Definition Of Acute Hcv Infection
Most experts define acute HCV infection as the 6-month time period following acquisition of HCV. The definition of acute HCV infection does not depend on the presence or absence of symptoms associated with the acute HCV infection because most infections are subclinical. The preferred accepted laboratory diagnosis of acute HCV infection includes documentation of either of the two following criteria:
- A positive HCV RNA in conjunction with a negative HCV antibody, or
- Positive HCV antibody with documentation of a negative HCV antibody in the past 12 months
What Can Happen If Viral Hepatitis Is Not Treated
Most people recover from hepatitis A with no treatment or long-lasting health problems.
Chronic hepatitis B and C can lead to serious health problems, such as:
- , or scarring of the liver
- Liver cancer
- Liver failure
People with liver failure may need a liver transplant to survive. In the United States, cirrhosis caused by chronic hepatitis C is currently the most common reason for needing a liver transplant. Viral hepatitis is also the most common cause of liver cancer.
Alcohol And Other Toxins
Excessive alcohol consumption can cause liver damage and inflammation. This is sometimes referred to as alcoholic hepatitis. The alcohol directly injures the cells of your liver. Over time, it can cause permanent damage and lead to liver failure and cirrhosis, a thickening and scarring of the liver.
Other toxic causes of hepatitis include overuse or overdose of medications and exposure to poisons.
Read Also: Hepatitis C Contagious Through Urine
Hepatitis C Testing And Diagnosis
Doctors will start by checking your blood for:
Anti-HCV antibodies: These are proteins your body makes when it finds the hep C virus in your blood. They usually show up about 12 weeks after infection.
It usually takes a few days to a week to get results, though a rapid test is available in some places.
The results can be:
- Nonreactive, or negative:
- That may mean you donât have hep C.
- If youâve been exposed in the last 6 months, youâll need to be retested.
If your antibody test is positive, youâll get this test:
HCV RNA: It measures the number of viral RNA particles in your blood. They usually show up 1-2 weeks after youâre infected.
- The results can be:
- Negative: You donât have hep C.
- Positive: You currently have hep C.
You might also get:
Liver function tests: They measure proteins and enzyme levels, which usually rise 7 to 8 weeks after youâre infected. As your liver gets damaged, enzymes leak into your bloodstream. But you can have normal enzyme levels and still have hepatitis C. Learn the reasons why you should get tested for hepatitis C.
Can You Prevent Hepatitis C Infection
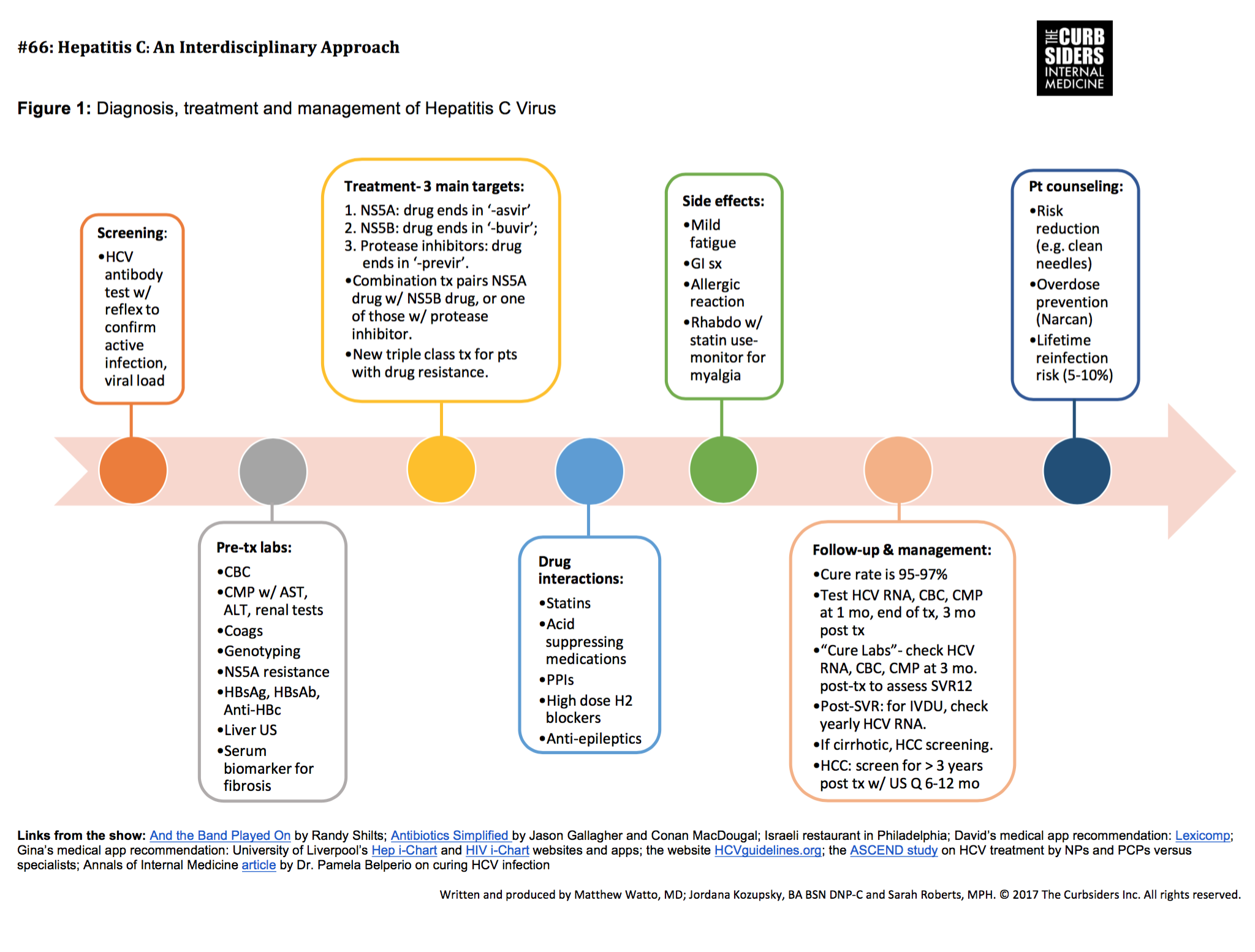
Thereâs no vaccine to prevent hepatitis C. To avoid getting the virus:
- Use a latex condom every time you have sex.
- Don’t share personal items like razors.
- Don’t share needles, syringes, or other equipment when injecting drugs.
- Be careful if you get a tattoo, body piercing, or manicure. The equipment may have someone else’s blood on it.
