Hepatitis B Titer Test Panelmost Popular
The Hepatitis B Titer Test Panel panel contains 3 tests with 4 biomarkers.
Hepatitis B Titer Test
- Hepatitis B Surface Antigen with Reflex Confirmation
- Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Immunity, Quantitative
- Hepatitis B Core Antibody, Total
The Hepatitis B Titer Test is ordered when a person needs proof of immunity to Hepatitis B or just want to check their immune status.
The Hepatitis Titer Test includes immunity testing for Hepatitis B. Hepatitis is a viral disease which affects the liver. Vaccinations for Hepatitis B can provide protective antibodies which immunize a person from catching the virus. Additionally, a person who has been affected by Hepatitis B and recovers can develop natural immunity. Titer testing looks for the antibodies which typically indicate that a person is immune to a particular virus or infection.
Hepatitis B Immunity
Not Immune and no active or prior infection may be a good candidate for vaccine
- Hepatitis B Surface Antigen = Negative
- Hepatitis B Surface Antibody = Negative
- Hepatitis B Core Antibody, Total = Negative
Immunity due to vaccination
Question 2 What Is The Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
The hepatitis B surface antibody is the antibody that is produced in response to hepatitis B surface antigen , a protein present on the surface of the hepatitis B virus. Anti-HBs appears after convalescence from acute infection and lasts for many years. It can also be produced in response to hepatitis B vaccination.
Other hepatitis B antibodies are not produced in response to vaccination. This is because these antigens are not in the vaccine.
Correlation Between The Anti
No new HBsAg carrier was detected during the follow-up period. Follow-up serum specimens obtained from 876, 788, and 197 subjects at 13, 14, and 15 years of age, respectively, were tested for anti-HBs levels by both EIA and RIA. The EIA titers and the RIA S/Ns of anti-HBs were compared for each participant thus, 1,861 pairs of data for 922 participants ages 13 to 15 years were collected. The correlation between the anti-HBs levels measured by RIA and EIA were assessed by a scatter plot. There was a good correlation between the serum anti-HBs levels measured by the RIA and the EIA methods .1). A linear regression equation of RIA to EIA level conversion was formulated as follows: log EIA titer =0.12 + .
Correlation between the anti-HBs levels tested by RIA versus EIA in 1,861 serum samples.
You May Like: What Is Hepatitis B Caused By
Hepatitis B Blood Tests
The Hepatitis B Panel of Blood Tests
Only one sample of blood is needed for a hepatitis B blood test, but the Hepatitis B Panel includes three parts. All three test results are needed to fully understand whether a person is infected or not. Below is an explanation of the 3-part Hepatitis B Panel of blood test results.
Can I Take The Test At Home

Samples for hepatitis B testing can be collected at home. At-home hepatitis B testing requires a patient to collect a blood sample, typically from a fingerstick using a very small needle provided in the test kit. Once a blood sample is collected, it is prepared according to the instructions contained in the test kit and mailed to a laboratory for testing.
Because there are numerous types of tests for HBV, it is important to look closely at the specific components of any at-home test kit. Many at-home test kits only look for hepatitis B surface antigen .
Also Check: Who Should Get Tested For Hepatitis C
Understanding Your Test Results
Understanding your hepatitis B blood tests can be confusing. It is important to talk to your health care provider so you understand your test results and your hepatitis B status. Are you infected? Protected? Or at risk? The Hepatitis B Panel of blood tests includes 3 tests and all three results must be known in order to confirm your status.
Below is a chart with the most common explanation of the test results, but unusual test results can occur. Please note that this chart is not intended as medical advice, so be sure to talk to your health care provider for a full explanation and obtain a printed copy of your test results. In some cases, a person could be referred to a liver specialist for further evaluation.
More Detailed Information About Hepatitis B Blood Tests
An acute hepatitis B infection follows a relatively long incubation period – from 60 to 150 days with an average of 90 days. It can take up to six months, however, for a person to get rid of the hepatitis B virus. And it can take up to six months for a hepatitis B blood test to show whether as person has recovered from an acute infection or has become chronically infected .
The following graphic from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention represents the typical course of an acute hepatitis B infection from first exposure to recovery.
According to the CDC, a hepatitis B blood test result varies depending on whether the infection is a new acute infection or a chronic infection.
Understanding Of Lab Tests Results
Please visit the site associated with The American Association for Clinical Chemistry for better understanding of tests. There you will find the most detailed and full information regarding lab tests. In “common questions” tab you will find answers on the most common questions.
