References And Further Reading
Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
NAFLD is usually seen in people who are overweight or obese.
According to the WHO , obesity is defined as an excess of weight by increasing the fat mass of an individual.1
However, it has been found in people of a normal weight whose diets are very high in fat and/or sugar content. A healthy liver should contain little or no fat and for most people, carrying a small amount of fat in the liver causes no major problems. Having high levels of fat in your liver is also associated with an increased risk of problems such as diabetes, heart attacks and strokes.2
If fat has been in the liver for a prolonged amount of time, the liver cells can become inflamed and the term NASH is then used. NASH may progress, like many liver diseases, to cirrhosis and liver cancer. See the diagram below:
Do not hesitate to read our article about FATTY LIVER DISEASE
References:
Fate Of Fatty Acids In The Liver
In the fasting state, adipocyte TAG is hydrolyzed to release FFAs, which are transported to the liver where they can serve as substrates for mitochondrial -oxidation. -oxidation of fatty acids is a major source of energy needed to maintain liver viability during fasting. It is also the source of the ketone bodies, acetoacetate and acetone. These are released into the blood and are essential fuel sources for peripheral tissues, when glucose is in short supply. Defects in hepatic -oxidation cause microvesicular steatosis of the liver, increase in oxidative stress due to extramitochondrial oxidative stress. ROS and peroxidation products lead to cytotoxic events, release of proinflammatory cytokines and activation of hepatic stellate cells and fibrosis.
Don’t Miss: Most Common Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
What Does Diagnosis Look Like
Hepatic steatosis can often be diagnosed by imaging techniques, such as ultrasound, computed tomography scan, or magnetic resonance imaging . All types of medical imaging can reveal diffuse fat content in the liver. This finding may also be described as lower liver attenuation, which means that healthy tissue is interrupted by fatty deposits. Imaging tests are performed by radiology specialists and interpreted by radiologists.
Ultrasound imaging is a type of sonography that is useful for detecting fat within the liver. Ultrasound technology utilizes sound waves to detect variations in structures and composition within body tissues. A higher measure of echogenicity will also accompany fat deposits in the liver parenchyma, which is the part of the liver responsible for carrying out the organs processes. Higher echogenicity means that sound waves more readily bounce off fat tissue and echo back to their source. An MRI might reveal a chemical shift that signifies the presence of fat within the liver.
Another type of imaging is called elastography. Elastography can reveal if soft tissue has hardened, indicating damage. For example, normally functioning liver tissue is soft in texture. Scarred or damaged liver becomes harder in texture.
