> > > a Damaged Liver Is Easily Reversible < < <
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is a condition where fat accumulates in the liver. This condition is usually reversible and is caused by inflammation. In some cases, if the condition is not treated, fibrosis can develop, eventually leading to cirrhosis. Furthermore, nonalcoholic steato hepatitis refers to a fatty liver caused by a non-alcoholic condition. The onset of nonalcoholic steato hepatitic disease is related to a metabolic syndrome, a disorder wherein the body produces more and processes fat than it should.
Fatty liver is caused by an abnormal accumulation of TRIGLYCERIDES in the liver. The accumulated lipids are a sign of a fatty liver. This accumulation is a common sign of fatty hepatitis. The presence of these TRIGLYCERIDES can indicate a disorder of the liver. In addition to the lipid accumulation, fatty hepatitis is associated with inflammation of the liver, which leads to yellowing of the organ.
The condition is often inherited and affects people of all ages. It is commonly caused by improper diet and alcohol consumption. Symptoms of fatty hepatitis include viral hepatitis, obesity, and fatty liver. Fortunately, it is relatively easy to treat fatty liver and prevent complications by preventing the disease. The following fatty-liver overview provides more information on the disease and how it is managed. Difference Between Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver And Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
===> How To Cure A Fatty Liver In Just Days < < <
Can You Prevent Fatty Liver Disease
To prevent ALD:
- Drink in moderation: Thatâs one drink a day for women and men over 65 and up to two for men 65 and younger.
- Protect yourself from hepatitis C: This viral liver infection can make you more likely to get cirrhosis if you drink.
- Check before you mix meds and alcohol: Ask your doctor if itâs OK to drink alcohol with the prescription medications youâre taking. Read the warning label on over-the-counter meds. Donât drink when youâre taking products like acetaminophen, which can damage your liver when combined with alcohol.
For NAFLD and NASH, It boils down to making better choices:
- Eat healthy food. Choose a plant-based diet with lots of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats.
- Stay at a healthy weight. Lose weight if you need to. If your weight is healthy, work to maintain it by choosing a healthy diet and exercising.
- Exercise. Get a workout most days of the week. Talk to your doctor first if you haven’t been active in a while.
Show Sources
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: âDefinition & Facts of NAFLD & NASH,â âCirrhosis,â âSymptoms & causes of NAFLD & NASH,â âDiagnosis of NAFLD & NASH,â âTreatment for NAFLD & NASH,â
American Liver Foundation: âAlcohol-Related Liver Disease.â
Mayo Clinic: âNonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease,â âAlcoholic hepatitis.â
American Academy of Pediatrics: âNonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Diagnosis and Management.â
Cleveland Clinic: âAscites.â
How Do I Know If I Have Hepatitis C
As many as two million people may have hepatitis C and not realize it. Thats because even chronic hepatitis C patients may not have symptoms until late in the disease. You may find out you have the disease accidently through routine screenings for other illnesses.
There are symptoms of hepatitis C that may or may not show up, including:
- Abdominal pain
- Light colored stools
- Loss of appetite
Some patients with hepatitis C can develop a complication called fatty liver disease. Fatty liver disease can also occur as a singular instance of liver illness.
Read Also: Who Should Get Tested For Hepatitis C
What Are The Symptoms And Complications Of Autoimmune Hepatitis
Often, the symptoms of autoimmune hepatitis are minor. When symptoms do occur, the most common are fatigue, abdominal discomfort, aching joints, itching, jaundice , enlarged liver, nausea and spider angiomas on the skin. Other symptoms may include dark urine, loss of appetite, pale stools and absence of menstruation. More severe complications can include ascites and mental confusion. In 10%-20% of cases, autoimmune hepatitis may present with symptoms like an acute hepatitis.
When Should I See A Doctor And What Treatments Are Available
If youre having symptoms of these disorders, or if any lab tests come back showing you have hepatitis C or that your liver enzymes are elevated, it is time to see a doctor. A diagnosis of hepatitis C is confirmed through a blood test.
To confirm the diagnosis of fatty liver, your doctor may order an ultrasound or CT scan to get a view of the liver. Your doctor may also order a liver biopsy to see how far the disease has progressed.
