What Is Acute Fulminant Hepatitis
Rarely, individuals with acute infections with HAV and HBV develop severe inflammation, and the liver fails . These patients are extremely ill with the symptoms of acute hepatitis already described and the additional problems of confusion or coma , as well as bruising or bleeding . In fact, up to 80% of people with acute fulminant hepatitis can die within days to weeks therefore, it is fortunate that acute fulminant hepatitis is rare. For example, less than 0.5% of adults with acute infection with HBV will develop acute fulminant hepatitis. This is even less common with HCV alone, although it becomes more frequent when both HBV and HCV are present together.
What Are The Forms Of Fatty Liver Disease
There are two main forms of fatty liver disease:
Alcoholic liver disease
Alcoholic fatty liver is the accumulation of fat in the liver as a result of heavy drinking. About 5% of people in the U.S. have this form of liver disease.
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease occurs in people who arent heavy drinkers. The condition affects one in three adults and one in 10 children in the United States. Researchers havent found the exact cause of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Several factors, such as obesity and diabetes, can increase your risk.
Deterrence And Patient Education
Vaccinations for both hepatitis A virus and hepatitis B virus have been available since the 1990s and have significantly decreased the incidence of these infections. Hepatitis A virus gets transferred by fecal-oral contamination, and improved food handling, water purification, and improved hygiene will reduce the risk of spreading infection. The risk of contracting hepatitis B and hepatitis C infection can be decreased by avoiding IV drug use and safe sex practices.
Accidently toxic ingestion of acetaminophen by children can be reduced with safe storage practices out of reach from children and utilizing packaging that utilize childproof safety precautions. Also, in adults, unintentional toxic ingestion can be reduced with education about the many non-prescription products which contain acetaminophen.
For stable minimally symptomatic patients, if an etiology for acute hepatitis is not determined initially, then they need follow-up to monitor for the normalization of the liver tests or further evaluation if the abnormal test results continue.
Also Check: What Is Hepatic Cirrhosis Of The Liver
What You Should Know:
- When you have non-alcoholic fatty liver disease , your liver has more fat in it than it should. Your liver is in the upper right side of your abdomen and under your lower ribs. It makes a fluid called bile that helps digest food to turn it into energy. You may have a mild form of NAFLD or a severe form called non-alcoholic steatohepatitis . With NASH, your liver cells may become damaged and inflamed . You may get very serious liver diseases such as cirrhosis and liver cancer. With NAFLD, you may have swelling or pain on the upper right side of your abdomen. You may have skin darkening, feel more tired than usual, or have extra fat around your waist.
- The cause of NAFLD is not known. People who have NAFLD are usually overweight and eat too many fatty foods. People who have NAFLD also may have diseases such as diabetes , hepatitis, or metabolic syndrome. NAFLD is usually diagnosed with blood tests, imaging tests, or a liver biopsy. Weight loss by diet and exercise is a common treatment for NAFLD. With treatment, you may be less likely to have NASH and other liver problems. Your liver may become healthier, less fatty, and may work better than before treatment.
How You Can Get Hepatitis A
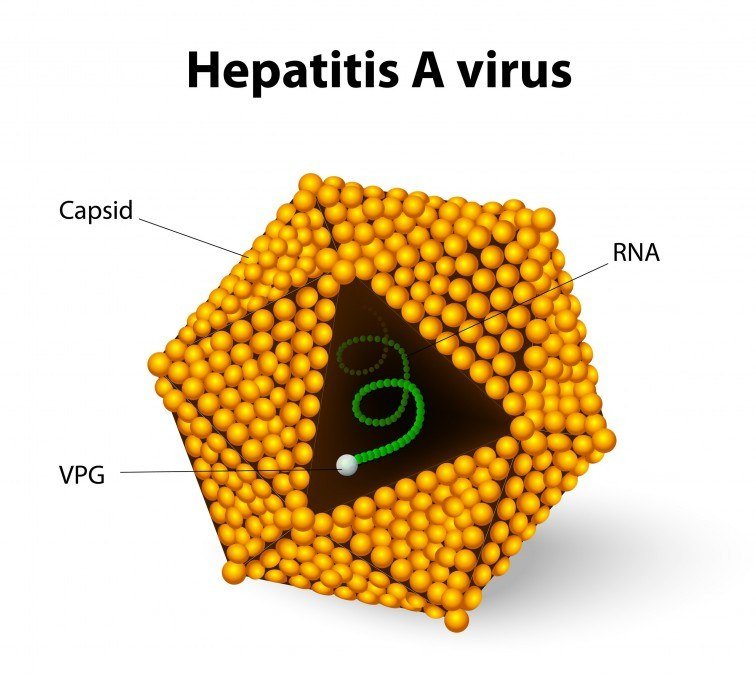
Hepatitis A is most widespread in parts of the world where standards of sanitation and food hygiene are generally poor, such as parts of Africa, the Indian subcontinent, the Far East, the Middle East, and Central and South America.