One of the most definitive ways to detect and diagnose fatty liver disease is through a liver biopsy. A liver biopsy requires taking a tiny sample of your liver and analyzing it for the presence of fat cells, lesions, and other abnormalities.
Living With Fatty Liver Disease
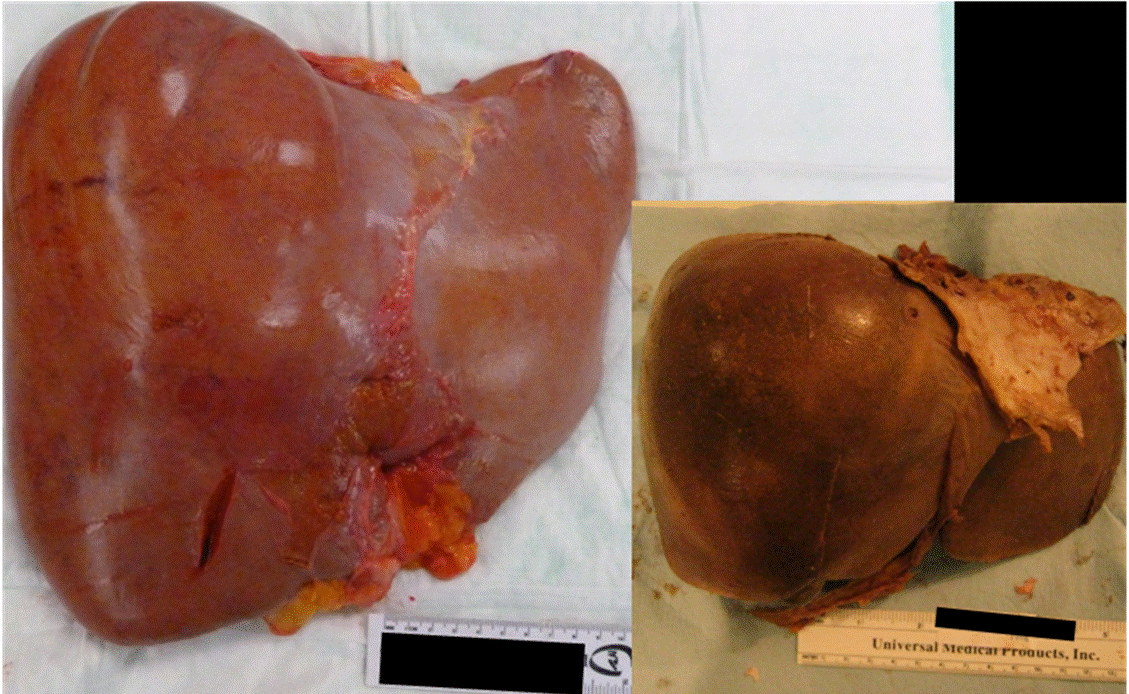
If you are living with fatty liver disease, learn as much as you can about your condition and work closely with your medical team. Since many medications can harm your liver, always let all your health care providers know about any medications you are taking. These include OTC drugs, dietary supplements, and vitamins. Other ways to manage fatty liver disease include maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, getting regular exercise, and continuing to avoid alcohol.
Don’t Miss: Signs You Have Hepatitis B
Steatosis And Fibrosis Progression In Hcv
High levels of TNF- have also been observed in human chronic hepatitis C patients. TNF- has been shown to induce IR in experimental animals and cultured cells. Inhibition of tyrosine phosphorylation of IRS 1 and 2 may be one of the mechanisms by which a high level of TNF- causes IR. Administration of an anti-TNF- antibody restores insulin sensitivity. These results provide direct experimental evidence for the contribution of HCV in the development of IR. There are experimental arguments for a direct role of insulin in fibrosis progression in HCV infection.
Epidemiological studies indicating that the state of IR now associated with NASH is also associated with an increased risk of HCC. It is worth mentioning that diabetes increases the risk of chronic liver disease and HCC.
Diagnosis Of Fatty Liver Disease
Your doctor may see something unusual in a blood test or notice that your liver is slightly enlarged during a routine check-up. These could be signs of a fatty liver. To make sure you dont have another liver disease, your doctor may ask for more blood tests , an ultrasound, a computed tomography scan or medical resonance imaging .If other diseases are ruled out, you may be diagnosed with NASH. The only way to know for sure is to get a liver biopsy. Your doctor will remove a sample of liver tissue with a needle and check it under a microscope.Some questions to ask your doctor after diagnosis include:
- What is the likely cause of my fatty liver?
- Do I have NASH? If not, how likely am I to develop NASH?
- Do I have cirrhosis? If not, how likely am I to develop cirrhosis?
- Do I need to lose weight? How can I do so safely?
- Should I be taking any medication to control my cholesterol and triglyceride levels?
- What medications or other substances should I avoid to protect my liver?
Recommended Reading: How Do You Pass Hepatitis C
What Are Some Lifestyle Changes That Can Help With Fatty Liver Disease
If you have any of the types of fatty liver disease, there are some lifestyle changes that can help:
- Eat a healthy diet, limiting salt and sugar, plus eating lots of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Get vaccinations for hepatitis A and B, the flu and pneumococcal disease. If you get hepatitis A or B along with fatty liver, it is more likely to lead to liver failure. People with chronic liver disease are more likely to get infections, so the other two vaccinations are also important.
