk Of Contracting Hepatitis C
You have a high risk of contracting hepatitis C if you:
- use or have used injection drugs even if it was just once or many years ago
- have received blood or blood products or an organ transplant before July 1990 in Canada
- have been in jail or
- have been injected or scratched during vaccination, surgery, blood transfusion or a religious/ceremonial ritual in regions where hepatitis C is common.
You have a high moderate risk of contracting hepatitis C if you:
- have tattoos or body piercing
- have multiple sexual partners
- have a sexually transmitted infection , including HIV or lymphogranuloma venereum
- have experienced traumatic sex or rough sex or have used sex toys or fisting that can tear body tissue
- have vaginal sex during menstruation
- have received a kidney treatment
- have received an accidental injury from a needle or syringe
- have another infectious disease
- were born to a hepatitis C infected mother or
- have a sexual partner infected with hepatitis C.
Hepatitis C is NOT passed from person to person by:
- coughing, sneezing
- breastfeeding unless your nipples are cracked and bleeding or
- oral sex, unless blood is present.
How Long Does It Take To Cure Hepatitis C
Depending on the drug combination, the specific genotype of hepatitis C that is to be treated, any prior treatment, and whether the person has cirrhosis, the duration of medical therapy may be as few as 8 weeks, or up to 24 weeks. Most regimens are for 12 consecutive weeks. This is much shorter than the interferon-based treatments years ago that lasted up to 48 weeks. Generally, a person is not considered “cured” until the “RNA viral load” is undetectable for 24 weeks after therapy is stopped. This is called “sustained virologic response” or SVR.
The presence of cirrhosis or liver fibrosis is determined by liver biopsy, noninvasive fibrosis scans, or formulas that estimate liver fibrosis based on blood tests, such as AST-to-platelet Ratio Index or Fibrosis-4 Index.3
A very important aspect of treatment is the elimination of all alcohol consumption. Alcohol adds fuel to the fire when it comes to chronic hepatitis. Drinking alcohol greatly worsens liver fibrosis and speeds progression to cirrhosis, and there is no “safe” amount to drink for someone with chronic hepatitis. Drinking alcohol also makes it harder for the medications to be effective and may interfere with proper dosing.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Catch Hepatitis B
How Are Hepatitis B And C Diagnosed
Hepatitis B is diagnosed by a series of blood tests. The test may show an ongoing infection or antibodies that indicate that the patient is protected against hepatitis B. In patients who have a positive screening test that suggests the possibility of ongoing infection, further testing is done to determine the levels of the virus in the bloodstream.
Hepatitis C is diagnosed via a blood test called a Hepatitis C Antibody Test. A positive result means that hepatitis C antibodies are present in the blood. But a positive antibody test doesnt necessarily mean a person has hepatitis C. A further blood test is needed to confirm the diagnosis. This second blood test quantifies the amount of the virus or the viral load in the liver and the bloodstream.