You can get the infection from:
- eating food prepared by someone with the infection who hasn’t washed their hands properly or washed them in water contaminated with sewage
- drinking contaminated water
- eating raw or undercooked shellfish from contaminated water
- close contact with someone who has hepatitis A
- less commonly, having sex with someone who has the infection or injecting drugs using contaminated equipment
Someone with hepatitis A is most infectious from around two weeks before their symptoms appear until about a week after the symptoms first develop.
Read more about the causes of hepatitis A.
You May Like: Hep Forte Hepatic Lipotropic Nutritional Support
What Are The Signs & Symptoms Of Hav Infection
Hepatitis A can be a mild infection, particularly in kids younger than 6, so many people might not ever know that they had an infection.
When symptoms do happen, they typically start 2 to 6 weeks after exposure to the virus and are more likely in adults and kids older than 6. HAV can cause vomiting and diarrhea, as well as fever, loss of appetite, darker than usual urine , jaundice , and abdominal pain.
HAV infections that cause serious symptoms can last for weeks or even months. Some people with HAV can feel ill for up to 6 months.
How Do Doctors Diagnose Hepatitis A
Doctors diagnose hepatitis A based on symptoms and a blood test. A health care professional will take a blood sample from you and send the sample to a lab. A blood test will detect antibodies to the hepatitis A virus called immunoglobulin M antibodies and show whether you have acute hepatitis A. If the blood test finds antibodies to the hepatitis A virus that are not IgM antibodies, then you are immune to hepatitis A, due to either past hepatitis A infection or hepatitis A vaccination.
Recommended Reading: How To Reverse Hepatic Steatosis
Types Of Hepatitis A Vaccine
There are 3 main types of hepatitis A vaccination:
- a vaccine for hepatitis A only
- a combined vaccine for hepatitis A and hepatitis B
- a combined vaccine for hepatitis A and typhoid fever
Talk to your GP about which vaccine is most suitable for you. All 3 types are usually available for free on the NHS.
If you’ve travelling abroad, try to plan your vaccinations in advance. They should ideally be started at least two or three weeks before you leave, although some can be given up to the day of your departure if necessary.
Extra doses of the vaccine are often recommended after 6-12 months if you need long-term protection.
You can find more information about the various hepatitis A vaccines on the NHS Fit for Travel website.
When Should I See A Doctor
Make an appointment if you have any of the symptoms and you recently:
- Traveled out of the country, especially if you went to Mexico, South America, Central America, or anywhere without good sanitation
- Ate at a restaurant that reported a hepatitis A outbreak
- Found out someone close to you, like a roommate or caregiver, was diagnosed with hepatitis A
- Had sex with someone who has hepatitis A
- Ate raw shellfish
- Used illegal drugs
When you see your doctor, they may spot some more signs that you’ve got the disease. For instance, they might find that you have:
You May Like: How Do Catch Hepatitis B
How Do Doctors Treat Hepatitis A
Treatment includes resting, drinking plenty of liquids, and eating healthy foods to help relieve symptoms. Your doctor may also suggest medicines to help relieve symptoms.
Talk with your doctor before taking any prescription or over-the-counter medicines, vitamins or other dietary supplements, or complementary or alternative medicinesany of these could damage your liver. You should avoid alcohol until your doctor tells you that you have completely recovered from hepatitis A.
See your doctor regularly to make sure your body has fully recovered. If you have symptoms for longer than 6 months, see your doctor again.
Obesity And Fatty Liver Disease
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is strongly associated with obesity. Excess fat causes insulin resistance and inflammatory signals. Insulin resistance means that the pancreas has to produce more insulin in order to maintain normal blood glucose levels, and is the first step towards developing diabetes.
