Treatment For Alcoholic Liver Disease
If you do not yet have cirrhosis, your liver may heal if you stop drinking alcohol. If you are alcohol dependent, you may need professional treatment to break your addiction.
If you have cirrhosis, your doctor will talk with you about how to manage your specific complications. At this stage, some patients need a liver transplant.
Racial And Age Differences In Incidence
Although no genetic predilection is noted for any particular race, alcoholism and alcoholic liver disease are more common in minority groups, particularly among Native Americans. Likewise, since the 1960s, death rates of alcoholic hepatitis and cirrhosis have consistently been far greater for the nonwhite population than the white population. The nonwhite male rate of alcoholic hepatitis is 1.7 times the white male rate, 1.9 times the nonwhite female rate, and almost 4 times the white female rate.
Alcoholic hepatitis can develop at any age. However, its prevalence parallels the prevalence of ethanol abuse in the population, with a peak incidence in individuals aged 20-60 years.
How Does Alcohol Effect The Liver
Drinking too much alcohol, either on a single occasion known as binge drinking or drinking a lot over time, can take a serious toll on your health and well-being. In addition to injuring the liver, alcohol has many effects on your body including:
- Lessening your ability to think clearly and move with coordination it can change your mood and behavior.
- Disrupting the processes involved in digestion, leading to malnutrition and weight loss.
- Weakening your immune system and the ability to fight infections. Increasing your risk of developing certain cancers including cancers of the colon, liver, esophagus, mouth, and breast .
Also Check: Medicine To Treat Hepatitis C
How Is Alcoholic Liver Disease Diagnosed
Your healthcare provider will do a complete health history and physical exam. Other tests used to diagnose alcohol-induced liver disease may include:
- Blood tests. Including liver function tests, which show whether the liver is working the way it should.
- Liver biopsy. This involves removing small tissue samples from the liver with a needle or during surgery. These samples are checked under a microscope to find out the type of liver disease.
- Ultrasound. This test uses high frequency sound waves to create a picture of the organs.
- CT scan. This imaging test uses X-rays and a computer to produce images of the body. A CT scan shows detailed images of any part of the body, including the bones, muscles, fat, and organs. CT scans are more detailed than general X-rays.
- MRI. MRI uses a magnetic field, radio frequency pulses, and a computer to make detailed pictures of internal body structures. Sometimes injecting dye into a vein is used to produce images of body parts. The dye helps show the liver and other organs in the abdomen .
Does Alcohol Cause Liver Disease
Yes, but alcohol is only one of the many known causes of liver disease. The risk of developing liver disease depends on how much you drink and over how long a period.
Other known causes of liver disease include:
- Viruses
- Reactions to drugs and chemicals
Scientists are still investigating the causes for the most serious liver diseases.
Don’t Miss: Can Chronic Hepatitis B Be Cured
What Is Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A is a viral infection that causes liver inflammation and damage. Inflammation is swelling that occurs when tissues of the body become injured or infected. Inflammation can damage organs.
Viruses invade normal cells in your body. Many viruses cause infections that can be spread from person to person. The hepatitis A virus typically spreads through contact with food or water that has been contaminated by an infected persons stool.
Hepatitis A is an acute or short-term infection, which means people usually get better without treatment after a few weeks. In rare cases, hepatitis A can be severe and lead to liver failure and the need for an emergency liver transplant to survive. Hepatitis A does not lead to long-term complications, such as cirrhosis, because the infection only lasts a short time.
You can take steps to protect yourself from hepatitis A, including getting the hepatitis A vaccine. If you have hepatitis A, you can take steps to prevent spreading hepatitis A to others.
How Long Does It Take For Alcoholic Hepatitis To Resolve
The length of time it takes to recover depends on how severe the case of alcoholic hepatitis is, and how early treatment begins. Within two years6 many patients show significant improvement, and appear to have normal liver function. For those with mild cases, recovery time can be quicker.
However, these improvements are dependent on patients continuing to abstain from alcohol, and some complications can remain for the long term. If youve recovered, you should continue to have yourself checked regularly for liver cancer. And if youve developed any cirrhosis of the liver from hepatitis, that damage will be permanent.
