Treatments For Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C can be treated with medicines that stop the virus multiplying inside the body. These usually need to be taken for several weeks.
Until recently, most people would have taken 2 main medicines called pegylated interferon and ribavirin .
Tablet-only treatments are now available.
These new hepatitis C medicines have been found to make treatment more effective, are easier to tolerate, and have shorter treatment courses.
They include simeprevir, sofosbuvir and daclatasvir.
Using the latest medications, more than 90% of people with hepatitis C may be cured.
But it’s important to be aware that you will not be immune to the infection and should take steps to reduce your risk of becoming infected again.
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
During the acute phase most persons have no symptoms or might experience a mild illness. Symptoms of acute HCV infection, when present, may include:
- Jaundice
- Dark-colored urine, light-colored stools
- Diarrhea
- Fever
During the chronic phase hepatitis C usually progresses silently, with no symptoms at all during the first 10-20 years. Signs of severe liver scarring may include:
- Ascites
- Star-shaped vein pattern developing on the swollen belly
- Jaundice
- Itching
- Easy bruising and bleeding
Because symptoms of hepatitis C are usually absent, persons with risk for HCV infection should be tested. The blood test for hepatitis C infection is called the hepatitis C antibody test. People who have hepatitis C infection will show positive antibodies on this test. In many cases, it is necessary to confirm a positive hepatitis C antibody test with a more specific test, such as a test for HCV virus RNA.
If you think you have hepatitis C or have risk for hepatitis C, you should contact your doctor. The Communicable Disease Control Unit may be able to help answer your questions.
What Are The Treatment Guidelines For Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C treatment is best discussed with a doctor or specialist familiar with current and developing options as this field is changing, and even major guidelines may become outdated quickly.
The latest treatment guidelines by the American Association for the Study of Liver Disease and Infectious Disease Society of America recommends use of DAAs as first-line treatment for hepatitis C infection. The choice of DAA varies by specific virus genotype, and the presence or absence of cirrhosis. In the U.S., specific insurance providers also might influence the choice due to the high cost of DAAs. Although the individual, public health, and cost benefits of treating all patients with hepatitis C is clear, the most difficult barrier to treating all people with HCV is the very high cost of the drug regimens. Patients are encouraged to discuss options with their health care professional.
Treatment is recommended in all patients with chronic hepatitis C unless they have a short life expectancy that is not related to liver disease. Severe life-threatening liver disease may require liver transplantation. Newer therapies with DAAs have allowed more and more patients to be treated.
What are the goals of therapy for hepatitis C infection?
The ultimate goals of antiviral therapy are to
- prevent transmission of hepatitis C,
- prevent progression to cirrhosis and liver cancer, and
- improve survival and quality of life.
Don’t Miss: Is Hepatitis B Virus A Std
How Is Hepatitis C Infection Prevented
Unfortunately, there is no vaccine to prevent hepatitis C. To reduce your risk of getting hepatitis C:
- Injection drug use is the most common way people get hepatitis C. Avoid injecting drugs to reduce your risk. If you do inject drugs, use sterile injection equipment. Avoid reusing or sharing.
- Avoid sharing personal care items that might have blood on them
- If you are a health care or public safety worker, follow universal blood/body fluid precautions and safely handle needles and other sharps
- Consider the risks if you are thinking about tattooing, body piercing, or acupuncture are the instruments properly sterilized?
- If youre having sex with more than one partner, use latex condoms correctly and every time to prevent the spread of sexually transmitted diseases, including hepatitis C.
What The Cdc Recommends
Were you born between 1945 and 1965? If so, then youre a member of the Hepatitis C generation. The CDC recently recommended that all people born between during this time have a 1-time screening test for Hepatitis C. We now have new drugs that can treat and cure Hepatitis C so you should go get tested today.
The life you save may be your own! Please contact your local healthcare provider.
Also Check: Can You Catch Hepatitis C Through Sex
The Types Of Viral Hepatitis
There are five main types of viral hepatitis known as hepatitis A , hepatitis B , hepatitis C , hepatitis D , and hepatitis E . That said, there have been cases of acute hepatitis that could not be attributed to one of these five types of hepatitis viruses, alcohol, drugs, or autoimmune disease, which lead researchers to try to find another cause.
