Who Is Most At Risk Of Contracting Hepatitis C
You have a high risk of contracting hepatitis C if you:
- use or have used injection drugs even if it was just once or many years ago
- have received blood or blood products or an organ transplant before July 1990 in Canada
- have been in jail or
- have been injected or scratched during vaccination, surgery, blood transfusion or a religious/ceremonial ritual in regions where hepatitis C is common.
You have a high moderate risk of contracting hepatitis C if you:
- have tattoos or body piercing
- have multiple sexual partners
- have a sexually transmitted infection , including HIV or lymphogranuloma venereum
- have experienced traumatic sex or rough sex or have used sex toys or fisting that can tear body tissue
- have vaginal sex during menstruation
- have received a kidney treatment
- have received an accidental injury from a needle or syringe
- have another infectious disease
- were born to a hepatitis C infected mother or
- have a sexual partner infected with hepatitis C.
Hepatitis C is NOT passed from person to person by:
- coughing, sneezing
- breastfeeding unless your nipples are cracked and bleeding or
- oral sex, unless blood is present.
When Is It Ordered
An acute viral hepatitis panel may be ordered when a person has had blood tests done as part of a health checkup that show abnormal results on liver tests or when someone has acute symptoms associated with liver damage, such as:
- Fever, fatigue
- Jaundice
- Itching
The acute viral hepatitis panel may sometimes be used to screen people when they are at an increased risk for hepatitis B or hepatitis C infection or when it is known that they have been exposed. Below are listed some examples of who may be screened using the panel:
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test
This is a test to find out if you have a current infection. HBsAg is the earliest sign of the virus and disappears from your blood as the infection clears. A positive result indicates infection. If the antigen is not found , this shows that either you have never been exposed to hepatitis B or that you have recovered from infection and cleared the virus. The term surface refers to the outer surface of the virus itself.
Also Check: What Lab Test For Hepatitis C
The 5 Types Of Viral Hepatitis
Viral infections of the liver that are classified as hepatitis include hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E. A different virus is responsible for each type of virally transmitted hepatitis.
Hepatitis A is always an acute, short-term disease, while hepatitis B, C, and D are most likely to become ongoing and chronic. Hepatitis E is usually acute but can be particularly dangerous in pregnant women.
Hepatitis B Blood Tests

The Hepatitis B Panel of Blood Tests
Only one sample of blood is needed for a hepatitis B blood test, but the Hepatitis B Panel includes three parts. All three test results are needed to fully understand whether a person is infected or not. Below is an explanation of the 3-part Hepatitis B Panel of blood test results.
Read Also: Can Chronic Hepatitis B Be Cured
How To Get Tested
Hepatitis B testing is typically prescribed by a doctor and performed in a hospital, lab, or other medical setting. Taking a hepatitis B test requires a blood sample, which can be collected by a health care professional.
For laboratory-based testing, blood is drawn from a patients vein. After blood is collected, the sample is sent to a laboratory for analysis.
Preparation Prior To Transport
Label the specimen container with the patients full name, date of collection and one other unique identifier such as the patients date of birth or Health Card Number. Failure to provide this information may result in rejection or testing delay.
Centrifuge if using SST. Place specimen in biohazard bag and seal. Specimens should be stored at 2-8°C following collection.
Specimens more than the following number of days post collection will not be tested:
- > 6 days for Hepatitis B surface antigen
- > 7 days for Hepatitis B e Antigen and Hepatitis B e Antibody
- > 10 days for Hepatitis B core Antigen and Hepatitis B surface Antibody
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedule For Adults
Is There A Way To Prevent Viral Hepatitis
Yes. There is a vaccine available for hepatitis A. It is recommended for all children at age one year and for people who are at an increased risk of exposure to the virus. Hepatitis A can also be prevented with good hygiene. This includes washing hands well after using the bathroom, after changing diapers, and before eating or starting any food preparation.
