Hepatitis C Testing And Diagnosis
Doctors will start by checking your blood for:
Anti-HCV antibodies: This blood test is the first — and sometimes only — one you may get. Also called the ELISA screen, it checks for antibodies that your body releases to fight the virus. These are proteins your body makes when it finds the hep C virus in your blood. They usually show up about 12 weeks after infection. Your test will be either negative or positive for antibodies. It usually takes a few days to a week to get results, though a rapid test is available in some places.
What the results mean
Negative . This is when your blood shows no signs of HCV antibodies. Most of the time, thatâs because you never came in contact with the virus and you do not have hep C.
Sometimes, your negative result can be false, meaning you have HCV. That may happen if you:
- Took the test too soon after your exposure. This test checks for only HCV antibodies, which can take several months to appear.
- Have HIV, a donated organ, or other conditions that weaken your immune system, which can suppress your antibodies
- Get hemodialysis for kidney problems
If youâve been exposed in the last 6 months, youâll need to be retested.
Positive . This means youâve been infected with HCV. But false positives are surprisingly common. More than 1 in 5 people who test positive donât actually have hepatitis C. Possible reasons include:
What the results mean
Question 10 I Am Treating My Hcv
If HCV RNA is detectable at week 4 of treatment, per AASLD guidelines, it is suggested to repeat quantitative HCV RNA viral load testing after 2 additional weeks of treatment. If quantitative HCV RNA testing at week 6 of treatment shows an increase of greater than 10-fold , discontinuation of HCV treatment is recommended. The cause of a positive HCV RNA test result at week 4, with decreasing levels at week 6 or week 8, is unknown. There is no recommendation to stop therapy or extend therapy for these patients.9
References
Hepatitis C Virus Antibody Confirmation Serum
Confirming the presence of hepatitis C virus -specific IgG antibodies in serum specimens that are reactive by HCV antibody screening tests
Distinguishing between true- and false-reactive HCV antibody screening test results
This test is not intended for use as an HCV antibody screening test for blood or human cells/tissue donors
This assay is not usefulfor detection of early or acute hepatitis C as immunocompromised patients may not develop detectable HCV antibodies in blood until 6 months after infection
This assay is not useful for differentiating between past and chronic hepatitis C
Don’t Miss: Is There A Cure For Hepatitis
Who Is Most At Risk Of Contracting Hepatitis C
You have a high risk of contracting hepatitis C if you:
- use or have used injection drugs even if it was just once or many years ago
- have received blood or blood products or an organ transplant before July 1990 in Canada
- have been in jail or
- have been injected or scratched during vaccination, surgery, blood transfusion or a religious/ceremonial ritual in regions where hepatitis C is common.
You have a high moderate risk of contracting hepatitis C if you:
- have tattoos or body piercing
- have multiple sexual partners
- have a sexually transmitted infection , including HIV or lymphogranuloma venereum
- have experienced traumatic sex or rough sex or have used sex toys or fisting that can tear body tissue
- have vaginal sex during menstruation
- have received a kidney treatment
- have received an accidental injury from a needle or syringe
- have another infectious disease
- were born to a hepatitis C infected mother or
- have a sexual partner infected with hepatitis C.
Hepatitis C is NOT passed from person to person by:
- coughing, sneezing
- breastfeeding unless your nipples are cracked and bleeding or
- oral sex, unless blood is present.
Other Hepatitis C Tests
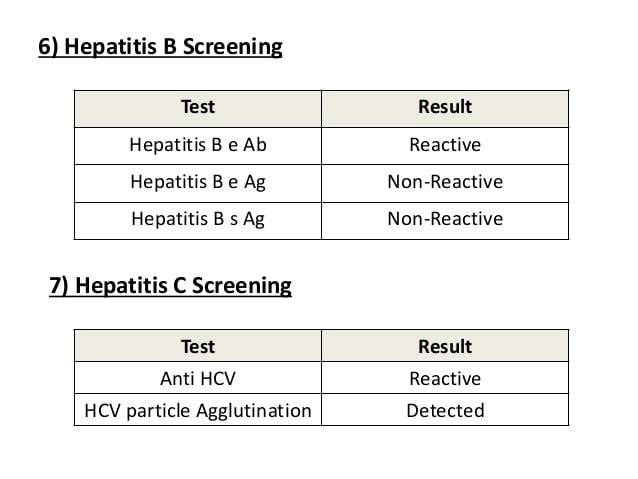
After an individual has received a reactive or positive result from a hepatitis C antibody test, they will need to have two follow-up tests.
