Hepatitis B During Pregnancy
If a woman with HBV becomes pregnant, they may transmit the virus to their baby. Women should inform the doctor who delivers their baby that they have HBV.
The infant should receive an HBV vaccine and HBIG with 1224 hours of birth. This significantly reduces the risk that they will develop HBV.
The HBV vaccine is safe to receive while pregnant.
People with a high risk of HBV include:
- the infants of mothers with HBV
- the sexual partners of people with HBV
- people who engage in sexual intercourse without contraception and those who have multiple sexual partners
- men who have sex with men
- people who inject illicit drugs
- those who share a household with a person who has a chronic HBV infection
- healthcare and public safety workers who are at risk of occupational exposure to blood or contaminated bodily fluids
- people receiving hemodialysis, which is a type of kidney treatment
- people taking medications that suppress the immune system, such as chemotherapy for cancer
- those who come from a region with a high incidence of HBV
- all women during pregnancy
People can prevent HBV infection by:
- wearing appropriate protective equipment when working in healthcare settings or dealing with medical emergencies
- not sharing needles
- following safe sexual practices
- cleaning any blood spills or dried blood with gloved hands using a 1:10 dilution of one part household bleach to 10 parts water
A vaccine against HBV has been available since 1982.
People who should receive this vaccine include:
What Should You Know About Pregnancy And Hepatitis B
A pregnant woman who has hepatitis B can pass the infection to her baby at delivery. This is true for both vaginal and cesarean deliveries.
You should ask your healthcare provider to test you for hepatitis B when you find out you are pregnant. However, while it is important for you and your healthcare provider to know if you do have hepatitis B, the condition should not affect the way that your pregnancy progresses.
If you do test positive, your provider may suggest that you contact another healthcare provider, a liver doctor, who is skilled in managing people with hepatitis B infections. You may have a high viral load and may need treatment during the last 3 months of your pregnancy. A viral load is the term for how much of the infection you have inside of you.
You can prevent your infant from getting hepatitis B infection by making sure that your baby gets the hepatitis B vaccine in the hours after they are born along with the hepatitis B immunoglobulin. These two shots are given in two different locations on the baby. They are the first shots needed.
Depending on the type of vaccine used, two or three more doses must be given, usually when the baby is 1 month old and then 6 months old, with the last by the time the baby is 1 year old. It is critical that all newborns get the hepatitis B vaccination, but even more important if you have hepatitis B yourself.
How Do You Get It
HAV can be present in the stool and blood of someone with the virus. Its mainly transmitted through the fecal-oral route, which involves ingesting virus thats present in the stool of someone with hepatitis A.
There are several ways you can get hepatitis A:
- having close person-to-person contact with someone who has hepatitis A, such as:
- taking care of someone whos currently sick
- having sex with someone who has the virus
You May Like: How Do I Know If I Have Hepatitis B
Recommendation For Test Of Cure
-
Not relevant for these infections.
-
Patients with newly diagnosed infection caused by HBV or HCV should have serological markers of infection measured 3 and 6months later to establish whether the infection has become chronic,,, .
-
Serological follow up after antiviral therapy is beyond the scope of this guideline.
Who Is At Risk For Hepatitis C
It only takes one exposure to hepatitis C to become chronically infected, so people who have injected illegal drugs even one time or many years previously could have chronic hepatitis C, and not know it since there are often no symptoms. People with blood transfusions prior to 1992 – when they started testing blood for transfusion for hepatitis C – also may have become chronically infected.
Recommended Reading: Symptoms Of Active Hepatitis C
Chronic Hepatitis C Treatment
Treatment of chronic hepatitis C has evolved, rendering many earlier drugs obsolete. The drugs currently used include pegylated interferon, ribavirin, elbasvir, grazoprevir, ledipasvir, sofosbuvir, paritaprevir, ritonavir, ombitasvir, dasabuvir, simeprevir, daclatasvir. These are always used in various combinations, never alone. Interferon is given by injection while the other medications are pills. Studies have shown that combinations of these drugs can cure all but a small proportion of patients however, serious side effects of treatment can occur.