Read Also: Royal Canin Hepatic Wet Dog Food
Hepatitis A And Hepatitis E
These can be picked up in a number of ways. Most people get them by eating food or drinking water which has been contaminated with infected faeces as a result of poor hygiene or inadequate cooking. Less commonly, they can be transmitted through cuts in the skin or mucous membranes – sharing razor blades, toothbrushes, or needles if injecting drugs are common risk factors. Hepatitis A can be also passed on by having unprotected sex with a person who already has the virus, usually between men who have sex with men. The hepatitis caused by HAV and HEV is usually mild, and doesnt require treatment, although hepatitis E can occasionally be serious in those with a weakened immune system. A vaccine is available to prevent hepatitis A – people with cirrhosis and those visiting developing countries should be vaccinated. There is not yet a commercially available vaccine for HEV. Find out more about hepatitis E here.
How Can I Get Free Or Low
The hepatitis A and hepatitis B vaccines are covered under most insurance plans.
- If you have insurance, check with your insurance provider to find out whats included in your plan.
- Medicare Part B covers hepatitis B vaccines for people at risk.
- If you have Medicaid, the benefits covered are different in each state. Check with your state’s program.
Find a clinic near you where you can get vaccines for hepatitis A and B.
Also Check: Hepatitis B Surf Ab Quant
Hep C Virus Rna Assays
An HCV RNA test shows whether people have an active hepatitis C infection or not. An HCV RNA test checks for the viral load to indicate the amount of the virus in the blood.
An HCV RNA test can also show how a person with a hepatitis C infection responds to treatment to see if medication is helping lower the viral load.
What Are The Treatments For Hepatitis
Treatment for hepatitis depends on which type you have and whether it is acute or chronic. Acute viral hepatitis often goes away on its own. To feel better, you may just need to rest and get enough fluids. But in some cases, it may be more serious. You might even need treatment in a hospital.
There are different medicines to treat the different chronic types of hepatitis. Possible other treatments may include surgery and other medical procedures. People who have alcoholic hepatitis need to stop drinking. If your chronic hepatitis leads to liver failure or liver cancer, you may need a liver transplant.
Recommended Reading: How Is Hepatitis B And C Transmitted
Introduction And Key Points
Possibly the key difference between this World Gastroenterology Organisation guideline and other publications on acute viral hepatitis is an awareness of the potential for mismanagement. After all, the single most important issue in the management of acute viral hepatitis is that in the great majority of cases treatment should be supportive and does not require hospitalization or medication. Surgical intervention may bedangerous. Anecdotal evidence suggests there is often mismanagement of this condition, especially in poorly resourced settings.