The first test checks to see whether a person still has the virus the other measures the amount of the virus in the blood.
The first test is the hep C RNA qualitative test, also known as the PCR test. A positive result means that a person has the hepatitis C virus. A negative result means that the body has cleared the virus without treatment.
The second test is the hep C RNA quantitative test. The result of this test is given as a number rather than a positive or negative. This is because the test compares the amount of the virus in the body before, during, and after treatment.
The number given as a result of this test is known as the viral load. The lower amount of the hepatitis C virus in the blood, the better the chances that a person can eliminate the virus from their body.
After hepatitis C virus is diagnosed, other tests may be needed:
Certain behaviors, experiences, and medical procedures increase the risk of getting the hepatitis C virus, which is transmitted by contact with blood.
The following are risk factors for contracting the virus:
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention advise all baby boomers get tested for hepatitis C. Baby boomers are people born between 1945 and 1965. They are five times more likely to have the virus than other adults.
Also Check: How Much Does A Hepatitis C Test Cost
Taking A Hepatitis C Test
Hepatitis C testing is conducted on a sample of blood. Blood samples can be collected by a doctor, nurse, technician, or other health care provider from an adult patients vein using a small needle or a skin prick on a childs heel.
For an at-home hepatitis C test, patients collect a blood sample according to the manufacturers directions. Instructions provided in the test kit detail the steps to obtain a small sample of blood and mail it for testing.
How Can I Cover Medication Costs
New therapies called direct-acting antivirals are effective and can achieve cures of over 90%. Because these new therapies are very new, they remain very expensive. As such, drug coverage from both government and private companies may require that your liver disease has progressed to a certain stage before they are willing to cover the cost of these drugs.
Talk with your healthcare provider about financial support that may be available.
Below are useful resources when looking for financial assistance:Private health insurance or drug plansIf you have private health insurance or a drug plan at work, you may be able to have the medication paid through your plan. Please consult your private health insurance or drug plan provider to see if your drug is covered.
Publicly funded plansEach provincial and territorial government offers a drug benefit plan for eligible groups. Some are income-based universal programs. Most have specific programs for population groups that may require more enhanced coverage for high drug costs. These groups include seniors, recipients of social assistance, and individuals with diseases or conditions that are associated with high drug costs. For more details, please contact your provincial or territorial health care ministry, or click on the appropriate link below.
Yukon
Available Patient Assistance Programs for Hepatitis C treatment Holkira Pak Maviret
MerckCare Hepatitis C Program 1 872-5773 Zepatier
Don’t Miss: Symptoms Of Advanced Hepatitis C
Question 8 What Do The Following Hcv Rna Results Mean: < 15 Iu/ml Detected Or < 15 Iu/ml Not Detected
The result < 15 IU/mL, Detected means that HCV RNA is detected, although at a level that is too low to be quantified. This result could indicate current active HCV infection if consistent with other clinical and laboratory data. NOTE: If this test is being performed for HCV diagnosis, then this < 15 IU/mL Detected result should be confirmed using a second sample from the patient.
In contrast, the result < 15 IU/mL, Not Detected means that HCV RNA is not detected and there is no evidence of current active infection.
Quest Diagnostics measures HCV RNA viral load with the Roche cobas® HCV methodology. This is a quantitative real-time PCR assay with a lower limit of quantification of 15 IU/mL the limit of detection is slightly lower, at 10 IU/mL to 13 IU/mL. If the viral load is just at or above this LOD, but less than 15 IU/mL, the assay can determine that HCV RNA is present but cannot provide a reliable quantitative result. In such cases, the qualitative result of < 15 IU/mL, Detected is provided.