While there is no medication specifically for fatty liver disease, treatment of hepatitis C has evolved over the last decade. Currently, hepatitis C can be treated with oral antiviral medications like Sofosbuvir with Velpatasvir. The typical regimen consists of daily oral medications for 8-12 weeks.
Also Check: What Is A Hepatitis Panel
Evaluation Of Liver Disease Based On Enzyme Levels
It is customary and useful to categorize liver diseases into three broad categories: Hepatocellular, in which primary injury is to the hepatocytes cholestatic, in which primary injury is to the bile ducts and infiltrative, in which the liver is invaded or replaced by non-hepatic substances, such as neoplasm or amyloid. Although there is a great deal of overlap in liver test result abnormalities seen in these three categories, particularly in cholestatic and infiltrative disorders, an attempt to characterize an otherwise undifferentiated clinical case as hepatocellular, cholestatic, or infiltrative often makes subsequent evaluation faster and more efficient. The AST, ALT, and alkaline phosphatase tests are most useful to make the distinction between hepatocellular and cholestatic disease.
The normal range for aminotransferase levels in most clinical laboratories is much lower than that for the alkaline phosphatase level. Accordingly, when considering levels of elevations, it is necessary to consider them relative to the respective upper limit of normal for each test compared. Consider a patient with an AST level of 120 IU/mL and an alkaline phosphatase of 130 IU/mL . This represents a hepatocellular pattern of liver injury because the AST level is three times the upper limit of normal, whereas the alkaline phosphatase level is only marginally higher than its upper limit of normal.
Table 2: Category of Liver Disease by Predominant Serum Enzyme Abnormality
Fatty Liver Disease Vs Cirrhosis: Know The Difference
Keeping a healthy digestive system is necessary for having great overall health, and one of the most important portions of the digestive tract is the liver. The liver is responsible for various life-sustaining processes, such as metabolizing fats, carbs, and proteins, producing bile, preserving glycogen and minerals, eliminating drugs and hormones, along with much more. However, when the liver is affected by disease, it can have a negative impact on your health. A couple of these illnesses are fatty liver disease and cirrhosis. At Metropolitan Gastroenterology Associates, our exceedingly experienced group of gastroenterologists in New Orleans, LA work with patients to better understand their health needs and identify any conditions.
What causes fatty liver disease?
Hepatic steatosis is a problem marked by the existence of fat cells within the liver. This condition has a couple of principal classifications: nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and alcoholic fatty liver disease . While AFLD is caused by an excess of drinking, NAFLD could be induced by obesity, type 2 diabetes, or high cholesterol, and it is the single most widespread kind of hepatic steatosis in the United States. It can be tough to recognize whether you have hepatic steatosis due to the fact that the problem usually does not lead to any notable symptoms, but it can be identified by our Metropolitan Gastroenterology Associates team with blood work, imaging tests, or sometimes a biopsy of the liver.
Recommended Reading: Purina Pro Plan Hepatic Cat
What Can Be The Symptoms Of Liver Diseases
Several symptoms may appear:
- Nausea, dizziness may cause vomiting.
- Pains in the upper part of the abdomen.
- A coloring of the skin in yellow, commonly called jaundice. This is the consequence of an excess of bilirubin in the blood and in the body.
- Fatigue and weakness: consider consulting a doctor if these relapses of fatigue persist.
- Fever: it can be coupled with pain in the abdomen. It is therefore important to take its temperature, because it can be an inflammation or an infection.
- Light colored stools: These are usually associated with a liver problem .
- Itching, due to the accumulation of bile under the skin.
- Bleeding and blues. Bleeding may be the cause of a protein deficiency caused by a dysfunction in the liver organ.
- Having these symptoms is not necessarily linked to a liver problem. It is up to your doctor to diagnose a liver infection.
Liver Icons ®Estherqueen999
Can Children Develop Fatty Liver Disease
Fatty liver disease is now becoming evident in children, due in large part to an alarming increase in childhood obesity. Currently:
- It is estimated that one Canadian child in 10 is overweight, a number that has almost tripled in the last decade.
- In Canada, fatty liver disease is thought to occur in one in five overweight or obese children.
- Fatty liver disease affects almost 3% of children and 2555% of obese children.
- Fatty liver disease can be found in children as young as two years of age.
- Fatty liver disease can also occur in children with healthy body weights but who may have larger waist circumferences than other children of the same weight and height.