Though the etiology of these viruses have not yet been fully established, researchers have identified three other types of viral hepatitis , which they have named hepatitis F , hepatitis G , and transfusions transmitted virus . As relatively new diseases and viral discoveries, information about them and how they work is relatively scarce. We do know, however, that cases of TTV have only been associated with hepatitis in people who have had a blood transfusion.
What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis
Each type of hepatitis is treated differently.
Hepatitis A often goes away on its own and home treatment is all that is needed to help the liver recover, such as:
- Rest
- Avoiding alcohol
- Avoiding certain medicines that can be harmful to the liver
Hepatitis B often goes away on its own in about 6 months, and can also be treated at home with the above remedies. Other treatments for hepatitis B include:
- Antiviral medications
- Liver transplant in severe cases
Treatment for hepatitis C is effective on certain forms of the hepatitis C virus. The choice of medications depends on the type of hepatitis C you have, whether you have been treated for the illness before, how much liver damage has occurred, any other underlying medical issues, and other medicines you take. Treatment for hepatitis C usually involves 8 to 12 weeks of oral antiviral medications, such as:
- Elbasvir-grazoprevir
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatitis A And B And C
Is Hepatitis Testing Recommended For People With Hiv
Yes. Everyone living with HIV should be tested for HBV and HCV when they are first diagnosed with HIV and begin treatment. People living with HIV who have ongoing risk factors for getting hepatitis B or hepatitis C should be tested annually.
In addition, new HCV screening recommendations from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention call for:
- One-time screening for all adults 18 years and older
- Screening of all pregnant women during every pregnancy
- Testing for all persons with risk factors, with testing continued periodic testing those with ongoing risk.
Treatment: Chronic Hepatitis C
The latest drug to be approved by the FDA is glecaprevir and pibrentasvir . This medication offers a shorter treatment cycle of 8 weeks for adult patients with all types of HCV who donât have cirrhosis and who have not been previously treated. The length of treatment is longer for those who are in a different disease stage. The prescribed dosage for this medicine is 3 tablets daily.
There are several other combination drugs available, as well as some single drugs that may be used in combination. Your doctor will choose the right one for you depending on the type of hepatitis C you have, how well your liver is functioning and any other medical problems you may have. Also be sure to discuss your insurance coverage since these medications are expensive.
Don’t Miss: What Is Hepatitis C From
How Is Hepatitis C Treated
There are some very effective options for the treatment of hepatitis C infection. They are listed on the Medicare PBS , which makes them available at a much lower cost.
Newer treatments differ from those available previously:
- they cure more than 95% of people
- their side effects are minimal
- treatments last just 8 to 12 weeks
- they involve just a few pills each day, with no injections required
Curing hepatitis C means clearing the virus from the body. It helps reduce liver inflammation and can also help reverse scarring and cirrhosis. You can be re-treated if your treatment doesnt work the first time.
You should check with your doctor before taking any other medication or supplements, and whether you need vaccinations against hepatitis A and hepatitis B. You should also avoid alcohol if you have hepatitis. If you have liver damage, you may also need to see a liver specialist
For more information on how to get treatment, contact the National Hepatitis Info Line on 1800 437 222.
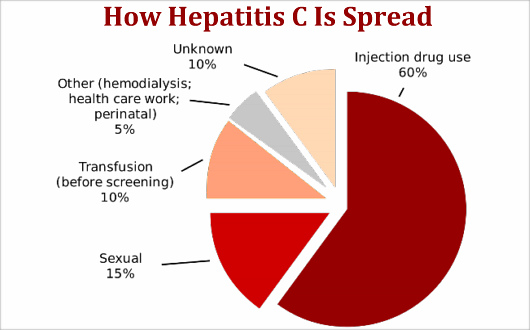
The Most Common Way That Hep C Can Spread
The most common way that hep C can spread from person to person is by sharing needles. For people who use injection drug users, using a new needle each time and then properly disposing of that needle can reduce the risk of contracting and spreading hepatitis C. When preparing to inject drugs, be sure that the equipment is not shared. There is no way to clean a drug injection kit that will guarantee the removal of the hepatitis C virus.
