Who Is Most At Risk Of Contracting Hepatitis C
You have a high risk of contracting hepatitis C if you:
- use or have used injection drugs even if it was just once or many years ago
- have received blood or blood products or an organ transplant before July 1990 in Canada
- have been in jail or
- have been injected or scratched during vaccination, surgery, blood transfusion or a religious/ceremonial ritual in regions where hepatitis C is common.
You have a high moderate risk of contracting hepatitis C if you:
- have tattoos or body piercing
- have multiple sexual partners
- have a sexually transmitted infection , including HIV or lymphogranuloma venereum
- have experienced traumatic sex or rough sex or have used sex toys or fisting that can tear body tissue
- have vaginal sex during menstruation
- have received a kidney treatment
- have received an accidental injury from a needle or syringe
- have another infectious disease
- were born to a hepatitis C infected mother or
- have a sexual partner infected with hepatitis C.
Hepatitis C is NOT passed from person to person by:
- coughing, sneezing
- breastfeeding unless your nipples are cracked and bleeding or
- oral sex, unless blood is present.
Fatigue And Associated Effects
Fatigue is among the most prevalent long-term symptoms of hepatitis C. In our 2018 Hepatitis C In America survey, over 40% of respondents said fatigue is the symptom that most impacts their daily life. Fatigue is characterized as an extreme tiredness that doesnt get better with sleep. It may be described as sleepiness, drowsiness, exhaustion, or feeling worn out. Fatigue can also make other symptoms of chronic HCV infection worse, such as depression, anxiety, or brain fog.
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Most people infected with hepatitis C have no symptoms. Some people with an acute hepatitis C infection may have symptoms within 1 to 3 months after they are exposed to the virus. These symptoms may include
If you have chronic hepatitis C, you most likely will have no symptoms until complications develop, which could be decades after you were infected. For this reason, hepatitis C screening is important, even if you have no symptoms.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B And C Test
What Happens To Your Health When You Arent Treated For Hepatitis C
Although medication can cure hepatitis C, millions of people arent taking it. The problem: Left untreated, the virus can lead to serious health complications.
Theres a reason the hepatitis C virus is called the silent killer. All too often, people dont realize theyve been infected. Out of the estimated 2.4 million people in the United States who have hepatitis C, more than half dont know they have it, according to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
Usually when someone gets infected with hepatitis C, they initially until the disease gets fairly advanced, says Hardeep Singh, MD, a gastroenterologist and hepatologist at St. Joseph Hospital in Orange, California. The median time it takes for symptoms…to develop is 30 years.”
While some people are able to clear the virus on their own, most arent, and more than 50 percent go on to develop long-term, or chronic, hepatitis C, says the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Over time, untreated hepatitis C can cause hardening and scarring of the liver, which can cause complications that eventually lead to liver failure.
Liver cirrhosis and liver failure usually cannot be reversed sometimes a liver transplant is the only treatment option once advanced liver damage occurs. With hepatitis C, your risk of liver cancer also rises.
Here are a few other conditions that can be caused by untreated hepatitis C.
Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
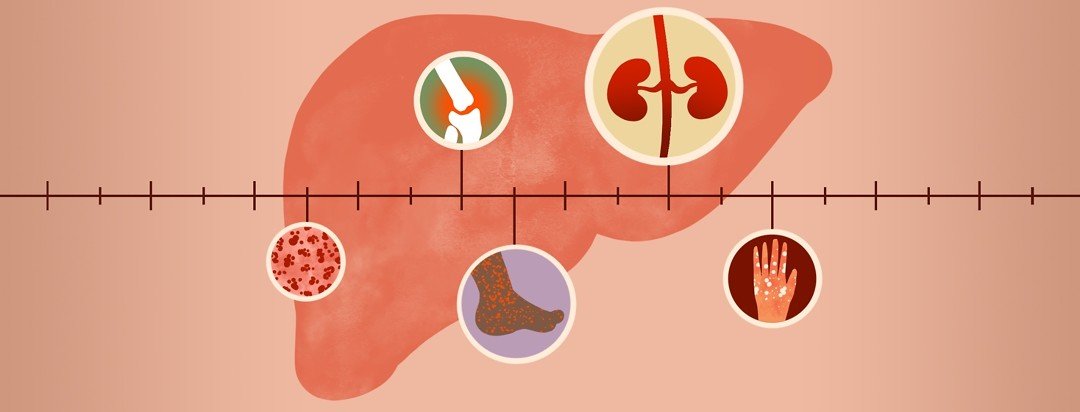
It is very important to know that not everyone with hepatitis C has symptoms. The only way to know if you have hepatitis is by talking to your doctor and getting a blood test.
