The Link Between Hepatitis And Liver Cancer
In medical terms, liver cancer is also known as hepatocellular carcinoma. The liver cells called hepatocytes make up 80 percent of your liver.
Scarring of your liver is usually caused by cirrhosis, which is recognized as the main risk factor for liver cancer. Cirrhosis can be caused by hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and viral hepatitis, alcohol abuse, autoimmune diseases, hemochromatosis, and other diseases that lead to chronic inflammation of the liver. Chronic hepatitis B or C infections may also lead to liver cancer.
Hpv And Cervical Cancer
A few types of HPV are the main causes of cervical cancer, which is the second most common cancer among women worldwide. Cervical cancer has become much less common in the United States because the Pap test has been widely available for many years. This test can show pre-cancer in cells of the cervix that might be caused by HPV infection. These pre-cancer cells can then be destroyed or removed, if needed. This can keep cancer from developing.
Doctors can now also test for HPV as part of cervical cancer screening, which can tell them if someone might be at higher risk for cervical cancer. Nearly all individuals with cervical cancer show signs of HPV infection on lab tests. Even though doctors can test people with a cervix for HPV, there is no treatment directed at HPV itself. But there is a vaccine that can help prevent it. If the HPV causes abnormal cells to start growing, these cells can be removed or destroyed.
See HPV and HPV Testing for more information on this topic.
Vi What’s The Evidence
Panel, AIHG. Hepatitis C guidance: AASLD-IDSA recommendations for testing, managing, and treating adults infected with hepatitis C virus.. Hepatology. vol. 62. 2015. pp. 932-54.
MMWR 2012. vol. 61. pp. 1945-1965.
Modi, AA,, Feld, JJ,, Park, Y. Increased caffeine consumption is associated with reduced hepatic fibrosis.. Hepatology. vol. 51. 2010. pp. 201
Gane, EJ,, Stedman, CA,, Hyland, RH. Nucleotide polymerase inhibitor sofosbuvir plus ribavirin for hepatitis C.. N Engl J Med. vol. 368. 2013. pp. 34
Jacobson, IM,, Gordon, SC,, Kowdley, KV. Sofosbuvir for hepatitis C genotype 2 or 3 in patients without treatment options.. N Engl J Med. vol. 368. 2013. pp. 1867
Scott, D., Holmberg,, M.D., M.P.H.,, Philip, R., Spradling,, M.D.,, Anne, C., Moorman,, M.P.H., and, Maxine, M., Denniston,, M.S.P.H.. Hepatitis C in the United States.. N Engl J Med. vol. 368. 2013. pp. 1859-1861.
No sponsor or advertiser has participated in, approved or paid for the content provided by Decision Support in Medicine LLC. The Licensed Content is the property of and copyrighted by DSM.
You May Like: Is There A Pill That Cures Hepatitis C
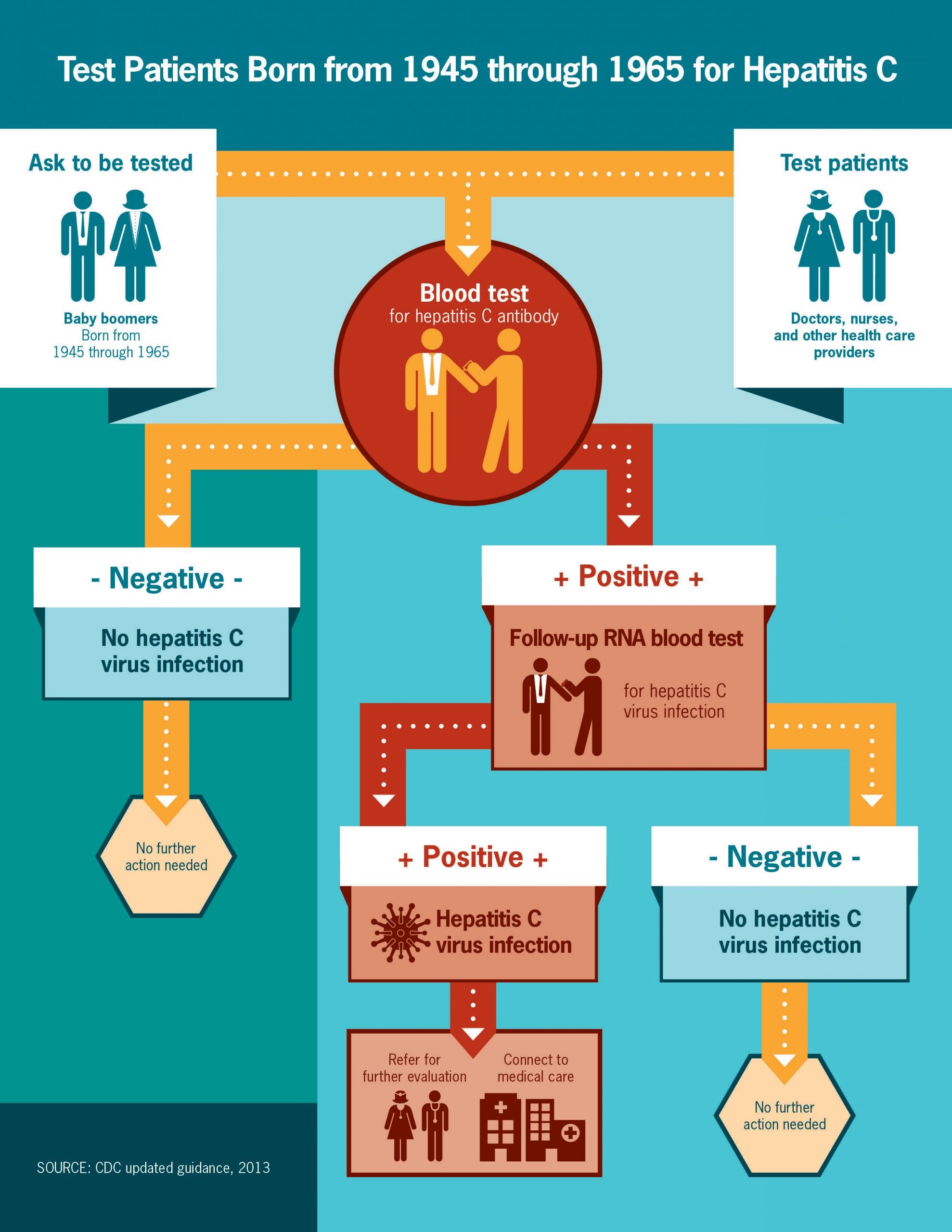
How Do I Know If I Have Hepatitis C Virus
Diagnosis of hepatitis C virus requires a blood test your doctor can order. Other blood tests can determine which subtype of HCV you have to better target your drug treatment, if needed. Your doctor will also want to know your viral load . In some patients, a liver biopsy is required to determine the level of damage.
Symptoms of chronic HCV may not appear for 2 to 3 decades after infection, so the disease may develop silently in your body for many years. This is the reason you should be tested for HCV infection, to start treatment if needed and to help protect your liver from damage.