- Get regular exercise, which can help you lose weight and reduce fat in the liver
Complications Of Fatty Liver Disease
The main complication for all these conditions is cirrhosis, or scarring of your liver. As your liver tries to stop the inflammation that comes with these conditions, it creates areas of scars. As inflammation spreads, so do the scars, and eventually, your liver canât do its job. That can result in:
- Fluid buildup in your abdomen
- Swollen veins in your esophagus that can burst and bleed
- Confusion and drowsiness
Recommended Reading: How Did I Get Hepatitis B
Can You Have Minimum Hepatomegaly With Hepatic Steatosis
Have your ammonia levels checked as well. my alt is 246 ast is 116 plasma ammonia is80 ug/dl.hepatomegaly 20cm steatosis .can i have minimum hepatic encepahlopathy if ifeel inattentiv/lethargy? May be: While you ammonia level is above the normal limit, your lethargy may be related to issues causing the liver disease.
What Is Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
NAFLD is a type of fatty liver disease that is not related to heavy alcohol use. There are two kinds:
- Simple fatty liver, in which you have fat in your liver but little or no inflammation or liver cell damage. Simple fatty liver typically does not get bad enough to cause liver damage or complications.
- Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis , in which you have inflammation and liver cell damage, as well as fat in your liver. Inflammation and liver cell damage can cause fibrosis, or scarring, of the liver. NASH may lead to cirrhosis or liver cancer.
Recommended Reading: How Is Hepatitis C Test Done
The Fatty Liver Disease Diet Plan
Following a diet plan for fatty liver disease can help you reverse fatty liver disease and prevent fatty liver disease progression to NASH and liver cirrhosis.
How long does it take to reverse fatty liver? The length of time required to reverse fatty liver depends on how progressed your condition is.
For more details about making lifestyle changes for fatty liver disease, check out this article on the fatty liver disease diet plan.
Why Is Fatty Liver Disease Bad
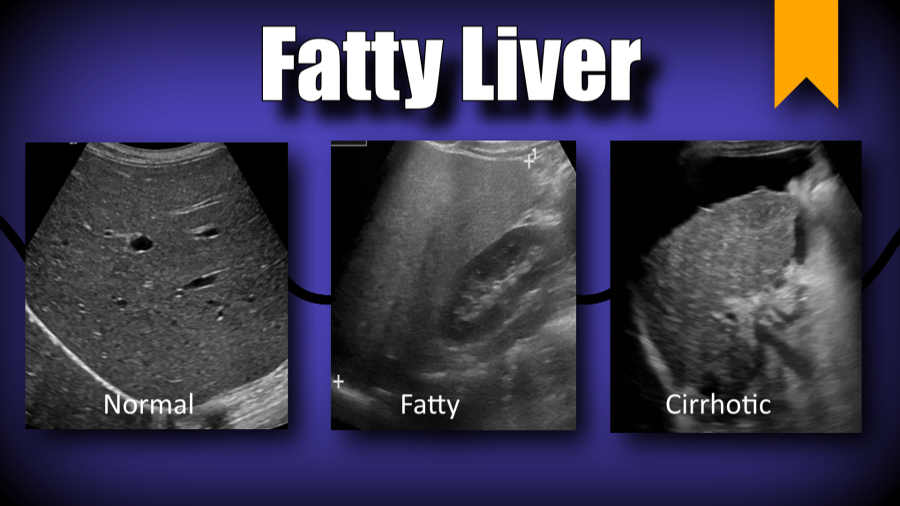
In most cases, fatty liver disease doesnt cause any serious problems or prevent your liver from functioning normally. But for 7% to 30% of people with the condition, fatty liver disease gets worse over time. It progresses through three stages:
Your liver becomes inflamed , which damages its tissue. This stage is called steatohepatitis.
Scar tissue forms where your liver is damaged. This process is called fibrosis.
Extensive scar tissue replaces healthy tissue. At this point, you have cirrhosis of the liver.
Cirrhosis of the liver
Cirrhosis of the liver is a result of severe damage to the liver. The hard scar tissue that replaces healthy liver tissue slows down the livers functioning. Eventually, it can block liver function entirely. Cirrhosis can lead to liver failure and liver cancer.
Read Also: Liver Disease Caused By Hepatitis C
Symptoms Of Fatty Liver Disease
With ALD and NAFLD, there are usually no symptoms. Some people may have signs such as tiredness or pain in the upper right side of the belly where your liver is.
