Ways You Wont Spread Hepatitis C
There are some ways in which you wont spread HCV, though. Go ahead and let your significant other have a bite of your sandwich or dessert. According to the CDC, hepatitis C isnt spread by sharing silverware or drinking glasses, or through water or foods. Showing affection by holding hands, hugging, or kissing is also safe, Lee says. And although germs from sneezing or coughing might cause you to get a cold, they wont give you hepatitis C.
Getting Tested For Hepatitis C
Seek medical advice if you have persistent symptoms of hepatitis C or there’s a risk you’re infected, even if you do not have any symptoms.
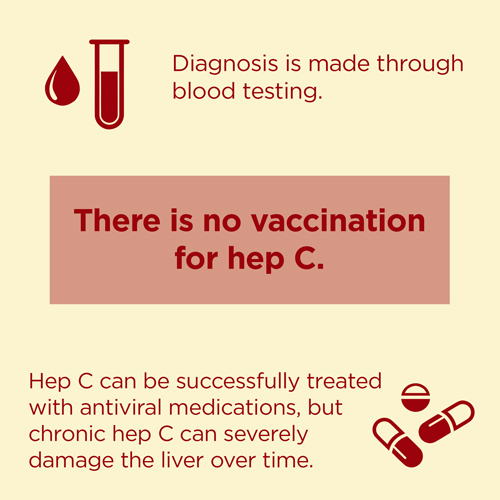
A blood test can be carried out to see if you have the infection.
GPs, sexual health clinics, genitourinary medicine clinics or drug treatment services all offer testing for hepatitis C.
Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent or limit any damage to your liver, as well as help ensure the infection is not passed on to other people.
How Can You Prevent Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B: Vaccination is the best way to prevent all of the ways that hepatitis B is transmitted. People with HIV who do not have active HBV infection should be vaccinated against it. In addition to the 3-dose series of hepatitis B vaccine given over 6 months, as of 2017, there is a 2-dose series given over 1 month.
Hepatitis C: No vaccine exists for HCV and no effective pre- or postexposure prophylaxis is available. The best way to prevent hepatitis C infection is to never inject drugs or to stop injecting drugs by getting into and staying in drug treatment. If you continue injecting drugs, always use new, sterile needles or syringes, and never reuse or share needles or syringes, water, or other drug preparation equipment.
You May Like: Is Hepatitis A Sexually Transmitted
Sweat May Spread Hepatitis B Virus
2 Min Read
NEW YORK – Findings from a study of Olympic wrestlers indicate that hepatitis B virus is found in the sweat of infected individuals, and so sweating might be a way that the virus could be passed between participants in contact sports.
Bleeding wounds and mucous membranes have been implicated in hepatitis B transmission during contact sports, but until now no study had looked to see if sweat carries the virus.
Dr. S. Bereket-Yucel, from Celal Bayar University in Izmir, Turkey, tested for DNA of the hepatitis B virus in blood and sweat samples from 70 male Olympic wrestlers.
The results indicated that 9 of the wrestlers had the hepatitis B virus in their blood. However, these were deemed occult infections because no antibodies to the virus were detected in any of the wrestlers, according to the investigators report released Thursday ahead of print by the British Journal of Sports Medicine.
In eight of the nine participants whose blood tested positive, DNA for hepatitis B was also detected in sweat.
Based on these results, Evidence is emerging that the incidence of occult HBV in Olympic wrestling is higher than expected and that transmission of HBV may also occur through sweat, the researcher concludes.
The advice of sports organizations about HBV testing should be changed, they recommend, making it obligatory for all participants involved in contact sports and playing under adult rules to be vaccinated against hepatitis B.
Complications Of Hepatitis C
If the infection is left untreated for many years, some people with hepatitis C will develop scarring of the liver .
Over time, this can cause the liver to stop working properly.
In severe cases, life-threatening problems, such as liver failure, where the liver loses most or all of its functions, or liver cancer, can eventually develop.
Treating hepatitis C as early as possible can help reduce the risk of these problems happening.
Don’t Miss: Good Food For Hepatitis C
How Do You Know If You Have Hepatitis B
Signs and symptoms can vary, in particular by the age of the individual. Many individuals may not show symptoms . When symptoms develop, they include fever, joint pain, abdominal pain, fatigue, lack of appetite, nausea, vomiting, dark urine, clay-coloured bowel movements, or jaundice.
Most infections are asymptomatic or mild. Occasionally, people with serious cases of hepatitis B require hospitalization. A very small proportion of these patients develop a critical form of the disease called “fulminant” hepatitis B. This condition results from a sudden breakdown of liver function.