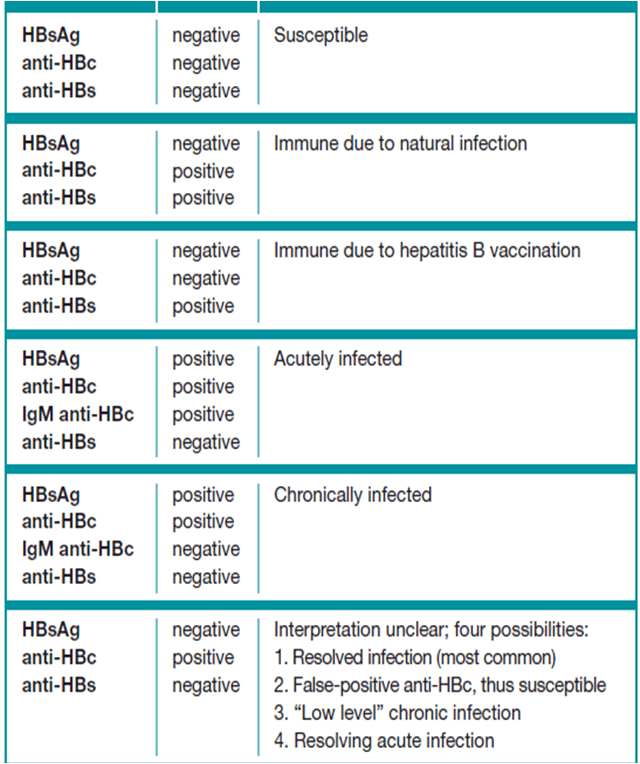
What Does A Reactive Hepatitis C Antibody Test Mean
A reactive hepatitis C antibody test means that the patient has hepatitis C antibodies in his blood. However, since a person who has cleared the hepatitis C virus still tests positive for antibodies, a follow-up test is required to determine if he is currently infected, says WebMD.
Hepatitis C is a liver infection caused by the hepatitis C virus. It is spread when blood from an infected person enters the blood stream of a healthy person. Infected people experience symptoms such as stomach pain, nausea, loss of appetite, fatigue, joint pain and jaundice. Some patients can live for years without any symptoms, which can lead to advanced liver disease due to delayed treatment. A hepatitis C antibody test is therefore the only sure determiner of a hepatitis C infection, says the
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Also Check: How Can You Contact Hepatitis C
Addressing Hepatitis For The First Time
It is crucial that a treatment counselor or health professional use a nonjudgmental and compassionate tone. Clients need to feel comfortable disclosing information about their health and risky behaviors. The following strategies can help initiate the conversation:
- Display posters, literature, or other -related items that could help prompt the client to ask questions about hepatitis. .
- Assess clients ability to discuss , based on their degree of openness in the counseling session, the amount of detail they provide in their responses, and the length of the therapeutic relationship.
- Raise the subject in a way that avoids making clients feel defensive or afraid. Consider introducing the subject by making parallels with other conditions that have been discussed. Say, for example, You said you were tested for HIV several times. Were you ever tested for viral ? or You mentioned that your friend is sick with HIV. Have you been tested for HCV or HIV? Tell me about those tests.
- Be patient and allow time for multiple, short conversations about the subject. This might ease feelings of fear, anxiety, or shame.
Home Screening Tests For Hepatitis C
At-home screening tests provide privacy if you prefer not to go to a doctor or clinic for testing. These tests typically look for antibodies to hepatitis C, but they may not always test for active viral infection. Make sure you know what type of test youll be taking before you buy.
Many at-home tests have close to or the same reliability as blood tests received by a medical professional.
If youve recently been exposed to hepatitis C, wait several weeks before testing at home.
You May Like: Antiviral Drugs For Hepatitis A
Hep C Antibodies Do Not Prevent Re
What does it mean, in any real terms? Well, in terms of my status as being cured, it means nothing at all, because we do believe, as a fact, that antibodies for hep C offer no protection and so have no real value. It is interesting to me, and that is only because of my interest in the science of why and how things work, and there is some science that points to diminished antibody presence over time, and is it the same with all treatments? We dont know, and no need to be concerned, unless you too have a mildly science and nerdy side like me.
Hcv Core Antigen Testing
The hepatitis C core antigen is a viral protein. Since the core antigen is part of hepatitis C virus, it can usually be found in the bloodstream two weeks after infection.