If you have NASH or get cirrhosis, you may have symptoms such as:
- Swollen belly
- Have chronic viral hepatitis, especially hepatitis C
- Have genes that make you more likely to get it
- Are an African-American or Hispanic male
- Age — the older you are, the more likely it becomes.
The reason why some people with NAFLD have simple fatty liver and others get NASH isnât known. Genes may be a reason. NAFLD or NASH is more likely if:
- Youâre overweight or obese
- Your body doesnât respond to insulin as it should or if you have type 2 diabetes
- You have high levels of triglycerides or âbadâ cholesterol, or low levels of âgoodâ cholesterol
- Youâre older
There are also some less common reasons why you may get NAFLD or NASH. They include:
- Medical conditions that affect how your body uses or stores fat
- Hepatitis C or other infections
- Taking certain medicines such as glucocorticoids, methotrexate , synthetic estrogen, tamoxifen , and others
- Gallbladder removal. Some people who have surgery to remove their gallbladder are more likely to have NAFLD.
Industry Influence On Research
In 2015, the New York Times published an article on the , a nonprofit founded in 2014 that advocated for people to focus on increasing exercise rather than reducing calorie intake to avoid obesity and to be healthy. The organization was founded with at least $1.5M in funding from the , and the company has provided $4M in research funding to the two founding scientists Gregory A. Hand and since 2008.
Don’t Miss: How To Catch Hepatitis C
Drinking Too Much Alcohol
Drinking excessive amounts of alcohol can cause a range of liver conditions, including alcoholic hepatitis, alcoholic fatty liver disease, or cirrhosis. If your healthcare provider suspects that you may have alcohol-related liver disease, he/she will take a thorough history and perform a physical examination to determine how much alcohol you consume and look for signs of advanced liver disease. The workup may also include blood tests or imaging.
It is critical to recognize the signs and symptoms of alcohol abuse early because patients often do not develop symptoms until they have life-threatening liver disease. Treatment for alcohol abuse may take many different forms, including counseling, residential treatment, or support groups. Occasionally, medications can be used as an adjunct to other types of therapy.
Delivery Of Fatty Acids From Peripheral Stores To The Liver
Triglycerides are stored in adipose tissue and released as FFAs into the circulation through the actions of lipoprotein lipase. FFAs released from peripheral stores are hydrophobic and are strongly bound to circulating albumin. FFAs are transported by albumin to the liver where they can then be used as a substitute for -oxidation, stored as TAG, or exported as VLDL.
Excess glucose is converted to the liver, the backbone of most amino acids, can be converted to pyruvate and then to acetyl-coenzyme A , which feeds directly into cytosolic fatty acid synthesis.
Processes that can lead to excessive FFAs delivery or impaired -oxidation or secretion can lead to hepatic steatosis, increased mitochondrial reactive oxygen species and lipid peroxidation products.
Don’t Miss: How Does A Person Contract Hepatitis
Avoid Chronic Drug Use
The liver metabolizes medications and drugs in the blood.
Chronic use of illicit drugs, such as heroin and cocaine, can lead to liver inflammation and damage.
Prescription and over-the-counter medications can also contribute to drug induced liver injury.
According to the , medications that can contribute to liver damage include:
- antibiotics, such as amoxicillin and erythromycin
- acetaminophen, which is an OTC pain and fever reducer
- cancer drugs, such as mercaptopurine, lapatinib, and pazopanib
- antianxiety and antidepressant medications, including duloxetine and nortriptyline
- immunosuppressants, including cyclosporine and methotrexate
Storage Disorders Of The Liver
This refers to a group of diseases where the liver stores too much carbohydrate, minerals, or other biological molecules. Often, the cause is genetic and may be exacerbated by diet or other factors in your environment. There are numerous liver storage diseasesexamples include hemochromatosis , Wilsons disease , or glycogenosis .
If left untreated, these diseases can cause life-threatening liver failure. Treatment is variable and can include dietary changes or medications which capture the offending molecules.