How Do Doctors Treat Hepatitis C
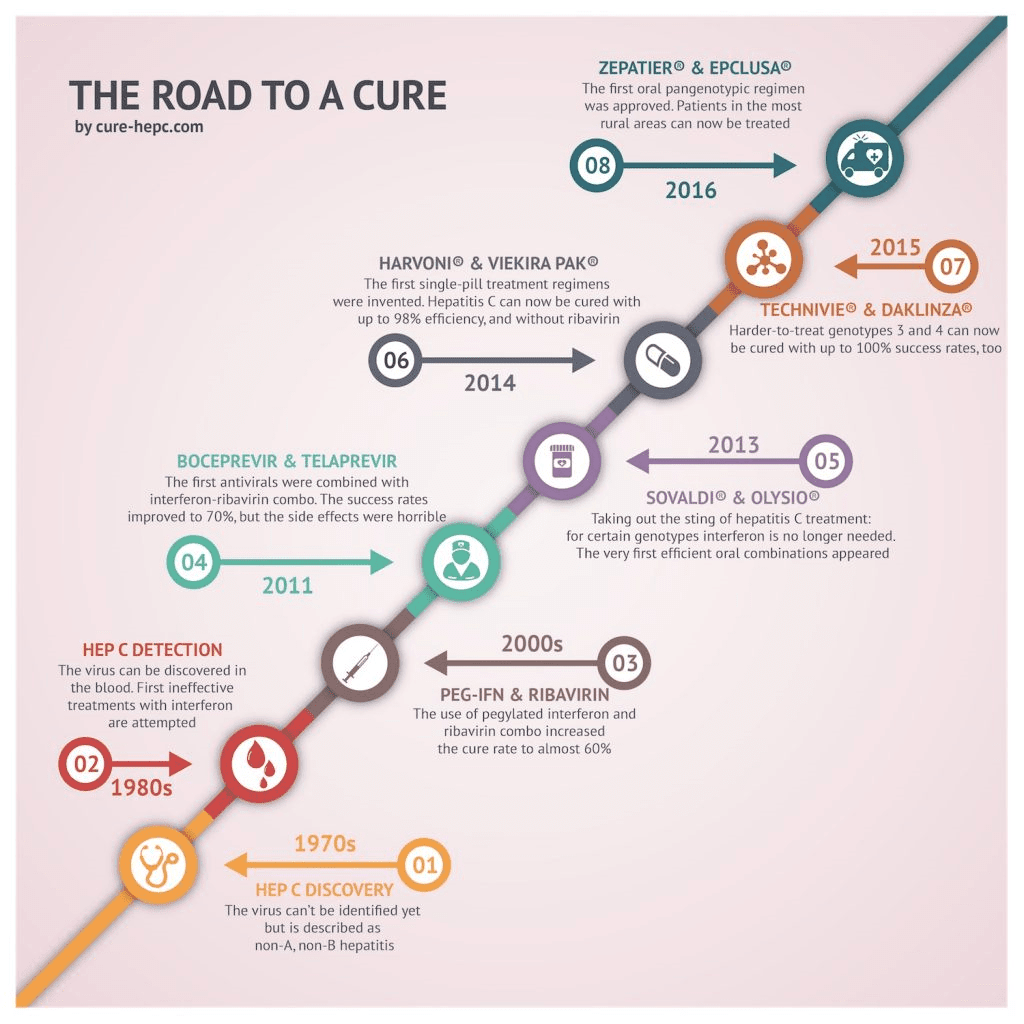
Doctors treat hepatitis C with antiviral medicines that attack the virus and can cure the disease in most cases.
Several newer medicines, called direct-acting antiviral medicines, have been approved to treat hepatitis C since 2013. Studies show that these medicines can cure chronic hepatitis C in most people with this disease. These medicines can also cure acute hepatitis C. In some cases, doctors recommend waiting to see if an acute infection becomes chronic before starting treatment.
Your doctor may prescribe one or more of these newer, direct-acting antiviral medicines to treat hepatitis C:
You may need to take medicines for 8 to 24 weeks to cure hepatitis C. Your doctor will prescribe medicines and recommend a length of treatment based on
- which hepatitis C genotype you have
- how much liver damage you have
- whether you have been treated for hepatitis C in the past
Your doctor may order blood tests during and after your treatment. Blood tests can show whether the treatment is working. Hepatitis C medicines cure the infection in most people who complete treatment.
Hepatitis C medicines may cause side effects. Talk with your doctor about the side effects of treatment. Check with your doctor before taking any other prescription or over-the-counter medicines.
For safety reasons, talk with your doctor before using dietary supplements, such as vitamins, or any complementary or alternative medicines or medical practices.
Don’t Miss: Which Hepatitis Is An Std
Innovating Against A Silent Killer
Imagine taking an injection and a pill that made you feel every day worse than you ever felt from the infection that was being treated. Alexea Gaffney-Adams, MD, infectious disease specialist
Hepatitis C is dubbed the silent killer as it typically progresses without symptoms, often leaving patients unaware they are infected until their condition is very serious. HCV damages the liver slowly over many years, often moving from inflammation to scarring to permanent, irreversible scarring .
Once a patient has cirrhosis, the liver is unable to heal itself, and this condition can rarely be reversed. For those with end-stage liver disease, treatment is more focused on preventing further damage in an effort to avoid complications, including liver cancer, liver transplantation, and premature death. Hepatitis C has also been associated with other serious conditions, including diabetes, kidney disease, and depression.
In 1987, scientists working at Chiron Corporation, later acquired by Novartis, partnered with the CDC. Using a novel molecular cloning approach, they officially identified and named the virus hepatitis C in 1989.
Interferon was the first, and for a time, the only treatment for hepatitis C. An interferon is a protein produced by the bodys immune system in response to an infection. Side effects were debilitating, and many patients dropped out of what was a very long course of treatment. It was also a largely ineffective treatment.