In addition, you can use a special form to ask the question. It is useful, if there is no answer on your question on the web site. A laboratory scientist will answer your question. It is a part of voluntary service provided by the American Society for Clinical Laboratory Science.
Also Check: How To Find Out If You Have Hepatitis
Sequence Following An Initial Negative Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Titer
As you obtain documentation, please submit documentation of each step to CastleBranch
- Initial Hepatitis B titer negative for immunity
- Receive Hepatitis B challenge dose/booster
- Repeat Hepatitis B titer 4-6 weeks after challenge/booster vaccine
Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
- Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
- Description
-
The Quantitative detection Hepatitis B virus Surface IgG antibody in human sera using the FDA approved Abbott ARCHITECT AUSAB-DIL test two-step chemiluminescent immunoassay.
In the first step, sample, assay diluent, and recombinant Hepatitis B surface Antigen coated paramagnetic microparticles are combined. Anti-HBs present in the sample binds to the rHBsAg coated microparticles. In the second step, rHBsAg acridinium-labeled conjugate is added, which binds to IgG anti-HBs. Then pre-trigger and trigger solutions are added to the reaction mixture. The resulting chemiluminescent reaction is measured as relative light units .
A direct relationship exists between the amount of anti-HBs in the sample and the RLUs. The concentration of anti-HBs in the sample is determined using an active ARCHITECT AUSAB calibration curve. Results are reported as mIU/mL.
For Batteries containing HBSAb see:
Hepatitis B Antibodies , Quantitative detection of Hepatitis B virus Surface IgG antibody and Hepatitis B virus Core IgG and IgM antibodies
Hepatitis B Battery , Quantitative detection of Hepatitis B virus Surface IgG antibody , Qualitative detection of Hepatitis B virus Surface Antigen and Qualitative detection of Hepatitis B virus Core IgG and IgM antibodies
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen & Antibody , Quantitative detection of Hepatitis B virus Surface IgG antibody and Qualitative detection of Hepatitis B virus Surface Antigen
- Synonyms
Also Check: Is Hepatitis B The Same As Hiv
What Is A Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Test
Hepatitis B surface antibody test is part of a panel of blood tests to diagnose HBV infection. Hepatitis B surface antibody test determines the presence and quantity of anti-HBs in the blood serum, which can indicate protection from HBV infection.
Hepatitis B disease affects the liver and commonly spreads through body fluids such as blood, semen, and vaginal secretions.
When Should I Get Hepatitis B Testing
Using hepatitis B tests to screen for HBV is recommended for certain groups that are at an increased risk of infection. Groups that may benefit from hepatitis B screening include:
- Pregnant people
- People born in parts of the world where hepatitis B is more common, including Africa, Asia, Eastern Europe, South America, and parts of the Middle East
- People who didnt receive a hepatitis B vaccine
- HIV-positive people
- Pain in the joints or abdomen
- Loss of appetite, nausea, or vomiting
- Yellowish skin and eyes
Using hepatitis B testing to assess immunity to HBV may be used before or after vaccination. Pre-vaccination testing is not always needed but may be performed if there is a chance that a patient has previously been infected with HBV or has already been vaccinated. Post-vaccination testing is used in certain groups of people who are at an especially elevated risk for HBV infection, including infants born to mothers with a hepatitis B infection.
Recommended Reading: Can Hepatitis C Go Away On Its Own
Question 7 Is Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Antibody Always Acquired After A Completed Vaccination Protocol
No. After three intramuscular doses of vaccine, > 90% of healthy adults and > 95% of those < 19 years of age develop immunity .1 However, there is an age-specific decline in development of immunity. After age 40 years, about 90% of people become immune, but by age 60 years, only 75% of people become immune.1 Larger vaccine doses or an increased number of doses are required to induce immunity in many hemodialysis patients and in other immunocompromised people.1
References
Taking A Hepatitis B Test
Testing for hepatitis B is performed on a sample of blood. A doctor, nurse, or other health care provider can obtain a blood sample using a small needle to draw blood from a vein.
At-home hepatitis B testing requires that users carefully follow instructions provided in the test kit to collect a small sample of blood, package the sample, and mail it to a lab for testing.
Read Also: What Is Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
Question 3 How Is The Quantitative Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Test Performed
An immunometric technique is used. The anti-HBs binds to HBsAg ad and ay subtypes, which are coated on the test wells. Binding of a horseradish peroxidase-labeled HBsAg conjugate to the anti-HBs completes the sandwich formation. Unbound materials are then washed away. In the next step, the horseradish peroxidase catalyzes oxidation of a luminogenic substrate, producing light. Light signals are detected and quantified. Intensity of the light is proportional to the amount of anti-HBs present in the patient sample. The result is standardized to an international unit system and reported as milliinternational units per milliliter .
Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Titer
SKU:
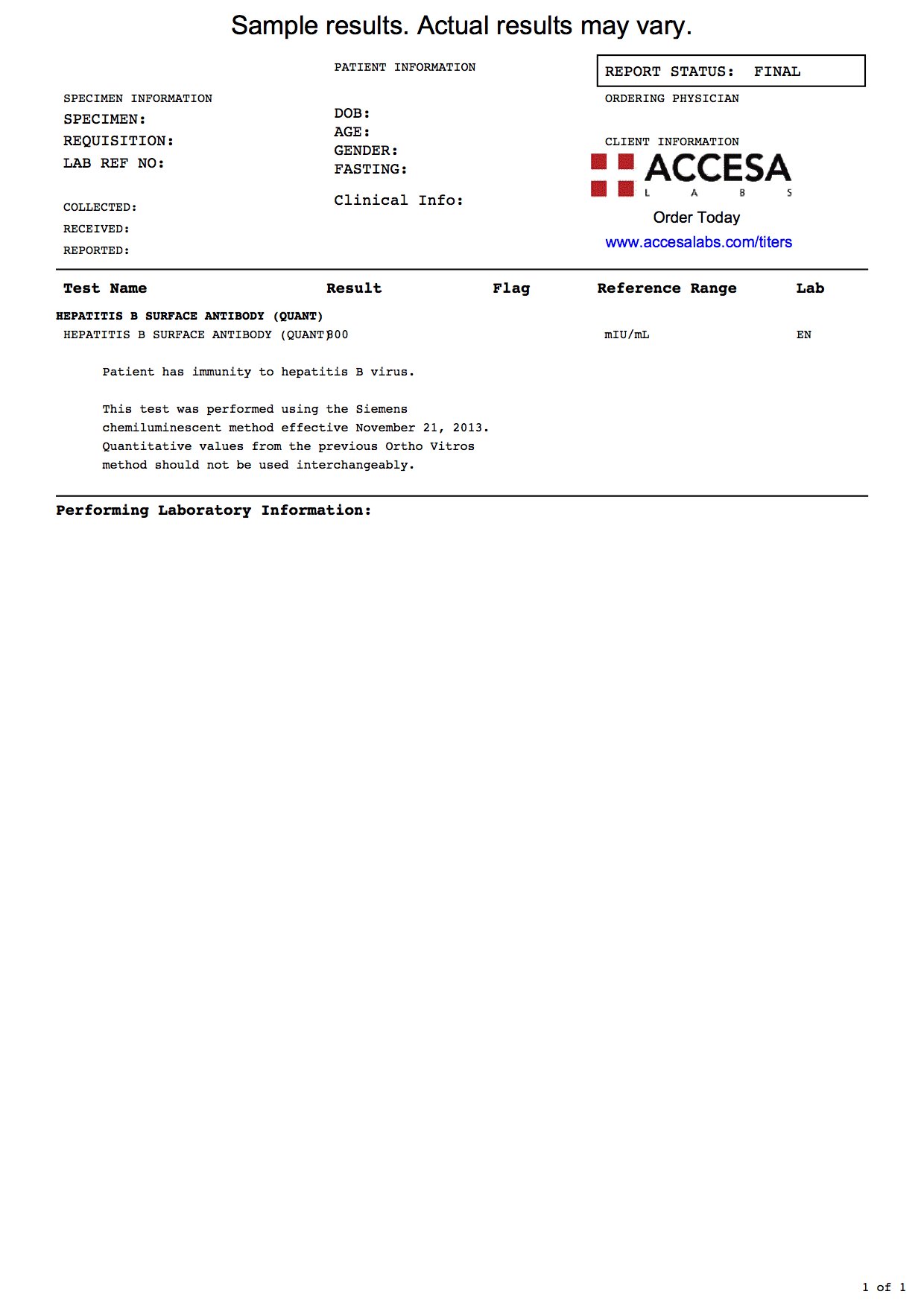
This antibody titer test checks for immunity to Hepatitis B.
Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Titer This test measures your Hepatitis B Surface Antibody IgG titer level.
Most people receive the Hepatitis B vaccine series when they are young and/or receive vaccine boosters as adults. As a consequence of either vaccination or prior exposure, people develop antibodies to Hepatitis B.
The Hepatitis B Titer Test measures the Hepatitis B IgG antibody levels in your blood. Positive results mean that you are considered immune to Hepatitis B according to accepted international standards.