Hiv And Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C Coinfection
Hepatitis B and hepatitis C are liver infections caused by a virus. Because these infections can be spread in the same ways as HIV, people with HIV in the United States are often also affected by chronic viral hepatitis.
Viral hepatitis progresses faster and causes more liver-related health problems among people with HIV than among those who do not have HIV. Liver disease, much of which is related to HBV or HCV, is a major cause of non-AIDS-related deaths among people with HIV.
Given the risks of hepatitis B or hepatitis C coinfection to the health of people living with HIV, it is important to understand these risks, take steps to prevent infection, know your status, and, if necessary, get medical care from someone who is experienced in treating people who are coinfected with HIV and HBV, or HIV and HCV.
Recommended Reading: How Do People Get Hepatitis
What Is The Hepatitis C Virus
The hepatitis C virus was first identified in 1989. It is a linear, single-stranded, encapsulated RNA virus that consists of 9,500 nucleotides. The HCV belongs to the Flaviviridae family.According to the World Health Organization , about 71 million people worldwide are chronically ill with hepatitis C. This corresponds to one per cent of the worlds population. Hepatitis C is common all over the world, but the eastern Mediterranean region is the most strongly affected. Humans are the only known host of hepatitis C. So far, no effective vaccination against it has been developed.
How Is Monitoring Done After Treatment For Hepatitis C
Once patients successfully complete treatment, the viral load after treatment determines if there is an SVR or cure. If cure is achieved , no further additional testing is recommended unless the patient has cirrhosis. Those who are not cured will need continued monitoring for progression of liver disease and its complications.
While cure eliminates worsening of fibrosis by hepatitis C, complications may still affect those with cirrhosis. These individuals still need regular screening for liver cancer as well as monitoring for esophageal varices that may bleed.
Because hepatitis B co-infection may reactivate or worsen even after treatment for HCV, monitoring for hepatitis symptoms may be needed after the end of therapy.
Also Check: My Husband Has Hepatitis B Can I Get It
What Medications Cure Hepatitis C Infection
Interferons, for example, Roferon-A and Infergen, and pegylated interferons such as Peg-IntronT, Pegasys, were mainstays of treatment for years. Interferons produced sustained viral response of up to 15%. Later, peglatedll forms produced SVR of 50%-80%. These drugs were injected, had many adverse effects, required frequent monitoring, and were often combined with oral ribavirin, which caused anemia. Treatment durations ranged up to 48 weeks.
Direct-acting anti-viral agents are antiviral drugs that act directly on hepatitis C multiplication.
Significance For Infections In Hospitals And In The Outpatient Sector:
It is advisable to maintain basic hygiene. Additional hygiene measures should be taken. These include wearing gloves during surgical/invasive procedures, use of instruments that minimise the risk of injury, use of protective clothing, protective goggles, visor or mouth and nose protection if necessary. The avoidance of needle puncture injuries is also of great importance here. Hepatitis C virus must be reported in Germany, Switzerland and Austria.
Read Also: Can Hepatitis B Be Treated
What Are The Side Effects Of Treatments For Hepatitis C Infection
Side effects of interferon or pegylated interferon
- The most common side effects of interferon or pegylated interferon include fever, flu-like symptoms, and depression. Patients must be monitored closely for depression. Risk of suicide is a reason to avoid interferons.
- Interferons also reduce white blood cell and/or red blood cell counts . This may cause increased susceptibility to infection. Interferons also increase the risk of certain cancers. Death rarely occurs as a result of therapy, but may occur from progression of liver failure in patients with advanced cirrhosis.
Side effects of ribavirin
- Ribavirin most commonly causes anemia due to destruction of red blood cells . This can be severe enough that people with heart disease may suffer a heart attack from insufficient blood flow, so people with heart disease should not receive this drug. Anemia improves with a reduction in the dose of ribavirin. Injected growth factor that stimulates the production of red blood cells often is used to improve the anemia associated with ribavirin. Ribavirin also accumulates in the testicles and ovaries and causes birth defects in animals. Although no birth defects have been reported in humans, both men and women should use contraceptive measures to avoid pregnancy during and for at least six months after ribavirin treatment.
Side effects of DAAs
- The most common and significant side effects of boceprevir , sofosbuvir , and ledipasvir/sofosbuvir include
- fatigue ,
Where Is The Hepatitis B Virus Found And How Is It Transmitted

Blood is the major source of the hepatitis B virus in the workplace. It can also be found in other tissues and body fluids, but in much lower concentrations. The risk of transmission varies according to the specific source. The virus can survive outside the body for at least 7 days and still be able to cause infection.