The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends anyone 18 years or older be tested for hepatitis C virus at least once in their lifetime. Women should be tested for hepatitis C testing during each pregnancy. Some high risk groups may need more frequent testing, such as people who share drug preparation equipment and those on hemodialysis.
Learn More: Oral Hepatitis C Treatments: The Evolving Landscape
Hepatitis C And Cancer: What To Know
Hepatitis C is one of the leading causes of liver cancer. Its also linked to non-Hodgkins lymphoma, cancer in the bile ducts, and possibly pancreatic and head and neck cancers. And if you already have any other type of cancer, it can cause additional complications. Thats why MD Anderson tests all new patients for hepatitis C.
The good news is that if its found early and treated, hepatitis C can be cured, reducing your risk for cancer and other complications. Thats why hepatitis C screening and treatment is so important.
Unfortunately, an estimated 3.2 million people in the U.S. living with a chronic hepatitis C infection and dont know theyre infected. In many cases, thats because chronic hepatitis C doesnt any symptoms until the liver shows signs of damage.
We talked to Harrys Torres, M.D., associate professor of Infection Diseases and founding director of the hepatitis C clinic at MD Anderson, about what you should know about hepatitis C. Heres what he had to say.
Whats the link between hepatitis C and cancer?
There are two types of hepatitis C:
- acute or short-term hepatitis C, which goes away on its own in less than six months
- chronic hepatitis C, which requires treatment
The reason chronic hepatitis C causes multiple types of cancer is complex and not fully understood. The good news is that in most cases, hepatitis C infection can be cured with medication, and treatment can prevent many associated cancers.
Who is at risk for hepatitis C?
Read Also: New Drug To Cure Hepatitis C
What Causes Hepatitis C
The hepatitis C virus causes hepatitis C. The hepatitis C virus spreads through contact with an infected persons blood. Contact can occur by
- sharing drug needles or other drug materials with an infected person
- getting an accidental stick with a needle that was used on an infected person
- being tattooed or pierced with tools or inks that were not kept sterilefree from all viruses and other microorganismsand were used on an infected person before they were used on you
- having contact with the blood or open sores of an infected person
- using an infected persons razor, toothbrush, or nail clippers
- being born to a mother with hepatitis C
- having unprotected sex with an infected person
You cant get hepatitis C from
- being coughed or sneezed on by an infected person
- drinking water or eating food
- hugging an infected person
- shaking hands or holding hands with an infected person
- sharing spoons, forks, and other eating utensils
- sitting next to an infected person
A baby cant get hepatitis C from breast milk.18
How Can I Cover Medication Costs
New therapies called direct-acting antivirals are effective and can achieve cures of over 90%. Because these new therapies are very new, they remain very expensive. As such, drug coverage from both government and private companies may require that your liver disease has progressed to a certain stage before they are willing to cover the cost of these drugs.