Hepatitis B Titer Test results are reported as quantitative IgG titers.
This information is for educational purposes only, and does not constitute medical advice, diagnosis or treatment in any way. This site does not replace the services of licensed health care professionals and all site users should consult with a physician regarding their health concerns.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B How Do You Catch It
Provides Information To Assist In Interpretation Of The Test Results
A positive result indicates recovery from acute or chronic hepatitis B virus infection or acquired immunity from HBV vaccination. This assay does not differentiate between a vaccine-induced immune response and an immune response induced by infection with HBV. A positive total antihepatitis B core result would indicate that the hepatitis B surface antibody response is due to past HBV infection.
Per assay manufacturer’s instructions for use, positive results, defined as anti-HBs levels of 12.0 mIU/mL or greater, indicate adequate immunity to hepatitis B from past hepatitis B or HBV vaccination. However, per current CDC guidance, individuals with anti-HBs levels greater than 10 mIU/mL after completing an HBV vaccination series are considered protected from hepatitis B.
Negative results, defined as anti-HBs levels of less than 5.0 mIU/mL, indicate a lack of recovery from acute or chronic hepatitis B or inadequate immune response to HBV vaccination. The US Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices does not recommend more than 2 HBV vaccine series in nonresponders.
Indeterminate results, defined as anti-HBs levels in the range from 5 to 11.9 mIU/mL, indicate inability to determine if anti-HBs is present at levels consistent with recovery or immunity. Repeat testing is recommended in 1 to 3 months.
How Much Does The Test Cost
The cost of hepatitis B testing depends on the tests that are performed, where the test is conducted, and a patients health insurance coverage. When testing is ordered by a doctor, patients with health insurance may find it helpful to discuss the cost of testing with their health insurance company as they may be responsible for testing costs as well as other out-of-pocket costs such as copays and deductibles.
For patients without health insurance or for whom insurance doesnt cover the cost of testing, it may be helpful to discuss the cost of hepatitis B testing with a doctor or hospital administrator.
The cost of at-home hepatitis B testing starts around $45. At-home test kits may also test for additional types of viral hepatitis in the same sample. The cost of test panels that look for more than one type of viral hepatitis start around $80.
Recommended Reading: Is There A Shot For Hepatitis C
Negative But Other Hepatitis Tests Are Positive
Your HBsAb test may be negative even when other hepatitis B tests are positive, showing active or chronic infection. Further testing is necessary, especially for the hepatitis B surface antigen , which shows that the virus itself is circulating in your bloodstream and that you have an active or chronic infection.
How To Get Tested
Hepatitis B testing is typically prescribed by a doctor and performed in a hospital, lab, or other medical setting. Taking a hepatitis B test requires a blood sample, which can be collected by a health care professional.
For laboratory-based testing, blood is drawn from a patients vein. After blood is collected, the sample is sent to a laboratory for analysis.
Read Also: How Is Hepatitis C Spread
Discusses Physiology Pathophysiology And General Clinical Aspects As They Relate To A Laboratory Test
Hepatitis B virus infection, also known as serum hepatitis, is endemic throughout the world. The infection is spread primarily through blood transfusion or percutaneous contact with infected blood products, such as sharing of needles among injection drug users. The virus is also found in virtually every type of human body fluid and has been known to be spread through oral and genital contact. HBV can be transmitted from mother to child during delivery through contact with blood and vaginal secretions, but it is not commonly transmitted via the transplacental route.
The incubation period for HBV infection averages 60 to 90 days . Common symptoms include malaise, fever, gastroenteritis, and jaundice . After acute infection, HBV infection becomes chronic in 30% to 90% of infected children younger than 5 years of age and in 5% to 10% of infected individuals age 5 or older. Some of these chronic carriers are asymptomatic, while others progress to chronic liver disease, including cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatitis B surface antigen is the first serologic marker, appearing in the serum 6 to 16 weeks following HBV infection. In acute cases, HBsAg usually disappears 1 to 2 months after the onset of symptoms with the appearance of hepatitis B surface antibody . Anti-HBs also appears as the immune response following hepatitis B vaccination.
Additional Specimen Collection Information
Collect blood in a lithium heparin, green-top, EDTA purple-topor red-top tube. PST and SST are acceptable. Serum orplasma should be separated from contact with the cells within 2hours of collection. Specimens not centrifuged within 4 hours ofcollection may be rejected. Refrigerate the specimen if unable toassay within 8 hours of collection. Samples with > 1+ lipemiamust be cleared prior to analysis.
Don’t Miss: How Did I Get Hepatitis C