How Many Victorians Are Affected By Hepatitis C And Who Is Affected
Hepatitis C is the most common blood borne virus in Australia with approximately 230,000 people currently living with hepatitis C in Australia and around 65,000 in Victoria.
The population most at risk of acquiring hepatitis C are people who currently inject drugs including people from Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander and culturally and linguistically diverse backgrounds, prisoners, older people, and young injectors and/or new initiates to injecting drug use.
With Which Drugs Do Daas Interact With
- Many drugs are metabolized from the body by enzymes in the liver. DAA are metabolized by one of the more important of these enzymes in the liver . As a result, drugs that enhance or reduce the activity of this liver enzyme will affect blood levels.
- Some drugs increase the activity of CYP3A and result in reduced levels of DAA and thereby reduce their effectiveness, for example, corticosteroids .
- Other drugs decrease the activity of CYP3A and result in elevated levels of the and possibly can lead to toxicity, for example, some of the anti-fungal drugs .
- SomeHIVmedications may need to be changed while taking some of the hepatitis C DAA.
- The list of drugs that interact with DAA is large and includes many commonly-used drugs. It is important to review all of the drugs that patients are taking to identify drugs that interact with these drugs before treatment is begun.
- Interferons include drugs such as peginterferon alfa-2a , peginterferon alfa-2b , recombinant interferon alfa-2a , and recombinant interferon alfa-2b .
- Pegylation slows the elimination of interferon from the body so that its effects last longer.
- Pegylated interferons are given by injection once weekly.
How do interferons work?
Who should not use interferons?
Individuals with autoimmune hepatitis, decompensated liver disease, or allergy to interferons should not use these medications. Peginterferon cannot be used in newborns.
Dosage Forms and Administration:
Drug or food interactions:
Side effects:
- fatigue,
Who Can Prescribe The New Drugs
A section 85 listing on the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme will allow general practitioners, as well as specialists, to prescribe the new treatments. This means that people with hepatitis C will be able to be treated by a general practitioner in the community. However, people with more advanced care needs, such as cirrhosis, may still need to see a specialist.
Read Also: Can You Live A Normal Life With Hepatitis C
Preemptive Hcv Treatment Before Immunotherapy Or Chemotherapy
Pregnancy
The risk of vertical transmission in mothers with an HCV monoinfection is 5% and is not diminished by cesarean section. Mothers are not advised against breastfeeding either.
There is an urgent indication for preemptive antiviral treatment in patients with a chronic hepatitis B infection before they undergo certain types of immunotherapy or chemotherapy . There is insufficient evidence at present for any recommendation of an analogous procedure for patients with chronic hepatitis C.
Needle Use Or Accidental Stick
You can get hepatitis C from:
- Sharing needles and other equipment used to inject drugs.
- Having your ears or another body part pierced, getting a tattoo, or having acupuncture with needles that have not been sterilized properly. The risk of getting hepatitis C in these ways is very low.
- Working in a health care environment where you are exposed to fresh blood or where you may be pricked with a used needle. Following standard precautions for health care workers makes this risk very low.
Recommended Reading: Side Effects Of Having Hepatitis C
Tests For Liver Problems
To check how well your liver is working, you may have:
- Liver function tests. These are blood tests that can help your doctor find out if you have liver damage.
- A liver biopsy. The doctor puts a needle in the liver to find out whether the virus has caused scarring or damage to your liver.
- Imaging tests such as a CT scan, an MRI, or an ultrasound to make sure that you don’t have liver cancer.