Talk with your healthcare provider about financial support that may be available.
Below are useful resources when looking for financial assistance:Private health insurance or drug plansIf you have private health insurance or a drug plan at work, you may be able to have the medication paid through your plan. Please consult your private health insurance or drug plan provider to see if your drug is covered.
Publicly funded plansEach provincial and territorial government offers a drug benefit plan for eligible groups. Some are income-based universal programs. Most have specific programs for population groups that may require more enhanced coverage for high drug costs. These groups include seniors, recipients of social assistance, and individuals with diseases or conditions that are associated with high drug costs. For more details, please contact your provincial or territorial health care ministry, or click on the appropriate link below.
Yukon
Available Patient Assistance Programs for Hepatitis C treatment Holkira Pak Maviret
MerckCare Hepatitis C Program 1 872-5773 Zepatier
Don’t Miss: Is Hepatitis C And Hiv The Same
Whats The Outlook For Hep C Thats Developed Into Cirrhosis Or Liver Cancer
Hepatitis C can lead to cirrhosis, especially if left untreated. Without treatment, cirrhosis can lead to liver cancer and liver failure.
Treating cirrhosis and liver cancer typically requires a liver transplant. A transplant can cure both cancer and liver function impairment. But a transplant is only available for a small number of people.
Liver Cancer Risk Factors
A risk factor is anything that increases your chance of getting a disease, such as cancer. Different cancers have different risk factors. Some risk factors, like smoking, can be changed. Others, like a person’s age or family history, can’t be changed.
But having a risk factor, or even several risk factors, does not mean that you will get the disease. And some people who get the disease may have few or no known risk factors.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Get Rid Of Hepatitis B
What Are The Treatments For Hepatitis C
Treatment for hepatitis C is with antiviral medicines. They can cure the disease in most cases.
If you have acute hepatitis C, your health care provider may wait to see if your infection becomes chronic before starting treatment.
If your hepatitis C causes cirrhosis, you should see a doctor who specializes in liver diseases. Treatments for health problems related to cirrhosis include medicines, surgery, and other medical procedures. If your hepatitis C leads to liver failure or liver cancer, you may need a liver transplant.
V Patient Safety And Quality Measures
In addition to traditional risk groups, the latest guidelines from CDC recommend one-time testing for all persons born during 1945-1965 without prior ascertainment of HCV risk. Studies have shown that point of care testing in urban hospital emergency departments can also identify a substantial number of new cases. All newly detected HCV cases should be referred to a specialist for further evaluation and consideration for antiviral treatment.
All patients with chronic hepatitis C should be tested for hepatitis A and hepatitis B and if found negative, should be vaccinated against hepatitis A and B as per the standard protocol.
All patients with chronic hepatitis C should be counselled on the risk of transmission to minimize transmission to others:
-
Patients should be informed about the low but present risk for transmission with sex partners.
-
Sharing personal items that might have blood on them, such as toothbrushes or razors, can pose a risk to others.
-
Cuts and sores on the skin should be covered to keep from spreading infectious blood or secretions.
-
Donating blood, organs, tissue, or semen can spread HCV to others.
-
HCV is not spread by sneezing, hugging, holding hands, coughing, sharing eating utensils or drinking glasses, or through food or water.
-
Patients may benefit from a joining support group.
Also Check: Where Can I Get My Hepatitis B Vaccine
B Physical Examination Tips To Guide Management
-
Chronic hepatitis C is generally asymptomatic. Abnormalities on physical exam will be found only in patients with cirrhosis or extrahepatic involvement.
-
Findings suggestive of cirrhosis include jaundice, parotid gland enlargement, gynecomastia, firm nodular liver on palpation, ascites, abdominal collaterals, pedal edema, muscle wasting, palmar erythema, asterixis.
-
Findings of extrahepatic involvement i.e., cryoglobulinemia include palpable purpura .
Can Hepatitis C Be Treated
Yes, since 2010 enormous progress has been made in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C. New therapies called direct-acting antivirals are pills that act on the virus itself to eradicate it from the body, unlike older medicines like interferon injections which work by stimulating an immune response. These new treatments are very effective and can achieve cure rates of over 90%. In most situations now, there is no need for interferon, which was responsible for many of the side effects previously associated with HCV treatment. The new treatment combinations require shorter treatment durations , have reduced side effects and appear to be effective at all stages of the disease.
