What Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is an infection of your liver. Itâs caused by a virus. There is a vaccine that protects against it. For some people, hepatitis B is mild and lasts a short time. These âacuteâ cases donât always need treatment. But it can become chronic. If that happens, it can cause scarring of the organ, liver failure, and cancer, and it even can be life-threatening.
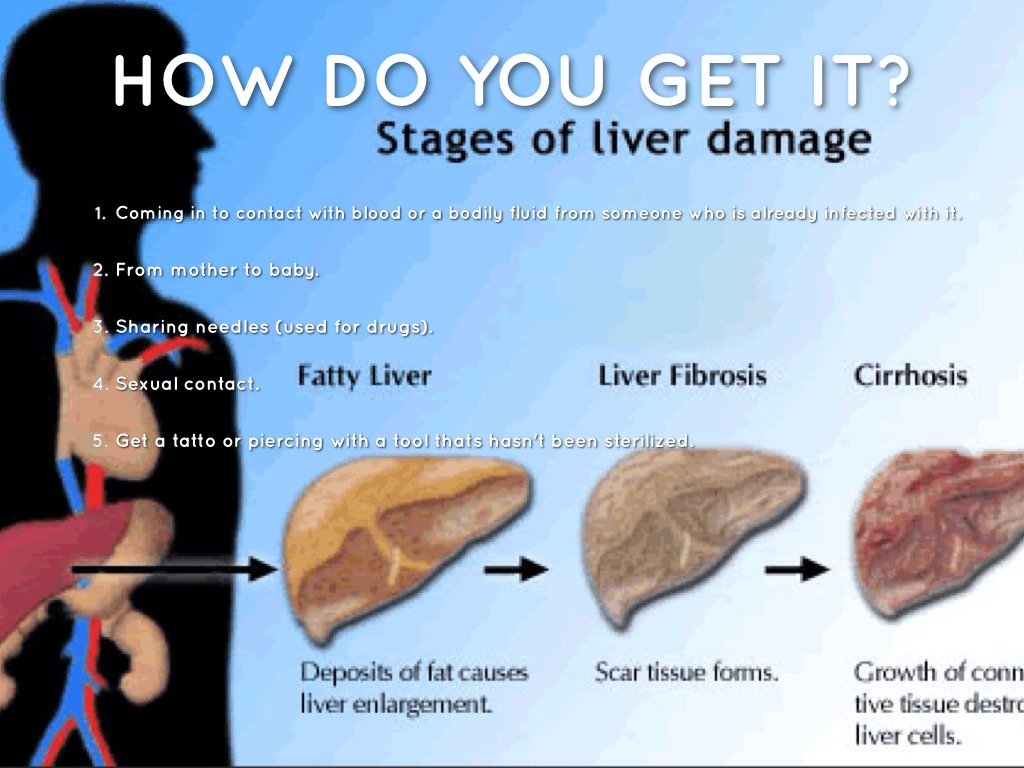
Itâs spread when people come in contact with the blood, open sores, or body fluids of someone who has the hepatitis B virus.
It’s serious, but if you get the disease as an adult, it shouldnât last a long time. Your body fights it off within a few months, and youâre immune for the rest of your life. That means you can’t get it again. But if you get it at birth, itâ unlikely to go away.
âHepatitisâ means inflammation of the liver. There are other types of hepatitis. Those caused by viruses also include hepatitis A and hepatitis C.
You Can Have It And Not Know It
What is hepatitis B?
Hepatitis B is a liver disease caused by the hepatitis B virus . HBV is far more infectious than HIV and can be prevented by a vaccine. People who have not been vaccinated may be at risk of getting infected.
About 95 percent of adults will recover within 6 months of becoming infected and as a result will develop lifelong protection against it. The remaining 5 percent are unable to clear the virus and will become chronically infected. Chronic hepatitis B infection is treatable.
It is estimated that less than 1 percent of Canada’s population is infected with either acute or chronic HBV. People who are infected before the age of 7 are at a higher risk of developing chronic infection. In 2011, the overall reported rate of acute hepatitis B infection in Canada was 0.6 reported cases per 100,000 people living in Canada.
Why is hepatitis B a health concern?
Many people infected with HBV do not know they have the virus because symptoms can take two to six months to appear and only about 50 percent of people develop symptoms. During this time, they can spread the infection to others. You may not know you have this infection until damage has already been done to your liver. Potential complications from chronic HBV infection include cirrhosis of the liver, liver failure, liver cancer and premature death.