Effective hepatitis B vaccines have been available in the U.S. since 1981, and beginning in 1991, healthcare practitioners in the U.S. began vaccinating all newborns. Children and adolescents who were not vaccinated at birth are routinely given the series of shots. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention also recommends that adults in high risk groups get vaccinated. Unless there is something in your medical history to the contrary, it is prudent to get the series of vaccinations.
Currently, there is no vaccine available for hepatitis C, although efforts are ongoing to develop one. Spread of hepatitis C can be prevented by avoiding exposure to blood and body fluids and the sharing of needles or other equipment to inject drugs.
What Does The Test Measure
Hepatitis B testing looks for antigens, antibodies, or the genetic material of the hepatitis B virus. HBV antigens are substances from the virus that cause a patients body to produce an immune response. Antibodies are substances made by the immune system in response to the hepatitis B virus.
Initial tests for hepatitis B measure antibodies and antigens related to HBV including:
If a patient is diagnosed with hepatitis B based on these initial tests, additional hepatitis B testing may be used to monitor the disease, guide treatment, and determine if a person can spread hepatitis B to others. These additional tests may include:
- Hepatitis B e antigen : Hepatitis B e antigen is a protein from the hepatitis B virus found in some patients who are positive for hepatitis B surface antigen. Measuring this antigen can help doctors understand infectivity, which describes a persons ability to spread HBV to others.
Don’t Miss: What Is Mild Hepatic Steatosis
What Is Hepatitis B And How Is It Transmitted
Hepatitis B is a virus that can infect and damage the liver. It is carried in the blood and bodily fluids. It is usually transmitted through blood to blood contact but can also be passed on through bodily fluids. This might be through sharing needles when injecting drugs, a cut in the skin that comes into contact with infected blood, use of unsterilised equipment when getting a tattoo or body piercing, or sharing razors or toothbrushes that are contaminated with infected blood or other bodily fluids.
It can be transmitted through sex, although this is rare and can be prevented by using a condom. However, it is 50 – 100 times more infectious than HIV.
What Happens During A Hepatitis Panel
A health care professional will take a blood sample from a vein in your arm, using a small needle. After the needle is inserted, a small amount of blood will be collected into a test tube or vial. You may feel a little sting when the needle goes in or out. This usually takes less than five minutes.
You may also be able to use an at-home kit to test for hepatitis. While instructions may vary between brands, your kit will include a device to prick your finger . Youll use this device to collect a drop of blood for testing. For more information on at-home testing for hepatitis, talk to your health care provider.
Also Check: Hepatitis B Blood Test Results
Hepatitis B Antibody And Antigen Test
Most people who come into contact with hepatitis B will clear the virus during the first six months of their infection. During this phase, the condition is known as acute hepatitis B. People who do not clear the virus after six months will be diagnosed as having chronic hepatitis B, which can cause liver damage.
Tests are carried out to look for antigens and antibodies in your blood. The results of these may indicate several possibilities:
- you have been infected by the virus in the past
- you have a new infection
- the infection is likely to go away by itself
- the infection has become chronic .