You May Like: How Do People Catch Hepatitis B
Facts About Liver Disease
According to the American Liver Foundation, at least 10 percent of Americans have some form of liver disease. Additionally, the American Liver Foundation reports that hepatitis C, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and liver cancer are all occurring with greater incidence.
Alcohol abuse, hepatitis viruses, and obesity all considered highly preventable are the leading three risk factors for death from liver disease. Other causes of liver disease include cancer, autoimmune diseases, and genetic or metabolic disorders.
Sadly, symptoms of many liver disorders do not manifest until serious sometimes irreversible damage has occurred. A population-based study found that 69 percent of adults with cirrhosis were unaware of having liver disease. Another study found that Hispanic Americans and African Americans are at greater risk for developing liver disease than Caucasians.
Hispanic Americans have greater risk due to heavier drinking and higher prevalence of obesity and diabetes, while African-Americans have a higher prevalence of obesity, diabetes, and hepatitis B or C.
Help For Signs Of Early Liver Disease
The recommended daily limits for alcohol consumption are no more than one drink per day for women and two for men.
If you or someone you know regularly exceeds these recommended daily limits, or is experiencing some early signs of liver disease, it is important to intervene early.
Medical treatment for addiction is vital. Quitting alcohol is a formidable challenge and withdrawing from alcohol at home can be life-threatening.
Getting a professional intervention early on is a persons best chance of reversing the strain alcohol puts on the liver. Let us help today.
This was originally posted on October 19, 2016 and was updated and republished February 11, 2019
Don’t Miss: How Do You Know If You Have Hepatitis A
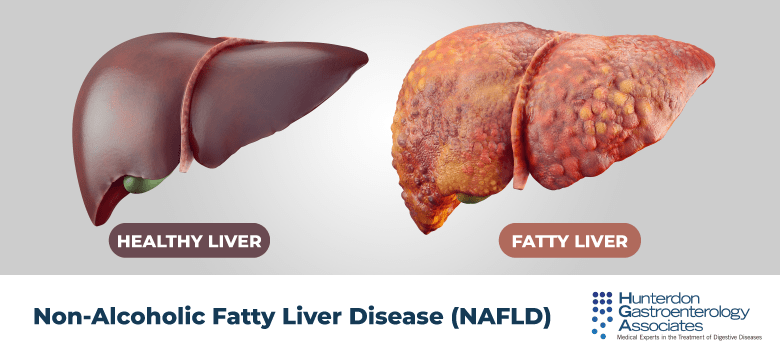
What Is Fatty Liver Disease
Fatty liver disease means you have extra fat in your liver. You might hear your doctor call it hepatic steatosis.
Heavy drinking makes you more likely to get it. Over time, too much alcohol leads to a buildup of fat inside your liver cells. This makes it harder for your liver to work.
But you can get fatty liver disease even if you donât drink a lot of alcohol.
Willowbrook State School Experiments
A New York University researcher named Saul Krugman continued this research into the 1950s and 1960s, most infamously with his experiments on mentally disabled children at the Willowbrook State School in New York, a crowded urban facility where hepatitis infections were highly endemic to the student body. Krugman injected students with gamma globulin, a type of antibody. After observing the temporary protection against infection this antibody provided, he then tried injected live hepatitis virus into students. Krugman also controversially took feces from infected students, blended it into milkshakes, and fed it to newly admitted children.
Also Check: Can Hepatitis C Be Passed From Mother To Child
Risk Factors For Alcohol Related Liver Disease
Not everyone who drinks heavily develops ALD. While the amount of alcohol and the length of time as a heavy drinker are the key risk factors, additional forces impact the outcome. They are:
- Obesity/Overweight: Carrying extra weight increases the risk of liver disease because fat builds up in the liver. The fat cells secrete acids which cause a reaction that destroys healthy cells in the liver, leading to scarring. Add alcohol to the mix and the combined effect adds additional liver damage.
- Malnutrition: Often people who drink heavily, eat poorly. They also may have trouble absorbing nutrients because alcohols toxic byproducts make it difficult to break down food. The lack of nutrients contributes to liver cell damage.