Many people living with hepatitis C feel well and only have symptoms once the disease has progressed and there is serious liver damage.
If you do not have symptoms this does not mean that the virus isnt causing damage.
When first infected, some people may find:
- their urine becomes dark
- their eyes and skin turn yellow
- they experience a minor flu-like illness.
These symptoms may disappear within a few weeks, but this does not necessarily mean that the infection has been cleared.
Over time, symptoms that may develop include:
- tiredness and fatigue
- flu-like symptoms
- pain in the abdomen where the liver is located
- not feeling hungry and indigestion.
Around 30% of people who have been infected may clear the virus from their blood naturally, with no treatment, within 6 months. These people no longer have the hepatitis C virus and are not infectious, but will always have hepatitis C antibodies in their blood. The presence of hepatitis C antibodies shows that someone has been exposed to the virus, but does not offer any immunity against hepatitis C. People can become reinfected after clearing the virus naturally, or after treatment.
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatitis A And B And C
How Common Is Hepatitis C In The United States
In the United States, hepatitis C is the most common chronic viral infection found in blood and spread through contact with blood.14
Researchers estimate that about 2.7 million to 3.9 million people in the United States have chronic hepatitis C.13 Many people who have hepatitis C dont have symptoms and dont know they have this infection.
Since 2006, the number of new hepatitis C infections has been rising, especially among people younger than age 30 who inject heroin or misuse prescription opioids and inject them.15,16
New screening efforts and more effective hepatitis C treatments are helping doctors identify and cure more people with the disease. With more screening and treatment, hepatitis C may become less common in the future. Researchers estimate that hepatitis C could be a rare disease in the United States by 2036.17
How Does Hepatitis C Affect Your Body
Hepatitis C is an inflammation of the liver. The hepatitis C virus is most often transmitted through infected blood, such as by sharing needles, says Alexander Kuo, MD, medical director of liver transplantation at Cedars-Sinai in Los Angeles.
Sexual transmission is very uncommon, he says. In healthy adults, youre more likely to catch HCV by sharing a toothbrush or razor than through sexual contact. Using barrier methods during sex decreases the risk further.
People who contract HCV often dont realize they have it. During the early stages of infection, the vast majority of people are symptom free, Dr. Kuo says, so it can be difficult to diagnose before it has already done lasting damage to your liver.
People who may have been exposed children of women who have hepatitis C people who have gotten at-home tattoos and those whove used intravenous drugs should get a onetime blood test to screen for HCV even before they experience symptoms, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . People who actively inject drugs should have routine screenings.
Over time, the chronic inflammation from untreated hepatitis C can lead to fibrosis, or scarring, in the liver. Kuo cautions that if this continues for 20 or more years, there is a risk that the liver can become hard from severe fibrosis, resulting in a condition called cirrhosis.
Recommended Reading: Life Insurance For Hepatitis B Carrier
What Are The Side Effects Of Treatments For Hepatitis C Infection
Side effects of interferon or pegylated interferon
- The most common side effects of interferon or pegylated interferon include fever, flu-like symptoms, and depression. Patients must be monitored closely for depression. Risk of suicide is a reason to avoid interferons.
- Interferons also reduce white blood cell and/or red blood cell counts . This may cause increased susceptibility to infection. Interferons also increase the risk of certain cancers. Death rarely occurs as a result of therapy, but may occur from progression of liver failure in patients with advanced cirrhosis.