These antigens and antibodies are known as serological or viral markers. Doctors will look for markers in your blood over the course of your infection to see how the virus is progressing and/or responding to treatment. In particular, finding surface and e antigens known as HBsAg and HBeAg and their corresponding antibodies will help your healthcare team understand more about the pattern of your disease, and how its likely to progress
What To Think About
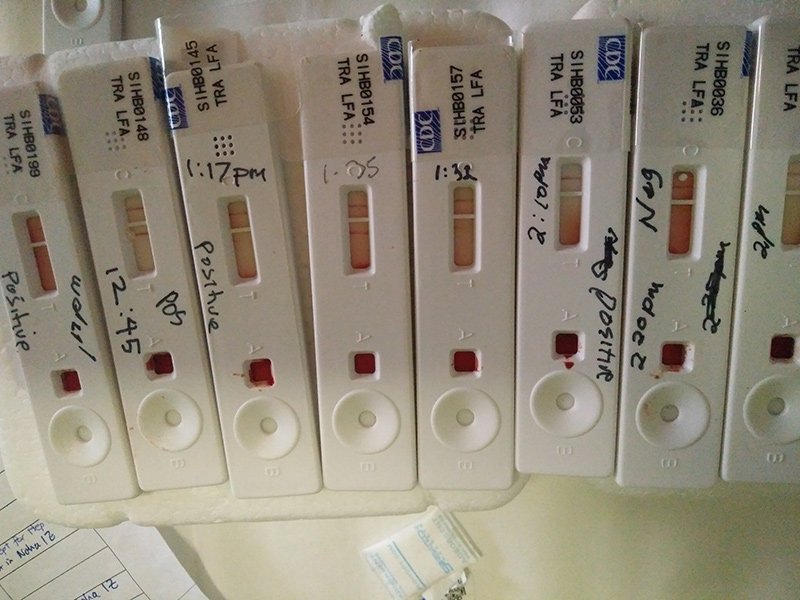
- Hepatitis A can be prevented by vaccination. To learn more, see the topic Immunizations.
- You also may be able to prevent a hepatitis A infection even after you have been exposed to the virus if you get a hepatitis A vaccination or a dose of immunoglobulin. To learn more, see the topic Hepatitis A.
- Hepatitis antibodies can take weeks or months to develop, so they might not show up in a test done early in the infection.
- Tests that show how well your liver is working are usually done if your doctor thinks you may have hepatitis. These tests may include measuring bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase, alanine aminotransferase, and aspartate aminotransferase.
You May Like: Difference Between Hiv And Hepatitis
Educating Clients About Viral Hepatitis
Clients may believe they know about viral , but their understanding of the disease may not be accurate. It is easy to confuse the three main types of viral , B, and C. Clients may have formed impressions based on limited or incorrect information. Counselors should briefly describe hepatitis A, B, and C, including their prevalence, , and relationship to drug use, as well as to other infections, such as HIV and sexually transmitted diseases. Specific strategies for speaking with clients include:
- Speak clearly and keep the message simple, focused, and brief.
- Use language, examples, and concepts that the client understands.
- Use appropriate visual aids.
- Frame numerical statements in terms that are easy to visualize. Say 5 out of 100 people rather than 5 percent of the population say more than half instead of the majority.
- Repeat the information at different times in different ways. The average client retains only approximately one-third of what he or she is told. Summarize essential points.
- Pay attention to a clients response to the information. For example, if a client stiffens his or her posture, consider saying, I notice that this topic seems to make you uncomfortable. It does for a lot of people. Please tell me what youre feeling right now. Id really like to help you with this.
- Use the opportunity to describe the potential detrimental effects of alcohol and other substance use on the liver of a person who is infected with HCV.
Shall I Tell My Partner I Have Hepatitis B
If you are diagnosed with hepatitis B you should tell anyone who you may have had blood to blood contact with, or unprotected sex with, since you became infected. In some cases this may be hard to work out, so it is best to discuss the risks to others with a clinician. Any contacts may have the virus without knowing it, and could pass it on to others, so it is important for them to get tested.
Read Also: How Is Hepatitis B And C Transmitted
Can Other Medical Conditions Have Similar Symptoms Like Hepatitis
Few viral infections also trigger similar symptoms like hepatitis. There are autoimmune conditions that may portray similar symptoms like hepatitis. In that case, the hepatitis panel test result may turn negative, which will prompt your doctor to order additional tests for you. Inherited disorders and drugs such as acetaminophen can cause hepatitis. Alcohol abuse can also result in this condition. Few viral infections such as Epstein-Barr virus and cytomegalovirus can cause hepatitis.
Can I Take The Test At Home
Samples for hepatitis B testing can be collected at home. At-home hepatitis B testing requires a patient to collect a blood sample, typically from a fingerstick using a very small needle provided in the test kit. Once a blood sample is collected, it is prepared according to the instructions contained in the test kit and mailed to a laboratory for testing.