Patients who have hypertension , have high cholesterol, are overweight or obese, and have diabetes or insulin resistance are at greater risk to develop fatty liver disease. Physicians and scientists do not fully understand why the excess fat causes these liver changes. They do know that by losing weight, liver enzymes may normalize and liver inflammation may improve.
- Malnutrition.
- Ingestion of poisonous wild mushrooms.
Like many progressive diseases, you may not notice any signs or symptoms of liver disease in the early stages. But, as liver function begins to decline, you may begin to notice some physical changes in certain areas of your body.
Abdominal Swelling
A swollen abdomen can point to a condition called ascites, in which liver malfunction leads to an imbalance of proteins and other compounds, and fluid builds up in the tissues.
The main symptom, potbelly, often signals cirrhosis.
Sometimes swelling occurs in the hands, feet and ankles, as gravity draws excess fluid down to these extremities.
Bruising
A damaged liver produces fewer of the proteins necessary for blood clotting, which means you may bleed and bruise more easily.
Fatigue and Weakness
Also Check: Side Effects Of Having Hepatitis C
Is Hepatitis A Contagious
Hepatitis A Transmission
Hepatitis A is a type of liver infection caused by a virus termed hepatitis A . Symptoms, if they occur, start about 2 to 6 weeks after exposure to HAV. About 80% of adults have symptoms while children seldom show symptoms. Symptoms of hepatitis A may include the following:
- Nausea and/or vomiting
- Jaundice
- Joint pain
Does Hepatitis A Always Cause Symptoms

There’s a lot of variety in how people feel when they have the disease. It’s possible you might not have any symptoms. But people often feel and look sick. You might even need to go to the hospital.
Symptoms and complications are more common as you get older. Most children under age 6 with hep A don’t have any.
Read Also: What Is Hepatitis A And B
How Is Viral Hepatitis Diagnosed
Diagnosis of viral hepatitis is based on symptoms and physical findings as well as blood tests for liver enzymes, viral antibodies, and viral genetic materials.
Symptoms and physical findings
Diagnosis of acute viral hepatitis often is easy, but the diagnosis of chronic hepatitis can be difficult. When a patient reports symptoms of fatigue, nausea, abdominal pain, darkening of urine, and then develops jaundice, the diagnosis of acute viral hepatitis is likely and can be confirmed by blood tests. On the other hand, patients with chronic hepatitis due to HBV and HCV often have no symptoms or only mild nonspecific symptoms such as chronic fatigue. Typically, these patients do not have jaundice until the liver damage is far advanced. Therefore, these patients can remain undiagnosed for years to decades.
Blood tests
There are three types of blood tests for evaluating patients with hepatitis: liver enzymes, antibodies to the hepatitis viruses, and viral proteins or genetic material .
Liver enzymes: Among the most sensitive and widely used blood tests for evaluating patients with hepatitis are liver enzymes, called aminotransferases. They include aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase . These enzymes normally are contained within liver cells. If the liver is injured , the liver cells spill the enzymes into the blood, raising the enzyme levels in the blood and signaling that the liver is damaged.
Examples of tests for viral antibodies are:
Hepatitis A Vaccine And Travel
If youâre going to a country where hepatitis A is common and youâve never had the virus or the vaccine, start the vaccination process as soon as you can. It takes 2 to 4 weeks after the first dose for the vaccine to work, but even one shot a few days before you leave will give you some protection.
People who are allergic to something in the vaccine and children younger than 6 months might instead get a shot of immune globulin , which will protect against hepatitis A for up to 2 months.
Read Also: How Long Before Hepatitis C Symptoms Appear
Who Is More Likely To Get Hepatitis A
People more likely to get hepatitis A are those who
- travel to developing countries
- have sex with an infected person
- are men who have sex with men
- use illegal drugs, including drugs that are not injected
- experience unstable housing or homelessness
- live with or care for someone who has hepatitis A
- live with or care for a child recently adopted from a country where hepatitis A is common
Hepatitis A And E Symptoms
Hepatitis A and hepatitis E present with similar symptoms. The diseases may develop without any signs or symptoms, or symptoms may be nonspecific. If you experience any of the symptoms below for more than two weeks, make an appointment with a gastroenterologist.
There are three phases of hepatitis A and E, and symptoms may differ depending on the stage. Early in the disease, called the prodromal phase, symptoms may include:
- Fever
Also Check: Can Hepatitis C Come Back
Causes Include Viruses Bacteria And Parasites
Diarrhea is the second leading cause of death in children in the developing world and a major contributor to work absenteeism and loss of productivity in the American workforce.