Treatment options need to be discussed with a knowledgeable physician, as the appropriate combination is dependent upon multiple factors. These include genotype , prior treatment and results, drug intolerances, presence of compensated liver disease or uncompensated cirrhosis, presence of HIV co-infection, other complicating conditions and liver transplantation.
Hepatitis B: How Does It Spread
You can get it through contact with the blood or body fluids of an infected person. In the U.S., it’s most often spread through unprotected sex. It’s also possible to get hepatitis B by sharing an infected person’s needles, razors, or toothbrush. And an infected mother can pass the virus to their baby during childbirth. Hepatitis B is not spread by hugging, sharing food, or coughing.
Also Check: How To Treat Viral Hepatitis
Who Should Be Vaccinated
Children
- All children aged 1223 months
- All children and adolescents 218 years of age who have not previously received hepatitis A vaccine
People at increased risk for hepatitis A
- International travelers
- Men who have sex with men
- People who use or inject drugs
- People with occupational risk for exposure
- People who anticipate close personal contact with an international adoptee
- People experiencing homelessness
People at increased risk for severe disease from hepatitis A infection
- People with chronic liver disease, including hepatitis B and hepatitis C
- People with HIV
Other people recommended for vaccination
- Pregnant women at risk for hepatitis A or risk for severe outcome from hepatitis A infection
Any person who requests vaccination
There is no vaccine available for hepatitis C.
How Is This Vaccine Given
This vaccine is given as an injection into a muscle. You will receive this injection in a doctor’s office or other clinic setting.
The hepatitis A and B vaccine is given in a series of 3 shots. The booster shots are given 1 month and 6 months after the first shot.
If you have a high risk of hepatitis infection, you may be given 3 shots within 30 days, and a fourth shot 12 months after the first.
Your individual booster schedule may be different from these guidelines. Follow your doctor’s instructions or the schedule recommended by the health department of the state you live in.
Recommended Reading: Can Hepatitis C Cause Liver Cancer
Treatment: Chronic Hepatitis C
The latest drug to be approved by the FDA is glecaprevir and pibrentasvir . This medication offers a shorter treatment cycle of 8 weeks for adult patients with all types of HCV who donât have cirrhosis and who have not been previously treated. The length of treatment is longer for those who are in a different disease stage. The prescribed dosage for this medicine is 3 tablets daily.
There are several other combination drugs available, as well as some single drugs that may be used in combination. Your doctor will choose the right one for you depending on the type of hepatitis C you have, how well your liver is functioning and any other medical problems you may have. Also be sure to discuss your insurance coverage since these medications are expensive.
Hepatitis A And B Vaccine Side Effects
Get emergency medical help if you have any of these signs of an allergic reaction:hives difficulty breathing swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Keep track of any and all side effects you have after receiving this vaccine. When you receive a booster dose, you will need to tell the doctor if the previous shot caused any side effects.
You should not receive a booster vaccine if you had a life-threatening allergic reaction after the first shot.
Becoming infected with hepatitis is much more dangerous to your health than receiving this vaccine. However, like any medicine, this vaccine can cause side effects but the risk of serious side effects is extremely low.
You may feel faint after receiving this vaccine. Some people have had seizure like reactions after receiving this vaccine. Your doctor may want you to remain under observation during the first 15 minutes after the injection.
-
numbness, tingling, or burning pain
-
red or blistering skin rash with burning or tingly feeling
-
easy bruising or bleeding or
-
unexplained muscle pain, tenderness, or weakness.
Common side effects include:
-
headache or
-
tired feeling.
This is not a complete list of side effects and others may occur. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report vaccine side effects to the US Department of Health and Human Services at 1-800-822-7967.