Recommended Reading: How Can Hepatitis B Be Transmitted
How Is Hepatitis Diagnosed
Chronic hepatitis can quietly attack the liver for years without causing any symptoms. Unless the infection is diagnosed, monitored, and treated, many of these people will eventually have serious liver damage. Fortunately, blood tests can determine whether you have viral hepatitis, and if so, which kind.
What Do You Do If You Become Ill

Talk to your health care provider about getting tested if you think you:
- are at risk
- may have hepatitis C
If you have hepatitis C, tell those who may have been exposed to your blood or bodily fluids. They should get tested and be treated if necessary. Bodily fluids, like semen and vaginal fluid, are a concern because they could be carrying small amounts of infected blood.
Some adults with hepatitis C will recover from the disease on their own within 6 months. Until your health care provider confirms your recovery status, you are still contagious and can spread the disease.
After recovery, you are no longer contagious because you will not have the disease anymore. But you can get hepatitis C again.
Unfortunately, most adults with hepatitis C:
- cannot recover on their own
- develop a more serious form of the disease if they are sick for longer than 6 months
You May Like: Is There A Vaccine Available For Hepatitis B
Giving Blood And Organ Donation
If you have hepatitis C, you cannot give blood.
In a recent research study in America kidneys from people with hepatitis C who had died were transplanted into patients who did not have the virus.
All of the recipients subsequently contracted hepatitis C but were treated for it and all were cured. The benefit of receiving a kidney outweighed the risk of not clearing hepatitis C.
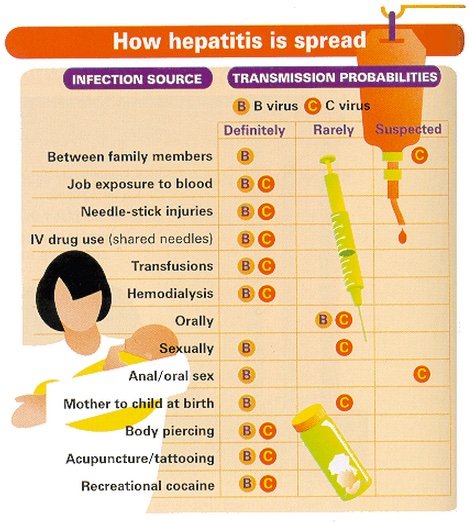
How Does Hepatitis C Spread
Hepatitis C is spread only through exposure to an infected person’s blood.
High-risk activities include:
- Sharing drug use equipment. Anything involved with injecting street drugs, from syringes, to needles, to tourniquets, can have small amounts of blood on it that can transmit hepatitis C. Pipes and straws to smoke or snort drugs can have blood on them from cracked lips or nosebleeds. Get into a treatment program if you can. At the very least, don’t share needles or equipment with anyone else.
- Sharing tattoo or piercing tools. Nonsterile items and ink can spread contaminated blood.
- Blood transfusions in countries that donât screen blood for hepatitis C.
- Nonsterile medical equipment. Tools that arenât cleaned properly between use can spread the virus.
- Blood or cutting rituals. Sharing the tools or exchanging blood can transmit hepatitis C.
Medium-risk activities include:
You May Like: How Contagious Is Hepatitis C
What Is The Treatment For People With Acute Hepatitis C Infection
When people first get hepatitis C, the infection is said to be acute. Most people with acute hepatitis C do not have symptoms so they are not recognized as being infected. However, some have low-grade fever, fatigue or other symptoms that lead to an early diagnosis. Others who become infected and have a known exposure to an infected source, such as a needlestick injury, are monitored closely.
Treatment decisions should be made on a case-by-case basis. Response to treatment is higher in acute hepatitis infection than chronic infection. However, many experts prefer to hold off treatment for 8-12 weeks to see whether the patient naturally eliminates the virus without treatment. Approaches to treatment are evolving. Patients with acute hepatitis C infection should discuss treatment options with a health care professional who is experienced in treating the disease. There is no established treatment regimen at this time.
How effective is hepatitis C treatment? Is hepatitis C curable?
