Possible Risk Factors For Hcv Acquisition In Jordan
Limited data were available regarding the possible routes for HCV acquisition among the study subjects. These data were available for 18 individuals who were inquired regarding the following possible risk factors: history of previous invasive surgery, history of invasive dental procedure, history of blood/blood product transfusion, use of contaminated needles, tattooing/piercing, birth at home for females, circumcision at home for males and hijama therapy . Seven individuals reported none of the aforementioned risk factors, while history of previous invasive surgery was reported by ten individuals. Three females reported history of previous invasive surgery, invasive dental procedure and birth at home altogether as possible risk factors for HCV acquisition. The median age for individuals who reported history of previous invasive surgery was older than the median age of the study population . For genotype distribution, the study subjects with history of previous invasive surgery were infected with genotype 4 , genotypes 1 and 3 . For individuals with history of invasive dental procedure, the majority were infected with genotype 4 .
Table 2 Possible self-reported risk factors for HCV acquisition in Jordan
Development Of Efficient Semi
Direct ORF sequencing of 1st-passage 3a identified three nucleotide changes, coding for Y788H , I1425T , and D2410G , which occurred in at least an estimated 50% of viral genomes .2). In reverse genetic studies, we introduced these changes individually in 3a. The 3a recombinant with the I1425T change infected most culture cells from day 35 posttransfection, reaching 3.2 log10 FFU/ml, while the other 2 recombinants did not spread . First- and 2nd-passage 3aI1425T, with peak titers of 3.5 and 4.4 log10 FFU/ml, respectively, had acquired 4 common changes coding for R9S , V414A , E2412K , and P2915S .2). The 3aI1425T recombinant with these additional changes spread to most culture cells on day 6, reaching 3.8 log10 FFU/ml . First-passage virus reached 3.9 log10 FFU/ml and did not acquire dominant coding nucleotide changes .2). This efficient JFH1-based 3a semi-FL recombinant represents the most advanced reported genotype 3a infectious culture system.
Hepatitis C Virus Genotype Serum
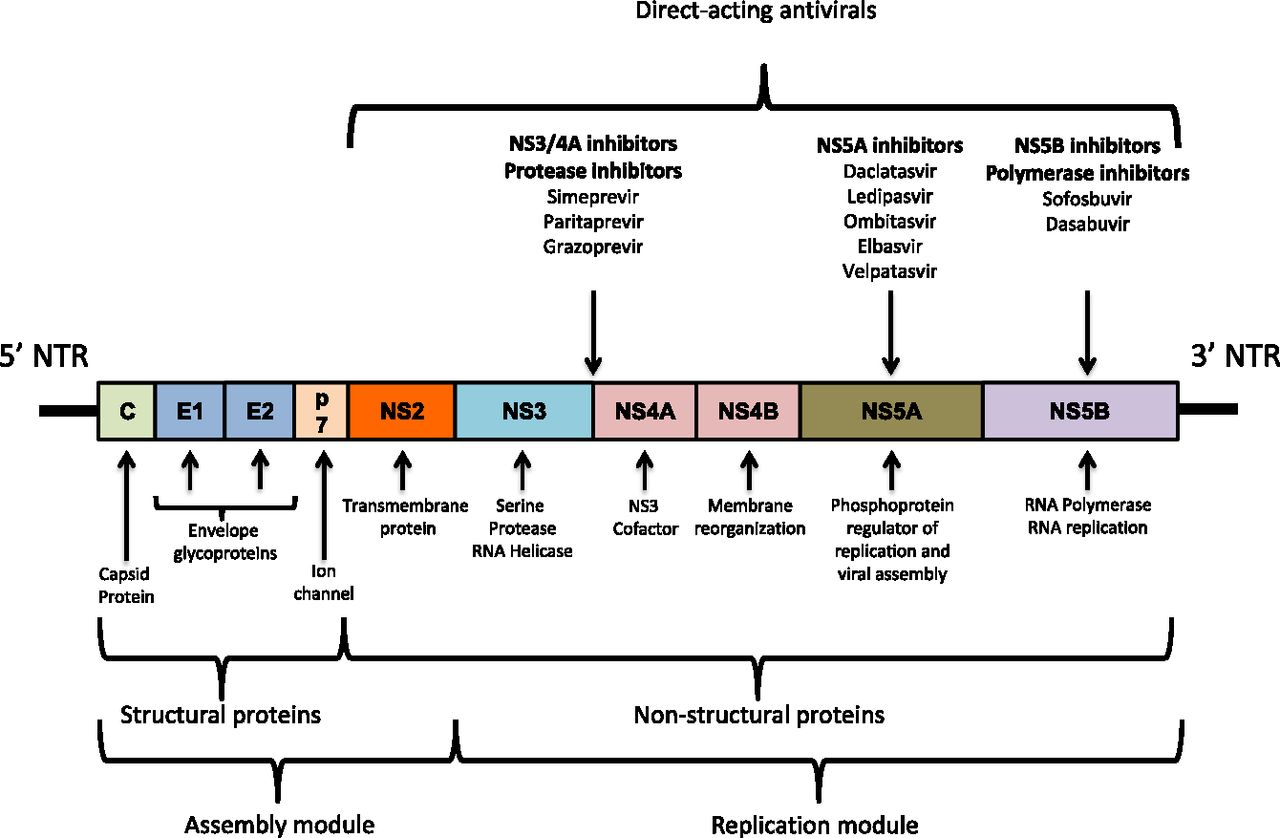
Determining hepatitis C virus genotype to guide antiviral therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis C
Differentiating between HCV subtypes 1a and 1b
This assay should notbe used as a screening test for HCV infection. It should be performed only on specimens obtained from patients confirmed to have HCV RNA levels in serum of 500 IU/mL or higher.
Also Check: How Is Hepatitis B Virus Transmitted
Clinical And Demographic Data
The disposition of 211 patients including 135 genotype 1b patients and 76 genotype 2a patients is shown in . By the end of the study, the data of 180 patients including 112 genotype 1b patients and 68 genotype 2a patients was analysed. There were no significant differences in the presence of HCV genotypes by sex, age, BMI, ALT, HCV RNA, liver fibrosis stage, or any other baseline variable . The HCV genotype 1b group and 2a group were well balanced with respect to patient characteristics.