- Fatty liver disease is more common in boys than girls and tends to occur in children of Caucasian or South Asian ancestry.
- Fatty liver disease is more common in children who have family members with fatty livers or type 2 diabetes.
- The cause of fatty liver disease is understood to be related to factors such as diets high in fatty foods and simple sugars and inactive lifestyles, particularly in children or adolescents who are overweight or obese.
In childhood, a fatty liver can be caused by a variety of disorders including those related to problems with copper metabolism , viral hepatitis, or a variety of autoimmune diseases. It is very important that your doctor makes sure that your child does not have these conditions first.
Waist-to-height ratio = WC
Height
You May Like: Hepatitis C Genotype 1b Treatment
The Typical Treatments Difference Between Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver And Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
If you have a fatty liver, you might be wondering what to do to treat it. Although the treatment options are limited, some of them can actually be beneficial. These include diets rich in raw vegetables, which contain many antioxidants. Eating these foods regularly also minimizes your risk of developing inflammation in the hepatic lining and the liver. Additionally, eating more vegetables helps you maintain a low glycemic index and develop a strong metabolically functioning organ.
Exercise is crucial in reducing the fat deposits in the liver. It can help with cholesterol levels and shed excess weight. Unlike other diseases, exercising does not require expensive equipment. Walking, jogging, dancing, cycling, and yoga are all effective exercises. In addition, its important to avoid alcohol, which is one of the leading causes of fatty hepatitis. This will not only improve your general health, but will allow your liver to heal and regenerate.
===> How To Cure A Fatty Liver In Just Days < < <
A high-carb diet can damage your liver and make it harder for it to perform its functions. The most common cause of liver disease is alcohol. It causes inflammation and damages the livers cells, and lowers the metabolism. As a result, the livers ability to perform its functions is weakened and eventually fails. A healthy diet will not only prevent the damage that alcohol can cause, but also help you recover from it.
Living With Fatty Liver Disease
If you are living with fatty liver disease, learn as much as you can about your condition and work closely with your medical team. Since many medications can harm your liver, always let all your health care providers know about any medications you are taking. These include OTC drugs, dietary supplements, and vitamins. Other ways to manage fatty liver disease include maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, getting regular exercise, and continuing to avoid alcohol.
You May Like: Need For Hepatitis C Screening Test
What Are The Symptoms Of Liver Disease
At the beginning of the spectrum of liver disease, it can be asymptomatic, says Lindenmeyer. Take hepatitis C, for example, she says: The majority of people who have hepatitis C have no idea, because they dont have symptoms, she says. This is why we recommend screening for hepatitis C for the baby boomer cohort, or everyone born between 1945 and 1965.
Early symptoms of cirrhosis may include feeling tired or weak, loss of appetite, weight loss, nausea and vomiting, and pain in the upper right side of your abdomen. With more advanced liver disease, as well as liver failure, symptoms include fluid accumulation in the abdomen or legs, yellowing of the skin or eyes, fatigue, mental confusion, and bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract, says Lindenmeyer.
Wait Is Hepatitis An Std Or Sti
Good question! Ultimately, it depends.
Autoimmune hepatitis and alcohol hepatitis cannot be transmitted through sexual activity. The other versions of viral hepatitis can be transmitted via sexual contact however, the risk level of transmission varies between the strains.
Hepatitis A: Hepatitis A is found in the poop and blood of an infected person. It is most commonly transmitted through contaminated food and water sources. For instance, if a chef with the virus has blood or feces on their hands and prepares your food, or if an unwashed/unpeeled fruit that was touched by a person with the virus makes its way into your mouth However, the virus can also be spread through needle sharing or dirty injectable drugs equipment. When it comes to sexual transmission of Hepatitis A, it can be shared through rimming or, any other sexual activity that results in fecal particles making their way into their mouth, whether intentionally or unintentionally .
Hepatitis B: Hepatitis B can be spread through most bodily fluids, including blood, semen, vaginal secretion, anal secretion, and breast milk. As such, it can be transmitted during breastfeeding, as well as through drug-injection equipment. “It can also be transmitted through most kinds of sexual contact,” says Dr. Pearlman. Actually, this is the strain of the virus most commonly dubbed an STI, she says.