- Genetic component: How a body metabolizes alcohol is influenced by genetics. If certain enzymes are missing, that can affect the risk of developing ALD.
- Demographic influencers: Rates of alcohol cirrhosis are higher in African-American and Hispanic males than they are in Caucasian males. Women are more susceptible than men to the impact of alcohol because they become more impaired than men after drinking equal amounts.
- Having viral hepatitis, especially hepatitis C: Adding alcohol to a liver already taxed by hepatitis increases the risk of developing liver disease, as well as liver cancer.
Alcoholic Hepatitis Symptoms And Complications

Alcoholic hepatitis symptoms are variable depending on how much damage has been done to your liver. If your case is mild, you may not even know you have it. The more damage there is, the more youll experience these initial symptoms:
- A loss of appetite
- Jaundice or icterus which is the yellowing of skin or eyes
- Negative changes in mental state, including confusion
Read Also: Can You Have Hepatitis C And Not Know It
The Spectrum Of Alcohol
Alcohol use can lead to several different types of liver problems:
-
Alcohol-associated fatty liver disease is a condition in which the liver accumulates excess fat deposits and is typically the earliest sign of alcohol-induced liver disease. It can be thought of as the precursor to cirrhosis. It usually doesnt cause any symptoms, and is even reversible within a couple weeks if alcohol consumption is stopped in this stage.
-
Alcoholic cirrhosis is the result of ongoing liver damage over time. It is a more serious, permanent type of liver damage that progresses from fatty liver disease. It can lead to other serious conditions, such as liver cancer and liver failure.
-
Alcoholic hepatitis is a condition in which the liver gets suddenly inflamed. While the above two conditions are long-term in nature, AH occurs more quickly. It can vary in severity but is treatable. This is the condition we will discuss here.
Role Of The Immune System
Active alcoholic hepatitis often persists for months after cessation of drinking. In fact, its severity may worsen during the first few weeks of abstinence. This observation suggests that an immunologic mechanism may be responsible for perpetuation of the injury. The levels of serum immunoglobulins, especially the immunoglobulin A class, are increased in persons with alcoholic hepatitis. Antibodies directed against acetaldehyde-modified cytoskeletal proteins can be demonstrated in some individuals. Autoantibodies, including antinuclear and antisingle-stranded or antidouble-stranded DNA antibodies, have also been detected in some patients with alcoholic liver disease.
B and T lymphocytes are noted in the portal and periportal areas, and natural killer lymphocytes are noted around hyalin-containing hepatocytes. Patients have decreased peripheral lymphocyte counts with an associated increase in the ratio of helper cells to suppressor cells, signifying that lymphocytes are involved in a cell-mediated inflammatory process. Lymphocyte activation upon exposure to liver extracts has been demonstrated in patients with alcoholic hepatitis. Immunosuppressive therapy with glucocorticoids appears to improve survival and accelerate recovery in patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B E Antibody Reactive Means
Mortality And Survival Rates
For alcoholic hepatitis, the percentage of people who are expected to die within the first 30 days after diagnosis is difficult to predict. The number can range from 0% to 50% and is dependent on how advanced the disease is at the time of diagnosis.
If you have alcoholic liver disease, your healthcare providers will try to predict your short-term prognosis. Different scoring models can be used to predict each person’s prognosis.
The MELD system is an example of a scoring system for people with liver disease. It is often used to identify liver transplant candidates. It is a calculation that includes a person’s results on various lab tests of liver function.
Scoring works like this:
- People who have a MELD score of less than 9 have a 1.9% to 3.7% risk of dying within the first three months.
- People who have a MELD score of 10 to 19 have a 6% to 20% risk of dying within the first three months.
- People who have a MELD score of 20 to 29 have a 19.6% to 45.5% risk of dying within the first three months.
- People who have a MELD score of 30 to 39 have a 52.6% to 74.5% risk of dying within the first three months.
- People who have a MELD score of over 40 have a 71% to 100% risk of dying within the first three months.
People with alcoholic liver disease who stop drinking have a much better chance of long-term survival. Overall, the five-year survival rate is 60% for those who stop drinking and less than 30% for those who don’t.