Why do I need my liver?
How is hepatitis B spread?
HBV is spread through contact with infected blood and body fluids including semen and vaginal fluid.
Keep Personal Items Personal
Any tools or implements that may have a bit of blood on them from infected people are potential sources of hepatitis B or C transmission. Toothbrushes, nail clippers, razors, needles, and washcloths may all contain trace amounts of blood that can transmit infection. Keep personal items such as these to yourself and never use personal items that belong to others.
You May Like: Liver Cancer Caused By Hepatitis C
How Can Hepatitis B Be Prevented
- Avoid sharing needles and syringes with others.
- Avoid sharing razors and toothbrushes with infected people.
- Practise safer sex with condoms.
- Use a condom during sexual intercourse.
- Vaccination, which is very effective against type B hepatitis, is available and three doses are recommended. The second and third doses are given one and six months after the first dose. Alternatively, for faster initial protection, the second and third doses can be given one and two months after the first dose, with a fourth dose then needed at 12 months.
- In some countries HBV vaccination is part of the routine immunisation schedule. Other countries have opted for vaccination for high risk groups.
- The vaccine is recommended for the following groups:
- family members of people with hepatitis B
- sexual partners of people with hepatitis B
- newborn babies whose mothers are infected with hepatitis Bvirus
- drug users
- hospital staff who frequently come into contact withblood.
How Do You Get Hepatitis A

The main way you get hepatitis A is when you eat or drink something that has the hep A virus in it. A lot of times this happens in a restaurant. If an infected worker there doesn’t wash their hands well after using the bathroom, and then touches food, they could pass the disease to you.
Food or drinks you buy at the supermarket can sometimes cause the disease, too. The ones most likely to get contaminated are:
- Shellfish
- Ice and water
You could catch or spread it if you’re taking care of a baby and you don’t wash your hands after changing their diaper. This can happen, for example, at a day care center.
Another way you can get hep A is when you have sex with someone who has it.
Read Also: Drinking Alcohol With Hepatitis C
How Can I Prevent Spreading Hepatitis B To Others
If you have hepatitis B, follow the steps above to avoid spreading the infection. Your sex partners should get a hepatitis B test and, if they arent infected, get the hepatitis B vaccine. You can protect others from getting infected by telling your doctor, dentist, and other health care professionals that you have hepatitis B. Dont donate blood or blood products, semen, organs, or tissue.
What Can Be Done At Home
- Be careful to protect your family and sexual partners from the virus.
- Abstain from all alcohol intake if blood samples show that the disease is active.
- Refrain from drinking alcohol daily if you have chronic hepatitis B.
- If you have chronic hepatitis, you should be reviewed regularly in a specialist clinic because there are several treatment options
- Eat a healthy, well-balanced diet.
Also Check: Hepatitis A Vaccine Cost Walmart
When To Get Medical Advice
Hepatitis B can be serious, so you should get medical advice if:
- you think you may have been exposed to the hepatitis B virus emergency treatment can help prevent infection if given within a few days of exposure
- you have symptoms associated with hepatitis B
- you’re at a high risk of hepatitis B high-risk groups include people born in a country where the infection is common, babies born to mothers infected with hepatitis B, and people who have ever injected drugs
You can go to your local GP surgery, drug service, genitourinary medicine clinic or sexual health clinic for help and advice.
A blood test can be carried out to check if you have hepatitis B or have had it in the past.
The hepatitis B vaccine may also be recommended to reduce your risk of infection.
Persons New To Canada
Health care providers who see persons newly arrived in Canada should review the immunization status and update immunization for these individuals, as necessary. In many countries outside of Canada, HB vaccine is in limited use.
All persons from a country that is endemic for HB should be assessed and vaccinated against HB if not immune and not infected. Individuals born in developing countries are more likely to be carriers of HB, necessitating vaccination of their sexual and household contacts based on review of their serologic test results. HB vaccine is recommended for all household contacts whose families have immigrated to Canada from areas in which there is a high prevalence of HB and who may be exposed to HB carriers through their extended families or when visiting their country of origin.
Children adopted from countries in which there is a high prevalence of HB infection should be screened for HBsAg and, if positive, household or close contacts in the adopting family should be immunized before adoption or as soon as possible thereafter. Adults going to pick-up children from these countries should be vaccinated before departure. Refer to Immunization of Persons New to Canada in Part 3 for additional information.