Recommended Reading: Is There Now A Cure For Hepatitis C
Deterrence And Patient Education
Patients with alcoholic hepatitis need long-term follow-up. Many can benefit from attending AA or a similar abuse treatment program. Serology for viral hepatitis should be ordered and period surveillance for liver cancer is recommended.
Patients with alcoholic hepatitis should be immunized against hepatitis A, hepatitis B, influenza A virus, and pneumococcus.
What Causes Autoimmune Hepatitis
Your immune system normally attacks bacteria, viruses and other invading organisms. It is not supposed to attack your own cells if it does, the response is called autoimmunity. In autoimmune hepatitis, your immune system attacks your liver cells, causing long-term inflammation and liver damage. Scientists dont know why the body attacks itself in this way, although heredity and prior infections may play a role.
You May Like: What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis
Aasld/acg/aga Guidelines For Workup Of Nafld
Recommendations from a 2018 practice guideline from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases , the American College of Gastroenterology , and the American Gastroenterological Association regarding the workup of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease are below , with the updated 2018 AASLD recommendations incorporated.
The 2018 ACG guidelines on alcoholic liver disease provided the following guidance :
-
Liver function tests and ultrasonography are recommended for patients with harmful alcohol use and/or alcohol disorders.
-
Liver biopsy is not routinely recommended for diagnosis of alcoholic fatty liver disease, but it and noninvasive tools of fibrosis may be considered for diagnosis of steatohepatitis and/or liver fibrosis.
-
The Alcohol Use Disorders Inventory Test is validated for identifying individuals with alcohol use and dependence.
How A Liver Becomes Fatty
It is unclear how a liver becomes fatty. The fat may come from other parts of your body, or your liver may absorb an increased amount of fat from your intestine. Another possible explanation is that the liver loses its ability to change fat into a form that can be eliminated. However, the eating of fatty foods, by itself, doesnt produce a fatty liver.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Virus Nucleic Acid Amplification Technology
Factors Associated With Disease Susceptibility And Progression
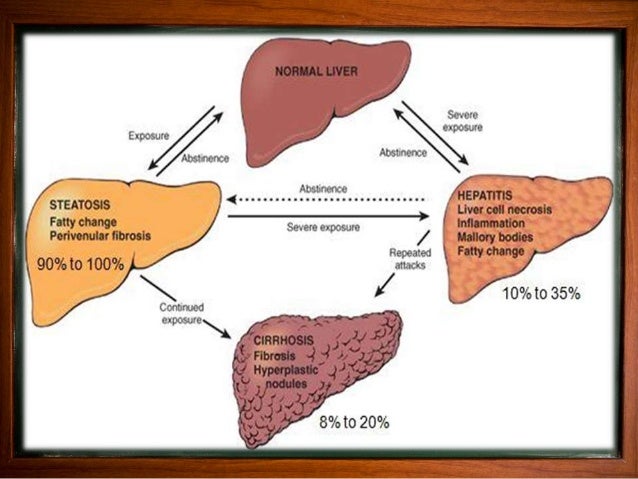
Simple hepatic steatosis occurs in most subjects who ingest excessive amounts of alcohol or food. However, only a small percentage of these individuals will develop advanced liver fibrosis or liver cirrhosis. Repeat liver biopsies at 4-year intervals in patients with ALD indicated that liver cirrhosis developed in 11% of the patients with simple hepatic steatosis and 39% of those with alcoholic hepatitis. A recent cohort study of patients with ALD estimated that the 5-year risk of cirrhosis was 6.9% for patients with simple hepatic steatosis and 16.0% for patients with steatohepatitis. Studies examining the histological course of NAFLD over a mean follow-up period of 3.2-13.8 years found that liver cirrhosis developed in 0%-8% of the patients without hepatic fibrosis and 11.3%-17.6% of those with hepatic fibrosis. A long-term follow-up study on simple hepatic steatosis observed that 22% of patients with ALD and 1.2% of those with NAFLD developed liver cirrhosis. A recent autopsy study found that the ratios of simple hepatic steatosis to steatohepatitis or liver cirrhosis were 2.33:1 in ALD patients and 3.60:1 in NAFLD patients. The differences in disease progression may be caused by environment-host interactions. Table contains the environmental and host factors that have been suggested by clinical and/or basic research. Recent advances in genetics have provided further insight into the host factors that can affect disease progression.