Study flow and disposition of patients. A total of 211 patients were enrolled into the study and assigned to the genotype 1b group and the genotype 2a group by HCV genotypes. The disposition of patients in the study was shown in . There were 31 dropout patients , including 23 patients with HCV genotype 1b and 8 patients with HCV genotype 2a, due to the adverse events or hepatic dysfunction . By the end of the study, the data of total 180 patients including 112 genotype 1b patients and 68 genotype 2a patients was collected and analysed.
Literature Selection And Data Extraction
The inclusion criteria included: 1) The study was conducted only in mainland China 2) Studies involving the HCV genotype and subtype distribution 3) The study object were hospitalized patients 4) Studies with clear sample size.
The exclusion criteria were as follows: 1) studies without exact sample size, publication year and methods 2) Overlapping or paradoxical studies: data from literature were repeat or inconsistent between the context 3) The study objects were blood donors or intravenous drug user 4) HCV GTs prevalence rate in patients with HIV/HCV co-infection 5) Comments, reviews or conference abstracts. When investigating the trends of HCV GT spatio-temporal distributions, literatures without exact study year were not included.
Read Also: How Is Hepatitis B Contracted
this Section Provides Information On The Tertiary And Secondary Structure Of A Protein
structurei
Secondary structure
| Graphical view | Length | |
|---|---|---|
| < p> This subsection of the < a href=”http://www.uniprot.org/help/structure%5Fsection”> ‘Structure'< /a> section is used to indicate the positions of experimentally determined helical regions within the protein sequence.< p> < a href=’/help/helix’ target=’_top’> More…< /a> < /p> Helixi | 175 185 | Combined sources
< p> Information inferred from a combination of experimental and computational evidence, without manual validation.< /p> < p> < a href=”/manual/evidences#ECO:0000213″> More…< /a> < /p> Automatic assertion inferred from combination of experimental and computational evidencei |
| 10 | ||
| < p> This subsection of the < a href=”http://www.uniprot.org/help/structure%5Fsection”> ‘Structure'< /a> section is used to indicate the positions of experimentally determined hydrogen-bonded turns within the protein sequence. These elements correspond to the DSSP secondary structure code ‘T’.< p> < a href=’/help/turn’ target=’_top’> More…< /a> < /p> Turni | ||
| 30 | ||
| < p> This subsection of the < a href=”http://www.uniprot.org/help/structure%5Fsection”> ‘Structure'< /a> section is used to indicate the positions of experimentally determined beta strands within the protein sequence.< p> < a href=’/help/strand’ target=’_top’> More…< /a> < /p> Beta strandi |
In Vitro Viability Of J6 Ns3 Helicase Partial Ns5b And 3 Utr Demonstrated By Analyses Of J6 Recombinants With Minimal Jfh1 Sequences And Identification Of Virus Production
The NS3 helicase, NS5B, and 3 UTR previously were found to be critical for the unique replication capacity of JFH1 , and these genome regions were all included in previously developed JFH1-based HCV genotype recombinants . Here we demonstrated that the J6 NS3 helicase, NS5B finger, palm, and partial thumb domains and 3 UTR were functional for virus production in Huh7.5 cells, and we identified virus production-enhancing mutations F1468L and A1676S . Moreover, we demonstrated that a short C-terminal region in JFH1 NS5B contained elements critical for virus production.