Since HCV core antigen testing is simpler and less expensive than viral-load testing, some experts suggest using it in resource-limited settings. Core antigen testing can be usedoften with HCV antibody testingto detect acute HCV or to confirm chronic HCV infection. HCV core antigen testing can also be used to measure treatment outcome. Although it does not detect low levels of HCV , usually the hepatitis C viral load is much higher in people who relapse after HCV treatment.
Don’t Miss: How Can You Catch Hepatitis C
Antibody Testing After Treatment
For many years, we have said that people will always have antibodies present when tested, even after being cured. It has mostly been in the context of a person being tested in some future medical investigation unrelated and showing a positive antibody test result. Some who have been cured have shared some confusion when they are informed they have hep C, despite being cured. As this is not always understood well in healthcare, there is no good explanation in that instance from the care provider.
To be fair, I am hearing this less from people, but I suspect it may still occur. I have had a few tests done in recent years as part of my work in testing and linkage to care. The most recent test was with a proven testing mode commonly used, point of care testing . In the process of filming an instructional video to show how these POCTs are done, I was the testing subject. I expected a positive result, as I had lived with hep C and I was cured 10 years ago. My test showed up as negative to my surprise. I retested and got the same result.
The Cdc Recommends You Get Tested If You:
- Are 18 years of age and older
- Are pregnant
- Currently inject drugs
- Have ever injected drugs, even if it was just once or many years ago
- Have HIV
- Received donated blood or organs before July 1992
- Received clotting factor concentrates before 1987
- Have been exposed to blood from a person who has hepatitis C
- Were born to a mother with hepatitis C
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Antibody Reactive Meaning
Rna Or Viral Load Test
If you test positively for hepatitis C antibodies, you will need to get a RNA or viral load test. The RNA test is a blood test that checks to see if hepatitis C is active in your body.
- Negative
- If your RNA test result is negative, you do not have hepatitis C.
- Positive
- If your RNA test result is positive, you may have chronic hepatitis C. Talk to your doctor right away about a treatment plan.
The Treatment Programs Role In The Screening Process
Medical staff members at substance abuse treatment programs might assume the primary role for screening individuals for and explaining the screening process and test results. Opioid treatment programs with medical staff members should screen for and C at intake and periodically as indicated. In programs without onsite medical staff, clients may be referred elsewhere for screening with minimal involvement of the substance abuse treatment program.
Regardless of the type of program, counselors should have a basic understanding of the importance of screening, the screening process, and the meaning of the results. Counselors can encourage clients referred for screening to follow through and complete the screening and evaluation process . Clients might feel anxious about being diagnosed with hepatitis, and they might delay or avoid getting screened.
Read Also: Side Effects Of Autoimmune Hepatitis
Who Should Get Tested
You should consider getting tested for hepatitis C if you’re worried you could have been infected or you fall into one of the groups at an increased risk of being infected.
Hepatitis C often has no symptoms, so you may still be infected if you feel healthy.
The following groups of people are at an increased risk of hepatitis C:
- ex-drug users and current drug users, particularly users of injected drugs
- people in the UK who received blood transfusions before September 1991
- UK recipients of organ or tissue transplants before 1992
- people who have lived or had medical treatment in an area where hepatitis C is common high-risk areas include north Africa, the Middle East and central and east Asia
- babies and children whose mothers have hepatitis C
- anyone accidentally exposed to the virus, such as health workers
- people who have received a tattoo or piercing where equipment may not have been properly sterilised
- sexual partners of people with hepatitis C
If you continue to engage in high-risk activities, such as injecting drugs frequently, regular testing may be recommended. Your doctor will be able to advise you about this.
How Much Does The Test Cost
The cost of hepatitis C testing depends on the tests that are performed, where the test is conducted, and a patients health insurance coverage. When testing is ordered by a doctor, patients with health insurance may find it helpful to discuss the cost of hepatitis C testing with their insurance company. In addition to the cost of testing, there may be other out-of-pocket costs such as copays and deductibles.
For patients without health insurance, or for whom insurance doesnt cover the cost of testing, it may be helpful to discuss the cost of hepatitis C testing with a doctor or hospital administrator.
At-home hepatitis C testing starts around $49. Some at-home kits test for multiple types of viral hepatitis at once, with the cost of these panels starting around $80.
Read Also: How Do You Get Hepatitis A B C