Because there are numerous types of tests for HBV, it is important to look closely at the specific components of any at-home test kit. Many at-home test kits only look for hepatitis B surface antigen .
Don’t Miss: Is Hepatitis A Sexually Transmitted Disease
Getting Tested For Hepatitis C
A blood test, called an HCV antibody test, is used to find out if someone has ever been infected with the hepatitis C virus. The HCV antibody test, sometimes called the anti-HCV test, looks for antibodies to the hepatitis C virus in blood. Antibodies are chemicals released into the bloodstream when someone gets infected.
Test results can take anywhere from a few days to a few weeks to come back. Rapid anti-HCV tests are available in some health clinics and the results of these tests are available in 20 to 30 minutes.
Screening For Hepatitis B & C
NYU Langone doctors provide screening for hepatitis B and hepatitis C, two forms of hepatitis that can become chronic and lead to serious liver damage without treatment.
Hepatitis is characterized by inflammation of the liver. Hepatitis B is caused by the hepatitis B virus, and hepatitis C is caused by the hepatitis C virus. These diseases are contagious and can be spread from person to person through contact with bodily fluids such as blood and semen. Hepatitis B and C can also be passed from mother to child during birth.
Hepatologists, or liver specialists, and infectious disease specialists at NYU Langone recommend screening for some people who may be at increased risk of becoming infected.
Even though hepatitis B and C may cause no symptoms for years or even decades after infection, the viruses still may damage the liver. For this reason, screening is an important tool for early detection and treatment. It can prevent serious illness, such as cirrhosis and liver cancer, and hinder the spread of infection.
Vaccination for hepatitis is also an important prevention tool.
Don’t Miss: Can You Cure Hepatitis A
Tests Used To Help Diagnose Hepatitis C
Diagnosing hepatitis C doesnt involve a single test. Instead, your doctor will likely conduct multiple tests to confirm or rule out an infection.
Before beginning testing, your doctor may ask about your medical history and any symptoms youre experiencing. Most people get a trivial illness that they dont even notice, but occasionally, people develop classic clinical hepatitis with muscle aches, fatigue, and jaundice, says Glenn Englander, MD, a board-certified internal medicine doctor and gastroenterologist practicing in Palm Beach County, Florida.
Other symptoms of hepatitis C can include:
- Fever
- Nausea
- Clay-colored stools
Your doctor may ask questions about your lifestyle to assess your risk, too. This includes whether youve ever had a blood transfusion or organ transplant, injected drugs, shared personal care items such as razors or toothbrushes, or had unprotected sex. They may even ask whether your mother has been diagnosed hepatitis C.
The Results Of My Hepatitis Panel Came Back Negative What Other Conditions Can Cause Similar Symptoms
Hepatitis can be caused by several different factors and conditions such as alcohol, drugs like acetaminophen, or inherited disorders. There are a few other viral infections that may cause similar symptoms, such as cytomegalovirus and Epstein-Barr virus . An autoimmune disease is another possibility your healthcare provider may need to consider if your hepatitis panel is negative. Typically, additional tests will be performed to help determine the cause of your condition.
Also Check: What Is Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
Addressing Hepatitis For The First Time
It is crucial that a treatment counselor or health professional use a nonjudgmental and compassionate tone. Clients need to feel comfortable disclosing information about their health and risky behaviors. The following strategies can help initiate the conversation:
- Display posters, literature, or other -related items that could help prompt the client to ask questions about hepatitis. .
- Assess clients ability to discuss , based on their degree of openness in the counseling session, the amount of detail they provide in their responses, and the length of the therapeutic relationship.
- Raise the subject in a way that avoids making clients feel defensive or afraid. Consider introducing the subject by making parallels with other conditions that have been discussed. Say, for example, You said you were tested for HIV several times. Were you ever tested for viral ? or You mentioned that your friend is sick with HIV. Have you been tested for HCV or HIV? Tell me about those tests.
- Be patient and allow time for multiple, short conversations about the subject. This might ease feelings of fear, anxiety, or shame.