You May Like: How Do You Get Hepatitis C From Alcohol
Looking To Get Tested
To know for sure if you have Hepatitis B, you need to get tested. We know that visiting a clinic can be a stressful and overwhelming process for some folks click here to find a place to get tested near you. Visit our Services and Supports Near You page for clinics and organizations that offer culturally relevant and trauma informed services.
What Is Acute Hepatitis B

Acute hepatitis B is a short-term illness that occurs within the first 6 months after someone is exposed to the hepatitis B virus. Some people with acute hepatitis B have no symptoms at all or only mild illness. For others, acute hepatitis B causes a more severe illness that requires hospitalization
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C How Is It Contracted
How Many People Have Hepatitis B
In the United States, an estimated 862,000 people were chronically infected with HBV in 2016. New cases of HBV infection in the United States had been decreasing until 2012. Since that time, reported cases of acute hepatitis B have been fluctuating around 3,000 cases per year. In 2018, 3,322 cases of acute hepatitis B were reported however, because of low case detection and reporting, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that there were 21,600 acute hepatitis B infections. New HBV infections are likely linked to the ongoing opioid crisis in the United States.
Globally, HBV is the most common blood-borne infection with an estimated 257 million people infected according to the World Health Organization .
What Is Hepatitis A And B Vaccine
Hepatitis A and B are serious diseases caused by virus.
Hepatitis A is spread through contact with the stool of a person infected with the hepatitis A virus. This usually occurs by eating food or drinking water that has become contaminated as a result of handling by an infected person.
Hepatitis B is spread through blood or bodily fluids, sexual contact or sharing IV drug needles with an infected person, or during childbirth when a baby is born to a mother who is infected.
Hepatitis causes inflammation of the liver, vomiting, and jaundice . Hepatitis can lead to liver cancer, cirrhosis, or death.
The hepatitis A and B vaccine is used to help prevent these diseases in adults. The vaccine works by exposing you to a small dose of the virus, which causes the body to develop immunity to the disease. This vaccine will not treat an active infection that has already developed in the body.
This vaccine is recommended for adults with risk factors for getting hepatitis A or B, including:
Like any vaccine, the hepatitis A and B vaccine may not provide protection from disease in every person.
You May Like: Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedule For Child
Recommendations For Frequency Of Repeat Testing In An Asymptomatic Patient
The frequency of testing depends on the history of sexual exposure and number of sexual partners. However, in the case of hepatitis A and B, once the patient has completed a course of vaccination no further repeat testing is required.
For those at continuing risk and who have not received a course of vaccination, the following is recommended.
How Is Hepatitis B Treated
Your healthcare provider will treat you based on what type of hepatitis B you have, acute or chronic.
Acute hepatitis B infections
If you develop an acute form of the condition, you probably wont need medical treatment. Instead, your doctor will likely suggest that you get plenty of rest, drink lots of fluids and maintain a healthy diet to support your body as it fights off the infection.
Chronic hepatitis B infections
If you have chronic hepatitis B, you might be a candidate for drug therapy. Usually, drug therapy is used only if you have active liver disease. There are seven drugs that are approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to treat hepatitis B. Two are injectable forms of interferon, while the five other antivirals are tablets.
You will need to take these medications every day. They help by slowing the viruss ability to multiply in your system. This helps reduce swelling and liver damage. Youll need to be regularly monitored for early signs of liver damage and liver cancer. Your healthcare provider will want to see you once or twice a year.
Also Check: Hepatitis B E Antibody Reactive Means
Is There A Cure For Chronic Hepatitis B
Currently, there is no complete cure for hepatitis B. But when managed properly, those living with the virus can expect to live a normal life. Maintaining a healthy diet and avoiding alcoholic beverages and tobacco products are crucial components in managing the disease.
You should also visit a doctor familiar with hepatitis B at least annuallythough twice a year might be best to monitor your liver through blood tests and medical imaging. As with most diseases, detecting it early leads to a better outcome. If youre exposed to the virus, you should get an antibody injection within 12 hours of exposure.