The elderly, young children, and people with compromised immune systems are especially vulnerable and are at an increased risk of complications related to severe diarrhea including dehydration, the need for hospitalization and fluid management, and rarely even death.
Causes Of Noninfectious Hepatitis
Although hepatitis is most commonly the result of an infection, other factors can cause the condition.
Alcohol and other toxins
Excess alcohol consumption can cause liver damage and inflammation. This may also be referred to as alcoholic hepatitis.
The alcohol directly injures the cells of your liver. Over time, it can cause permanent damage and lead to thickening or scarring of liver tissue and liver failure.
Other toxic causes of hepatitis include misuse of medications and exposure to toxins.
Autoimmune system response
In some cases, the immune system mistakes the liver as harmful and attacks it. This causes ongoing inflammation that can range from mild to severe, often hindering liver function. Itâs three times more common in women than in men.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Know You Have Hepatitis
How Is Hepatitis A Diagnosed
Your healthcare provider will listen to your symptoms and will take a blood test to confirm the diagnosis of hepatitis A. If the test finds immunoglobulin M antibodies, you have an acute hepatitis A. If there are antibodies, but not IgM antibodies, you are immune to the virus either because you had a case of it and recovered, or you got the hepatitis A vaccine.
Could You Have Fatty Liver Disease Learn The Symptoms
Is your liver overweight? Fatty liver disease, once seldom seen except in heavy drinkers, has become an increasingly common problem in the 21st century. As many as one in three people may develop the disease, and the risk goes up if you have type 2 diabetes. But what is fatty liver disease, and what can you do about it? Today, the experts at Digestive Disorders Associates explain.
Recommended Reading: How To Cure Diarrhea While Pregnant
Also Check: What Are The Ways You Can Get Hepatitis C
Is There A Hep A Vaccine
Yes, and it is safe and effective. It has been required for children at public schools in Oregon since 1995, but many adults may not have been vaccinated against Hep A.
In general, the recommends the hepatitis A vaccine for any adult who:
- Has had close contact with someone sick with hepatitis A.
- Has chronic liver disease.
Side Effects Not Requiring Immediate Medical Attention
Some side effects of hepatitis a adult vaccine may occur that usually do not need medical attention. These side effects may go away during treatment as your body adjusts to the medicine. Also, your health care professional may be able to tell you about ways to prevent or reduce some of these side effects.
Check with your health care professional if any of the following side effects continue or are bothersome or if you have any questions about them:
More common
- change in the amount of bleeding during periods
- change in the pattern of monthly periods
- lack or loss of strength
- tenderness or warmth at the injection site
- unusual stopping of menstrual bleeding
Rare
- collection of blood under the skin
- deep, dark purple bruise
- feeling of constant movement of self or surroundings
- increased sensitivity of the eyes to sunlight
- loss of taste
- welts
Incidence not known
- Bleeding, blistering, burning, coldness, discoloration of the skin, feeling of pressure, hives, infection, inflammation, itching, lumps, numbness, pain, rash, redness, scarring, soreness, stinging, swelling, tenderness, tingling, ulceration, or warmth at the injection site
- sleepiness or unusual drowsiness
Applies to hepatitis a adult vaccine: intramuscular suspension
Don’t Miss: Natural Cure For Hepatitis A
Who Is At Risk Of Getting Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A is usually spread from person to person, making it highly contagious. However, certain factors can increase your risk of contracting it, including:
- living in an area where hepatitis A is common, including most countries with low sanitation standards or a lack of safe water
- injecting or using illegal drugs
- living in the same household as someone who is hepatitis A-positive
- having sexual activity with someone who is hepatitis A-positive
- being HIV-positive
Possible Side Effects From Vaccines
Any vaccine can cause side effects. For the most part these are minor and go away within a few days. Listed below are vaccines licensed in the United States and side effects that have been associated with each of them. This information is copied directly from CDCs Vaccine Information Statements , which in turn are derived from the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices recommendations for each vaccine.
Remember, vaccines are continually monitored for safety, and like any medication, vaccines can cause side effects. However, a decision not to immunize a child also involves risk and could put the child and others who come into contact with him or her at risk of contracting a potentially deadly disease.
Recommended Reading: How To Find Out If You Have Hepatitis