Screening And Linkage To Care
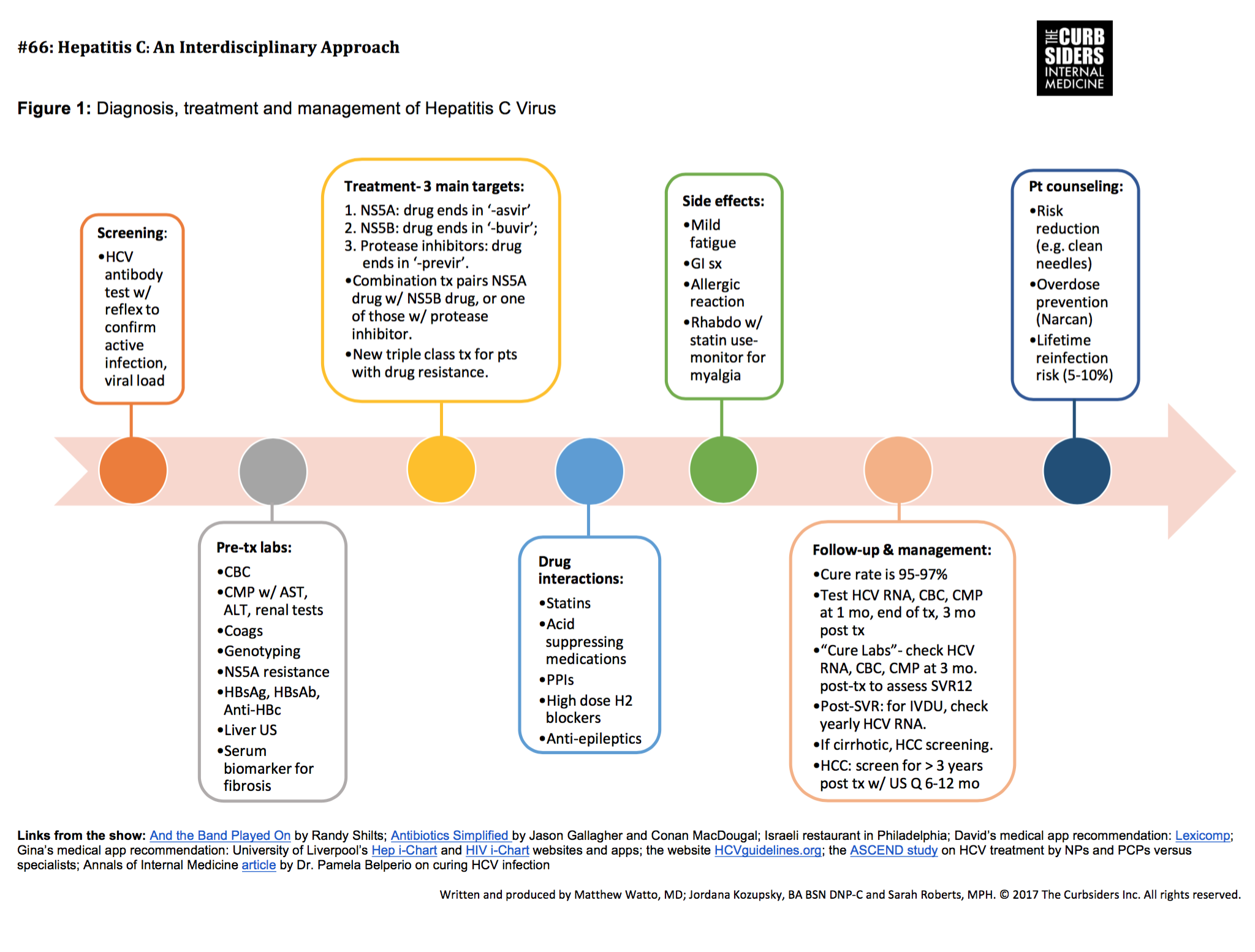
To increase the identification of the large proportion of persons living with undiagnosed HCV, we recommend that screening be both risk-based and target the birth cohort of individuals born from 1945 to 1975, which currently encompasses the majority of persons chronically infected with HCV in Canada .
A high proportion of Canadians with chronic HCV infection remain undiagnosed, with credible estimates ranging from 44% to 70%., The asymptomatic nature and slow progression of the infection require that individuals be identified through screening. Individuals at increased risk of infection should be tested for HCV . In addition, based on a high prevalence and low testing rate among baby boomers, a strategy of one-time screening of all individuals born between 1945 and 1975 has been shown to be cost-effective and should be implemented in Canada.
Recommended regimens and durations for patients with compensated cirrhosis who have never been treated, according to HCV genotype*
For each HCV genotype, multiple approved regimens are available. The comprehensive efficacy and safety data supporting the recommendation of each regimen for each population are provided in Appendix 1.
Genotype 1
Genotype 2
Genotype 3
Genotypes 4, 5, 6
Posttreatment follow-up
Patients who achieve sustained virologic response and do not have cirrhosis require no specific liver-related follow-up. In those with ongoing risk exposures, annual HCV RNA testing to assess for reinfection is suggested .
Don’t Miss: How To Know If I Have Hepatitis
Should I Be Screened For Hepatitis C
Doctors usually recommend one-time screening of all adults ages 18 to 79 for hepatitis C. Screening is testing for a disease in people who have no symptoms. Doctors use blood tests to screen for hepatitis C. Many people who have hepatitis C dont have symptoms and dont know they have hepatitis C. Screening tests can help doctors diagnose and treat hepatitis C before it causes serious health problems.
Contagious And Incubation Periods
The incubation periodthe time it takes for symptoms to appear after the hepatitis C virus has entered your bodyis from 2 weeks to 6 months. But not all people have symptoms when they are first infected.
You can spread the virus to someone else at any time after you are infected, even if you don’t have symptoms.