Can You Drink Alcohol If You Have Hepatitis C
Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver. Hepatitis C viral infection causes this inflammation. There are several risk factors for contracting HCV infection due to the hepatitis C virus. One serious risk factor is drinking alcohol with HCV infection. The combination of HCV and alcohol can cause complications, and may result in more severe and serious liver injury including chronic cirrhosis . It also increases your chances of developing liver cancer having an alcohol induced increase in viral replication and rapid mutation of the hep C virus,which creates complications like:
- Greater viral capacity
Hepatitis refers to any cause of liver inflammation, with or without scarring of the liver . It is contagious, and is spread from person-to-person by blood-to-blood contact. Other viral causes of hepatitis include hepatitis A, B, C, and E. Other types of noninfectious causes of hepatitis include:
- Excessive alcohol intake
- Medications such as some prescription medications or even acetaminophen, for example, Tylenol liver damage and drug induced liver disease.
- Bacteria and viruses other than the hepatitis viruses
How are hepatitis A, B, and E spread?
- Transmission of hepatitis A and E: These forms of the virus are acquired from improper hygiene during food or drink preparation by someone who’s infected.
- Transmission of hepatitis B: This form is spread by blood-to-blood or sexual contact.
Recommended Reading: How Long Does A Person Live With Hepatitis C
Can I Drink Alcohol If I Have Hepatitis C
The combination of any cause of hepatitis, such as alcohol on top of HCV, adds to and accelerates liver damage. Both hepatitis B and C can cause chronic hepatitis and progression to cirrhosis and liver cancer, although the disease is much more likely to become chronic in the U.S. Therefore, people with chronic HCV should not drink alcohol and should talk to a doctor about vaccines for other hepatitis viruses.
How Do People Get Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C virus is found in the blood of people with HCV infection. It enters the body through blood-to-blood contact.
Until reliable blood tests for HCV were developed , people usually got hepatitis C from blood products and blood transfusions. Now that blood and blood products are tested for HCV, this is no longer the typical means of infection.
Currently, people usually get hepatitis C by sharing needles for injection drug use. An HCV-infected woman can pass the infection to her baby during birth. It is also possible to get hepatitis C from an infected person through sexual contact, an accidental needlestick with a contaminated needle, or improperly sterilized medical, acupuncture, piercing, or tattooing equipment.
Also Check: Is There A Vaccine For Hepatitis B And C
How Much Does Hepatitis C Treatment Cost
It is impossible to say what the exact cost is for the various regimens, but it is in the tens of thousands of dollars. In general, out of pocket cost would be very high for the average person, and most people are treated through a health insurer, federal health benefits, or veteran’s benefits. The cost of hepatitis C and the care of its complications, however, is much higher over a person’s lifetime, and the roughly estimated savings is believed to make treatment a good health and financial investment. Liver transplantation alone may cost several hundred thousand dollars for the procedure alone, followed by several hundred thousand for the medications needed in the first 6 months afterward.2 This does not include the many complications of liver transplantation.
Because negotiations are confidential business contracts, little is known about how much is actually paid for medical treatments by these drugs. One example is the medication sofosbuvir. Estimated costs for a standard 12-week treatment with sosobuvir was $84,000 in the US. Actual costs to individuals depend upon price contracts between pharmaceutical companies and health insurers, as well as government and private organizations. Thus, an individual with healthcare coverage may only pay a monthly co-pay.4
Study Underscores The Powerful Effect Of Direct
- Date:
- Henry Ford Health System
- Summary:
- Researchers report that patients with chronic hepatitis C who are treated with direct-acting antiviral medicines are less likely to be hospitalized or seek emergency care for liver and non-liver related health issues. The study underscores the extraordinary effect of these newer antivirals, which have been shown to cure hepatitis C in 98 percent of patients who take them.
Researchers at Henry Ford Health System, as part of a national hepatitis C collaborative, report that patients with chronic hepatitis C who are treated with direct-acting antiviral medicines are less likely to be hospitalized or seek emergency care for liver and non-liver related health issues.
The study, published online in Clinical Infectious Diseases, underscores the extraordinary effect of these newer antivirals, which have been shown to cure hepatitis C in 98 percent of patients who take them. Patients are said to be cured when the virus is no longer detectable in their blood.