Whereas most acute infections are asymptomatic, when symptoms are present they appear to be similar for all five types of virus. It is important to establish which virus is involved, as the risks of progression differ:
- Hepatitis A: self-limiting. The rate of fulminant hepatic failure rate is very low there is a 1% fatality rate in those over the age of 40.
- Hepatitis B: self-limiting in 95% of cases , but not in children under the age of 5.
- Hepatitis C: self-limiting in 2050% of cases .
- Hepatitis D: self-limiting if HBV is self-limiting.
- Hepatitis E: self-limiting. The overall mortality rate in FHF is 13% in pregnant women the rate is 1525%.
For the most part, only supportive treatment is required. If HAV is endemic, hepatitis A infection can be excluded, as earlier infection induces lifelong immunity.
Key points to remember:
Fig. 1 Decision algorithm in the diagnosis of acute hepatitis
Further information on AVH:
History And Physical Exam
To diagnose hepatitis, first your doctor will take your history to determine any risk factors you may have for infectious or noninfectious hepatitis.
During a physical examination, your doctor may press down gently on your abdomen to see if theres pain or tenderness. Your doctor may also feel to see if your liver is enlarged. If your skin or eyes are yellow, your doctor will note this during the exam.
Don’t Miss: Does Hepatitis C Cause Itching
Viral Load And Treatment: Favorable Arguments
It is known that maintained high levels of HBV DNA are associated with progressive liver disease. Serum DNA levels are a prognostic factor, and contribute to define the phase of CHB infection, the treatment indication, and allow an assessment of the efficacy of antiviral therapy. High levels of HBV DNA are an independent risk factor for cirrhosis and HCC in Asia.
The REVEAL -HBV study group followed a cohort of 3653 HBsAg-positive patients in Taiwan. Their average age was 45 years and they acquired HBV infection perinatally. A baseline high HBV-DNA level > 10000 copies/mL was associated with a significant increased risk of HCC and with progression towards cirrhosis. Those patients that have persistently high levels of viral replication, for up to four decades, are at highest risk for HCC/cirrhosis after adjusting for HbeAg status, age, sex, ALT level, cigarette smoking and alcohol consumption. Many Asian patients may be in an immunotolerant phase, and the applicability of these data to western countries is not clear.
The interpretation of serum DNA level is not easy, because we do not know the cut-off value for defining indication for and response to treatment. The 2000 National Institutes of Health conference chose an arbitrary value of 20000 UI/mL . As DNA levels have a fluctuating nature, monitoring changes in serum DNA levels is an essential tool.
How Serious Is It
- People can be sick for a few weeks to a few months
- Most recover with no lasting liver damage
- Although very rare, death can occur
- 15%25% of chronically infected people develop chronic liver disease, including cirrhosis, liver failure, or liver cancer
- More than 50% of people who get infected with the hepatitis C virus develop a chronic infection
- 5%-25% of people with chronic hepatitis C develop cirrhosis over 1020 years
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B What Is It
Treatment For Hepatitis A
Because is always acute, its treatment is generally limited to addressing symptoms, monitoring liver health, and letting the run its course. Clients recently exposed to hepatitis A virus might be advised by their medical care providers to receive the HAV vaccination or injection to reduce the likelihood of becoming ill .
In rare cases, leads to severe liver problems that require medication, hospitalization, or transplantation. If left untreated, liver problems can lead to life-threatening conditions. Therefore, a client who might have been infected with HAV should seek the care of a medical care provider.
Suggestions for counseling clients who have include the following:
- Assure clients that their symptoms are temporary.
- Reinforce prevention with messages such as, You will recover from lets talk about what you can do to make sure you never get the more serious types. A vaccine against can protect you, and there are ways to reduce the risk of getting .
- Encourage clients to take care of themselves. Say, for example, Your body is working hard to fight off the . It is very important that you take care of yourself now.
- Reinforce the importance of maintaining SUD recovery activities. Say, Your liver is injured. If you drink or use drugs, you could make it worse. Lets talk about everything youre doing to stay free of alcohol and other substances.
Acute Hcv Treatment Data
Overall, treatment of acute HCV infection has been shown to result in high sustained virologic response rates, even prior to the modern era of treatment with direct-acting antiviral medications. Studies of peginterferon alpha-2b monotherapy in intent-to-treat analyses showed SVR rates of 71 to 96%. A meta-analysis of 22 studies using either standard interferon or peginterferon monotherapy reported an overall SVR rate of 78%. The SVR rates observed with interferon-based therapy of acute HCV are significantly higher than SVR rates observed with interferon- or peginterferon-based treatment of chronic HCV. With interferon-based therapy, the highest SVR rates in the acute infection setting have occurred in persons who received treatment within 12 weeks following acute HCV diagnosis. Highly successful outcomes were seen even in typically more challenging populations, including in persons who inject drugs and persons with HIV. The following summarizes limited data on the newer DAA regimens in clinical trials that are underway or completed for the treatment of acute HCV infection.