Recommended Reading: Best Treatment For Hepatitis C
Hiv Treatment And Prevention
Simple, effective treatments for HIV are widely available in Australia. In addition to protecting the health and wellbeing of people living with HIV, these treatments significantly reduce the risk of HIV transmission. Almost all people on HIV treatments have very low levels of virus in their body. This is called having an undetectable viral load. There is no risk of HIV transmission from a person with an undetectable viral load. This is sometimes referred to as undetectable equals untransmissible, or U=U.
For people who do not have HIV, but may be at higher risk of it, affordable medication is available that is more than 99 per cent effective at preventing HIV. Known as PrEP , this medication is available through the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme from your regular GP.
What Occupations Have Increased Risk Of Hepatitis B
In general, occupational groups with increased risk include:
- Health-care workers repeatedly exposed to blood or blood products or those who are at risk of needlestick injury.
- Pathologists, laboratory personnel, or embalmers.
- Dentists, dental assistants, and dental hygienists.
- Certain staff members of institutions for the developmentally handicapped.
- Staff of institutions where workers may be exposed to aggressive, biting residents.
Travellers to regions with intermediate or high rates of endemic HBV infection may also consider being vaccinated.
Recommended Reading: Medicine To Treat Hepatitis C
Hepatitis: How Can I Protect Myself From Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is a liver disease caused by the hepatitis B virus . The virus interferes with the functions of the liver and causes pathological damage. A small percentage of infected people cannot get rid of the virus and become chronically infected these people are at higher risk of death from cirrhosis of the liver and liver cancer.
HBV is spread by contact with blood or body fluids of an infected person the same way as the human immunodeficiency virus . However, HBV is 50 to 100 times more infectious than HIV.
The main ways of getting infected with HBV are:
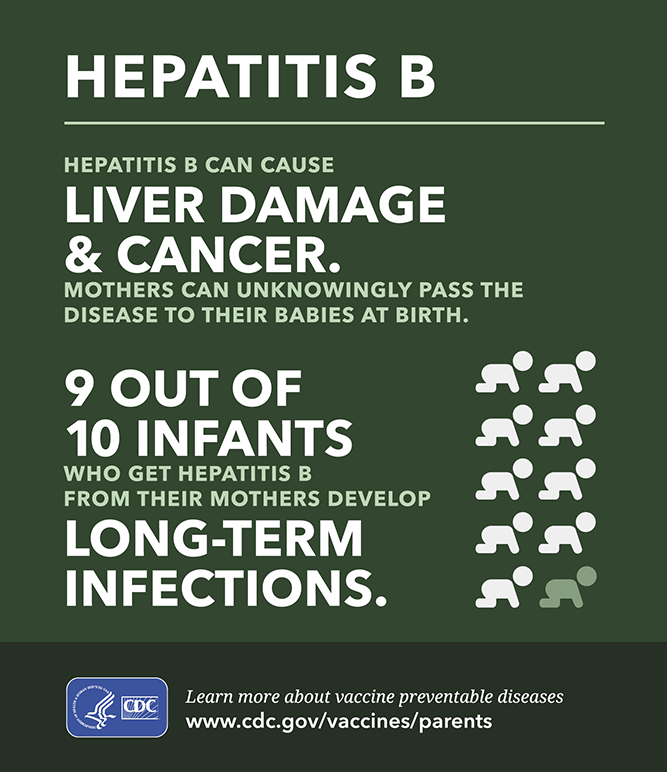
- from mother to baby at the birth
- from child-to-child
- unsafe injections and transfusions
- unprotected sexual contact.
Worldwide, most infections occur from mother-to-child, from child-to-child , and from reuse of unsterilized needles and syringes. Before the widespread use of the hepatitis B vaccine, almost all children in developing countries used to become infected with the virus.
What Type Of Doctor Treats Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is treated by either a gastroenterologist, a hepatologist , or an infectious disease specialist. The treatment team may include more than one specialist, depending on the extent of liver damage.Surgeons who specialize in surgery of the liver, including liver transplantation, are part of the medical team and should see patients with advanced disease early, before the patient needs a liver transplant. They may be able to identify issues that need to be addressed before surgery can be considered. Other persons who can be helpful in managing patients include dietitians to consult on nutritional issues and pharmacists to assist with management of drugs.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Viral Load Quest
How Is Hepatitis C Diagnosed
Blood tests for hepatitis C
There are several blood tests for the diagnosis of hepatitis C infection. Blood can be tested for antibody to hepatitis C . It takes about 8-12 weeks on average, and up to 6 months, for antibodies to develop after the initial infection with hepatitis C, so screening for antibodies may miss a few newly infected individuals. Having antibodies is not an absolute indication of active, multiplying hepatitis C virus, but if the antibody test is positive , the statistical probability of active infection is greater than 99%.