Read Also: Signs You Have Hepatitis B
Eating Diet And Nutrition For Hepatitis B
If you have hepatitis B, you should eat a balanced, healthy diet. Obesity can increase the chance of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease , and NAFLD can increase liver damage in people who have hepatitis B. Talk with your doctor about healthy eating and maintaining a healthy weight.
You should also avoid alcohol because it can cause more liver damage.
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test
A hepatitis B surface antigen test shows if youre contagious. A positive result means you have hepatitis B and can spread the virus. A negative result means you dont currently have hepatitis B. This test doesnt distinguish between chronic and acute infection. This test is used together with other hepatitis B tests to determine the .
Don’t Miss: Is Hepatitis C Sexually Transmissible
Hepatitis B In The United States
In the United States, about 862,000 people have chronic hepatitis B.6 Asian Americans and African Americans have higher rates of chronic hepatitis B than other U.S. racial and ethnic groups.10 Researchers estimate that about half of the people living with chronic hepatitis B in the United States are Asian Americans and Pacific Islanders.11 Chronic hepatitis B is also more common among people born in other countries than among those born in the United States.7
The hepatitis B vaccine has been available since the 1980s and, in 1991, doctors began recommending that children in the United States receive the hepatitis B vaccine. The annual rate of acute hepatitis B infections went down 88.5 percent between 1982 and 2015.12 In 2017, the annual number of hepatitis B infections rose in some states.13 Experts think the rise was related to increases in injection drug use. Injection drug use increases the risk of hepatitis B infection.
How Common Is Hepatitis B

The number of people who get this disease is down, the CDC says. Rates have dropped from an average of 200,000 per year in the 1980s to around 20,000 in 2016. People between the ages of 20 and 49 are most likely to get it.
About 90% of infants and 25-50% of children between the ages of 1-5 will become chronically infected. In adults, approximately 95% will recover completely and will not go on to have a chronic infection.
As many as 1.2 million people in the U.S. are carriers of the virus.
Also Check: How To Treat Hepatitis C Virus
When To Call The Doctor
- The child has not felt hungry or wanted to eat in the past 24 hours.
- Your childs fever is over 100.4 degrees Fahrenheit for more than 2 days.
- Your child has a stomachache.
- Your child vomits more than 2 times in an hour.
- Your child’s skin or the white part of the eyes turns yellow.
- Your child is overly tired for more than 2 days.
Who Are Hepatitis B Carriers
Hepatitis B carriers are people who have the hepatitis B virus in their blood, even though they dont feel sick. Between 6% and 10% of those people whove been infected with the virus will become carriers and can infect others without knowing it. There are over 250 million people in the world who are carriers of HBV, with about 10% to 15% of the total located in India. Children are at the highest risk of becoming carriers. About 9 in 10 babies infected at birth become HBV carriers, and about half of children who are infected between birth and age 5 carry the virus. A blood test can tell you if you are a hepatitis B carrier.
You May Like: How Do You Know If You Have Alcoholic Hepatitis
Can Hepatitis B Be Prevented Or Avoided
The best way to prevent hepatitis B is to always have protected sex and, if you use intravenous drugs, avoid sharing needles.
A vaccine is available to prevent hepatitis B. It is now routinely given in the first year of life to all newborn infants. It is safe and requires 3 shots over a 6-month period. This vaccine should be given to people who are at high risk for this illness, such as healthcare workers, all children, people who travel to areas where the infection is widespread, drug users, and those who have multiple sex partners.
Treatments For Hepatitis B
Treatment for hepatitis B depends on how long you have been infected for.
If you have been exposed to the virus in the past few days, emergency treatment can help stop you becoming infected.
If you have only had the infection for a few weeks or months , you may only need treatment to relieve your symptoms while your body fights off the infection.
If you have had the infection for more than 6 months , you may be offered treatment with medicines that can keep the virus under control and reduce the risk of liver damage.
Chronic hepatitis B often requires long-term or lifelong treatment and regular monitoring to check for any further liver problems.
Recommended Reading: Treatment For Liver Cirrhosis Hepatitis B
How Is Hepatitis B Transmitted
Hepatitis B is spread in several distinct ways: sexual contact sharing needles, syringes, or other drug-injection equipment or from mother-to-child at birth.
In the United States, in 2018, injection drug use was the most common risk factor reported among people with an acute HBV infection, followed by having multiple sex partners. Less commonly reported risk factors included accidental needle sticks, surgery, transfusions, and household contact with a person with HBV infection. In the United States, healthcare-related transmission of HBV is rare.