Side effects of ribavirin
- Ribavirin most commonly causes anemia due to destruction of red blood cells . This can be severe enough that people with heart disease may suffer a heart attack from insufficient blood flow, so people with heart disease should not receive this drug. Anemia improves with a reduction in the dose of ribavirin. Injected growth factor that stimulates the production of red blood cells often is used to improve the anemia associated with ribavirin. Ribavirin also accumulates in the testicles and ovaries and causes birth defects in animals. Although no birth defects have been reported in humans, both men and women should use contraceptive measures to avoid pregnancy during and for at least six months after ribavirin treatment.
Side effects of DAAs
- The most common and significant side effects of boceprevir , sofosbuvir , and ledipasvir/sofosbuvir include
- fatigue ,
Spread Of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is spread through blood-to-blood contact when blood from a person with hepatitis C enters another persons bloodstream.
The most common way people become infected with hepatitis C in Australia is by sharing injecting equipment such as needles, syringes, spoons and tourniquets. It is possible to be infected with hepatitis C after only one risk event.
Hepatitis C may also be spread through:
- tattooing and body piercing with equipment that has not been properly cleaned, disinfected or sterilised such as backyard tattoos’. Registered parlours with appropriate infection control procedures are not a risk
- needlestick injuries in a healthcare setting
- receiving blood transfusions in Australia prior to 1990 before hepatitis C virus testing of blood donations was introduced
- medical procedures, blood transfusions or blood products and mass immunisation programs provided in a country other than Australia
- pregnancy or childbirth there is a 5% chance of a mother with chronic hepatitis C infection passing on the virus to her baby during pregnancy or childbirth.
Breastfeeding is safe, however if nipples are cracked or bleeding cease breastfeeding until they have healed.
Less likely possible routes of transmission of hepatitis C include:
Hepatitis C cannot be transmitted by:
- kissing
- sharing food, cups or cutlery
- shaking hands or day-to-day physical contact.
Recommended Reading: Hepatomegaly With Diffuse Hepatic Steatosis
Chronic Hep C Infection
- Antiviral Medications: If you have chronic hepatitis C, your doctor may recommend antiviral medications to clear the virus from your body. Researchers have made significant progress recently in creating direct-acting antiviral drugs. These medications have fewer side effects and shorter treatment times, typically 8-12 weeks. Which medication your doctor chooses will depend on your specific profilewhich virus genotype you have, whether you have existing liver damage, and your medical history and prior hepatitis treatments.
- Liver transplantation: If you have serious complications from chronic hepatitis C infection, your doctor may recommend liver transplantation. A liver transplant doesnt cure hepatitis C, and the infection may return and require treatment with antiviral medications to clear the virus and prevent damage to the new liver, but a liver transplant can be a lifesaving procedure for those who need it.
- Vaccines: There is no vaccine for hepatitis C, but your doctor may recommend vaccines for hepatitis A and B viruses, which can also cause liver damage and worsen hepatitis C.
Acute Phase Of Hepatitis C
Acute means ‘new’ or ‘for a short time’. This phase lasts for the first six months. When first infected with the virus, most people have no symptoms, or only mild ones. If symptoms do occur, they develop about 7-8 weeks after being exposed to the virus and may include feeling sick , being sick and feeling generally unwell. Some people go ‘yellow’ . This is due to a build-up of the chemical bilirubin which is made in the liver and spills into the blood in some liver conditions. It is unusual to have severe symptoms.
Following the initial infection:
- In about one quarter to one half of cases the virus is cleared from the body by the immune system within 2-6 months. If this happens then you will have no long-term effects from the virus. Younger people and women are more likely to clear the virus in this way.
- In 5 to 8 out of 10 cases, the virus remains active in the liver and bloodstream long-term. This is called chronic infection with hepatitis C.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C How Does It Spread
How Mavyret Treats Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a liver infection caused by the hepatitis C virus. Mavyret works to treat hepatitis C by preventing the virus from replicating . When a virus is unable to replicate, it will eventually die and be cleared from your body.
Because Mavyret works on viruses, it belongs to a medication class called direct-acting antivirals. Mavyret contains two active medications: glecaprevir and pibrentasvir.
How Are Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C Spread From Person To Person

Like HIV, the hepatitis B and hepatitis C viruses spread:
- From mother to child: Pregnant women can pass these infections to their infants. HIV-HCV coinfection increases the risk of passing on hepatitis C to the baby.