Number Of Doses Required
Depending on the persons age, 2 or 3 doses of the vaccine are required to ensure the best possible protection.
For people under age 20, 1 dose of hepatitis A and hepatitis B vaccine, followed by 1 dose of hepatitis B vaccine, are enough to ensure effective protection.
People aged 20 or older will need 3 doses of the combined hepatitis A and hepatitis B vaccine.
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatitis B Virus
How Long Does It Last
Hepatitis A can last from a few weeks to several months.
Hepatitis B can range from a mild illness, lasting a few weeks, to a serious, life-long condition. More than 90% of unimmunized infants who get infected develop a chronic infection, but 6%10% of older children and adults who get infected develop chronic hepatitis B.
Hepatitis C can range from a mild illness, lasting a few weeks, to a serious, life-long infection. Most people who get infected with the hepatitis C virus develop chronic hepatitis C.
Treatment: Chronic Hepatitis B
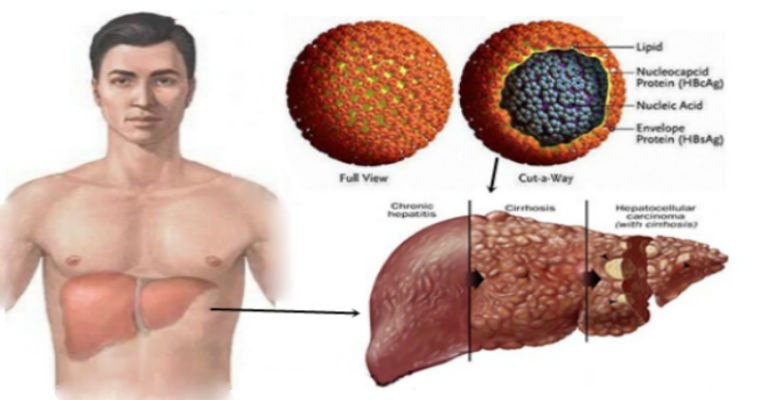
The goal of treating chronic hepatitis B is to control the virus and keep it from damaging the liver. This begins with regular monitoring for signs of liver disease. Antiviral medications may help, but not everyone can take them or needs to be on medication. Be sure to discuss the risks and benefits of antiviral therapy with your doctor.
Also Check: Vaccine Available For Hepatitis B
Who Should Be Tested For Hepatitis
Testing is important for anyone with the risk factors we’ve mentioned, particularly injected drug users and people who have had multiple sex partners. Health advocates are also urging people of Asian heritage to get tested. Stanford University’s Asian Liver Center estimates that 1 in 10 Asians living in the U.S. has chronic hepatitis B. Many of them have probably had the virus since birth.
Also, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends that health care providers offer a one-time hepatitis C screening for anyone born between 1945 and 1965.
Who Is Most Affected
In the United States, rates of new HBV infections are highest among adults aged 40-49 years, reflecting low hepatitis B vaccination coverage among adults at risk. The most common risk factor among people with new HBV infections is injecting drugs, related to the opioid crisis.
The highest rates of chronic hepatitis B infection in the United States occur among foreign-born individuals, especially people born in Asia, the Pacific Islands, and Africa. Approximately 70% of cases in the United States are among people who were born outside of the United States. CDC developed this map of the geographic distribution of hepatitis B around the world – PDF. Other groups who have higher rates of chronic HBV infection include people who inject drugs and men who have sex with men.
You May Like: Can Hepatitis C Be Treated
Treatment Options For Hepatitis B
Acute hepatitis B usually doesnt require treatment. Most people will overcome an acute infection on their own. However, rest and hydration will help you recover.
Antiviral medications are used to treat chronic hepatitis B. These help you fight the virus. They may also reduce the risk of future liver complications.
You may need a liver transplant if hepatitis B has severely damaged your liver. A liver transplant means a surgeon will remove your liver and replace it with a donor liver. Most donor livers come from deceased donors.