Mother-to-child transmission of HBV is especially concerning, because it is preventable. An estimated 25,000 infants are born to mothers diagnosed with HBV each year in the United States, and approximately 1,000 mothers transmit HBV to their infants. Without appropriate medical care and vaccinations, 90% of HBV-infected newborns will develop chronic infection, remaining infected throughout their lives. Up to 25% of people infected at birth will die prematurely of HBV-related causes. For this reason, the standard of care for pregnant women includes an HBV test during each pregnancy so that the appropriate steps can be taken to prevent HBV-positive mothers from transmitting the disease to her infant.
Guidance On Reporting Adverse Events Following Immunization
Vaccine providers are asked to report, through local public health officials, any serious or unexpected adverse event temporally related to vaccination. An unexpected AEFI is an event that is not listed in available product information but may be due to the immunization, or a change in the frequency of a known AEFI.
Refer to Reporting Adverse Events Following Immunization in Canada and Adverse events following immunization in Part 2 for additional information about AEFI reporting.
Recommended Reading: Antibody Titer Test For Hepatitis B
How Is Hepatitis B Spread
You can become infected with hepatitis B through exposure to blood, semen and other bodily fluids of an infected person. You can get the infection by:
- Having unprotected sex.
- Sharing or using dirty needles for drug use, tattoos or piercing.
- Sharing everyday items that may contain body fluids, including razors, toothbrushes, jewelry for piercings and nail clippers.
- Being treated medically by someone who does not use sterile instruments.
- Being bitten by someone with the infection.
- Being born to a pregnant woman with the infection.
Hepatitis B is not spread by:
- Kissing on the cheek or lips.
- Coughing or sneezing.
- Hugging, shaking hands or holding hands.
- Eating food that someone with the infection has prepared.
- Breastfeeding.
Persons With Inadequate Immunization Records
Evidence of long term protection against HB has only been demonstrated in individuals who have been vaccinated according to a recommended immunization schedule. Independent of their anti-HBs titres, children and adults lacking adequate documentation of immunization should be considered susceptible and started on an immunization schedule appropriate for their age and risk factors. Refer to Immunization of Persons with Inadequate Immunization Records in Part 3 for additional information.
Also Check: What Does Hepatitis B Mean
How Do People Get The Hbv Virus
Hepatitis B virus is found in the blood of people with HBV infection. It enters the body through blood-to-blood contact.
Reliable blood tests for HBV were developed many years ago. Since blood donors and blood products are tested for HBV, this is no longer the typical means of infection.
In many parts of the world, hepatitis B virus infects more than 8% of the population. HBV-infected women pass the infection to their babies during the birth process. People can also get hepatitis B by sharing needles for injection drug use, through sexual contact with an infected person, by an accidental needlestick with a contaminated needle, or from improperly sterilized medical, acupuncture, piercing, or tattooing equipment.
Immunisation For Hepatitis B
Immunisation is the best protection against hepatitis B infection. A course of vaccination is recommended for all babies and people in high-risk groups.
Immunisation can be with a vaccine against hepatitis B alone or with a combination vaccine. To be immunised, contact your doctor or local council.
Protection against hepatitis B is available free of charge under the National Immunisation Program Schedule. In Victoria, immunisation against hepatitis B is free for:
- Babies at birth immunisation against hepatitis B alone as soon as possible after birth.
- Babies at 2, 4 and 6 months combination immunisation in the form of a diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough, hepatitis B, polio and Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine .
- Premature babies at 12 months premature babies born under 32 weeks gestation or under 2,000g birth weight receive a single booster dose.
- Children up to and including 9 years of age.
- People aged less than 20 years having a catch-up immunisation.
- Refugees and humanitarian entrants aged 20 years and above.
In Victoria, free hepatitis B vaccine is provided for people who are at increased risk of infection, including:
Immunisation is also recommended, but not necessarily free, for people who are at increased risk of infection, including:
You May Like: Hepatitis B Can It Be Cured
What Laboratory Tests Are Available For Hepatitis B
Tests are available to detect the types of antigens used to identify the hepatitis B virus. The tests determine if the virus is present in the body tissue or blood. The amount of each type of antigen present indicates how advanced the disease is and how infective the individual has become.
Other tests are available to detect the body’s reaction to the viral infection or the body’s reaction to vaccination against the virus. These tests work by measuring the number of antibodies present in the blood.