Don’t Miss: Causes And Symptoms Of Hepatitis
Fibrosis Progression In Nash
Progression of fibrosis in NASH has been histologically demonstrated in 32%-37% of the patients. Estimated rates of cirrhosis development over 10 years of 5%-20% have been reported by 3 independent studies . NASH patients with advanced fibrosis are at risk of developing liver complications. Obesity, diabetes, IR and the initial severity of the fibrosis are the factors most conspicuously associated with fibrotic progression.
The mechanisms by which IR promotes fibrosis progression include: steatosis, hyperleptinemia, increased TNF production, impaired expression of PPAR- receptors. Hepatic injury in NASH induces oxidative stress, ROS and peroxidation products which lead to cytotoxic events, release of proinflammatory cytokines that activate hepatic stellate cells and deposition of collagen.
HCC has been detected in several NASH patients, most often at the time of diagnosis, and rarely, during follow up. In the larger Olmsted County Community Study, 2 of 420 NAFLD patients developed HCC during a 7-year follow-up period. The estimated rate of liver-related deaths over 10 years was 12% for NASH patients.
Ultrasonography Ct Scanning And Mri
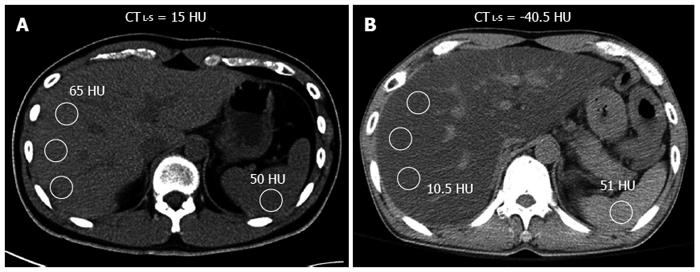
Noninvasive studies such as ultrasonography , computed tomography scanning, and magnetic resonance imaging are useful in helping to establish a diagnosis of steatosis, as well as in finding evidence for portal hypertension these imaging tests are also helpful in ruling out biliary dilation in patients with a cholestatic pattern of liver test result abnormalities.
However, these imaging modalities can neither define the cause of steatosis nor reliably distinguish between benign steatosis and steatohepatitis. Benign steatosis may be focal or diffuse, whereas steatohepatitis is usually diffuse.
In patients with alcoholic steatosis, the liver appears diffusely echogenic on US. In patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease , the liver is hyperechogenic or bright. Steatosis is detected only when substantial fatty change is present. Studies in patients who are about to undergo gastric bypass surgery indicate that US has a 93% predictive value for NAFLD, with an accuracy of 76%. Patients with steatosis on US have a higher incidence of coronary artery disease and should undergo cardiac evaluation if suspicious symptoms are present.
The mean CT count is lower in the liver than in the spleen. CT scans may be used to monitor the course of the disease on successive scans. Focal fatty lesions may be identified by dual-energy CT scans that demonstrate increased attenuation with increasing energy.
Also Check: Is Hepatitis C And Hiv The Same
Biological Role Of Insulin
Insulin, after binding its receptor, induces the phosphorylation of receptor substrates in the liver and muscles, and triggers several steps toward the transactivation of glucose transporter-4 .This increases glucose uptake by cells and its storage as glycogen, and inhibits the net production of glucose by the liver, thus blocking glycogenolysis and neoglycogenesis. Moreover, insulin promotes lipid storage by inhibiting lipolysis. When insulin is unable to induce glucose uptake, pancreatic -cells increase insulin production and the hyperinsulinemic state prevents hyperglycemia. Thus, IR depends on insulin secretion and insulin sensitivity.
Get A Subspecialty Second Opinion Today
The DocPanel platform enables people all over the world to get an expert second opinion in as little as 24 – 72 hours.
An easy 3-step process – instantly upload your scans, select an expert subspecialty radiologist , and submit your request. Upon uploading your scans, youll also have the opportunity to ask any questions you might have about your case.Not sure what a subspecialist is? Learn more with our in-depth article on the importance of getting a second opinion from a subspecialty radiologist.
Also Check: Medication For Hepatitis C Cure