Several tests are available to measure the amount of hepatitis C virus in a person’s blood . The hepatitis C virus’s RNA can be identified by a type of test called polymerase chain reaction that detects circulating virus in the blood as early as 2-3 weeks after infection, so it can be used to detect suspected acute infection with hepatitis C early infection. It also is used to determine whether active hepatitis is present in someone who has antibodies to hepatitis C, and to follow the viral load during treatment.
Blood tests are also performed to identify the genotypes of HCV. Genotypes respond differently to different treatment, so this information is important in selection of the most appropriate treatment regimen.
Estimation of liver fibrosis using blood tests also is quite reliable in diagnosing clinically significant scarring these include FIB-4, FibroSure, Fibrotest, and aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index .
Who Is At High Risk And Should Be Tested For Hepatitis C Infection
The U.S. Preventive Health Services task force recommends that all adults born between 1945 and 1965 be tested once routinely for hepatitis C, regardless of whether risk factors for hepatitis C are present. One-time testing also is recommended for:
- People who currently inject drugs or snort drugs, or ever did so, even once many years previously
- People with persistently elevated alanine aminotransferase level, a liver enzyme found in blood
- People who have HIV infection
- Children born to HCV- or HIV-infected mothers
- People who were ever on long-term hemodialysis
- People who got a tattoo in an unregulated setting, such as prison or by an unlicensed person
- People who received clotting factor produced before 1987
- People who received transfusions or organ transplants before July 1992, or who were notified that they received blood from a donor who later tested positive for hepatitis C infection
- Health care, emergency medical, and public safety workers after a needlestick, eye or mouth exposure to hepatitis C-infected blood
People who may have been exposed to hepatitis C in the previous 6 months should be tested for viral RNA load rather than anti-HCV antibody, because antibody may not be present for up to 12 weeks or longer after infection, although HCV RNA may be detectable in blood as soon as 2-3 weeks after infection.
You May Like: Early Signs Of Hepatitis C And Treatments To Know
How Hiv And Hepatitis B And C Are Spread
HIV damages the immune system and can cause acquired immune deficiency syndrome if untreated. Hepatitis B and C are viruses that can cause serious damage to the liver. To become infected with HIV or hepatitis B or C while playing sports, body fluids such as blood from an infected person would need to enter your bloodstream through:
- a significant abrasion on your skin
- a bleeding wound
- your mucous membranes .
HIV and hepatitis B are spread in similar ways. Because both HIV and hepatitis B are found in blood, semen and vaginal fluids, these infections are transmitted:
- from mother to baby during childbirth or breastfeeding.
HIV cannot be transmitted by a person who is on treatment and who has low levels of virus in their body . In other words, there is no risk of HIV transmission through exposure to blood during sport from a person has an undetectable viral load.
Hepatitis C is spread through blood-to-blood transmission only, but is not thought to be sexually transmitted unless blood is present.
Protecting Everyone Involved In Sport Against Hiv And Hepatitis
Consult your sporting organisations infection control policies. Simple and inexpensive procedures can prevent the spread of HIV, hepatitis B and C, including:
- Remember to cover all pre-existing wounds before starting a game.
- Wear protective gloves when giving first aid to bleeding players.
- If someones eyes have been splashed with blood with the eyes open, rinse the area gently but thoroughly with water or normal saline, rinsing away from the nose.
- If blood gets in your mouth spit it out and rinse your mouth with water several times.
- Standard practice is to stop play if a player is bleeding and allow them to return to play only after bleeding is controlled and the wound is properly covered.
- Bandage any wounds that occur, and properly clean any playing surfaces and change any clothes exposed to blood before play restarts.
- Have your own drink bottle and towel, mouth guard and other personal items, including razors, to reduce the possibility of small amounts of blood-to-blood transmission.
- If you are concerned about potential infection, contact a doctor or health information line for further advice.
If a player is injured while playing sport:
- Remember to wear protective gloves when giving first aid to a player who is bleeding.
- Stop the bleeding from the wound.
- Dress the wound.
- Clean up the blood.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Know You Have Hepatitis C