J6 NS5B finger-to-partial thumb domain was functional for virus production.
JFH1 with Core-NS2 and NS5A from J6CF replicated efficiently in Huh7.5 cells . Here J6/JFH1_J6NS5A recombinants in which we replaced the JFH1 NS5B finger domain , finger-palm domains , or finger-palm-partial thumb domains with J6 sequences were found viable in transfected Huh7.5 cells , indicating that wild-type J6 NS5B was functional for virus production.
Sequence analysis of J6 recombinants with JFH1 complete or partial NS5B-to-3 UTR
Identification of virus production-enhancing mutations F1468L and A1676S through adaptation of J6 recombinant with JFH1 NS5B thumb domain and 3 UTR.
C-terminal JFH1 NS5B amino acids 465591 contained elements essential for J6 virus production.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Transmission Routes Cdc
Determination Of Intracellular And Extracellular Hcv Infectivity Titers And Core Levels
For single-cycle production assays, HCV RNA was transfected into a Huh7-derived CD81-deficient cell line, S29 . Intracellular and extracellular HCV infectivity titers, as well as HCV Core levels, were determined 48 h post transfection. Briefly, S29 cells of 3.5 × 105 cells/well were seeded in 6-well plates 24 h prior to transfection. HCV RNA of 5 g was transfected, and at 48 h post transfection culture supernatants were collected, filtered, and used for determination of extracellular Core levels by Western blotting and of infectivity titers by FFU assay. For intracellular infectivity titers, transfected S29 cells were harvested and washed three times with PBS and then resuspended in complete DMEM and subjected to five quick freeze-thaw cycles to release intracellular virus particles. Cell debris was removed by centrifugation at 14,000 rpm for 15 min. HCV infectivity titers were performed in triplicate determinations, and FFU were enumerated by manual count. Both intracellular and extracellular Core antigen levels were determined by mouse anti-HCV Core antibody C7-50. The secondary antibody was Goat anti-mouse IgG-horseradish peroxidase . The -actin was determined by HRP-anti–actin mouse monoclonal antibody .
Hcv Gts And Severity Of Hepatitis
Considering these conflicting and complex results above, we extracted the qualified literature from the screened hospitalized patients to summary the related cases in mainland China among different GTs based on severity of hepatitis , and performed the statistical analysis. The overall result showed significant difference , which may indicate HCV GT is associated with severity of hepatitis. Significant difference was found between subtypes 1b and 2a, 3b, and the significant difference was not found in the other subtypes . The possible reason for subtype 1b being more inclined to cause severe LD than subtypes 2a and 3b may be that subtype 1b has stronger pathogenicity and replication ability. In addition, the host factor should also be considered. Based on the above results, this may provide useful and instructional information for clinical treatment, and further mechanism study may be badly needed to clarify the association between HCV GTs and severity of hepatitis.
Table 5 Comparison of severity of Hepatitis with different genotypes
Read Also: How Does One Get Hepatitis C
How Other Genotypes Are Treated
Treatment for genotypes 1, 3, 4, 5, and 6 also depend on a variety of factors such as viral load and the extent of liver damage. Genotypes 4 and 6 are less common, and genotypes 5 and 6 are rare in the United States.