Read Also: How Long Does Hepatitis C Live Outside The Body
What Is Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a viral infection that causes liver inflammation and damage. Inflammation is swelling that occurs when tissues of the body become injured or infected. Inflammation can damage organs.
Viruses invade normal cells in your body. Many viruses cause infections that can be spread from person to person. The hepatitis C virus spreads through contact with an infected persons blood.
Hepatitis C can cause an acute or chronic infection.
Although no vaccine for hepatitis C is available, you can take steps to protect yourself from hepatitis C. If you have hepatitis C, talk with your doctor about treatment. Medicines can cure most cases of hepatitis C.
Why Should People Take Antiviral Medications For Hepatitis C
The purpose of taking antiviral medications for hepatitis C is to:
- remove all the hepatitis C virus from your body permanently
- stop or slow down the damage to your liver
- reduce the risk of developing cirrhosis
- reduce the risk of developing liver cancer
- reduce the risk of liver failure and the need for a liver transplant
Also Check: Hiv Hepatitis B And C
What Causes Hepatitis C
The hepatitis C virus causes hepatitis C. The hepatitis C virus spreads through contact with an infected persons blood. Contact can occur by
- sharing drug needles or other drug materials with an infected person
- getting an accidental stick with a needle that was used on an infected person
- being tattooed or pierced with tools or inks that were not kept sterilefree from all viruses and other microorganismsand were used on an infected person before they were used on you
- having contact with the blood or open sores of an infected person
- using an infected persons razor, toothbrush, or nail clippers
- being born to a mother with hepatitis C
- having unprotected sex with an infected person
You cant get hepatitis C from
- being coughed or sneezed on by an infected person
- drinking water or eating food
- hugging an infected person
- shaking hands or holding hands with an infected person
- sharing spoons, forks, and other eating utensils
- sitting next to an infected person
A baby cant get hepatitis C from breast milk.18
Management Of Competing Interests
Members of the guideline panel have financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies related to HCV therapeutics. All members signed a commitment and competing interest statement at the outset of guideline development. Individuals with relevant disclosures were not excluded from voting on recommendations. However, in order to manage competing interests, the final guideline was vetted by the Canadian Association for the Study of the Liver membership, and specifically by the associations executive, to evaluate the presence of commercial bias. No funding, direct or in kind, was provided to the guideline panel for this work.
Recommended Reading: How Can A Person Get Hepatitis B
What Are The Symptoms
Most people have no symptoms when they are first infected with the hepatitis C virus. If you do develop symptoms, they may include:
- Feeling very tired.
- Sore muscles.
- Dark urine.
- Yellowish eyes and skin . Jaundice usually appears only after other symptoms have started to go away.
Most people go on to develop chronic hepatitis C but still don’t have symptoms. This makes it common for people to have hepatitis C for 15 years or longer before it is diagnosed.
Will A Specialist Need To Be Involved
In order to prescribe, general practitioners including physicians with expertise in viral hepatitis, will be required to first consult with a gastroenterologist, hepatologist or infectious diseases physician to ensure patients with liver disease or other complex needs are appropriately referred to specialist care. A face to face consult with the specialist is not required and patients with complex needs will likely be referred to specialist care where appropriate.
Patients affected by hepatitis C with severe or advanced liver disease may still need to access the treatments under the care of a specialist – such as a gastroenterologist, hepatologist, or an infectious disease physician with experience in treating chronic hepatitis C infection.
Read Also: Can You Get Rid Of Hepatitis C For Good
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Most people infected with hepatitis C have no symptoms. Some people with an acute hepatitis C infection may have symptoms within 1 to 3 months after they are exposed to the virus. These symptoms may include
If you have chronic hepatitis C, you most likely will have no symptoms until complications develop, which could be decades after you were infected. For this reason, hepatitis C screening is important, even if you have no symptoms.
When Should You Call Your Doctor
911 or other emergency services immediately if you have hepatitis C and you:
- Feel extremely confused or are having hallucinations.
- Are bleeding from the rectum or are vomiting blood.
- You think you may have been infected with hepatitis C.
- You have risk factors for hepatitis C, such as IV drug use.
- You have symptoms of hepatitis C and you think you may have been exposed to hepatitis C.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C How Does It Spread
See A Liver Specialist
Ask your primary doctor for a referral to a liver specialist, if you arent already under the care of one.
Depending on your insurance company, it might cover the cost of hepatitis C medication only when prescriptions come from a liver specialist.
Note that the copay for a liver specialist is typically higher than that of a primary care physician.
Avoid Alcohol And Drugs
One of the most important jobs of your liver is to break down drugs and alcohol. If you have hepatitis C, one of the best things you can do is to avoid substances that may harm your liver, such as alcohol and illegal drugs. If you have cirrhosis, you also may need to avoid certain medicines.