If the hepatitis C RNA remains undetectable at the end of the treatment and follow-up period, this is called a sustained virologic response and is considered a cure. Over 90% of people treated with DAAs are cured. These people have significantly reduced liver inflammation, and liver scarring may even be reversed.
About 5% of people who are treated for HCV infection are not cured by some of the older regimens. These people may still have options for cure with the newer regimens.
Hepatitis A: Who Is At Risk
A prime risk factor for hepatitis A is traveling to or living in a country with high infection rates. You can check the CDC’s travel advisories to learn about recent outbreaks. Eating raw foods or drinking tap water can raise your risk while traveling. Children who attend daycare centers also have a higher risk of getting hepatitis A.
Recommended Reading: What Is Autoimmune Hepatitis C
Diagnosis Of Hepatitis C
If you are at risk of hepatitis C infection, or think you may have been exposed to hepatitis C in the past, see your doctor for an assessment of your liver health. This will include blood tests and possibly a non-invasive test for liver damage .
There are 2 blood tests used to diagnose hepatitis C. Usually these can be done at the same time but sometimes they will be done separately.
The first test known as a hepatitis C antibody test can tell you whether you have ever been exposed to hepatitis C.
It may take 2 to 3 months from the time of infection until a blood test can detect antibodies to hepatitis C, so there is a window period during which you cannot tell if you are or have been infected. In this time, take precautions to prevent the potential spread of the virus.
The second test is called hepatitis C PCR, which will be done if the antibody test is positive. This determines if the virus is still present in your blood or liver or if you have already cleared the infection.
If you have cleared the virus or had successful treatment to cure it, the PCR test will be negative.
A liver ultrasound or Fibroscan can also be performed to assess if you have any liver damage.
If your doctor is inexperienced in diagnosing hepatitis C you can call the LiverLine on for information, and to find a GP who can help you.
Treatment Of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is treated with antiviral medications that aim to clear the virus from your body.
New all-tablet treatments have greatly improved the outcomes for people with hepatitis C. These treatments can cure more than 95% of individuals with chronic hepatitis C. There are several new tablets that are used in combination to treat all hepatitis C strains . They are effective for people with no liver damage and those who have more advanced liver damage or cirrhosis.
These new tablet medications are available and subsidised on the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme, and can be prescribed by specialists, general practitioners and specialised nurse practitioners.
There are no restrictions on accessing treatment it is available for all adults with a Medicare card. People under 18 are able to access treatment and it is recommended they are referred to a pediatrician experienced in the treatment of hepatitis C.
For more information on the new medications for the treatment of hepatitis C, see our video: Hepatitis C Cure what it means for Victorians.
If your doctor does not know about the new treatments, you can call the LiverLine on for information, and to find a GP who can help you.
Talk with your doctor about treatment options and the potential for interactions with other medications, herbal preparations and other drugs. If you take prescribed medication this will be managed so you can access treatment.
In general, if you have hepatitis C you will feel better if you:
Read Also: What Causes Hepatitis Of The Liver
Hepatitis C And Blood Spills
When cleaning and removing blood spills, use standard infection control precautions at all times:
- Cover any cuts or wounds with a waterproof dressing.
- Wear single-use gloves and use paper towel to mop up blood spills.
- Clean the area with warm water and detergent, then rinse and dry.
- Place used gloves and paper towels into a plastic bag, then seal and dispose of them in a rubbish bin.
- Wash your hands in warm, soapy water then dry them thoroughly.
- Put bloodstained tissues, sanitary towels or dressings in a plastic bag before throwing them away.
Hepatitis A And B Vaccines
There are vaccines to protect against hepatitis A and B. The CDC recommends hepatitis A vaccination for all children ages 12 to 23 months and for adults who plan to travel or work in areas with hepatitis A outbreaks or who have other risk factors. People with chronic hepatitis B or C should also get the hepatitis A vaccine if they don’t already have immunity to the disease. The hepatitis B vaccine is recommended for all infants at birth and for adults who have any of the risk factors we discussed earlier. There is no vaccine for hepatitis C.
You May Like: Can You Get Hepatitis From Donating Plasma