Antiviral medications may include these drugs or combinations of them:
- daclatasvir
- ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir and dasabuvir
- simeprevir
Treatment length can vary by genotype.
If liver damage is serious enough, a liver transplant might be recommended.
Neutralization And Inhibition Assays
The neutralization assay protocol was performed similarly to previously described methods, with modifications noted below . Briefly, diluted sera or monoclonal antibody was added to HCVcc diluted to 500 TCID50/ml, and the mixture was incubated for 1hour at 37°C. The virus/antibody mixture was then added to Huh7.5 cells plated on 96-well plates for 6hours, followed by replacement with fresh growth medium. At 48hours postinfection, cells were lysed in Nano-Glo luciferase assay buffer and substrate . The luminescence was measured using the EnSpire 2300 multilabel reader . The percent neutralization was calculated by subtracting the treatment signal from the presera well signal and dividing by the total possible infection . Percent neutralization was plotted with GraphPad Prism 7 software. Half-maximal inhibitory concentration values were determined by finding the nonlinear regression of a variable slope using the software GraphPad Prism 7.
For Fc-SR-B1 and Fc protein inhibition assays, proteins were preincubated with HCVcc diluted to 500 TCID50/ml for 1hour prior to addition to Huh7.5 cells. Cells were infected for 6hours, followed by replacement with fresh medium. At 48hours postinfection, cells were lysed, and the luciferase signal was detected as described above.
You May Like: How Much Cost Hepatitis C Treatment
Determination Of Hcv Genotype By Sequence Analysis
To investigate the accuracy of the newly developed VERSANT HCV genotype 2.0 assay for genotype 6 identification, we selected a set of samples from SEA HCV-positive blood donors to encompass mainly genotype 1 and 6 viruses. A total of 75 samples, 50 from Vietnam and 25 from Thailand, were included in the present study. Viral RNA served as a template for RT-PCR amplification of 5UTR-core and NS5b sequences. Amplicons were sequenced twice in both orientations. Degenerate sequences were preserved in order to determine the specificity of the line probe hybridization assays . To determine the HCV genotype, phylograms were constructed with reference strains for the 5UTR-core and NS5b regions . Only samples that showed genotype consistency of both regions were selected , and two discordant samples , which turned out to be a recombinant virus and a mixed infection, were characterized by full-length genome analysis as described elsewhere . As evident from the 5UTR-core phylogenetic analysis ,1), our sample collection contained genotype 1 , 2 , 3 , and 6 viruses.
Sequence Analysis Of The Culture
ORF sequence analysis of the J6 recombinant viruses with JFH1 sequences was described previously . ORF RT-PCR primers for J6 and J8 full-length viruses are given in Table S6. The 5 UTR and 3 UTR sequences were determined using 5 RACE Systems for Rapid Amplification of cDNA Ends with dA or dC tailing technology, as described previously . HCV RNA extracted from culture supernatant was used for 5 UTR 5 RACE . HCV-negative-strand RNA extracted from infected cells was used in 5 RACE to determine the 3 UTR sequence primers are given in Table S6.
Also Check: Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedule For Child
Construction Of Plasmids Rb10
The hRLuc gene and the sequence of the 2A protease of FMDV from pBB7M4hRLuc were introduced into monocistronic subgenomic HCV replicon RB10 through an AscI site to generate RB10-hR. The fragment containing four single mutations on pBB7M4hRLuc was used to replace the corresponding fragment on RB10-hR, resulting in RB10-hR-SM.
Genotype 2a Hepatitis C Virus Subgenomic Replicon Can Replicate In Hepg2 And Imy
- AffiliationsDepartment of Microbiology, Tokyo Metropolitan Institute for Neuroscience, Tokyo 183-8526, JapanDepartment of Clinical Molecular Informative Medicine, Nagoya City University Graduate School of Medical Sciences, Nagoya 467-8601, Japan
- Department of Microbiology, Tokyo Metropolitan Institute for Neuroscience, Tokyo 183-8526, JapanInstitute of Virology, Chinese Academy of Preventive Medicine, Beijing 100052, People’s Republic of China
- Masashi MizokamiAffiliationsDepartment of Clinical Molecular Informative Medicine, Nagoya City University Graduate School of Medical Sciences, Nagoya 467-8601, Japan
- Takaji WakitaCorrespondenceTo whom correspondence should be addressed: Dept. of Microbiology, Tokyo Metropolitan Institute for Neuroscience, 2-6 Musashidai, Fuchu, Tokyo 183-8526, Japan. Tel.: 81-423-25-3881 Fax: 81-423-21-8678
- Author Footnotes* This work was supported in part by a grant-in-aid for Scientific Research from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science and the Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare of Japan, by a grant from Toray Industries, Inc., and by the Program for Promotion of Fundamental Studies in Health Sciences of the Organization for Pharmaceutical Safety and Research of Japan. The costs of publication of this article were defrayed in part by the payment of page charges. This article must therefore be hereby marked in accordance with 18 U.S.C. Section 1734 solely to indicate this fact.