Elbasvir-Grazoprevir
Glecaprevir-Pibrentasvir
Ledipasvir-Sofosbuvir
Sofosbuvir-Velpatasvir
- Sofosbuvir-Velpatasvir : In this phase 3, randomized, international study, investigators plan to enroll 250 adults who inject drugs who are diagnosed with recent HCV infection to receive treatment with sofosbuvir-velpatasvir for either 6 or 12 weeks .
Recommended Reading: Signs And Symptoms Of Hepatitis
Treatment For Hepatitis C
Because most people who have have mild symptoms or no symptoms, clients often do not know they are infected and, therefore, do not seek hepatitis treatment until severe hepatitis C -related diseases have produced other symptoms or their infections are found in a screening test. Approximately one in five people clears HCV without treatment. In rare cases, acute HCV infection quickly leads to liver failure . Therefore, any client diagnosed with hepatitis C is a potential candidate for antiviral treatment.
Home Remedies And Lifestyle
Healthcare and sanitation workers who have a higher chance of exposure to needle pricks should take additional precautions to prevent the accidental spread of infection. If you use injection drugs or live with someone who does, seek help immediately to reduce your exposure to long-term consequences.
Getting a hepatitis B vaccination can protect you against contracting hepatitis D, so talk to your doctor if you believe youre at risk.
Abstaining from alcohol will minimize strain on your liver. If you choose to drink, its essential to drink responsibly. Health authorities define responsible drinking as no more than one drink per day for women and no more than two drinks per day for men.
Binge drinking is harmful, especially when your liver function is already compromised from hepatitis.
Following safe sex practices will keep you from contracting additional infections and help keep your partner from getting hepatitis D. Safe sex to prevent the spread of hepatitis D is particularly important for men who have sex with other men.
Don’t Miss: What’s The Difference Between Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C
How Long Do The Hepatitis A And B Vaccines Protect You
During your lifetime, you need:
- One series of the hepatitis A vaccine
- One series of the hepatitis B vaccine
Most people dont need a booster dose of either vaccine. But if you have had dialysis, a medical procedure to clean your blood, or have a weakened immune system, your doctor might recommend additional doses of the hepatitis B vaccine.
Is There A Vaccine For Hepatitis
There are vaccines for hepatitis A and hepatitis B that are available in the U.S. There is no vaccine for hepatitis C. Since you can only get hepatitis D if you have hepatitis B, getting the vaccine against B should protect you against hepatitis D. There is no FDA approved vaccine against hepatitis E, but vaccines against hepatitis E exist overseas .
Also Check: How Do You Get Hepatitis A B C
Treatment For Hepatitis B
All cases of begin as an acute and most cases resolve without treatment. However, if the person does not recover completely within 6 months, the infection is considered chronic. Clients diagnosed with B should get regular monitoring by a medical care provider, and some might undertake treatment. Several medications are used for chronic hepatitis B. Treatment might be started with any of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration -approved antiviral medications, but , , or are preferred . These medications might be prescribed individually or in combination .
Medications for Chronic Hepatitis B.
Any treatment for has benefits and risks. Antiviral treatment generally lasts 6 months1 year and can extend for years longer . Managing side effects can be difficult. The decision to undertake treatment should not be made in haste because ending some antiviral medications early can reactivate the HBV . Many people elect to delay hepatitis B treatment until they are better able to adhere to it. provides counseling tips for addressing clients concerns about hepatitis B.
Counseling Tips for Addressing Concerns About Chronic Hepatitis B. Help clients understand that although their symptoms might have diminished, they remain infected. Explain, I know you feel better now, but remember that you still have the infection
Questions For Your Doctor

When you visit the doctor, you may want to ask questions to get the information you need to manage your hepatitis C. If you can, have a family member or friend take notes. You might ask:
Read Also: How Dangerous Is Hepatitis C
How Do You Get Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A is found in an infected persons stool .
Hepatitis A is spread through:
- Eating or drinking contaminated food or water
- You can get hepatitis A by eating food prepared by a person with the virus who didnt wash his or her hands after using the bathroom and then touched the food.
- You can get hepatitis A by eating raw or undercooked shellfish that came from sewage-contaminated water.
You are more likely to get hepatitis A if you travel out of the country to a developing country with poor sanitation or without access to clean water and have not gotten vaccinated for hepatitis A. Ask your doctor if you need a hepatitis A vaccination.