Symptoms And Warning Signs
If you’re worried you might have alcoholic liver disease, see a doctor right away. A variety of factors can affect your symptoms, including:
- Pre-existing conditions
- Disease progression
In the early stages, you may not have any symptoms. If you do have symptoms, they may seem to worsen after a period of heavy drinking.
The three main categories of symptoms are:
- Digestive problems: This includes abdominal swelling, dry mouth, and bleeding from enlarged veins in your esophagus. The esophagus is the tube that connects your throat to your stomach.
- Skin issues: This can include yellowing of the skin, red spider-like veins, and redness on your feet.
- Brain and nervous system problems: This may include memory problems, numbness in extremities, and fainting.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedule For Adults
Complications Of Alcoholic Hepatitis
Alcoholic hepatitis can cause many complications within your body as the liver has so many functions. When the liver doesnt work properly, the symptoms can turn into scary health issues. These complications can be life threatening or at the very least, quite uncomfortable. Portal hypertension is one of the complications associated with liver damage, which can cause symptoms like:
- Fluid build up in the abdomen
- Confusion or changes in behavior caused by a poison build up in the body that would normally be broken down or removed by the liver
- Bleeding within the esophagus or stomach
- The spleen enlarges
- Liver or kidney failure
Further complications can arise such as multi-organ conditions that are non-liver conditions.
Alcohol hepatitis can lead to hepatic encephalopathy where toxins filtered out by the liver stay in your blood. These toxins can cause brain damage and possibly lead to a coma. Alcohol hepatitis symptoms are sometimes not present for a long time which can lead to complications such as liver failure or death. The symptoms will vary for each person and will change during periods of heavy drinking if the disease is severe.
Assessment Of Disease Stage
Following a differential diagnosis, the assessment of disease severity and stage is vital for optimal patient management. Although a liver biopsy is the gold standard, this procedure is invasive and costly and is accompanied by patient discomfort, which affects its feasibility. Non-invasive methods for assessing the stage of fibrosis have been recently developed, including fibrosis indices and transient elastography. Many fibrosis indices have been devised based on clinical parameters, and the usefulness of these indices has been tested in patients with chronic liver diseases. The AST/platelet ratio index , the FIB-4 index, and the FibroTest have been validated for use in assessing the fibrosis stage in patients with both ALD and NAFLD. The AUROC of the FibroTest for the diagnosis of liver cirrhosis in patients with ALD was 0.95 , while a more recent study found that the AUROCs of the APRI, the FIB-4 index, and the FibroTest for liver cirrhosis in patients with ALD were 0.67, 0.80, and 0.94 , respectively. In patients with NAFLD, the AUROCs of the APRI and the FIB-4 index for the diagnosis of advanced fibrosis were 0.73 and 0.80 , respectively, and in another study, the AUROCs for the APRI and the FIB-4 index were 0.82 and 0.87 , respectively. Another study in patients with NAFLD indicated that the AUROCs of the FibroTest for the diagnosis of advanced fibrosis in two independent cohorts were 0.92 and 0.81, respectively.
Recommended Reading: Is There A Pill That Cures Hepatitis C
How Is It Diagnosed
- Medical history. Your doctor may ask about your medical past to see if thereâs reason to believe you may have alcohol-related liver problems.
- Questionnaire. Theyâll ask you questions to determine if your drinking has become a problem.
- Blood tests. These will check your liver enzymes. Abnormally high levels are a sign of liver damage.
- Liver biopsy. Your doctor may request one in addition to blood tests.
Who Should Be Vaccinated
Children
- All children aged 1223 months
- All children and adolescents 218 years of age who have not previously received hepatitis A vaccine
People at increased risk for hepatitis A
- International travelers
- Men who have sex with men
- People who use or inject drugs
- People with occupational risk for exposure
- People who anticipate close personal contact with an international adoptee
- People experiencing homelessness
People at increased risk for severe disease from hepatitis A infection
- People with chronic liver disease, including hepatitis B and hepatitis C
- People with HIV
Other people recommended for vaccination
- Pregnant women at risk for hepatitis A or risk for severe outcome from hepatitis A infection
Any person who requests vaccination
There is no vaccine available for hepatitis C.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Get Hepatitis A And B