If you use illegal drugs or drink alcohol, it is important to stop. Being honest with your doctor about your drug and alcohol use will help you deal with any substance use disorders. If you don’t feel that you can talk openly with your doctor, you may want to find a doctor you feel more comfortable with. If you want to stop using drugs or alcohol and need help to do so, ask your doctor or someone else you trust about drug and alcohol treatment options.
Because many medicines can stress your liver, talk to your doctor before you take any prescription or over-the-counter medicines. This includes herbal remedies as well.
Read Also: Hepatitis B Vaccine Dose For Newborns
Reach Out To Drug Companies
If your insurance provider will not cover your hep C medication, you might qualify for patient assistance programs. This is also an option if youre uninsured or cant afford expensive medications.
To get started, contact drug manufacturers or pharmaceutical companies directly to see if youre eligible to receive financial assistance. This includes Abbvie, Merck, and Bristol Myers Squibb.
Additionally, Support Path is a program that helps eligible people pay for generic hepatitis C treatment whether youre insured or uninsured. If eligible for the program, you might pay as little as $5 per copay for your medication.
How Do Doctors Treat Hepatitis C

Doctors treat hepatitis C with antiviral medicines that attack the virus and can cure the disease in most cases.
Several newer medicines, called direct-acting antiviral medicines, have been approved to treat hepatitis C since 2013. Studies show that these medicines can cure chronic hepatitis C in most people with this disease. These medicines can also cure acute hepatitis C. In some cases, doctors recommend waiting to see if an acute infection becomes chronic before starting treatment.
Your doctor may prescribe one or more of these newer, direct-acting antiviral medicines to treat hepatitis C:
You may need to take medicines for 8 to 24 weeks to cure hepatitis C. Your doctor will prescribe medicines and recommend a length of treatment based on
- which hepatitis C genotype you have
- how much liver damage you have
- whether you have been treated for hepatitis C in the past
Your doctor may order blood tests during and after your treatment. Blood tests can show whether the treatment is working. Hepatitis C medicines cure the infection in most people who complete treatment.
Hepatitis C medicines may cause side effects. Talk with your doctor about the side effects of treatment. Check with your doctor before taking any other prescription or over-the-counter medicines.
For safety reasons, talk with your doctor before using dietary supplements, such as vitamins, or any complementary or alternative medicines or medical practices.
Don’t Miss: Foods To Avoid With Hepatitis
The Management Of Chronic Hepatitis C: 2018 Guideline Update From The Canadian Association For The Study Of The Liver
-
Hepatitis C is a major public health problem in Canada that is underdiagnosed and undertreated birth cohort screening would benefit population health outcomes.
-
Pretreatment evaluation of an infected patient should include clinical evaluation, viral load, genotype and a fibrosis stage assessment.
-
The treatment of hepatitis C has become safer, better tolerated and more effective owing to the availability of direct-acting antivirals for nearly all patients this guideline advocates against the use of any interferon-based treatment regimens and for the use of all-oral regimens for all infected patients.
-
The treatment of infected patients should be individualized to maximize chance of success, especially for difficult-to-cure populations, including patients with renal failure, decompensated cirrhosis, and active substance use disorders.
-
After treatment, the follow-up of successfully treated patients depends on whether they are cirrhotic patients with cirrhosis require life-long surveillance for the development of hepatocellular cancer.
Since the last Canadian guideline on the management of chronic HCV infection from the Canadian Association for the Study of the Liver was published in 2015, there have been remarkable treatment advances. Thus, there was a need for an updated, evidence-based guideline.
How Common Is Hepatitis C In The United States
In the United States, hepatitis C is the most common chronic viral infection found in blood and spread through contact with blood.14
Researchers estimate that about 2.7 million to 3.9 million people in the United States have chronic hepatitis C.13 Many people who have hepatitis C dont have symptoms and dont know they have this infection.
Since 2006, the number of new hepatitis C infections has been rising, especially among people younger than age 30 who inject heroin or misuse prescription opioids and inject them.15,16
New screening efforts and more effective hepatitis C treatments are helping doctors identify and cure more people with the disease. With more screening and treatment, hepatitis C may become less common in the future. Researchers estimate that hepatitis C could be a rare disease in the United States by 2036.17
You May Like: Hepatitis C Symptoms Mayo Clinic
Treatment If The Condition Gets Worse
Severe liver damage caused by chronic hepatitis C usually takes 20 or more years to develop.
If your hepatitis C continues to get worse, it can cause your liver to stop working, a condition called end-stage liver failure. In this case, a liver transplant may be the only way to extend your life. But if you are drinking alcohol, are sharing needles to inject drugs, or have severe depression or certain other mental illnesses, liver transplant may not be an option.