- Sexually: Both viruses can also be transmitted sexually, but HBV is much more likely than HCV to be transmitted sexually. Sexual transmission of HCV is most likely to happen among gay and bisexual men who are living with HIV.
You May Like: Where Can I Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine For Free
Viral Hepatitisa Very Real Consequence Of Substance Use
Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver. It can be caused by a variety of toxins , autoimmune conditions, or pathogens .1 Viral hepatitis is caused by a family of viruses labeled A, B, C, D, and E. To learn more about the route of transmission and prognosis for each virus, visit the Centers for Disease Control and Preventions Division of Viral Hepatitis. Hepatitis B and hepatitis C are the most common viral hepatitis infections transmitted through the sometimes risky behaviors of people who use drugsparticularly among people who inject drugs. An estimated 862,000 people are living with HBV chronic infections, with about 22,000 acute infections recorded in 2017. An estimated 2.4 million Americans are living with HCV based on 2013-2016 annual average, with an estimated 44,700 new cases of acute HCV in 2017. In fact, new cases of acute HCV have increased rapidly in the US since 2010, and have most often been associated with injection drug use.6 Three out of four people living with HCV are baby boomers born between 1945 and 1965.7
How Do Doctors Treat Hepatitis C
Doctors treat hepatitis C with antiviral medicines that attack the virus and can cure the disease in most cases.
Several newer medicines, called direct-acting antiviral medicines, have been approved to treat hepatitis C since 2013. Studies show that these medicines can cure chronic hepatitis C in most people with this disease. These medicines can also cure acute hepatitis C. In some cases, doctors recommend waiting to see if an acute infection becomes chronic before starting treatment.
Your doctor may prescribe one or more of these newer, direct-acting antiviral medicines to treat hepatitis C:
You may need to take medicines for 8 to 24 weeks to cure hepatitis C. Your doctor will prescribe medicines and recommend a length of treatment based on
- which hepatitis C genotype you have
- how much liver damage you have
- whether you have been treated for hepatitis C in the past
Your doctor may order blood tests during and after your treatment. Blood tests can show whether the treatment is working. Hepatitis C medicines cure the infection in most people who complete treatment.
Hepatitis C medicines may cause side effects. Talk with your doctor about the side effects of treatment. Check with your doctor before taking any other prescription or over-the-counter medicines.
For safety reasons, talk with your doctor before using dietary supplements, such as vitamins, or any complementary or alternative medicines or medical practices.
Recommended Reading: Does Hepatitis C Weaken Your Immune System
How Common Is Hepatitis C
The exact number of people infected is not known. There are around 200,000 people chronically infected with hepatitis C in the UK. Worldwide, over 180 million people are infected. Rates of infection have been relatively stable in recent years, but deaths from hepatitis C have reduced, thought to be because treatment options have become better.
Most cases are in people who inject illegal drugs. It is estimated that up to half of injecting drug users become infected with hepatitis C.
What Do I Do If I Find Out I Have Viral Hepatitis
After learning from your doctor that you have hepatitis, your first step will be to learn more about the virus. Read government resources, like the websites listed below, to find current, scientific information. Adopting a healthy lifestyle is important to prevent the virus from becoming serious. Dont drink or misuse drugs because they are hard on your liver. Get plenty of rest, eat healthy foods, and exercise. Work to protect others by not donating blood or participating in risky behaviors, including sharing needles when using drugs or having unprotected sex.
Don’t Miss: How Hepatitis C Affects The Body
What Happens To People With Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C, or HCV, replicates in the liver. During this process, parts of the virus trigger your immune system into action. In the process of trying to rid your body of the HCV infection, the immune system actually kills infected liver cells. Over a slow process of many years, the interaction between the immune system and your liver can result in scarring of the liver and loss of liver function.
Most people who are infected with hepatitis C develop a chronic infection with the virus. But for some people, their body gets rid of the virus on its own very early after they are first infected. More than half of people with hepatitis C will never have any health problems from it. The disease generally progresses slowly, over the course of 10 to 40 years.