Because these new therapies are very new, they remain very expensive. As such, drug coverage from both government and private companies may require that your liver disease has progressed to a certain stage before they are willing to cover the cost of these drugs.
Your primary care physician may refer you to a specialist to determine whether you are eligible for treatment. A specialist will help you decide which drug therapy is best for you based on the severity of your liver disease, your virus genotype and whether or not you have been treated in the past.
Read Also: Hepatitis E Causes And Treatment
Keep Personal Items Personal
Any tools or implements that may have a bit of blood on them from infected people are potential sources of hepatitis B or C transmission. Toothbrushes, nail clippers, razors, needles, and washcloths may all contain trace amounts of blood that can transmit infection. Keep personal items such as these to yourself and never use personal items that belong to others.
Myth: Most People Infected With Hepatitis C Contracted The Virus During Unprotected Sex
In most cases hepatitis C is spread when blood from an infected person enters the body of an uninfected person. Before the virus was screened from the nations blood supply, hepatitis C was commonly spread through blood transfusions and organ transplants. Today most people become infected by sharing needles or other equipment to inject drugs.
Only about 1 to 2 percent are infected through unprotected sex, Nguyen said.
Also Check: What Kills The Hepatitis C Virus
Hepatitis C Linked To Increased Risk Of Liver Cancer Other Cancers
Researchers have long known that patients with hepatitis C are at increased risk of liver cancer. But a new study recently presented at the European Association for the Study of the Livers 50th International Liver Congress in Vienna, Austria, finds hepatitis C may also raise the risk of developing other cancers.
Hepatitis C is a condition characterized by inflammation of the liver, resulting from infection with the hepatitis C virus . It is estimated that in the US, around 3.2 million people have chronic HCV, although 70-80% of these are unaware they are infected as the condition may not present any symptoms.
Hepatitis C is primarily spread through contact with the blood of an infected person. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , most people become infected with HCV by sharing needles or other drug-injecting equipment.
Though less common, HCV can also be spread through having sexual contact with an infected person, sharing personal care items such as toothbrushes and razors that may have come into contact with the blood of an infected individual, or being born to a mother with hepatitis C.
It is well established that infection with HCV can increase a persons risk of liver cancer. The CDC state that 1-5 in every 100 people with HCV die from liver cirrhosis or liver cancer.
How To Reduce Your Risk
Dont share needles or other drug-use equipment. If you use intravenous drugs, take part in a needle exchange program.
Dont share personal care articles, such as razors, scissors, nail clippers or toothbrushes, with an infected person.
If you get a tattoo, body piercing or acupuncture, make sure all equipment is clean and sterile. Needles should always be new, not used, and never homemade.
Wear latex gloves whenever you might come into contact with someone elses blood or body fluids.
Read Also: Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection
Does Hiv Cause Cancer
Human immunodeficiency virus is a virus that affects the immune system, so the body is less able to get rid of other infections that can cause cancer. HIV increases the risk of Kaposis sarcoma, lymphoma, eye cancer, cervical cancer and anal cancer.
Anti-retroviral therapy can help keep HIV under control and reduce the risk of developing HIV-linked cancer.
People with HIV who develop acquired immune deficiency syndrome are at higher risk of cancer than those who dont develop AIDS.
Hepatitis B Virus And Hepatitis C Virus
Both HBV and HCV cause viral hepatitis, a type of liver infection. Other viruses can also cause hepatitis , but only HBV and HCV can cause the long-term infections that increase a persons chance of liver cancer. In the United States, less than half of liver cancers are linked to HBV or HCV infection. But this number is much higher in some other countries, where both viral hepatitis and liver cancer are much more common. Some research also suggests that long-term HCV infection might be linked with some other cancers, such as non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
HBV and HCV are spread from person to person in much the same way as HIV through sharing needles , unprotected sex, or childbirth. They can also be passed on through blood transfusions, but this is rare in the United States because donated blood is tested for these viruses.
Of the 2 viruses, infection with HBV is more likely to cause symptoms, such as a flu-like illness and jaundice . Most adults recover completely from HBV infection within a few months. Only a very small portion of adults go on to have chronic HBV infections, but this risk is higher in young children. People with chronic HBV infections have a higher risk for liver cancer.
For more information, see Liver Cancer.
You May Like: How Does Hepatitis C Affect The Liver
Fact: The Only Way To Find Out If You Have Hepatitis C Is To Be Tested
A blood test that looks for hepatitis C antibodies can determine if youve ever been infected with the virus.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that all baby boomers be tested for hepatitis C. If you were born between 1945 and 1965 and have not yet been screened for the virus, talk to your doctor about testing. Other people at high risk for hepatitis C include: current and past injection drug users, those who received a blood product before 1987, and people with known exposure to hepatitis C. For a comprehensive list of people at increased risk, visit the CDC website.