“The findings of our study show that curing hepatitis C not only gets rid of the virus, it also improves the overall health of patients,” said Stuart Gordon, M.D., Director of the Division of Hepatology at Henry Ford and the study’s lead author. “This is consistent with our earlier studies that showed effective treatment of hepatitis C also reduces the risk of patients developing other health conditions like diabetes, kidney disease, stroke and heart attacks.”
Key findings of the study:
Don’t Miss: How Often Should You Get Tested For Hepatitis C
What A Hepatitis C Cure Means
Scientists have a very specific definition of what it means to be cured of hepatitis C. In order to be considered cured, patients must have undetectable HCV RNA on an HCV test 12 or 24 weeks after completing a course of therapy. The lack of detectable HCV is what is known as a sustained virological response .
At first, scientists were reluctant to consider an SVR an actual cure. However, research has shown that when HCV RNA is undetectable in both the blood and the liver, the virus has been cured. In theory, this means it may be possible to eliminate all hepatitis C.
More than 95 percent of hepatitis C patients are theoretically curable by an eight- to 12-week treatment regimen with DAAs.
Is There A Cure
Though there is no vaccine for Hepatitis C, treatments can reduce the viral load to undetectable levels which is considered cured or in remission.
The virus is considered cured when it is not detected in your blood 12 weeks after treatment is completed. This is otherwise known as a sustained virologic response .
Hepatitis C is one of the most serious hepatitis viruses. However, with newer treatments developed over the past few years, the virus is much more manageable than it was in the past.
Current antiviral drugs that help cure hepatitis C may also help prevent the health complications of chronic liver disease.
The reports less than half of people who contract the hepatitis C virus may clear it from their bodies without treatment. For this group of people, the virus will be a short-term acute condition that goes away without treatment.
But for most people, acute hepatitis C will likely develop into a chronic condition that requires treatment.
Since the virus often doesnt produce symptoms until after more significant liver damage occurs, its important to get tested for hepatitis C if you think you might have been exposed.
approved the antiviral drug Mavyret for an 8-week treatment period for people with all genotypes of hepatitis C.
This treatment is now being used for many people instead of the 12-week treatment that was previously required.
Noninvasive ways to test for liver damage caused by hepatitis C are also now available to aid in diagnosis.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C How Does It Spread
Can Hepatitis C Be Cured
Considerable progress has been made by past clinical trials in the medical treatment of hepatitis C. The rate of cure has increased with the development of direct-acting, all-oral antiviral regimens, and the length of therapy is much shorter. Treatment recommendations continue to change as new medicines become available. Treatment helps to reduce progression of liver damage to cirrhosis, may prevent liver cancer, and may prevent spread of the infection to other people.
With The Momentum Growing Around Hepatitis B Drug Discovery Research We Are Closer Than Ever To A Cure
From the Spring 2016 B Informed Newsletter
With the momentum growing around hepatitis B drug discovery research, how far are we from a cure?
Closer than ever, according to Timothy Block, PhD, president and co-founder of the Hepatitis B Foundation and its research arm, the Baruch S. Blumberg Institute. He points out that hepatitis C, initially thought to be incurable, can now be cured with new combination treatments.
Hepatitis B is in a similar position, Block believes. And the need for a cure has never been greater, with over 240 million people living with chronic hepatitis B infection worldwide, resulting in 1 million deaths per year from related liver failure and liver cancer.
Treatments are available, explains Block, but we have become a little too comfortable with the seven medications that are currently approved for use. While these drugs are effective, the interferons have many side effects and the oral antivirals require lifelong use. Moreover, they work in only about half of the infected population, and reduce the rate of death due to liver disease by only about 40 to 70 percent.
For those who benefit from treatment, the antiviral drugs prove that medications can be effective. However, there are millions who do not benefit and are still left vulnerable. We should not accept that a significant number of people will still die from hepatitis B-related complications despite taking the current drugs, Block declares.
What would a cure look like?
cccDNA Inhibitors
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis A What Is It
Sometimes The Infection Goes Away On Its Own
Acute hepatitis is C is a short-term illness that occurs within the first six months after being exposed to the virus. Like the human papillomavirus , early acute hepatitis C can clear on its own without treatment this happens about 25% of the time.
However, it’s more likely that the virus will remain in your body longer than six months, at which point it’s considered to be chronic hepatitis C infection.
“Being younger or a woman tends to be a factor in whether the virus clears on its own, and genetics may play a role,” Reau says. “But we can’t determine with certainty which people are certain to clear the infection and which aren’t.”