in vitro
Read Also: Is Hepatitis Ca Sexually Transmitted Disease
Influence Of Hvr1 On Viral Interactions With Entry Receptors Cd81 And Sr
We hypothesized that HVR1 might also affect virus-receptor interactions. Therefore, we investigated if HVR1 differentially affects the CD81-dependent or SR-B1-dependent entry of J6 and JFH-1 virus. The inhibition of virus entry by anti-CD81 was not significantly different between J6 and JFH-1 or between J6 and either J6-JFH-1 HVR1 or J6-HVR1 . However, JFH-1 virus containing the HVR1 of J6 showed reduced sensitivity to anti-CD81 antibody inhibition compared to both J6 and JFH-1 virus . IC50 values were similar, with the exception of those for JFH-1-J6 HVR1 virus . These data indicate a potential strain-specific role for HVR1 in CD81 engagement.
this Section Provides Information On The Location And The Topology Of The Mature Protein In The Cell
subcellular Locationi
-
Manual assertion based on experiment ini
- Ref.13“The identification of three sizes of core proteins during the establishment of persistent hepatitis C virus infection in vitro.”
Manual assertion based on experiment ini
Manual assertion based on experiment ini
Manual assertion inferred from sequence similarity toi
Manual assertion inferred from sequence similarity toi
Manual assertion inferred from sequence similarity toi
-
Manual assertion based on experiment ini
- Ref.2“Hepatitis C virus p7 protein is localized in the endoplasmic reticulum when it is encoded by a replication-competent genome.”
Manual assertion based on experiment ini
- Ref.2“Hepatitis C virus p7 protein is localized in the endoplasmic reticulum when it is encoded by a replication-competent genome.”
Manual assertion based on experiment ini
Manual assertion inferred from sequence similarity toi
Also Check: Is Viral Hepatitis C Contagious
What Are The Potential Complications
Hepatitis C genotype 2 is often curable. But chronic infection can lead to serious complications.
Most people with hepatitis C experience no symptoms or only mild symptoms, even when the liver is becoming damaged.
The first six months after infection is defined as acute hepatitis C infection. This is true whether you have symptoms or not. With treatment, and sometimes without treatment, many people clear the infection during this time.
Youre unlikely to have serious liver damage during the acute phase, though in rare cases its possible to experience fulminant liver failure.
If you still have the virus in your system after six months, you have chronic hepatitis C infection. Even so, the disease generally takes many years to progress. Serious complications can include cirrhosis, liver cancer, and liver failure.
Statistics for complications of genotype 2 on its own are lacking.
For all types of hepatitis C in the United States, the
Determination Of Virus Infection Hcv Infectivity Titers And Hcv Rna Titers
Monoclonal anti-core antibody B2 was used for immunostaining for HCV core for J6/JFH1 and full-length J6 viruses, and monoclonal anti-NS5A antibody 9E10 was used for J8 viruses, as previously described . The percentage of HCV antigen-positive cells was estimated using fluorescence microscopy and was used as an indication of the status of HCV infection in the culture.
HCV infectivity titers were determined by FFU assay as previously described . Primary monoclonal anti-core antibody C7-50 was used in 1/500 dilutions for J6 recombinant and full-length viruses . 9E10 was used in 1/1,000 dilutions for J8 viruses. The number of FFU was counted manually using an inverted light microscope or automatically by an ImmunoSpot Series 5 UV Analyzer with customized software . The viral infectivity titers are averages from three independent infections.
Supernatant HCV RNA titers were determined using the real-time RT-PCR TaqMan assay as previously described .
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Is More Infectious Than Hiv